Food is the combination of various organic and inorganic substances which is capable of providing
(i) Energy for the various metabolic activities.
(ii) Materials for repair / replacement of worn-out tissues in the body.
(iii) Materials for growth & reproduction.
(iv) Regulatory substances, body secretions and metabolic activities etc. 70% of India’s economy is based on agriculture and 40% of G.N.P (Gross National Product) comes from agriculture.
(a) Agriculture : (Ager means field ; culture means cultivation). It is the applied biological science which deals with
the production of plants and raising of animals useful to man, involving soil cultivation, breeding and management of crops and livestock.
(b) Horticulture : (Hortus-garden ; cultura-cultivation). It is the branch of agriculture and the science of growing vegetables, fruits and ornamental plants.
(c) Silviculture: (Sylvan- wood and trees) Cultivation of wood and trees e.g.-pine, teakwood, sesamum etc.
(d) Sources of food : Plants provide us with foods like cereals, pulses, oil seeds, fruits and vegetables, on this basis plants are classified as follows :
(e) Crop Seasons : Different types of crops require different climatic conditions like :
(i) Temperature
(ii) Photoperiod (duration of light
(iii) Completion of life cycle
(f) Depending upon the growing season, there are two groups of crops :
Kharif crop/ Rainy season crop Rabi crop/ Winter season crop
(a) Grown during monsoon/rainy season (a) Grown during winter season
(b) They require warm and wet weather (b) They require cold and dry weather
(c) They are sown in June-July and (c) They are sown in October/November & harvested in harvested September/Octobe harvested in March-April
(d) Examples- Rice, Jowar, Bajra, Cotton,(d) Examples- Wheat, Barley, Gram, Peas, Groundnut,Urad, Moong etc. Mustard, Potato etc.
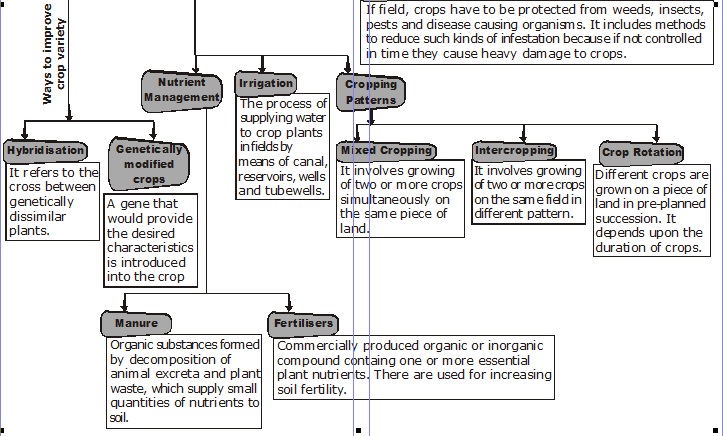
To obtain the high yields from our forms the following three scientific approaches are adopted.
(a) Varietal improvement of crop through genetic manipulation.
(b) Crop Production Management.
(c) Crop protection management.
In India, there has been a four times increase in the production of food grains from 1960 to 2004. How ever, cultivable land area has increased by only 24 per cent.
The yield of a crop can be increased by adopting number of improved agricultural practices, from sowing to harvesting. The various practices that are followed at various stages of production are. as follows :
(i) Preparation of soil (ii) Sowing
(iii) Application of manures and fertilizers (i v) Irrigation
(v) Weed control (vi) Crop protection
(vii) Harvesting, threshing and winnowing (viii) Storage
(ix) Crop improvement
(x) Rotation of crops, mixed and multiple cropping.
(a) Varietal Improvement of crops through genetic manipulation : The principal aim of varietal improvement is to get as many o
f the desirable & economic characters as possible in one variety.
1. Aims of crop improvement are :
(i) Increased yield-Developing high yielding varieties
(ii) Improved quality
(iii) Early and uniform maturity
(iv) Insensitivity to light and temperature
(v) Wider adaptability
(vi) Lodging-resistant varieties
(vii) Desirable agronomic charades
2. Plant Breeding : The technique of producing improved varieties of crop chants by the introduction of-several desired characters into them is called as plant breeding.
Scientists concerned with the improvement of crop varieties are called as plant breeders.
3. Aims of plant breeding : New varieties of crop plants have :
(i) Higher yield.
(ii) Resistance to heat, frost, drought
(iii) Pest resistance
(iv) Early maturing varieties
4. Methods for the genetic improvement of crop plants :
(i) Introduction
(ii) Selection
(iii) Hybridization
(i) Introduction : It refers to the taking of superior varieties of crop plants from the place of their natural cultivation to the place where they were never grown earlier.
(ii) Selection: It is the process in which economic plants having best desired characters are picked up from the given population and seeds of such plants are used for future cultivation
For e.g. Maize & Cabbage are represented by their cultivated varieties only.

(iii) Hybridization: It means the process of crossbreeding of two genetically dissimilar varieties of cropplants (each having a specific and better characteristics) to
obtain a new crop plant having both the desired characteristics is called as hybridization. Crop plants produced in this way are called as hybrid varieties or high yielding varieties.
Parent 1 × Parent 2
(with a desired ¯ (with a desired
character, like character,
high-yield) like disease -resistance)
Hybrid variety
(High-yielding and disease-resistant)

II. Green Revolution was a process by which India’s production of wheat, rice, maize and several other food grains was tremendously increased in
the late 1960s and early 1970s. India, which was earlier said to carry a ‘begging bowl’ to the West for foodgrain, claimed self sufficiency,
This revolution was due to the new agricultural technologies whereby high - yielding hybrid varieties of wheat and rice were grown in India.
Fertilizers and pesticides were used. Irrigation facilities were improved. Dr. M.S. Swaminathan played a key role in bringing about the ‘green revolution’.
III. Dr. M.S. Swaminathan Padam Vibhushan Professor M.S. Swaminathan, FRS, is the Father of’green revolution ‘ in India. He stressed the need for
the reorientation of the breeding programme and his work led to the era of dwarf varieties in India. In 1967, he developed a high-yield dwarf variety of wheat,
Sharbati Sonara. Being a plant geneticist, he has contributed to the development or agriculture in India.He has held various important positions in India and abroad.
(b) Crop Poduction Management : In order to improve and manage our crop production system, we have to focus on cheaper and farmer friendly approaches.
As there is direct co-relationship between the higher yields and input applications.
(i) Successful crop production depends upon:
(a) Understanding how crops develop and grow.
(b) How various factors affect the growth and development of crops and
(c) How each factor can be modified and managed.
(ii) Approaches for crop production includes:
(a) Nutrient management (b) Irrigation (c) Mixed cropping
(d) Inter cropping (e) Crop rotation
1. Nutrient management: Plant nutrients are the mineral elements needed by the plants for their growth, development and maintenance.
Plants absorb a large number of elements from soil, besides water and air, only (16) elements are essential nutrients for plants, out of (40) elements present in plant ash. They are-
(i) Carbon (ii) lron (iii) Hydrogen (iv) Manganese (v) Oxygen
(vi) Boron (vii) Nitro gen (viii)Zinc (ix) Phosphorus (x) Copper
(xi) Potassium (xii) Molybdenum (xiii) Magnesium (xiv) Chlorine (xv) Sulphur (xvi) Calcium
Sources of Plant nutrient: The plants obtain their nutrients mainly from the soil.Out of the total 16 nutrients, as many as 13 are absorbed from the soil.
Soil Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, Sulphur, Iron, Manganese, Boron, Zinc, Copper, Molybdenum Chlorine
Air Carbon, Oxygen
Water Hydrogen
I. Characteristics of an essential plant nutrient:
(i) In the absence of such element, the plant is not able to complete its life cycle.
(ii) Such element must have a direct influence on the plant nutrition and metabolism.
(iii) The requirement of such element must be specific and cannot be replaced by another element
(iv) Deficiency of such element can be corrected or prevented only by supplying that nutrient.
II. Classification of plant nutrients: On the basis of quantities required, (13) mineral nutrients obtained from soil needed for plant growth have been grouped into two categories.
(i) Macronutrients (ii) Micronutrients
Macronutrients- Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen,Phosphorus, Potassium, Calcium, Magnesium, Sulphur.
Micronutrients- Iron, Manganese, Copper, Zinc, Boron, Molybdenum, Chlorine.
Of the sixteen essential nutrients, some are required by plants in relatively large amounts than the others
.The nutrients required in relatively large quantities are called macronutrients or major elements, while the ones required in very small quantities or traces are called micronutrients or minor elements.
Deficiency of the nutrients affects physiological processes in plants as well as their reproduction,
growth. and susceptibility to diseases.To overcome the deficiency of nutrients, the soil can be enriched by adding manures and fertilisers.
Besides these, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen are called framework elements.
1. Food supplies all the required nutrients for the development, growth and health of the body.
2. Cereals like wheat, provide carbohydrates, pulses (grams) provide proteins and oil seeds provide fats.
3. Hybridization is crossing between genetically dissimilar plants
(inter varietal, inter specific or inter generic).
4. Improvement of agriculture is done for higher yield, biotic and abiotic resistance, improved quality grade, adaptability and other factors.
5. Macronutrients are those that are required in large quantities by the body
(N, P, K, Ca, Mg, S, etc.).
6. Micronutrients are those that are required in small quantities (Mn, B, Zn, etc.).
7. Manure contains organic matter and supplies nutrients to the soil. It is prepared by the decomposition of
animal excreta and plant waste.
8. The process in which waste material is decomposed is known as composting. Composts prepared by
using earthworms is called vermi compost.
9. Fertilizers are commercially produced and supply nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
10. Continuous use of fertilizers in an area can destroy soil fertility and also lead to water pollution.
11. To reduce the harmful effects of fertilizers organic farming (use of biofertilizers & organic manure) should be practiced.
12. Use of wells, canals, river lift systems, tanks, rain water harvesting and watershed management has
increased the water availability for agriculture.
13. Mixed cropping is growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land. For example
wheat and mustard are often grown together.
14. Inter cropping is growing of two or more crops in the same field but in a definite pattern. For example
maize and soyabean crops are grown alternately.
15. Insects, rodents, fungi, bacteria, etc. cause loss to the stored grains.
16. Animal husbandry is the scientific management of animal livestock.
17. Milk producing animals are called milch animals and those that are used for farm labour are called
draught animals.
18. Exotic or foreign breeds have less resistance to diseases when compared to their local counterparts.
19. Poultry is undertaken to increase the production of meat and eggs.
20. Food given to broilers is proteinaceous in nature.
21. Mariculture is done to meet the demands of marine fish.
22. Fish culture is sometimes done in combination with rice crop.
23. Five or six species of fish are raised (grown) in a single pond in order to reduce competition for food.
This is called composite fish culture. For example catlas (surface feeders), rohas (middle zone) and
mrigals (bottom feeders) are raised together.
24. Rearing of honeybees is called beekeeping or apiculture.
25. Apis cerana indica (Indian bee), A. dorsata (Rock bee), Apis florae (little bee), Apis mellifera (Italian
bee) are generally used in the commercial production of honey.
26. Italian bees have high honey collection capacity.
Manures :
Manure are organic substances obtained from the decomposition of animal wastes, like cow dung and vegetable wastes by the action of microbes.
Types of Manures :
(i) Farmyard Manure (FYM) -
It is formed by the decomposition of a mixture of cattle excreta (dung), urine of cattle, litter and roughage.
By the action of micro-organisms all these materials decompose and are used as farmyard manure (FYM).
(ii) Compost :
Compost is a biological process in which the above mentioned organic matter is decomposed by both aerobic and anaerobic micro-organisms.
(iii) Green Manuring :
The practice of green manuring includes growing turning or ploughing and mixing of green crops with soil to improve physical structure and soil fertility.
Green manures may include both leguminous and non leguminous plants.
Fertilizers are the sources of plant nutrients manufactured commercially from chemicals.
They are inorganic or organic compounds containing necessary plant nutrients such as nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.
The chemical substance which can be used as a fertilizer must have the following characteristics:
Fertilizers are classified according to the element (N, P or K) which they supply to the soil.
(i) Nitrogeneous fertilizers
(ii) Phosphatic fertilizers
(iii) Potash fertilizers
(iv) NPK fertilizers
(i) Nitrogenous Fertilizers :
The important nitrogenous compounds used as fertilizers are :
Ammonium sulphate, (NH4)2SO4
Calcium cyanamide, CaCN2
Calcium ammonium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2, NH4NO3
Basic calcium nitrate, Ca(NO3)2, CaO
Urea, (NH2–CO–NH2)
(ii) Phosphatic Fertilizers :
The minerals of phosphorus such as phosphorite, [Ca3(PO4)2] and apatire, [3Ca3(PO4)2·CaF2] are sparingly soluble in
water and thus do not serve as source of phosphorus for plants. These are, therefore, converted into soluble materials which can act as good fertilizers. The important phosphatic fertilizers are :
Calcium superphosphate
Nitrophosphate
Triple phosphate
Phosphatic slag
(iii) Potash Fertilizers :
Potassium nitrate, potassium chloride and potassium sulphate are used as fertilizers.
(iv)NPK Fertilizers :
Fertilizers containing N, P and K in suitable adjusted proportions are known as NPK fertilizers.
These are obtained by mixing nitrogenous, phosphatic and potash fertilizers in suitable proportions.
Irrigation the process of providing water to the soil for the purpose of supplying moisture essential for plant growth.
² Irrigation method :
² Mixed Croppoing :
The process of mixing seeds of two or more different crops and then sowing then in the same field is called mixed cropping.
Example of mixed cropping -
(a) Wheat + mustard
(b) Maize + urad
(c) Arhar + mung
(d) Ground nut + sunflower
² Advantages of Mixed Cropping :
There is lesser risk of total crop failure because if one crop fails, then the other crop helps the farmers to overcome his loss.
Farmers get a variety of products for their family by growing crops under the mixed cropping system, e.g. cereals, pulses, fodder and vegetables may be grown simultaneously.
² Intercropping :
Intercropping is a special type of mixed cropping in which two or more crops are grown simultaneously in the same field following a definite row pattern.
Differences between mixed cropping and intercropping :
The growing of different crops on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession is called crop rotation.
Depending upon the duration, crop rotation may be of following three types :
(a) One year rotation
1. Maize - Mustard
2 Rice - Wheat
(b) Two years rotation
1. Maize - Mustard-Sugarcane - Fenugreek
2 Maize - Potato- Sugarcane - Peas
(c) Three years rotation
1. Rice - Wheat - Mung - Mustard
2. Sugarcane - Berseem
3. Cotton - Oat - Sugarcane - Peas - Maize - Wheat
² Selection of Crops of Rotation :
Source of moisture (through rain or irrigation).
Status of nutrients in the soil.
Availability of inputs (such as fertilizers, pesticides, man power and machine power).
Duration of crop short or long
Marketing and processing facilities.
² Advantages of Crops Rotation :
Crop rotation helps in replenishment of soil fertility.
It prevents depletion of selective nutrients.
It prevents building up of diseases and pests of particular crop.
It enhances the production by increasing the soil fertility.
² Organic Farming :
Manures are natural fertilizers. They are bulky sources of organic matter which supply nutrients in small quantities but organic matter in large quantities.
Manures include farmyard manure (FYM). Compost, green manures, vermicompost, etc.
² Advantages of Manures :
Manures affect the soil in following three ways :
The manures enrich the soil with nutrients. They replenish the general deficiency of nutrients in the soil.
Since manures contain nutrients in small quantities, they are needed to be applied in large quantities.
The manures add organic matter (called humus) to the soil which restores the soil texture for better retention of water and for aeration of soil.
For example, organic matter present in the manures increases the water holding capacity in sandy soils and drainage in clayey soil
The organic matter of manures provide food for the soil organisms (decomposers such as bacteria, fungi, etc.) which help in making nutrients available to plants.
Thus, organ is manures help to improve the physical properties of soil, reduce soil erosion, increase the moisture holding capacity of
soil and above all these advantages, they are low cost nutrient carriers.
² Crop protection management :
Field crops are affected by a large number of weeds, pestes disease which cause damage the crops & reduce their productivity.
² Weeds :
Weeds are unwanted plants which complete with main crop for nutrition & reduce the growth of crop.
Examples of weeds : -
* Wild sorghum
* Chaulai
* Bathua
* Parthenium
² Methods of weed control :
Mechanical methods
Chemical or use of weedicides
Biological
² Pests :
Harmful creatures for our crop plants are small insects which attack the plants in three ways :
² Insect Pest Control :
Based on the mode of attack, the insect pests are of following three types :
² Chewing Insects :
They cut and chew root, stem and leaves of the plants with the help of their chewing type of mouth parts. e.g., grass hoppers, locusts, caterpillars, grubs etc.
² Sucking Insects :
They suck the cell sap from different parts of the plants with the help of piercing and sucking mouth parts. eg. Aphids, leaf hoppers, plant bugs, etc.
² Borer Insects :
They bore and enter different plant parts, and feed on the plant tissues eg. Sugarcane borer, pod borers, cotton ball weevil, grain weevils, etc.
² Methods of Insect Pest Control :
The root cutting type of insects can be controlled by mixing insecticide in the soil.
The stem and leaf cutting and boring type of insects can be controlled by dusting or spraying the contact insecticides. eg., malathion, lindane.
The sap sucking insects can be controlled by spraying systemic insecticides.
A wide variety of plant pathogens such as bacteria, viruses and fungi, exist in our environment.
Pest infect and cause serious diseases in our crops.
The diseases caused by these pathogens include blast in paddy (rice), rust in wheat, red rot in sugarcane.
Based on the mode of transmission, plant diseases are of following four types -
Seed Borne Diseases :
The diseases which spread through seeds are called seed borne diseases, e.g., loose smut of wheat, leaf spot of rice.
Soil Borne Diseases :
The soil borne diseases mostly affect roots and stems of crop plants, e.g., smut of bajra, tikka disease of groundnut.
Air Borne Diseases :
The air diseases attack all aerial parts of the plants like leaves, flowers and fruits. e.g., rust of wheat, blast of rice.
² Water Borne Diseases :
The diseases which are transmitted through water are termed as water borne diseases. e.g., bacterial blight of rice.
Proper and safe storage of food grains is necessary to ensure their availability throughout the year.
The various factors that contributes to this loss can be placed into two categories -
Biotic Factor :
Such as insects, rodents (e.g., squirrel, rat), birds (e.g., sparrow, crow, pigeon), fungi, mites and bacteria.
Abiotic Factor :
Such as moisture content and temperature.
Higher temperature (i.e., 30 – 32ºC) of stored grains make them liable to decay.
The various types of damages caused by the above factors include
(a) Infestation in insects,
(b) Degradation in quality,
(c) Loss in weight,
(d) Poor germinability,
(e) Discolouration of produce
(f) Poor marketability
Science which deals with the scientific management of farm animals including their feeding. breeding. weeding and heeding (disease control) is called as Animal husbandry.
There are four main practices involved in keeping of animals or animal husbandry
.
² Animal food mainly comes from:
(i) Milk: From cattle such as cow, buffaloes, goat, camel.
(ii) Egg: From birds (oultry).
(iii) Meat: Animals like pigs, fishes, poultry etc.
(iv) Honey: From honey bees.
Various types of animal farming are:
(i) Cattle farming - (Milk producing or milch animals)
(ii) Poultry farming - (Egg yielding animals)
(iii) Fish farming - (meat providing fishes)
(iv) Bee keeping - (Honey providing bees)
Farming of cattle for milk and labour is called cattle farming.
(A) Milk producing breeds: Milk providing animals are - cows, buffaloes, goalts, camels.
Breeds of Cow: Cows are a good source of milk for food of human beings and bullocks help in
farming and transport purposes. Based upon the milk production and other utility, various breeds of cow are categorized in three types i.e.
(i) Milch breeds or dairy breeds
(ii) Draught breeds
(iii) Dual purpose or general utility breeds.
(I) Milch or Dairy breeds: Milch or dairy breed cows are of three types in India I.e.
(a) Indigenous breeds
(b) Exotic breeds and
(c) Cross breeds.
(a) Indigenous breeds: These are the Indian breeds of milch or dairy cows. These are
(i) Red Sindhi (ii) Sahiwal (iii) Gir
(b) Exotic breeds: These are foreign breeds of cows which have been introduced in our country.
The selected breeds of cows that have been successfully used for cross breeding in our country are:
(i) Jersey: England
(ii) Holstein Friesian: Hoiland
(iii) Brown Swiss :A dual purpose breed of cow from Switzerland
(c) Cross breedsllmproved breeds of cows: Cross or improved breeds of dairy cows have been developed in
India at National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI) Kamal (haryana).The successful
Cross breeds of cow in our country are:
(i) Karan Swiss: This is the cross breed of Brown Swiss and Sahiwal.
(ii) Karan Fries : This is the cross breed of Holstein-Friesian from Holland and Tharparkar of India.
The yield of milk from new cross breed cows has increased two to three times more than our indigenous cows.
(II) Draught breeds: Cattle of this breed are strong and sturdy. They are the "beasts of burden: I.e. are used for drawing bullocks carts
, ploughing land of crop fields are transporting materials from one place to another.The cows of these breeds produce less milk. S
ome of the common examples of these breeds are Malvi, Nageri, Hllikar, Kangayam etc.
(III) Dual Purpose or General utility breeds: In these breeds, the cows are good milk yielders and bullocks are good for draught work.
Some of the breeds of this category are Haryana, Tharparkar, Ongole, Kankrej etc.
² Breeds of Buffalo: Buffaloes are major source of milk in our country. These are domesticated in great number. The important breeds of buffaloes with high yield of milk are:
(a) Mehsana (b) Surti (c) Murrah
² Most notable effort for dairy development & milk production in India is being carried out by NODS (National Dairy Development Board) and is called "operation flood" to increase milk production.
² It has resulted in White revolution in India.

* Cattle food is of two types:
* Roughage: Rich in fibre content. It includes green fodder, silage, hay.
* Concentrate: Rich in all types of nutrients, lacks fibre. It includes maize, oat, barley, jowar etc
* Diseases of Cattle A healthy animal is recognized by :
(a) Its regular feeding,
(b) Normal posture,
(c) A definite body temperature
(d) Normal pulse and respiration rates.
A sick animal shows following symptoms.
(a) The animal stops eating and becomes lethargic, looks tired and remains isolated.
(b) The animal shivers with high body temperature.
(c) The animal shows excessive formation of saliva which sometimes hangs from the mouth,
(d) Blisters appear on skin surface, eyes turn red, and the animal may have a running nose,
(e) The animal passes loose dung and coloured urine.
(f) The lips and ears of the animal droop.
(g) Milk yield, egg-laying capacity or working capacity of the animal is reduced.
* Diseases: Diseases caused are broadly of three types:
Parasitic
Infectious
Non - infectious

² Prevention and Control:
Providing proper shelter.
Ensuring animal hygiene (frequent bathing and grooming) and proper disposal of dead animals and animal wastes.
Periodic screening of animals for diseases and immediate isolation of diseased animals.
Providing proper diet and suitable medicines under the advice of a veterinary doctor.
Hygienic handling of all animal products and by products,
Compulsory vaccinations.
Poultry: Poultry is the collective term for domestic birds such as chicken, ducks, pheasants, geese etc. raised for their egg and meat. Rearing,
breeding and caring of fowls and related birds for eggs and meat is called Poultry farming. An egg laying poultry bird is called hen and the poultry birds reared for obtaining meat are called chicken (broilers).
(A) Indigenous (desi) breeds of hen
Aseel (Indian game)
Ghagus (kadaknath)
Basara (Burrsa)
Chittagong (Chattisgarh)
Brahma
Cochin
(B) Exotic breeds used in India
White Leghorn
Rhode Island Red
Black Minorcha
Plymouth
Light Sussex
² Silver Revolution: Increase in egg production on large scale.
(C) Improvement of poultry breeds: It involves:
Developing of new varieties. They have following advantages.
Number & quality of chicks are increased.
Summer adaptation capacity.
Low maintenance requirements.
Dwarf broilers present for commercial chick prod uction.
(D) Poultry diseases : These birds suffer from many diseases caused by bacteria, fungi, viruses and parasites along with nutritional deficiencies.
² Diseases of poultry birds:
² These can be prevented by proper cleaning sanitation and spraying of disinfectants.
² Poultry farming offers other advantages like:
(a) Investment involved is small.
(b) Area required is small.
(c) Maintenace is easy, and
(d) Returns are quick.
² Fish Farming: Fishes have been used as protein rich diet for human beings since pre-historic period.
Fishes are aquatic animals and their production is called fish farming or water agriculture.
² Various ways to obtain fishes:-
² Capture fishing - From natural resources.
² Culture fishing - Fish farming in land water fishes, ponds, lakes, marine fishes.
• Our fresh water edible fish include cat fishes such as Wallago, mystus etc.
• Indian major carps such as Catla, Rohu, Mrigal (Cirrhina).
• Exotic varieties such as Silver carp and Grass carp.
• Catla is the fastest growing carp of great economic significance.
• Marine fisheries: India's marine fishery resources include 7500 km of coastline and the deep seas beyond it.
• Popular marine fish varieties are pomphret, mackerel, tuna. sardines and Bomby duck.
• Yield are increased by locating large schools of fish in the open sea using satellites and echo-sounders.
• Some marine fish of high economic value are also farmed in seawater.
• This includes finned fishes like mullets. bhetki , and pearl spots, shellfish such as prawns mussels and oysters as well as seaweed .
• Marine fish culture is called mariculture.
• Inland fisheries : Fresh water resources include canals, ponds, reservoirs and rivers.
• Catlas are surface feeders.
• Rohus feed in middle zone of the pond.
• Mrigals and common Carps feed on the weeds.
² Definition: Apiculture is the process of rearing of honey bees in the artificial hives, called apiaries, for the production of honey at commercial level.
² Species of Honey bees: Honey bees belong to phylum Arthropoda and class Insecta
. There are several species of honey bees some of which are indigenous while some of them are exotic which have been introduced to increase the yield of honey.
(a) Indigenous Species:
(i) Apis dorsata: It is commonly called rock bee or giant bee (being largest sized)
. Though it produces maximum amount of honey but is ferocious and migratory bee so it is difficult to domesticate this variety.
(ii) Apis indica: It is commonly called Indian bee. It can be domesticated easily as it is very gentle in nature but is less producing species.
(iii) Apis florae: It is commonly called little bee (being smallest sized). It is also very docile but yield is less.
(b) Exotic Species:
• Apis mellifera : It is commonly called Italian bee. It is preferred over the indigenous species for the commercial production of honey because of its docile nature
, high yield of honey, prolific egg production, less swarming and with good defence mechanism.
• Honey Bee Colony and Social Organisation: Honey bees are social and polymorphic insects. These live in large colonies, c
alled hives or combs, of about 40,000 to 100,000 individuals. In a colony, there are three castes of bees which are structu rally
and functionally different from one another so polymorphism is associated with division of labour. These three castes are:
(i) Queen: Every healthy colony has only one fertile female called queen. It is the mother of the colony and has well developed ovaries.
It has long tapering abdomen, short legs and wings. Its sole function is to lay the eggs at the rate of 1500 to 2000 in a day,
while during its life span of about 3 years, a queen lays about 1.5 to 2.0 million eggs. A queen lays two types of eggs :
fertilized and unfertilized eggs. Queen and workers develop from fertilized eggs while drones develop from unfertilized eggs.
(ii) Workers: These are largest in number (about 50,000 to 60,000) but smallest sized members.
These are most active and perform variety of jobs like: attend the queen and nursery. clean the hives. form a new hive and produce wax. repair the comb, keep the comb cool,
defend the members etc. So the workers have strong wings, long mouth parts. wax glands on abdomen, pollen collecting apparatus on the legs and a sting at the end of abdomen.
(iii) Drones: These are male members of the colony and are of intermediate size. These have reduced mouth parts and are sluggish Their sole function is to copulate with the queen.
• Products of honey bees include honey, bees wax, bee venom and royal jelly.
(i) Honey: It is produced by the workers from the collected nectar and cane sugar. It is formed of levulose, dextrose (23%),
maltose (40%), enzymes and pigment (25%), minerals, vitamins and water.
(ii) Bees wax: It is used in cosmetics, paints. ointments, polishes etc.
(iii) Bee venom: It is used to cure certain diseases like gout and arthritis.
(iv) Royal jelly : It is used as tonic to heart patients and growing children.
² Management: Involves all those steps which are required to be undertaken to obtain good quality and higher yield of honey from the honey bees. It involves following considerations:
(a) Bee Forage or Pasturage: It includes all those flowering plants which provide pollens and nectar to the honey bees e.g. Mango,
coconut, almond, tamarind, ber, berseem, litchi, cotton, shisham, apple, mahua, coriander, cashew, coffee. rubber plant, guava, sunflower, etc
Their poilens form the protein-rich food for honey bees while their nectar acts as raw material of honey. The pasturage is different from region to region and depends upon the geographical location.
The quality and taste of honey depend, upon the nature of flora from which the nectar is collected. For increased yield. the pasturage should be easily available near the apiary.
(b)Apiary or Bee Hive: An artificial and movable bee hive, commonly called apiary, is about 46 x 23 cm in size and is a wooden box formed of following parts :
(i) Stand: It is the base on which the whole hive is placed.
(ii) Bottom Board: It forms the base of the hive and has two apertures which act as entrance and exit for the worKers and drones.
(iii) Brood chamber: It contains 5 to 10 wooden frames, each of which has a wax-sheet of the hexagonal frames, called comb foundation, on which the honey form the combs,
(iv) Super: It provides extra space for the expansion of the hive.
(v) Inner cover: It is a hole-bearing wooden cover.
(vi)Top cover: It is a plain zinc sheet for the protection of hive.
(c) Location of Apiary: To get maximum yield of honey, a number of bee hives should be placed in that area where abundance
of bee-flora is available within 1 or 2 kms radius for honey collection.
(d) Honey Flow Season: The yield of honey upon the total penod for which large number of nectar and pollen-yielding plants are available in the vicinity of the apiary is called honey flow period.
So honey yield will be more if the bee hives are established in an area having abundance of bee flora for longer period. While the period when no nectar and pollen is available is called dearth period.
(e) Swarming: It is the process of leaving off the colony by the old queen with some workers and drones to establish a new colony at a new place and to provide the existing hive for the progeny.
It normally occurs by the end of spring or early summer. But the frequent swarming decreases the yield of honey and increases
the maintenance cost of the bee hives. So to get higher yield of honey, less swarming variety of honey bees (e.g. Apis mellifera) should be reared.
(f) Bee Pest and their Control:
(g) Bee Diseases:
(i) Septicemia: A bacterial disease caused by Bacillus aspisepticus.
(ii) Nosema disease: A protozoan disease caused by Nosema apis.
(iii) Acarine disease: Caused by a parasite mite Acarapis
(iv) Fungal disease: Caused by Aspergillus species
Q.1 What is Animal Husbandry ?
Sol. Animal Husbandry is the scientific management of animal livestock. It includes various aspects such as feeding, breeding and disease control.
Q.2 Why is irrigation necessary ?
Sol. Irrigation is necessary because plants take up nutrients in liquid form.
Q.3 What is fumigation ?
Sol. Fumigation is a method in which the insecticides solution is converted into fumes, i.e., vapour or gas, to kill the insects.
The insecticides which are used for making fumes are called fumigants.
Q.4 Which all activities are adopted for improving crop yields ?
Sol. The activities which are adopted for improving crop yields are :
(i) Crop variety improvement
(ii) Crop production improvement
(iii) Crop protection management.
Q.5 What are genetically modified crops ?
Sol. Genetically modified crops are those crops in which a gene is introduced to provide the desired characteristic.
Q.6 What determines the quality of honey?
Sol. The value or quality of honey depends upon:
(i) The pasturage i.e., the kind of flowers available.
(ii) Apiary location.
Q.7 What are the problems of composite fish farming ?
Sol. The problems with composite fish farming are
(i) Many of the fish breed only during monsoon.
(ii) Lack of availability of good quality seed.
Q.8 What is apiculture ?
Sol. The practice of bee keeping to get honey, bees wax, etc., is called apiculture.
Q.9 Why should biological control methods be preferred for protecting crops ?
Sol. Biological control methods should be preferred for protecting crops because :
(i) They do not harm useful organisms.
(ii) They do not cause poisoning of the stored food grains.
Q.10 What preventive and control measures should be taken before storage of grains?
Sol. The preventive and control measures that should be taken before storage of grains are :
(i) Strict cleaning of the produce before storage.
(ii) Proper drying of produce first in sunlight and then in shade.
(iii) Fumigation using chemicals that can kill pests.
Q.11 What are the advantages of intercropping?
Sol. The advantages of intercropping are :
(i) It makes better use of the natural resources of sunlight, land and water.
(ii) It ensures maximum utilisation of the nutrients supplied.
(iii) It also prevents pest and diseases from spreading to all the plants belonging to one crop in a field.
Q.12 What are the advantages of crop rotation ?
Sol. The advantages of crop rotation are :
(i) It controls pests and weeds.
(ii) It reduces the need of fertilizers.
(iii) If crop rotation is done properly then two or three crops can be grown in a year with good harvests.
Q.13 What are pests ? How do they attack the plants or crop ?
Sol. A pest is any destructive organism which causes great economic loss by destroying crop plants or products obtained from them. Generally pests attack the plants in three ways
(i) They cut the root, stem and leaf.
(ii) They suck the cell sap from various parts of the plant.
(iii) They bore into stem and fruits.
Q.14 How can pests be controlled ?
Sol. Pests can be controlled by various methods. They are :
(i) Use of resistant varieties of crop plants.
(ii) Timely sowring of crops.
(iii) Clean cultivation.
(iv) Intercropping and crop rotation.
(v) Summer ploughing.
Q.15 What factors may be responsible for losses of grains during storage ?
Sol. Factors which are responsible for losses of grains during storage are :
Biotic : Insects, rodents, fungi, mites and bacteria.
Q.1 Define – green manure and vermicompost.
Q.2 Differentiate between bee keeping and poultry farming.
Q.3 Give two merits and two demerits of fish culture.
Q.4 Suggest two preventive measures for the diseases of poultry birds.
Q.5 List out four useful traits in improved crop?
Q.6 What is a GM crop ? name any one such crop which is grown in india ?
Q.7 Define the term photoperiod.
Q.8 Group the following and tabulate them as energy yielding, protein yielding oil yielding and fodder crop Peanut plant, mustard plant, Barseem, Rice plant
Q.9 What type of crops are generally raised in green fields ?
Q.10 Write four points on human dependence on plants and animals for food.
Q.11 Why do we select crops which have different nutrient requirement for inter – cropping? Give two reasons.
Q.12 The use of manure is better than the use of fertilizers. Mention any two points in support of this statements.
Q.13 What are the factors responsible for storage of grain losses ? Give any two preventive control measures before storage of grains.
Q.14 A farmer grows soyabeen in five rows and maize in another five rows and follows the same pattern throughout
his one acre of land Name the type of cropping pattern, define the term and state two advantages.
Q.15 Differentiate between manures and fertilisers.
Q.16 Why micronutrients and macronutrients ar called so ? What role do they play ?
Q.17 Why should preventive measures and biological control methods be preferred for protecting crops ?
Q.18 Genetic manipulation is considered asuseful agrivcultural prictice. Why ?
Q.19 why are manure and fertilizers used in fields.
Q.20 why good animal husbandry practices are considered very benefical for the farmers.
Q.21. How do biotic and abiotic factors affect crop roductin ?
Q.22 Compare the use of manure and fertilizers in maintaining soil fertility.
Q.23 what are the advantages of inter-cropping and crop rotation ?
Q.24 (a) What is composting ?
(b) How orgainc farming is done ?
Q.25 What is the composition of normal animal feed
Q.26 How do plants get nutrients ?
Q.27 How are fish obtained ?
Q.28 Why are manures and fertilisers used in fields ?
Q.29 For increasing production, what is common in poultry, fisheries and bee-keeping?
Q.30 Name two fertilisers supplying N, P, K to crops.
Q.31 What are the factors on which irrigation requirements depend ?
Q.1 DDT is :-
(A) A non-degradable pollutant
(B) A biodegradable pollutant
(C) An antibiotic
(D) Not a pollutant
Q.2 Which amongest the following is a fungicide:-
(A) 2-4 D (B) DDT (C) Bordeaux mixture (D) BHC
Q.3 The pesticides need to be replaced because these :-
(A) Are very costly
(B) Cannot be stored for a long time
(C) Are mostly toxic and non-biodegradable (D) Cause abnormalities in the target population
Q.4 Heat of damp grain in storage occurs due to:-
(A) Infestation by insects
(B) Decrease in atmospheric pressure
(C) Decrease in humidity
(D) High moisture content and growth of moulds
Q.5 Fumigants are used for :-
(A) Preserving food materials
(B) Killing insects harming food grains
(C) Increasing nutrients of plants
(D) Preserving dairy products
Q.6 Ethylene dibromide is used as a :-
(A) Fumigant (B) Fertilizer (C) Food preservative (D) Source of vitamins
Q.7 Malathion is used as :-
(A) Fungicide (B) Insecticide (C) Weedicide (D) Biocide
Q.8 Storage grains produce aflatoxin due to growth of :-
(A) Yeast (B) Mould
(C) Aspergillus (D) Virus
Q.9 Materials of biological origin which are commonly used to maintain and improve soil fertility are :-
(A) Green manures (B) Biofertilizers
(C) Bioinsecticides (D) Both (A) and (C)
Q.10 Find out the organochlorines among the following :-
(A) Malathion, fenitrothion, parathion (B) Carbofuran, propoxur, aldicarb
(C) Phrethrin, triazines, simazine (D) DDT, BHC, dieldrin, endosulphan
Q.11 Heterotrophs are organisms which :-
(A) make their own food
(B) derive food from animals
(C) derive food from plants
(D) derive food from the biomass of other organisms
Q.12 Autotrophs are organisms which :-
(A) make their own food
(B) derive food from animals
(C) derive food from plants
(D) derive food from the biomass of other organisms
Q.13 The increase in foodgrain production after the introduction of improved varieties of crops is often referred as :-
(A) White Revolution (B) Green Revolution (C) Yellow Revolution (D) Blue Revolution
Q.14 The minerals required by a plant in very small quantities are called :-
(A) macronutrients (B) micronutrients (C) manures (D) fertilizers
Q.15 The process of preparing manure with the help of earthworms and kitchen wastes is called :-
(A) green manuring (B) manuring (C) Vermicoposting (D) farming
Q.16 Growing two or more crops at the same time in a field is called :-
(A) mixed farming (B) mixed cropping (C) farming (D) intercropping
Q.17 The practice of growing two or more crops simultaneously in definite rows in the same field is called :-
(A) mixed cropping (B) mixed farming (C) intercropping (D) farming
Q.18 A pulse crop is grown in the time interval between two cereal crops to compensate for the :-
(A) loss of phosphate (B) loss of water (C) loss of sulphur (D) loss of nitrogen
Q.19 The science of improving crop varieties is called :-
(A) hybridization (B) selection (C) plant breeding (D) introduction
Q.20 Plant breeding aims to produce :-
(A) disease-free varieties
(B) high-yielding varieties
(C) early-maturing varieties
(D) all the above
Q.21 Increase in oil production is :-
(A) Golden revolution (B) Yellow revolution
(C) White revolution (D) Blue revolution
Q.22 Pulses are rich in :-
(A) Proteins (B) Carbohydrates (C) Oils (D) Vitamins and minerals
Q.23 Kharif crop is :-
(A) Summer season crop
(B) Winter season crop
(C) Spring season crop
(D) Autumn season crop
Q.24 Rabi crops are sown in
(A) August (B) September (C) October (D) March
Q.25 The method used to obtain variety with high yield and other desirable characters is :-
(A) Introduction (B) Selection (C) Hybridisation (D) Both A and B
Q.26 Pusa lerma is an improved variety of :-
(A) Rice (B) Maize (C) Soya bean (D) Wheat
Q.27 Which one is a micronutrient :-
(A) Iron (B) Calcium (C) Magnesium (D) Potassium
Q.28 The common biofertilizers used in organic farming are :-
(A) Margosa
(B) Pyrethrum
(C) Green manure
(D) Nitrogen fixing bacteria and cyanobacteria
Q.29 Cultivation of two or more crops together in the same field is :-
(A) Mixed cropping (B) Intercropping
(C) Crop rotation (D) All the above
Q.30 Growing different crops in the same field in a preplanned succession is :-
(A) Crop management (B) Crop rotation
(C) Intercropping (D) Plant breeding
1. What nutrients mainly we get from vegetables, spices and fruit crops?
2. What is hybridisation?
3. What are manures?
4. What is composting?
5. Write one main aim of mixed cropping.
6. Name the process by which two different crops are sown alternately in the same field.
7. What does cattle feed include?
8. Which vitamins are kept at high level in the poultry feed?
9. Name major indigenous breeds of fish which are cultivable.
10. Write two advantages of bee-keeping.
11. Define aquaculture.
12. What is induced breeding ?
1. What is composite fish culture? Write the advantages of composite fish culture?
2. What is poultry farming? Name two Indigenous and exotic poultry breeds.
3. Discuss the various measures for safe storage of grains.
4. Enlist various methods of weed control.
5. Name various species of bees which one of them is most useful and why?
Section-A
· Fill in the blanks
1. Raising domestic fowl for chicken, meat and egg is _________________
2. Worms are ____________ parasites.
3. _____________ animal used for tilling and carting.
4. Before storage __________________ is done to remove insects.
5. Period of milk production after birth of calf is _________________ period.
6. ______________ adds humus to soil.
7. _______________ is growth and flowering in plants with respect to duration of sunlight.
8. _______________ increase water holding capacity of soil.
9. Culturing of aquatic plants and animals is called _________________.
10. _________________ Molluscan animals can produce pearls.
Section-B
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. Organisms preparing own food are
(A) Photoautotrophs (B) Chemoautotrophs (C) Both (D) Hetrotrophs
2. Abiotic factors includes
(A) Drought (B) Salinity (C) Temperature (D) All
3. Most important source of nutrient for plants is
(A) Soil (B) Water (C) Air (D) None
4. Manure is prepared by
(A) Microbial decomposition (B) Chemical treatment
(C) Physical processing (D) All
5. During inter-cropping, nutrient requirement of plants must be
(A) Different (B) Same (C) Uncertain (D) All
6. Long loctation period is found in
(A) Jersey (B) Red Sindhi (C) Sahiwal (D) All
7. Which is not technique of crop improvement
(A) Introduction (B) Selection (C) Hybridization (D) Feeding
8. Broiler chicken are given
(A) More protein (B) No protein (C) Less protein (D) None
9. The production and management of fish is
(A) Sculpture (B) Apiculture (C) Aquaculture (D) Both (B) and (C)
10. Process of cross-breeding two individuals of different variety is
(A) Hybridisation (B) Feeding (C) Intermixing (D) None
11. Cattle feed includes
(A) Roughage (B) Concentrates (C) Both (D) None
12. Worms are
(A) External parasite (B) Internal parasite (C) Freindly (D) None
13. Leghorn is
(A) Exotic breed (B) Indeginous breed (C) Both (D) None
14. Crops grown in winter are
(A) Kharif (B) Rabi (C) Both (D) None
Section-C
· Assertion & Reason
Instructions: In the following questions as Assertion (A) is given followed by a Reason (R). Mark your responses from the following options.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(C) Assertion is true but Reason is false
(D) Assertion is false but Reason is true
1. Assertion: It is not good idea to rely on rainfall as source of irrigation
Reason: Timing of monsoon season is highly fluctuating,
2. Assertion: All living organisms requires food.
Reason: Plant can synthesize there own food.
Section-D
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II.
Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Rearing honeybee (P) Pisciculture
(B) Manure (Q) Add humus
(C) Culturing fish (R) Unwanted plant
(D) Weeds (S) Apiculture
Section-A
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. Which of following is milch animal?
(A) Apis spp. (B) Bos indicus (C) Bos bubalis (D) Both (B)&(C)
2. Bees are kept for
(A) Honey (B) Wax (C) Medicine (D) All
3. Vermicompost is
(A) Manure (B) Excreta of earthworm (C) Both (A) & (B) (D) None
4. BGA is
(A) Pesticide (B)Biofertilizer (C) Both (D) None
5. Fertilizers
(A) Add humus (B) Do not add humus (C) Uncertain (D) None
6. Type of irrigation method.
(A) Tilling (B) Sprinkle (C) Drip (D) Both (B)&(C)
7. Example of Green manure is
(A) Neem (B) Legumes (C) Both (D) None
8. Source of protein
(A) Oat (B) Sudan (C) Soyabean (D) All
9. Wheat is
(A) Rabi crop (B) Kharif crop (C) Both (D) None
10. To prevent lodging crop should be
(A) Tall (B) Dwarf (C) No relation in night and lodging (D) All of the above
Section-B
· Multiple choice question with one or more than one correct answers
1. Livestock includes
(A) Goat (B) Cattle (C) Wild animal (D) Poultry
2. Weeds includes
(A) Parthenium (B) Xanthium (C) Wheat (D) Rice
3. Crop rotation
(A) Ensure proper utilization of nutrients (B) Keeps pest and disease low
(C) Reduce soil fertility (D) Waste time
4. Problems with composite fish culture
(A) Breeding only in monsoon season (B) competition among fish varieties
(C) Lack of good quality fish seed (D) All
5. Factors considered for storage of grain
(A) Temperature (B) Moisture (C) Fungus (D) Insects
Section-C
· Comprehension
Apiculture is done for producing honey, wax and medicine. The varieties used for apiculture includes A. dorsata, A. florae etc because they sting less and live longer in given beehive.
1. Rearing of bee is done for
(A) Honey (B) Wax (C) Furfural (D) Both (A) & (B)
2. Honey bee are kept in
(A) Cage (B) Cave (C) Beehive (D) All
3. Useful honey bee is/are
(A) A. Florae (B) A. dorsata (C) Both (D) None
Section-D
· Match the following (one to many)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II.
One or more than one entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II may have one or more than one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Poultry (P) Manure
(B) Livestock (Q) Broiler & Layer
(C) Organic (R) Produce egg & meat
(D) Biodegradable (S) Cattle
1. What nutrients mainly we get from vegetables, spices and fruit crops?
2. What is hybridisation?
3. What are manures?
4. What is composting?
5. Write one main aim of mixed cropping.
6. Name the process by which two different crops are sown alternately in the same field.
7. What does cattle feed include?
8. Which vitamins are kept at high level in the poultry feed?
9. Name major indigenous breeds of fish which are cultivable.
10. Write two advantages of bee-keeping.
11. Define aquaculture.
12. What is induced breeding ?
1. What is composite fish culture? Write the advantages of composite fish culture?
2. What is poultry farming? Name two Indigenous and exotic poultry breeds.
3. Discuss the various measures for safe storage of grains.
4. Enlist various methods of weed control.
5. Name various species of bees which one of them is most useful and why?
EXERCISE-III
Section-A
· Fill in the blanks
1. Raising domestic fowl for chicken, meat and egg is _________________
2. Worms are ____________ parasites.
3. _____________ animal used for tilling and carting.
4. Before storage __________________ is done to remove insects.
5. Period of milk production after birth of calf is _________________ period.
6. ______________ adds humus to soil.
7. _______________ is growth and flowering in plants with respect to duration of sunlight.
8. _______________ increase water holding capacity of soil.
9. Culturing of aquatic plants and animals is called _________________.
10. _________________ Molluscan animals can produce pearls.
Section-B
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. Organisms preparing own food are
(A) Photoautotrophs (B) Chemoautotrophs (C) Both (D) Hetrotrophs
2. Abiotic factors includes
(A) Drought (B) Salinity (C) Temperature (D) All
3. Most important source of nutrient for plants is
(A) Soil (B) Water (C) Air (D) None
4. Manure is prepared by
(A) Microbial decomposition (B) Chemical treatment
(C) Physical processing (D) All
5. During inter-cropping, nutrient requirement of plants must be
(A) Different (B) Same (C) Uncertain (D) All
6. Long loctation period is found in
(A) Jersey (B) Red Sindhi (C) Sahiwal (D) All
7. Which is not technique of crop improvement
(A) Introduction (B) Selection (C) Hybridization (D) Feeding
8. Broiler chicken are given
(A) More protein (B) No protein (C) Less protein (D) None
9. The production and management of fish is
(A) Sculpture (B) Apiculture (C) Aquaculture (D) Both (B) and (C)
10. Process of cross-breeding two individuals of different variety is
(A) Hybridisation (B) Feeding (C) Intermixing (D) None
11. Cattle feed includes
(A) Roughage (B) Concentrates (C) Both (D) None
12. Worms are
(A) External parasite (B) Internal parasite (C) Freindly (D) None
13. Leghorn is
(A) Exotic breed (B) Indeginous breed (C) Both (D) None
14. Crops grown in winter are
(A) Kharif (B) Rabi (C) Both (D) None
Section-C
· Assertion & Reason
Instructions: In the following questions as Assertion (A) is given followed by a Reason (R). Mark your responses from the following options.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(C) Assertion is true but Reason is false
(D) Assertion is false but Reason is true
1. Assertion: It is not good idea to rely on rainfall as source of irrigation
Reason: Timing of monsoon season is highly fluctuating,
2. Assertion: All living organisms requires food.
Reason: Plant can synthesize there own food.
Section-D
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II.
Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Rearing honeybee (P) Pisciculture
(B) Manure (Q) Add humus
(C) Culturing fish (R) Unwanted plant
(D) Weeds (S) Apiculture
Section-A
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. Which of following is milch animal?
(A) Apis spp. (B) Bos indicus (C) Bos bubalis (D) Both (B)&(C)
2. Bees are kept for
(A) Honey (B) Wax (C) Medicine (D) All
3. Vermicompost is
(A) Manure (B) Excreta of earthworm
(C) Both (A) & (B) (D) None
4. BGA is
(A) Pesticide (B)Biofertilizer (C) Both (D) None
5. Fertilizers
(A) Add humus (B) Do not add humus (C) Uncertain (D) None
6. Type of irrigation method.
(A) Tilling (B) Sprinkle (C) Drip (D) Both (B)&(C)
7. Example of Green manure is
(A) Neem (B) Legumes (C) Both (D) None
8. Source of protein
(A) Oat (B) Sudan (C) Soyabean (D) All
9. Wheat is
(A) Rabi crop (B) Kharif crop (C) Both (D) None
10. To prevent lodging crop should be
(A) Tall (B) Dwarf
(C) No relation in night and lodging (D) All of the above
Section-B
· Multiple choice question with one or more than one correct answers
1. Livestock includes
(A) Goat (B) Cattle (C) Wild animal (D) Poultry
2. Weeds includes
(A) Parthenium (B) Xanthium (C) Wheat (D) Rice
3. Crop rotation
(A) Ensure proper utilization of nutrients (B) Keeps pest and disease low
(C) Reduce soil fertility (D) Waste time
4. Problems with composite fish culture
(A) Breeding only in monsoon season (B) competition among fish varieties
(C) Lack of good quality fish seed (D) All
5. Factors considered for storage of grain
(A) Temperature (B) Moisture (C) Fungus (D) Insects
Section-C
· Comprehension
Apiculture is done for producing honey, wax and medicine. The varieties used for apiculture includes A. dorsata, A. florae etc because they sting less and live longer in given beehive.
1. Rearing of bee is done for
(A) Honey (B) Wax (C) Furfural (D) Both (A) & (B)
2. Honey bee are kept in
(A) Cage (B) Cave (C) Beehive (D) All
3. Useful honey bee is/are
(A) A. Florae (B) A. dorsata (C) Both (D) None
Section-D
· Match the following (one to many)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II.
One or more than one entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II may have one or more than one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Poultry (P) Manure
(B) Livestock (Q) Broiler & Layer
(C) Organic (R) Produce egg & meat
(D) Biodegradable (S) Cattle
Answers
Exercise-III
Section-A
1. Poultry farming 2. Internal 3. Drought
4. Fumigation 5. lactation 6. Manure
7. Photoperiodism 8. Manure 9. Aqua culture
10. Bivalve
Section-B
1. (C) 2. (D) 3. (A) 4. (A) 5. (A) 6. (A)
7. (D) 8. (A) 9. (C) 10. (A) 11. (C) 12. (B)
13. (A) 14. (A)
Section-C
1. (A) 2. (B)
Section-D
1. (A)-(S), (B)-(Q) , (C)-(P) , (D)-(R)
Section-A
1. (D) 2. (D) 3. (C) 4. (B) 5. (B) 6. (D)
7. (B) 8. (C) 9. (A) 10. (B)
Section-B
1. (A,B,D) 2. (A,B) 3. (A,B) 4. (A,C) 5. (A,B,C,D)
Section-C
1. (D) 2. (C) 3. (C)
Section-D
1. (A)-(Q,R), (B)-(R,S), (C)-(P), (D)-(P)