The World Health Organisation [W.H.O.] gave the following definition of health in 1948. Health is state of complete physical,
mental and social well being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity.
The WHO definition of health recognizes three dimension of health i.e. Physical, mental and social.
In 1978 this definition was updated by including- the ability to lead a "Socially and economically productive life".
It is rightly said that Health is Wealth. There are various factors which influence health.
These factors lie both within the individual and also in the society in which he or she lives
. The internal factors are basically the genetic make-up of an individual while external factors lie in the environment to which he/she is exposed.
Personal health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being. Community health comprises of maintaining, improving
and protecting the health of entire community.
The various factors that help in maintaining community health are :
(i) Maintaining proper hygienic and sanitary conditions of the environment.
(ii) Providing good socio-economic conditions.
(iii) Providing health care services.
(iv) Imparting health education and promoting public awareness.
(v) Providing proper facilities for preventing diseases.
Basic conditions for good health :
Sound mind in a sound body is the old saying and expresses the importance of good health.
(i) Balanced diet (ii) Personal hygiene (iii) Clean surroundings
(iv) Clean food and water (v) Clean air (vi) Exercise and relaxation
(vii) No addictions (viii) Good economic conditions
DISEASE
The word disease (dis-ease) literally means disturbed ease or uncomfortable.
Thus disease can be defined as "Malfunctioning of the body or a part of it due to one reason or the other".
Or
Disease is a condition of the body or a part of it in which functions are disturbed or deranged.
Signs and symptoms help in the diagnosis of a disease Diagnosis means the process of identifying a disease.
In many case doctor also needs the help of laboratory tests of blood, urine, stool etc and diagnostic images like x rays to diagnose a disease.
Pathogens - Disease causing organisms are called pathogens or infectious agents.
Vectors - Animals or insects that carry the infectious agents from one person to another and spread a disease are called vectors.
Insect vector Disease Transmitted
1. Mosquitoes
(i) Anopheles Malaria
(ii) Culex Filariasis
(iii) Aedes Yellow fever, Dengue, Filariasis
2. Flies
(i) House fly Thyphoid, Diarrhoea, Dysentry, Cholera,
Tuberculosis, Conjunctivitis
(ii) Sand fly Kala azar, Oriental Sore
(iii) Tse-tse fly Sleeping sickness
3. Louse Epidemic typhus
4. Rat flea Bubonic plague
DO YOU KNOW ?
Hippocrates : First to look for scientific explanation for diseases. He is remembered today as FATHER OF MEDICINE.
Susruta : He used non poisonous leeches as an anticoagulant during surgery so he is called father of surgery.
Charaka : He first gave concept of digestive metabolism and immunity. He is known as Father of Ayurveda [Ayu- Life, veda- knowledge]
Rudolf virchow : Father of Modern pathology.
Father of Immunity : Edward Jenner (small pox vaccine)
Father of Modern bacteriology : =Robert Koch (Anthrax T.B., cholera)
ACUTE AND CHRONIC DISEASE
A disease that occurs suddenly and lasts for a short period of time is called an acute disease e.g. common cold, Malaria disease.
A disease that lasts for a long time is called chronic disease e.g. tuberculosis.
DISEASE AND ITS CAUSE
Human health is affected by various factors causes or sources, these factors can be of two major types:-
(i) Intrinsic or internal factors : Factors inside the body or within the body.
(ii) External or extrinsic factors : Factors out side the body.
MEANS OF SPREAD :- Disease causing microbes can spread through the air. This occurs through the little
droplets thrown out by an infected person who cough or sneezes. Disease can also be spread through water. When infectious agents get mixed with drinking water.
Some diseases are spread by sexual contacts or blood transfusions animals can also carry infectious agents.
ORGAN SPECIFIC AND TISSUE SPECIFIC MANIFESTATIONS
Different species of microbes enters through various points of body and there are many possible places organs or tissues where they could go.
If they enter from the air via nose, they are likely to go to the lungs. If they enter through the mouth they can stay in gut lining.
Malaria causing microbes enter through a mosquito bite and will go to the liver and then to Red blood cells
but virus of Japanese encephalitis or brain fever will similarly enter through mosquito bite will enter in brain or goes to infect brain.
The signs and symptoms of a disease will thus depend on the tissue or organs which the microbes target.
PRINCIPLES OF TREATMENT
The immune system is a major factor that determines the number of microbes surviving in the body.
There are two ways to treat an infectious disease, i.e.
, (i) to reduce the effects of the disease and
(ii) to kill the cause of the disease.
In the first case, treatment is provided to reduce the symptoms which are due to inflammation.
Doctor gives medicine to the patient so as to bring down fever, reduce pain or loose motions.
The patient is also advised to take bed rest, so that he/she can conserve his/her energy. This will enable him/her to have more energy to focus on healing.
To cure the disease, the microbes have to be killed by the use of medicine. As you know that microbes can be classified into different categories.
They are viruses, bacteria, fungi or protozoa. Each of these groups of organisms will have some essential biochemical life processes,
which is peculiar to that group and not shared with the other groups. These processes may be pathways for the synthesis of new substances or respiration.
For example, our cells may make new substance by a mechanism different from that used by bacteria.
Therefore, the drug that can block the bacterial synthetesis pathway without affecting our own, is used to cure a bacterial disease.
The antibiotic drugs work on the same principle. Similarly, there are drugs that kill protozoa such as malarial parasite without affecting our body.
Since viruses have only a few biochemical mechanisms of their own. This is the reason that making antiviral medicines is difficult than making antibacterial medicines.
The viruses enter the host cells and use host's machinery for their life processes. Therefore, there are relatively few virus drugs, which
check a number of viral diseases including HIV infection.
PRINCIPLES OF PREVENTION
There are two ways for prevention of disease one is general and one is specific to each disease.
First one is we can prevent exposure by providing good living conditions.
Safe drinking water and clean environment other is immune system of our body immune system of our body is normally fighting
off microbes we have cells that specialise in killing infecting microbes
. These cell go into action when microbes enter into body. The immune cells manage to kill off the infection long before it assumes major proportions.
The functioning of the immune system will be good if proper and sufficient nourishment and food is available.
There are some specific ways also for preventing infections like vaccination for particular disease.
BACTERIAL DISEASE
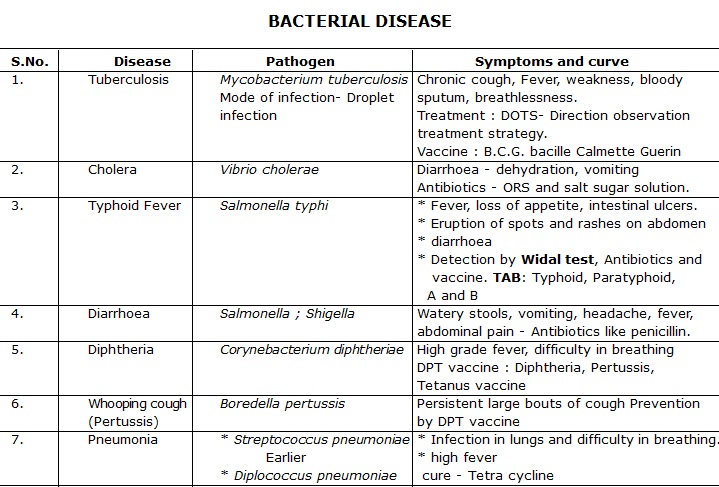
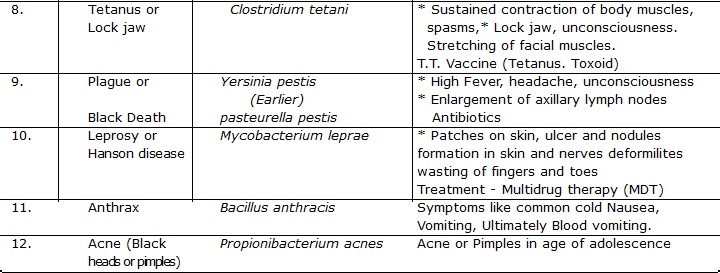
SALMONELLOSIS
Food poisoning by bacteria Salmonella is called salmonellosis. Bacteria Salmonella is present in the sick farm animals.
So the infection of bacteria Salmonella which causes food poisoning is contracted from the sick farm animals through
their contaminated food products such as milk, eggs and meat.
Toxins released by Escherichia coli cause mild diarrhoea to severe dehydration. Shigellosis, caused by Shigella,
is characterised by frequent passage of stools with blood and mucus and abdominal cramps.
Clostridium botulinum causes food poisoning or botulism from taking preserved foods (dibba-bund food).
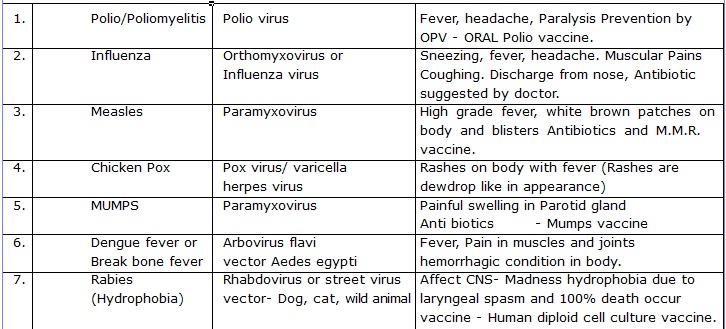
VIRAL DISEASE
PROTOZOAN DISEASE
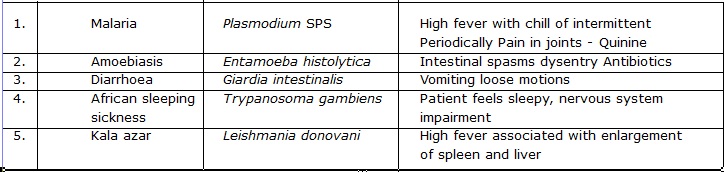
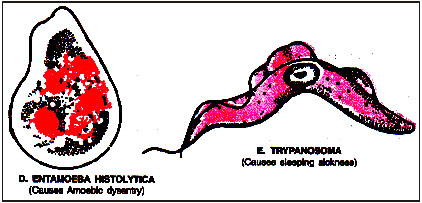
The name Malaria was proposed by Macculoch (1827). C.L.A. Laveran (1880), a French physician, discovered the
Malarial parasite-Plasmodium in the blood of malaria patient. He received Nobel Prize for this discovery in 1907.
Sir Ronald Ross (1887), a British physician, confirmed that malaria is caused by malaria parasite and mosquito is the vector. He received
Nobel Prize for this discovery in 1902.
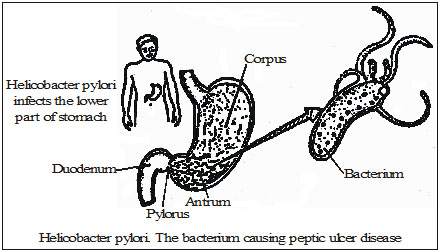
The Nobel Prize of year 2005 in Physiology and Medicine was awarded to two Australian scientists – Barry J.
Marshall (born 1951) and J. Robin Warren (born 1937). They discovered that inflammation in the stomach (gastritis) as well as ulceration of
the stomach or duodenum (peptic ulcer disease) is the result of an infection of the stomach caused by a bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
By using techniques generally available (such as fibre endoscopy, silver staining of histological sections and culture techniques for microaerophilic bacteria)
they made an irrefutable case that the bacterium Helicobacter pylori is causing this chronic disease (peptic ulcer disease).
By culturing the bacteria they made them amenable to scientific study. Helicobacter pylori is a spiral shaped Gram-negative bacterium
that colonizes the stomach of about 50 percent of all humans.
CANCER (crab = cancer)
Uncontrolled , abnormal and excessive mitotic division of cells is called cancer
Oncology : Study of cancer is called oncology.
Cancerous cells : The abnormal and undifferentiated cells are called cancerous cells.
Cancer is a non infections disease but cancer cells spread from one part to another part of body through blood lymph etc.
Tumour or Neoplasm : The abnormal tissue that grows continuously forms a tumour. Tumour's are of two types (1) Benign, (2) Malignant
Carcinogens : The factor that induce cancer are called carcinogens they include (i) Pollutants (ii) Radiations (iii) Tobacco (iv) Biological agents (v) Mechanical agents.
Symptoms : Initially a lump or swelling or sore development followed by unexplained loss of weight, difficulty in swallowing, Persistent cough etc.
Types of cancer depending on the organs affected
(i) Carcinoma : In skin glands, lungs, breast, pancreas and stomach
(ii) Sarcoma : In connective tissues, bones, muscles.
(iii) Leukemia : Increase in no. of white blood cells.
Metastasis : The stage of cancer in which it becomes malignant and spreads to different body is called metastasis.
Diagnosis can be done by endoscopy and biopsy
Cure : (i) Radiation therapy (ii) Chemo therapy (iii) Surgery
AIDS
AIDS : Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome.
Casual Agent : Human immuno deficiency virus H.I.V. This virus belong to retrovirus group of viruses.
HIV gradually reduces the efficiency of human immune system. This make the body vulnerable to other
life threatening disease that finally causes patient's death.
How does a person get infected with HIV ?
This virus is transmitted through blood, semen and breast milk. Thus a person can get HIV by :-
(i) Transfusion of infected blood.
(ii) Sharing of needle with an infected person.
(iii) Having sexual intercourse with an infected person.
(iv) An unborn child can get infection from the mother.
(v) Infected mother's milk can infect an infant.
HIV is not contracted by touching an infected person nor can it be contracted by breathing in the virus when patient coughs or sneeze.
Signs and symptoms of AIDS : (i) Swollen lymph glands (ii) Weight loss (iii) Frequent fever (iv) Night sweat (v) Diarrhoea
The disease may affect the central nervous system which may cause memory loss and difficulty in speaking.
Prevention and control : No drug has been developed to cure AIDS only prevention is cure.
A patient is usually given a combination of drug that manage to slow down the progress of that disease.
Scientists are working on drugs that promise to cure this disease in the near future.
1. For blood transfusion always use blood which has been screened for HIV.
2. Use of disposable needles and syringes blade or razors
3. Avoid multiple sex partnership
4. Condoms can be used to prevent the transmission of HIV through sexual fluids.
The drug zidovudine (AZT) stops HIV replicating by binding with reverse transcriptase enzyme and blocking its action
. But it has a side effect, i.e., it causes anaemia.
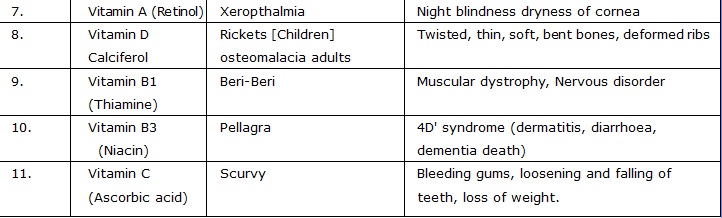
JAUNDICE/ HEPATITIS
Hepatitis is a disease in which liver became enlarged.
(i) Yellowing of skin and whites of eyes This condition referred to as jaundice
(ii) Dark urine
Symptoms :(iii) Whitish Stools
Note : The yellowing is because of the presence of excessive bilirubin (a bile pigment) in the blood.
Viral hepatitis is caused by different strains of hepatitis virus. Hepatitis caused by a virus is named after it
. Thus we have hepatitis A, hepatitis B....... hepatitis G. Named after the strains ABCDEF and G.
TRANSMISSION OF HEPATITIS
(i) Some strains of Hepatitis like hepatitis A is transmitted through contaminated food or water.
(ii) Hepatitis B ® Through blood, semen, saliva, breast milk.
General Hepatitis patient need 4 weeks to recover but certain types of hepatitis can cause death.
Prevention and Control : A hepatitis patient is advised to take light food with high carbohydrate and low fat
to give rest to the liver An antiviral injection (interferon) controls disease. The patient should take bed rest.
Good sanitation prevent the spread of disease by food and water use clean and hygienic water for drinking.
Tested blood should be used for transfusion. use of disposable needle and syrings.
vaccine like A- vaccine, Engerix B, Shenva-B, Enivac-B, Provides immunity against hepatitis A and B.
HAEMOPHILIA
Hemophilia is sex linked hereditary disease. Genes of this disease found on sex chromosomes.
Characters : In case of disease blood clots very slow so patient die due to excess of hemorrhage.
Hemophilia is caused by a recessive gene due to presence of two X chromosome.
The disease is not developed in woman inspite of presence of gene for hemophilia on X chromosome.
This is due to suppression of expression of recessive gene in presence of dominant gene.
While in man the recessive gene can be expressed if present on X chromosome.
Due to presence of only one X chromosome and Y chromosome in the genotype. Women is known as a carrier,
she herself does not show the symptoms but pass the gene to off spring.
COLOUR BLINDNESS / DALTONISM
It is a recessive sex linked defect in which human beings are unable to distinguish red and green colour.
Its genes are also situated on sex chromosome X. In colour blindness womens are found generally as carrier and men as patients.
Heredity of colour blindness is similar to that of haemophilia.
THALASSEMIA
It is a genetic disease that leads to synthesis of defective subunits of haemoglobin Blood of a sufferer child have to change frequently.
Cause of this disease is a recessive gene. only a homozygous child with recessive gene shows the symptoms and heterozygous remains normal.
ANTIBIOTICS AND INTERFERON
Antibiotics are chemical substances produced by living organisms such as bacteria and fungi, etc.,
which can kill or stop the growth of some pathogenic (disease producing) microorganism such as bacteria and fungi.
Some of the important antibiotics which are used for the treatment of disease caused by bacteria and fungi : 1. Penicillin; 2. Tetracycline;
3. Streptomycin; 4. Chloromycetin;
5. Quinclones; 6. Cephalosporin; 7. Gentamicin; 8. Chloramphenicol and 9. Rifampicin.
The treatment of viral infections is more difficult than that of bacterial infection. For each type of viral infection,
human body produces its own antiviral protein, called interferon (IFN). Interferon is released from the infected and dying host cells.
On reaching the un infected cells, IFN makes them resistant to the virus infection. Interferon have been proved to be effective in treating influenza and hepatitis.
IMMUNIZATION
Stimulating the body to produce antibodies by artificial means is known as Immunization.
Vaccine : Preparation of weakened infectious agents or their products that can be injected or given orally to prevent specific disease.
HISTORY OF VACCINES AND VACCINATION
The modern term vaccination comes from the Latin word vacca means cow and vaccinia means cowpox An English physician Edward
Jenner observed that people who got cow pox (A mild
disease) did not suffer from small pox. (a more severe disease).
jenner took some pus with a sterile needle from the cowpox rashes of an infected girl and injected in the scratches made in skin of
an uninfected boy who soon got cowpox. After he recovered Jenner infected the boys arm with pus
from the spots of a person suffering from small pox luckily the boy did not get small pox and jenner experiment was successful.
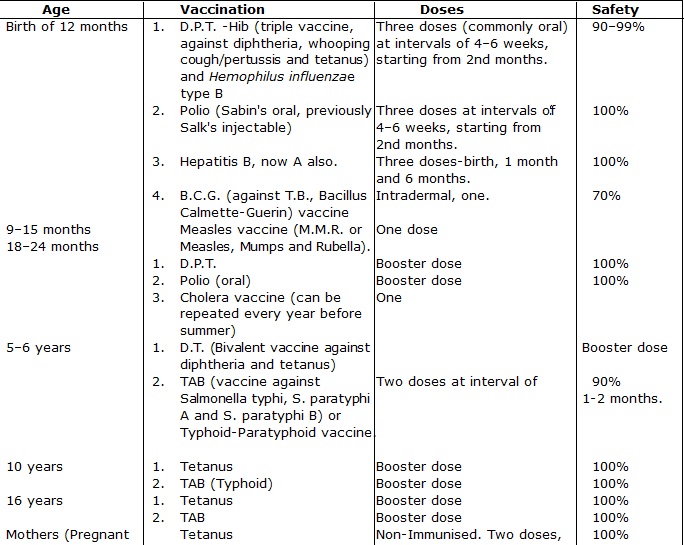
Vaccination Schedule for Babies/Children
NATIONAL DISEASE ERADICATION PROGRAMME
To control and eradicate different disease, Government of India has prepared a National Health Programme with help of several
International Organisations like World Health Organisation, UNICEF, World bank, etc. Under this programme environment cleanliness,
population control, vaccination, improvement of nutritional habits, village health programme are included. Some programmes are -
(a) National Malaria Eradication Programme- This programme was started in India as National Malaria Control Programme (NMCP) in 1953
In 1958 it was renamed a National Malaria Eradication Programme (NMEP). The aim of this programme is to eradicate the disease with community cooperation.
In this programme workers of primary health centre and department of malaria collects blood samples of the persons suffering from fever and test them,
if patients are reported malaria positive then drug are distributed through health workers and members of Panchyat Samiti. Insecticides
are also sprayed to control malaria.
(b) National Leprosy Eradication Programme - This programme was started in 1955.
The aim of this programme is to identify the patients in early stage and treat them with multi drug therapy (M.D.T.) and rehabilitate them.
For this purpose leprosy control centre were established.
(c) National Tuberculosis Eradication Programme - This programme was started in 1962. Under this scheme disease eradication programme
is run in leader ship of District tuberculosis- disease Incharge. In this programme patient are examined, identified, treated and educated.
(d) National Naru Eradication Programme- This programme was started during sixth five years plan.
In this programme importance was given to cleanliness of drinking water. People were educated to
consume water after boiling and cooling and not use unsafe water. It can be said that
programme was a success because no patient of Naru is reported after year 2000 from Rajasthan.
(e) National AIDS Control Programme - Reporting of first AIDS patient from
India in 1986 and knowing severity of the disease this programme was started in 1987. In 1991,
an action plan was prepared to console AIDS with help of World Health Organisation.
At present on national level, National AIDS Control
Organisation (NACO) and at state level Rajasthan AIDS Control Society are working.
The aim of these organisatiem aware towards AIDS and sexual transmitted diseases.
(f) Pulse Polio Vaccination Campaign - To eradicate polio, this programme was
started on 9th December 1995. The aim of this programmes to replace natural poliovirus with vaccinated virus so that the disease can be eradicated.
FOR COMPETITIVE EXAMS
HELMINTH DISEASE
1. Ascariasis Ascaris lumbricoides ,loosemotion, restlessness Abdominal spasm, insomia, vomiting .
2. Dracunculiasis Dracunculus medinensis Blisters on skin of arms shoulder and legs
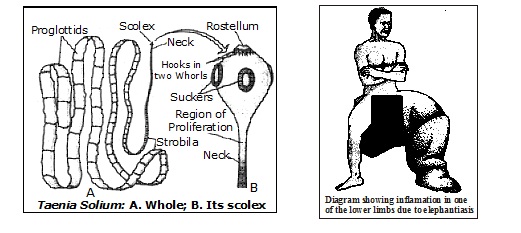
3. Elephantiasis or Wuchereria bancrofti Swelling of hand scrotum testis and filariasis breasts
4. Taeniasis Taenia solium Abdominal pain, nausea, Anemia, loss of appetite, indigestion, nervous disorders
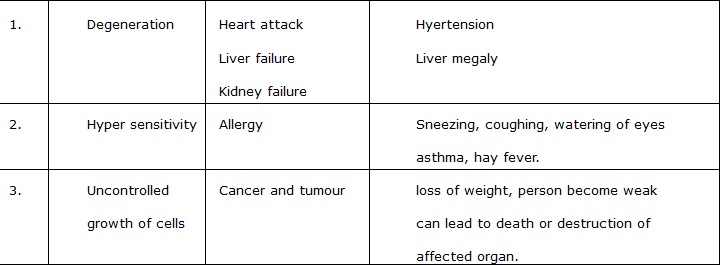
NON COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
Degenerative diseases
Some (STD) their Pathogens and symptoms
(Sexual Transmitted Disease )
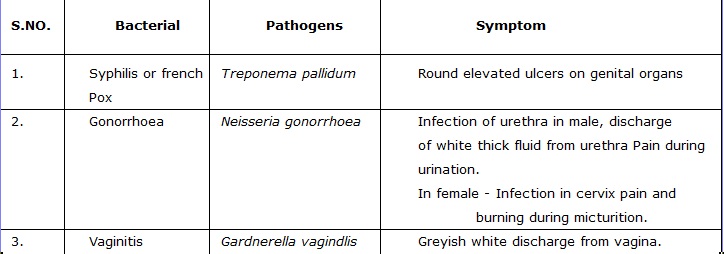
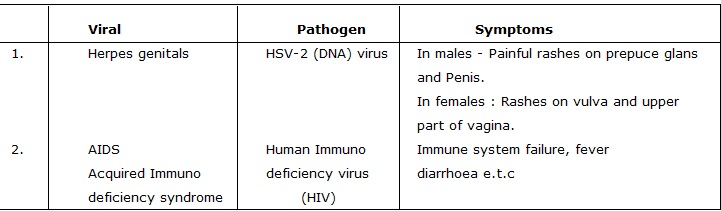
QUICK REVISION OF THE CHAPTER
1. Health is a state of physical, mental and social well being and not merely the absence of disease.
2. Health of a person depends upon one's personal habits as well as one's environment.
3. Good economic condition through proper job helps in maintaining health of the individuals due to procurement of proper, healthy and balanced diet.
4. A disease is a condition of the body or a part of it in which functions are disturbed or damaged.
5. Disease causing organisms are called pathogens.
6. Transmission of communicable diseases can be by direct (contact with infected person, soil, animal bite, etc.) or indirect (by vector, air borne, toys, etc.)
7. Disease can be :
Communicable – transmitted from infected person to healthy person.
Noncommunicable – cannot be transmitted from infected persons.
8. Acute diseases begin abruptly and last only for a short time, whereas chronic diseases develop slowly, last for long periods of time and
often cause permanent damage.
9. The various causes of diseases are pathogens, lack of nutritious diet and lack of public health services.
10. The infectious agents are bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoans and helminths.
11.The infectious agents may attack the same organ where they have entered or they may enter some other organ.
12.There are two main principles of treatment–killing the microbe and reducing the effect of the disease.
13 We can prevent infection by general practices (like proper habits, nutrition, exercise and relaxation) and by immunisation.
14.Vaccines are available against diphtheria, whooping cough, tuberculosis, polio, typhoid, measles, etc.
15Jaundice is yellowness of sclera of eyes and skin.
16. Rabies is transmitted by bite of rabid dog or cat. The patient fears from water (hydrophobia).
17. AIDS (Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome) is caused by HIV.
This virus weakens the human body’s immunity or self defence mechanism.
It can be transmitted through transfusion of infected blood, use of infected needle, infected mother to child and through sexual
contact with infected person.
18. Diarrhoea is caused by bacteria, protozoa or even virus. In this, patient passes frequent stools with blood and mucus. It results in
muscular cramps and dehydration. ORS is useful.
19.Typhoid is caused by Salmonella typhi. TAB vaccine provides immunity.
20. Tuberculosis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. BCG vaccine provides immunity. This disease mostly affects lungs.
21. Malaria is caused by Plasmodium which is transmitted by female Anopheles mosquito.
SOLVED EXAMPLES
Ex.1 How many of these ways we can think of are events that would occur when the disaster is actually happening ?
Sol.(i) Disease caused due to shortage of drinking water.
(ii) Health affected by the shortage of food.
(iii) Diseases caused to due sanitary problems.
(iv) Health affected due to unavailabilities of shelter.
Ex.2 How many of these health-related events would happen long after the actual disaster, but would still be because of the disaster ?
Sol. (i) Diseases caused due to accumulation of dirty water e.g., malaria.
(ii) Spread of water borne diseases like cholera, dysentry etc.
(iii) Diseases caused due to rotting things in the debris.
Ex.3 Why would one effect on health fall into the first group, and why would another fall into the second group ?
Sol. This is because the disease or the effect on health which are placed in
the first group are caused immediately after the disaster takes place. But, the effect or diseases in the second group, however are ultimately
due to disaster, but takes time to take place.
Ex.4 List any three reasons why you would think that you are sick and ought to seek a doctor. If only one of these symptoms were present,
would you still go to the doctor ? Why or why not ?
Sol. Some general symptoms -
(i) Headache (ii) Cough (iii) Dysentery
If any of the above symptoms is observed, the person should immediately contact the doctor.
Cause : Any of the symptoms can be the cause of disease. If these are ignored, the person may have to face a dangerous situation.
Ex.5 In which of the following case do you time the long-term effects on your health are likely to be most unpleasant?
(i) If you get jaundice.
(ii) If you get lice.
(iii) If you get a acne.
Sol. In Jaundice because, it is a chronic disease which may stay for a long-time.
Ex.6 Why are we normally advised to take bland and nourishing food when we are sick ?
Sol. During infection, the immune power of the body decreases. So, to maintain the immune power we are suggested to take sufficient and easily digestible food.
Ex.7 What are the different means by which infectious diseases are spread ?
Sol. Following are the means of spread of diseases -
(i) By air : By sneezing and coughing, the microbes spread into the air and enter the body of healthy man.
(ii) By water : The microbes enter our body by drinking polluted and contaminated water.
(iii) By sexual contact : some disease like AIDS, spread by sexual contact with infected person.
(iv) By vectors : Some organisms like female anopheles mosquito also work as the vector of disease causing agent and hence spread diseases.
Ex.8 What precautions can you take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases ?
Sol. (i) By preventing gathering of people.
(ii) By making available clean and fresh drinking water.
(iii) By keeping ground and class rooms clean.
(iv) By using handkerchief to cover mouth while sneezing or coughing.
(v) By preventing accumulation of water in and around the school.
(vi) By using vaccines and immunisation
(vii) By keeping the toilet clean.
(viii) By avoiding the use of uncovered food and fruits.
Ex.9 What is immunisation ?
Sol. The process of developing immune power in the body to fight against the diseases is called immunisation.
Ex.10 A baby is not able to tell her/his caretakers that she/he is sick. What would help us to find out
(a) that the baby is sick ?
(b) what is the sickness ?
Sol. (a) Some particular symptoms e.g., cough, cold, dysentery, etc. Indicate that child is sick.
(b) (i) Every disease has its own particular symptoms which tell us about the disease.
(ii) By carrying tests in the laboratory, the disease can be diagnosed.
Ex.11 Under which of the following conditions is a person most likely to fall sick ?
(a) When she is recovering from malaria.
(b) When she has recovered from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox.
(c) When she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox. Why ?
Sol. (c) When she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chicken-pox.
Reason : (a) due to unavailability of sufficient and balanced diet and weakened immune system.
Ex.1 Under which of the following conditions are you most likely to fall sick ?
(a) When you are taking examinations.
(b) When you have travelled by bus and train for two days.
(c) When your friend is suffering from measles. Why
Sol.(c) WheEn my friend is suffering from measles.
Reason : In this condition, I will frequently visit my friends address. Measles is an airborne disease.
When my friend coughs or sneezes, small drops from his mouth containing microbes mix in the air.
The microbes may be carried away by air. So, the chance of getting infected increases. Hence, in this case I may fall severely sick.
NCERT QUESTIONS WITH SOLUTIONS
Q.1 State any two conditions essential for good health.
Ans. Clean surroundings and availability of adequate and nutritious food are the two conditions essential for good health.
Q.2 State any two conditions essential for being free of diseases.
Ans. In order to remain free from diseases, we must avoid the unhygienic things in our daily habits in terms of our food and cleanliness.
Secondly, we must get vaccinated against common infectious diseases.
Q.3 Are the answers to the above questions necessarily the same or different? Why?
Ans. Answers to above questions are different but interconneted because disease free person is not always healthy.
Q.4 List any three reasons why you would think that you are sick and ought to see the doctor.
If only one of these symptoms were present, would you go still to the doctor? Why orwhy not?
Ans. Three reasons of feeling sick are having fever, diarrhoea or persistent headache. If there are any of these symptoms I would surely
visit doctor to avoid any further complications in the health.
Q.5 In which of the following cases do you think the long term effects on your health are likely to be most unpleasant?
If you get jaundice if you gelt lice if you get acne. Why?
Ans. The long terms effects on the health can be due to jaundice. It makes the person weak, reduces weight, and decreases appetite.
It takes much more time than acne and lice to recover. Also, this have more long term effects.
Q.6 Why are we normally advised to take balanced nourishing food when we are sick?
Ans. During sickness, our appetite is reduced and our digestive system also does not function property.
We become weak during sickness. Thus, we are normally advised to take balanced nourishing food to get energy and to recover fast from disease.
Q.8 What are the various means by which infection (disease) spreads?
Ans. The different means by which infection spreads are-(i) contaminated water, (ii) undernourished food,
(iii) unhealthy environment, (iv) bad habits, (v) use of items used by an infected person and (vi) physical and sexual contact with a diseased person.
Q.9 What precautions can you take inyour school to reduce the incidence ofinfectious disease?
Ans. The precautions we cantake in school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases are
(i) having clean drinking water
(ii) vaccination against infectious disease
(iii) frequent washing of hands
(iv) use of tissue paper or handkerchief while sneezing or coughing
(v) avoid unhealthy food
(vi) not going to school if suffering from an infection
Q.10 What is immunisation?
Ans. Immunisation is a technique in which vaccines are administered either orally or by injections in order to develop temporary or permanent
immunity against a particular infectious disease.
Q.11 What are the immunisation programmes available at the nearest health centre in your locality? Which of these diseases are the major
health problems in your area?
Ans. In our nearest health centre, immunisation programmes are available for prevention of following diseases –polio, diphtheria, whooping
cough, tuberculosis, tetanus and measles.
Students may find out about the major health problems in the area and write.
Q.12 How many times did you fall ill in the last one year? What were the illnesses?
(a) Think of one change you could make in your habits in order to avoid any/most of the above illnesses.
(b) Think of any change you would wish for in your surroundings in order to avoid any/most of the above illnesses.
Ans. Statements will differ from student to student. Students may write their own answer with the help of teacher.
Q.13 A doctor/nurse/health-worker is exposed to more sick people than others in the community. Find out how she/he avoids getting sick herself/himself.
Ans. The doctor/nurses exposed to sick people avoid getting sick by using preventive measures such assterilising work place,
sterilising utnesils and tools, washing hands with soap after examining the patient, using gloves and masks at the time of examining patients.
Q.14 Conduct a survey in your neighbourhood to find out about the three most common diseases.
Suggest three steps that could be taken by your local authorities to bring down the incidence of these diseases.
Ans. The three most common neighbourhood diseases are-flue (cough and cold), diarrhoea and typhoid.
Preventive measures which should be taken by the local authorities to bring down the incidence of these diseases are-
(i) provision of clean drinking water,
(ii) clean surroundings with regular dsiposal of garbags and sanitation and
(iii) regular immunisation programmes
Q.15 A baby is not able to tell her/his caretakers thatshelhe is sick. What would help us to find out?
(a) That the baby is sick? (b) Whatis the sickness?
Ans. (a) Symptoms which can help us to find that baby is sick are-continuous crying, restlessness, inadequate food intake, increased body
temperature, loose motion (b) diarrhoea.
Q.16 Under which of the following conditions is a person most likely to fall sick?
(a) When she isrecovering from malaria.
(b) When she has recovered from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chickenpox.
(c) When she is on a rom-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chickenpox. Why?
Ans. (c) When she is on a four-day fast after recovering from malaria and is taking care of someone suffering from chickenpox because
malaria and four day fast would made her body weak and prone to infections.
Q.17 Under which of the following conditions are you most likely to fall sick?
(a) When you are taking examinations.
(b) When youhave travelled by bus and train for two days.
(c) When yourfriend is suffering from measles. Why?
Ans. (c) We are most likely to fall sick when our friend is suffering from measles because measles is an infectious disease.
EXERCISE 1
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS :
Q.1 Give two examples of viral diseases.
Q.2 Give two examples of bacterial diseases.
Q.3 Give one example of protozoan diseases.
Q.4 Name the disease in which
(a) Patient fears from water
(b) Yellowing of skin takes place
Q.5 Name one sexually transmitted viral disease.
Q.6 What is ORS ?
Q.7 Name the causal organism and vector of malaria respectively.
Q.8 Name the causal organism of
(a) Tuberculosis (b) Typhoid
Q.9 Name two diseases against which vaccines are available.
Q.10 Expand AIDS.
Q.11 Name two animals, which transmit rabies to human beings.
Q.12 Name two modes of transmission of AIDS.
Q.13 Mention two preventive measures against rabies.
Q.14 Name the toxin released by tuberculosis bacteria.
Q.15 Mention the modes of transmission of tuberculosis.
Q.16 Name the disease caused by the smallest virus.
Q.17 Name the disease in which legs become paralysed.
Q.18 When was the Pulse Polio Immunization Programme launched in India ?
Q.19 Expand BCG.
Q.20 Name the causal organism of diarrhoea.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.21 How does dehydration set in during diarrhoea? How can the former be prevented.
Q.22 In a cluster of hutments, many people are suffering from malaria.
Mention the unhygienic conditions that must be prevailing in that locality. How does a doctor confirm malaria ?
Q.23 State two precautions to be observed by the people suffering from typhoid and tuberculosis.
Q.24 It was diagnosed that the body of a patient has lost its power of fighting any infection
. Name the disease he is suffering from. What type of microbe is responsible for this disease and how does it spread from one person to the other.
Q.25 After eating mutton in a party, a number of people complained of nausea, vomiting, pain in abdomen and passage of stools with blood and mucus
What type of disorder are they suffering from Name the microbe responsible for their condition.
Q.26 Name any three diseases of man caused by bacteria and three diseases caused by virus.
Q.27 Write two symptoms each of’ tuberculosis and polio.
Q.28 Write notes on
(a) Modes of transmission of AlDS
(b) Rabies.
Q.30 Write short note on Pulse Polio programme.
Q.29 Explain the methods of prevention of Malaria.
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
Q.31 Write short notes on
(a) Malaria (b) AIDS
Q.32 Write short notes on bacterial diseases.
Q.33 Write short notes on viral diseases.
Q.34 Write short notes on
(a) Polio (b) Tuberculosis.
Fill in the blanks :
Q.1 Impairment of functioning of some body system is called ...................
Q.2 Tuberculosis is a ................... disease.
Q.3 Disease that can be transmitted from one individual to another are called communicable or ................... disease.
Q.4 The bad odour associated with unwashed bodies is caused by ...................
Q.5 An animal that spreads a disease is called a ...................
Q.6 Malaria is transmitted by the female ................... Mosquito.
Q.7 Disease present from the birth are called ...................
Q.8 Any organism capable of producing a disease is called ...................
Q.9 Disease are of two main kinds : congenital and ...................
Q.10 Rabies is also called ...................
Q.11 ............... medicines are difficult to make as the pathogens have very few biochemical mechanisms of their own.
Q.12 In AIDS patients even small cold can become .................
Q.13 Sleeping sickness is caused by ............... a protozoan.
Q.14 The two important contributory causes of diseases are ............... and ............... make up.
Q.15 Health is state of well being physically, ............... and socially.
Alternate Response Type Questions (True / False)
Q.1 Health of an individual depends on the surroundings.
Q.2 Gainful employment has no relation to individual health.
Q.3 On the basis of symptoms, physicians look for signs of disease.
Q.4 High blood pressure is an infectious disease.
Q.5 Penicillin is effective against bacteria because it inhibits their wall formation.
Q.6 In open spaces, air borne human diseases spread rapidly.
Q.7 AIDS spreads through sex, blood to blood contact and from mother to child.
Q.8 Personal hygiene is basic to prevent infectious diseases.
Matching Type Questions
Q.9 Match the contents of the columns I and II (single matching)
Column-I Column-II
(a) Vaccination (i) Vector
(b) Bed rest (ii) Kala-azar
(c) Mosquito (iii) Jenner
(d) Leishmania (iv) Energy for healing
Q.10 Match the description in column A with term / statement in column B :-
Column A Column B
(i) Health (a) Disease
(ii) Antibodies (b) Ronald Ross
(iii) AIDS (c) Tuberculosis
(iv) BCG (d) Measles
(v) Impairing of Health (e) Brain fever
(vi) Malaria-mosquito relation ship (f) Immunity
(vii) Communicable disease (g) State of normal functioning
(viii) Japanese encephalitis (h) Sexual transmitted disease
EXERCISE
Q.1 Typhoid is an infectious disease caused by :-
(A) virus (B) bacteria
(C) Protozoan (D) Worm
Q.2 Common cold is a :-
(A) Chronic disease (B) Congenital disease (C) acute disease (D) genetic disorder
Q.3 Elephantiasis is a disease that result in :-
(A) long-term effects on health
(B) short-term effects on health
(C) no effect on health
(D) occasional bad effects on health
Q.4 Haemophilia is a :-
(A) Chronic disease
(B) congenital disease
(C) acute disease
(D) deficiency disease
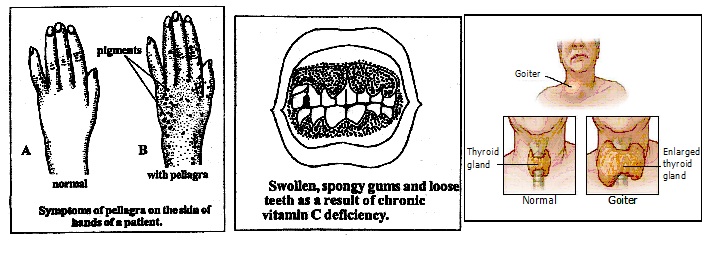
Q.5 Goitre is caused due to deficiency of :-
(A) Vitamin A (B) Fluorine (C) Iodine (D) Vitamin C
Q.6 The interval between infection and appearance of a disease is known as :-
(A) inoculation (B) Penetration
(C) infection (D) incubation period
Q.7 AIDS day is celebrated on :-
(A) 5th June (B) 1st October
(C) 11th june (D) 1st December
Q.8 Vector of malaria is :-
(A) Female Anopheles
(B) Male Anopheles
(C) Female Culex
(D) Male Culex
Q.9 Disease-causing factors existing within the body itself are called :-
(A) extrinsic factors
(B) hereditary factors
(C) congenital factors
(D) intrinsic factors
Q.10 The disease that can be transmitted through body fluids are :-
(A) TB and cholera
(B) typhoid and cholera
(C) Cholera and rabies
(D) AIDS and hepatitis B
Q.11 A healthy person is one who is free from :-
(A) disease
(B) mental tension
(C) disease and mental tension
(D) bacteria
Q.12 Fruits and vegetables bought from the market :-
(A) may be coated with pesticides
(B) may carry germs
(C) may carry egg of worms
(D) all the above
Q.13 Breathing polluted air causes diseases of the :-
(A) nervous system
(B) circulatory system
(C) respiratory system
(D) digestive system
Q.14 Which disease is likely to occur in crowded areas ?
(A) Non infections (B) Infections
(C) Genetic (D) Deficiency disease
Q.15 What kind of a disease is arthritis ?
(A) An acute disease
(B) A chronic disease
(C) An infectious disease
(D) A communicable disease
Q.16 Which of the following is due to external causes ?
(A) Jaundice (B) Diabetes
(C) Arthritis (D) Cataract
Q.17 House flies are the vectors of :-
(A) Cholera (B) Malaria (C) Dengue (D) Yellow fever
Q.18 Mosquitoes spread :-
(A) influenza (B) rabies (C) malaria (D) AIDS
Q.19 Tuberculosis is caused by :-
(A) a bacterium (B) a virus (C) a protozoan (D) Air pollution
Q.20 The infectious agents responsible for which disease can be spread when the patient coughs ?
(A) AIDS, TB and hepatitis
(B) TB, influenza and cholera
(C) TB and influenza
(D) TB and hepatitis
Q.21 The disease that can be transmitted through body fluids are :-
(A) AIDS and hepatitis B
(B) TB and typhoid
(C) influenza and cholera
(D) cholera and rabies
Q.22 A patient was advised to take asprin and bed rest by her doctor. She must have been suffering form :-
(A) hepatitis (B) influenza
(C) cholera (D) beri beri
Q.23 The opposite to innate Immunity is :-
(A) Phagocytosis
(B) Passive immunity
(C) Acquired immunity
(D) None of these.
Q.24 Humoral-immune system comprises :-
(A) B lymphocytes (B) Blood
(C) T Lymphocyte (D) monocytes
Q.25 The study of resistance to disease :-
(A) Pathology (B) Cytology (C) Immunology (D) None of these.
Q.26 Oral vaccine prevents the attack of :-
(A) Typhoid (B) Polio (C) Tetanus (D) Cholera
Q.27 Causative agent of T.B. is -
(A) Salmonella
(B) Mycobacterium
(C) Streptococcus
(D) Pneumococcus
Q.28 Which of the following is a bacterial disease :-
(A) Poliomyelitis (B) Filariasis (C) Tetanus (D) Malaria
Q.29 Typhoid is caused by -
(A) Escherichia (B) Giardia (C) Shigella (D) Salmonella typhi
Q.30 Which of the following pairs is characterized by swollen lips, thick pigmented skin of hands and legs and irritability
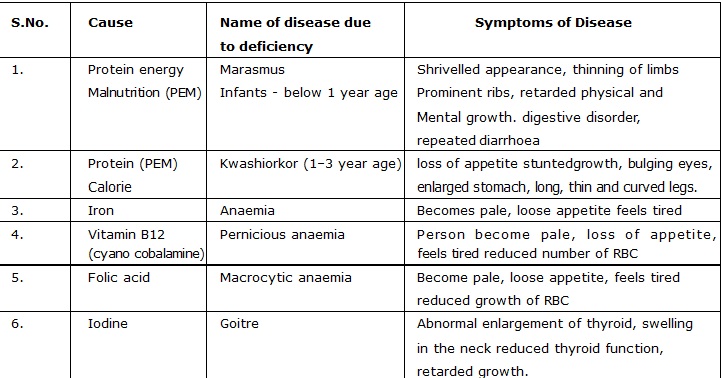
(A) Thiamine deficiency – Beri-beri (B) Protein deficiency – kwashiorkor
(C) Nictoinamide deficiency – pellagra (D) Iodine deficiency – goitre
Q.31 Blood capillaries can easily rupture due to the deficiency of :–
(A) Vitamin A (B) Vitamin C
(C) Vitamin D (D) Vitamin K
Q.32 Which one is correct statement :-
(A) Sunshine vitamin is vitamin C
(B) Antixerophthalmic and undisturbed vitamins are B and C
(C) Prolonged deficiency of nicotinic acid produces pellagra
(D) Vitamins A, D, E, K are water soluble
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :
Q.33 Which one of the diseases is not communicable
(A) Typhoid (B) Cancer (C) Measles (D) Leukemia
Q.34 AIDS is mainly caused by :-
(A) Sexual intercourse (B) Bacteria
(C) Through placental transfusion (D) Protozoa
Q.35 Which is insoluble in water :–
(A) Retinol (B) Thiamine (C) Calciferol (D) Ascorbic acid
Q.36 Which of the following is water soluble -
(A) Vitamin A (B) Vitamin B
(C) Vitamin D (D) Vitamin C
Q.37 Anaemia is caused due to deficiency of :–
(A) Sodium (B) Iron (C) Calcium (D) Cyanocobalamin
PASSAGE : 1 (Q.38 to Q. 41)
AIDS stands for “Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome” (It is a fatal disease). The disease AIDS is caused by retrovirus (a RNA virus)
known as Human Immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
AIDS virus attacks white blood cells, (WBCs) or lymphocytes (T4 helper cells) of human beings and weakens the human body’s immunity
or self-defence mechanism.
The AIDS disease usually spreads through unprotected, sexual contact with an infect person carrying AIDS virus
. The AIDS disease also spreads through the transfusion of blood contaminated with AIDS virus.
Q.38 The disease of AIDS is caused by :–
(A) Bacteria (B) Virus (C) Fungi (D) None of these
Q.39 AIDS virus attacks on :–
(A) Red blood cells (R.B.Cs)
(B) White blood cells (W.B.Cs) and lymphocytes (T4 helper cells)
(C) Both
(D) None of these.
Q.40 Immunodeficiency syndrome could develop due to:–
(A) Defective lives (B) Defective thymus
(C) AIDS virus (D) None of these
Q.41 AIDS spread by :–
(A) Homosexuality
(B) Immortal way of life
(C) Infected needles and syringes
(D) All the above.
ANSWER KEY
1. B 2. C 3. A 4. B
5. C 6. D 7. D 8. A
9. D 10. D 11. C 12. D
13. C 14. B 15. B 16. B
17. A 18. C 19. A 20. C
21. A 22. B 23. C 24. A
25. C 26. B 27. B 28. C
29. D 30. C 31. B 32. C
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS :
33. B,D 34. A,C 35. A,C 36. B,D
37. B,D 38. B 39. B 40. C
41. D