All the substances around us have different shape, size and texture. Everything in universe is made up of matter. The air we breathe,
the food we eat, the water we drink, the pen with which we write, the book we read, are made up of matter. In this chapter, we shall discuss
the matter in our surroundings.
1. Material :– The term used to describe a particular kind of matter, is called material e.g. – wood,
water and marble.
Type of material :–
2. Matter : It is substance which occupies space and has mass. Air, Earth, Fire, Sky and water five basic element, "The Panch Tatva"
according to the earlier Indian Philosophers. According to them everything i.e., living or non-living is made up of these five elements.
3. Classification of Matter : Nowadays scientists have classified matter in the following two ways :
(i) The physical classification based on physical properties of matter and
(ii) The chemical classification based on chemical composition of matter.
4. Physical Nature of Matter : Matter is made up small particles and there is space between particles of matter. It can be proved with
the help of following experiment.
Experiment: To show that there is space between particles of matter.
Materials Required : 100 ml beaker, water, salt, glass rod.
Procedure :
Take a 100 ml beaker and fill it with water and mark the level of water.
Dissolve the given salt with the help of glass rod.
Observe the change in the water level and record your observations.
Observations :The salt gets dissolve in water. The particle of salt have entered the space between water molecules, therefore,
the level of water does not change.
Conclusion : The salt consists of large number of small particle which occupy the space between molecules of water.
5. Size of Particles of Matter : The particles of matter are extremely small in size which cannot be seen even with powerful microscope.
Their size can be observed with the help of following experiment.
Experiment : To show that matter is made up of very small particles.
Materials Required : Crystals of KMnO4 (potassium permagnate), water, 3 separate beakers.
Procedure :
Take 2-3 crystals of KMnO4 and dissolve them in 50ml of water in beaker 1.
Take 5 ml of solution from beaker 1 and put it into 50 ml of water in beaker 2 and observe the colour of solution.
Take 5ml of solution from beaker 2 and put it into 50 ml of water in beaker 3 and observe the colour of solution.
Observations : The colour of solution remains purple in all the beakers.
Conclusion : It shows that even 2-3 crystals of KMnO4 consists of millions of small particle which dissolve in water giving purple colour to the solution.
6. Space between Particles of Matter : When we dissolve sugar, salt or KMnO4 in water,
particles get evenly distributed in water. Similarly, when we prepare tea or coffee, the
particles of one type of matter diffuse into space between
particles of the other. This shows that there is enough space between particles of matter.
7. Continuous movement of Particles :
Particles of matter are continuously moving, i.e., they possess kinetic energy which increases with increases in temperature.
Experiment : To show the particles of matter are continuously moving.
Materials Required : Incense stick or agarbati, match box.
Procedure :
Put an unlit incense stick in a corner of your class.
Go close to the incense stick to smell it.
Now light the incense stick. And try to get the smell from a distance.
Observations : The smell of unlit incense stick can be observed only by going close to it whereas the smell of lighted incense stick can be
observed from a distance.
Conclusion : The particles of matter of continuously moving but the speed of particles is very slow. The speed of particles increase with
the increase in temperature.
8. Diffusion : The process of intermixing of particles of two or more substance on their own is called diffusion. The rate of diffusion increases
on heating that is why an incense stick gives smell only when we come close to it, but on lighting the stick we get smell even far away from it.
9. Attraction between Particles of Matter :
There is force of attraction between particles of matter. It can be explained with the help of following game in the field.
Make four groups and form human chains as follows.
The first group should hold each other from back and lock arms like Bihu dancers.
The second group should hold hands to form human chain.
The third group should from a chain by touching each other with only their finger tips.
The fourth group should run around and try to break three human chains one by one into groups as small as possible.
Observations and Conclusions
The third group is easily to break because of least force of attraction. It is similar to particles in gaseous state.
The first group is most difficult to break due to maximum force of attraction. It represents particles present in solid state.
The second group requires little force to break which shows it has force of attraction less than first group but more than third group. It
represents particles in the liquid state.
Even in solids, the force of attraction differs from one substance to another. There is maximum force of attraction between particles of iron nail,
less in a piece of chalk and least in rubber band.
It is difficult to cut a stream of water with the help of fingers due to force of attraction between particle of liquids. Thus, there is force of attraction
between particles of matter which keeps the particle together. The strength of forces varies in different kinds of matter.
10. Classification of Matter on the basis of Physical State : Matter can be classified into Solid, Liquid and Gas.
11. Properties of the Solid State :
They have fixed shape.
They have fixed volume.
They are rigid an have fixed boundaries.
They are incompressible because intermolecular space is less.
They have high density as compared to other states of matter.
They have strong force of attraction between the particles.
The particles are closely packed in solid, therefore, there is less intermolecular space between the particles.
The kinetic energy of particles in solid is very less. They vibrate only at their mean position that is why solids have rigid shape.
Solid diffuse into solids to very less extent, e.g., it is difficult to rub a blackboard on which something is written in chalk without cleaning for 10-15 days.
12. dsVolume : The space occupied by a substance is called volume. Its SI unit is cubic metre (m3). Its common unit is litre. (1L = 1dm3, 1L = 1000 ml, 1ml = 1cm3).
13. Density : The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density.
Density = mass/volume. The SI unit of density is km/m3 where common
unit is g/cm3. (CGS unit)
14. Kinetic Energy : The energy possessed by particles by virtue of its motion is called kinetic energy.
15.Properties of the Liquid State :
Liquids do not have fixed shape or boundaries.
They have fixed volume.
They can flow, i.e., they have fluidity.
They have low compressibility but more than solids.
They have lower density as compared to solids.
The intermolecular forces of attraction are weaker as compared to solids.
The intermolecular space is more than that of solids.
The particles in liquid state can move freely and hence have higher kinetic energy than solids but less than that of gases.
They shows the property of intermixing and thus they can diffuse. It can be shown by the following experiment.
Experiment : To compare the rate of diffusion of liquids having different densities.
Materials Required : Two beakers filled with water, blue ink, honey
Procedure :
Take two beakers filled with water.
Add a drop of blue ink into first beaker slowly and honey in the second beaker.
Leave them undistributed at you home or in a corner in the class.
Record you observations.
Observations :
The blue ink diffuses into water and water become light blue in colour.
Honey diffuses very slowly into water, therefore, takes lots of time to diffuse evenly.
Conclusion : Liquids with higher density, diffuse slower than liquids having lower density.
Factor Affecting Rate of Diffusion :
(i) Density : The rate of diffusion depends upon density of liquids. Higher the density, lesser will be the rate of diffusion.
(ii) Temperature : The rate of diffusion depends upon temperature, i.e, the rate of diffusion increase with an increase in temperature
which can be shown experimentally.
(iii) Physical State : Solids can diffuse into liquids slowly whereas liquids can diffuse into liquids faster and gases can also diffuse into liquids.
Experiment : To study the variation of rate of diffusion with temperature of solid in liquids.
Materials Required : Copper sulphate, two beakers, cold water and hot water.
Procedure :
Take 50ml of cold water in a beaker.
Take 50ml of hot water in another beaker.
Add a crystal of copper sulphate into the beaker containing 50ml of cold water.
Add a crystal of copper sulphate into the beaker containing 50ml of hot water.
Leave them undisturbed.
Record the observations.
Observations : The colour of solutio in first beaker becomes blue slowly whereas the colour becomes blue faster in second beaker.
Conclusion : The rate of diffusion increases with increase in temperature because kinetic energy of molecules increases.
16. Diffusion of Gases in Liquids : Gases can also diffuse in liquids. Oxygen and carbon dioxide get dissolved in water which is essential for
growth of aquatic plants and animals.
17 Properties of Gaseous State :
Gases do not have fixed shape, i.e., they take the shape of container.
They do not have fixed volume, therefore no definite boundaries.
They can flow in all directions, hence gases also show fluidity.
They are highly compressible.
They have lower densities as compared to liquids and solids.
They have higher kinetic energy as compared to liquids and solids.
The rate of diffusion is fastest in gases.
There is weak intermolecular force of attraction.
There is large intermolecular space, therefore, gases can be easily compressed.
Gases can be compressed more easily than liquids which can be shown by following experiment.
Experiment : To show that gases can be compressed more easily than liquids.
Material Required : Two 10ml syringes, rubber cork, vaseline.
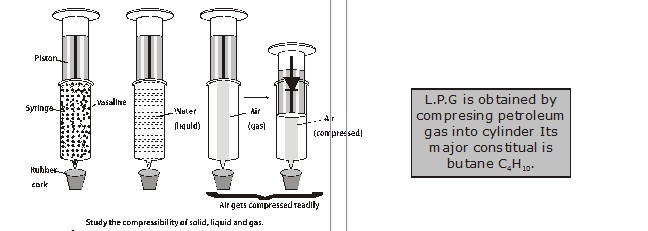
Procedure :
Take two 10ml syringes and close their nozzle by inserting them in a rubber cork as shown in figure.
Remove the piston from both the syringes.
Allow the air to fill the space inside one syringe and fill water in the other.
Insert type pistons back into syringes.
Apply some vaseline on the piston fro smooth movement.
Now try to compress by pushing piston in the syringe.
Record your observations.
Observations : In case or air, piston is easily pushed in as compared to syringe filled with water.
Conclusion : The bases can be compressed more easily than liquids. It is because there are weak intermolecular forces of attraction between particles,
so the distance between the particles in gaseous state is very large as compared to solids and liquids, e.g., CNG is compressed natural gas which
is being used in vehicles. LPG is liquified petroleum gas which is used for cooking.
18. Pressure : It is defined as force exerted per unit area, e.g., gases exert pressure on the walls of the containing. The kinetic energy of the particles
in gaseous state i maximum.
The particles are in state of constant random motion therefore, they collide with themselves as well as with the walls of the container and exert pressure.
19. Change of state : The state of substance depends upon temperature and pressure, e.g., water exists as solid at 0ºC, as liquid at room
temperature whereas in gaseous state at 100ºC. The state of matter will change with change in temperature which is shown by following experiment.
Experiment : To study the effect of temperature on solids and liquids.
Materials Required : Ice, thermometer, beaker.
Procedure :
Take about 50g of ice in a beaker and hang a laboratory thermometer in it so that bulb is in contact with ice.
Start heating the beaker at low flame.
Now down the temperature when ice starting melting.
Note the temperature when all the ice has converted into water.
Record your observations for conversion of solid into liquid state.
Now put a glass rod in the beaker and heat while constant stirring till the water starts boiling.
Keep a close look at the thermometer reading till most of the water has vapourised.
Record your observations for the conversion of ice into liquid water and then into vapour state.
Observations and Conclusion : When temperature of solid is increased, the kinetic energy of particles increases. Due to increase in kinetic energy,
the particle starts vibrating at a greater speed and overcome intermolecular forces of attraction. A stage is reached when intermolecular forces become so
less that it changes into liquid. When temperature is further increased, a state comes when liquid changes into vapour.
20. Melting Point : The temperature at which solid changes into liquid completely is called melting point.
Melting point of solids gives indication of the strength of intermolecular forces of attraction. Higher the melting point, more will be intermolecular
forces of attraction.
21. Melting : The process in which solid changes into liquid is called melting. It is also called fusion.
22. Kelvin : It is SI unit of temperature. 0ºC = 273.16 K.
If we want to change K into ºC, subtract 273.16 from the temperature given in Kelvin. For converting ºC to Kelvin (K), add 273.16 (For convenience we take 0ºC = 273K)
23.Latent heat of fusion : The amount of energy that is required to change 1kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure without any change of
temperature at its melting point is called latent heat of fusion.
24. Boiling Point : The temperature at which a liquid changes into gas or vapour is known as boiling point. It also indicates strength of intermolecular
force of attractions. Greater then intermolecular forces of attractions, higher will be the boiling point. The boiling point of water is 100ºC (373K).
25. Boiling : The process of converting liquid into vapour is called boiling. It is bulk phenomenon, i.e, particles from inside the liquid gain enough energy
to change into vapour state. It takes place only at boiling point.
26. Latent Heat of Vapourisation : The amount of energy that is required to change 1kg of liquid into vapours at atmospheric pressure without any change
in temperature at its boiling point is called latent heat of vapourisation.
27. Gas : It is stable state as compared to vapours, e.g., O2, N2, H2, CO2, etc.
28. Vapour : It is unstable state. On cooling, vapours change into liquid state. The work 'vapour' is used to describe those gases which usually exist as liquid at room temperature.
29. Vapourisation : It is process in which liquid changes into vapour. It is a surface phenomenon. It takes place at all temperatures. It is a slow process
and its rate increase with increase in temperature.
30. Volatile Liquids : Those liquids which can change into vapours easily are called volatile liquids, e.g., petrol, alcohol, acetone, ether, etc. evaporate easily
because they have low boiling points due to weak intermolecular forces of attraction. Water has high boiling point due to strong intermolecular
forces of attraction.
31. Sublimation : It is a process in which solid directly changes into vapours without changing into liquid state, e.g., camphor, I2, NH4Cl, naphthalene
can sublime. It can be shown experimentally.
Experiment : To show the process of sublimation experimentally.
Materials Required : Solid iodine, funnel, tripod stands, china dish, wire gauze, burner or spirit lamp, cotton.
Procedure :
Take 2g of iodine in china dish.
Put an inverted funnel over it whose stem is closed by cotton plug and set the apparatus as shown in diagram.
Heat and china dish so that vapours are formed and record the observations.
The vapours of iodine get condensed on the walls of the funnel.
Observations : The violet coloured vapours of iodine get condensed and change into solid iodine.
Conclusion : Iodine can sublime and can be purified by sublimation.
32. Effect of Pressure on Change in State : When we apply pressure and compress the gas, intermolecular force of attraction increases and molecules
come close to each other.
It may be change into liquid depending upon temperature and nature of the gas.
33 Liquidification of Gases : Gases can be liquified at low temperature and high pressure, e.g., H2, N2 and O2 can be liquified at low
temperature at high pressure. NH3 can be liquified at room temperature. CO2 can be solidified at low temperature and high pressure.
Solid CO2 is also called dry ice.
34. Atmosphere (atm) : It is unit of measuring pressure exerted by a gas. The pressure of air in atmosphere is called atmospheric pressure.
35. Pascal (Pa) : It is unit of measuring pressure exerted by a gas. The pressure of air in atmosphere is called atmospheric pressure.
1 atm = 1.01 × 105 Pa
The atmospheric pressure at seal level is 1 atmosphere and is taken as normal atmospheric pressure. As we go higher, atmospheric pressure decreases.
36. Evaporation : It is a process in which liquid changes into vapours e.g., water changes into vapours if left uncovered. Wet clothes dry up because
water gets evaporated.
The particles of water collide with each as well as with particles of gases in atmosphere. After some time, the particles on the surface gain sufficient
energy so as to change into vapours. It is a surface phenomenon.
37. Factor Affecting evaporation :
(a) Surface area : Greater the surface area, more will be the rate of evaporation because it is a surface phenomenon. There will be more number of
molecules on the surface which will change into vapour easily.
(b) Humidity : It is amount of water vapours present in air. The air around us cannot hold more than a definite amount of water vapours at a given temperature.
If the amount of water in air is already of water is air is already high, the rate of evaporation decreases. Decrease in humidity leads to increase in rate of evaporation.
(c) Temperature : The rate of evaporation increases with increase in temperature because more number of particles gain enough kinetic energy to go to vapour state.
(d) Wind speed : The rate of evaporation increase with increase in wind speed because particles of water vapours are taken away decreasing the
amount of water vapours in atmosphere.
38.Effect of Evaporation : Evoparation leads to cooling because high energy molecules leave the surface and average energy of remaining molecules decreases,
which results in drop in temperature of the part of liquid that is left. Therefore, evaporation cause cooling.
Evaporation causes cooling:–
During evaporation, cooling is always caused. This is because evaporation is a phenomenon in which only the high energy particles leave the liquid surface. As a result,
the particles having low energy are left behind. Therefore, the average molecular energy of the remaining particles left in the liquid state is lowered.
As a result, there is decrease in temperature on the part of the liquid that is left. Thus evaporation causes cooling.
Example:– (i) When we pour some acetone on our palm, we feel cold. This is because the particles gain energy from our palm or surroundings and leave the palm feeling cool.
(ii We sprinkle water on the root or open ground after a sunny hot day. This cools the roof or open ground. This is because the large latent heat of vaporization of water helps to cool the hot surface.
Some other examples of evaporation:–
(i) We should wear cotton clothes in hot summer days to keep cool and comfortable.
This can be explained as follows. We get a lot of sweat on our body in hot summer days. Cotton is a good absorber of water, so it absorbs the sweat
from our body and exposes it to the air for evaporation.
The evaporation of this sweat cools our body. The synthetic clothes (made of polyester etc) do not absorb much of sweat, so they fail to
keep our body cool in summer.
(ii) We see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass containing ice-cold water.
Take some ice-cold water in a glass. Soon we will see water droplets on the outer surface of the glass. The water vapour present in air,
on coming in contact with the cold glass of water loses energy and gets converted to liquid state, which we see as water droplets.
(iii) Water keeps cool in the earthen pot (matki) during summer:–
When the water oozes out of the pores of an earthen pot, during hot summer, it evaporates rapidly. As the cooling is caused by evaporation,
therefore, the temperature of water within the pot falls and hence it becomes cool.
(iv) Rapid cooling of hot tea:–
If tea is too hot to sip, we pour it in the saucer. In doing so, we increase the surface area and the rate of evaporation. This, in turn, causes
cooling and the tea attains a desired temperature for sipping
(v) A wet handkerchief is placed on the fore head of a person suffering from high fever. The logic behind placing wet cloth is that as the water
from the wet cloth evaporates
, it takes heat from the skull and the brain within it. This, in turn, lowers the temperature of brain and protects it from any damage due to high temperature.
(vi) We often sprinkle water on the road in summer. The water evaporates rapidly from the hot surface of the road, there by taking heat away from it. Thus, the road becomes cool.
39. Effect of Temperature on Clothes : Cotton is good absorber of water, helps in absorption of sweat and exposing it to atmosphere for easy
evaporation during summers. It causes cooling of our body.
40. Plasma : It is fourth state of matter. It consists of super energetic and super excited particles which are in the form of ionised gases. The
fluorescent tube, neon sign bulbs consist of plasma. Inside
the neon bulb, there is neon gas whereas inside the fluorescent
tube, there is helium gas or some other gas. The gas gets ionised, i.e., gets charged when electrical energy flows through it. This charging up
creates glowing plasma inside the tube or bulb.
he plasma glows with a special colour depending upon the nature of the gas. The sun and stars glow because of presence of plasma in them. The
plasma is created in stars due to very high temperature.
41. Bose-Einstein Condensate (B.E.C.) is fifth state of matter which is formed from matter that has been cooled to near absolute zero
(–273ºC). When a group of atoms is cooled to a very low temperature, the velocity decreases because they have very low energies.
This causes the individual atoms to overlap each other forming a single super atom with all of its constituting atoms sharing
a single energy state.
A rotating B.E.C. could be used as model black hole, allowing light to enter but not to escape.
Condensate can also be used to 'free' pulses of light, to be released again when condensate break down. Research in this field is going on.
1. Matter
(i) Anything which occupies space and has mass is called matter.
(ii) Food, water, air, clothes, table, chair, plants and trees.
(iii) Indian philosophers said that all the matter living or non-living, was made up of five basic elements air, earth, fire, sky and water
(iv) On the basis of its physical properties and on the basis of its chemical properties.
(v) On the basis of chemical properties the matter is classified as elements, compounds and mixtures.
(vi) Everything around us is made of tiny pieces or particles. The particles make up matter are atoms or molecules.
a. Characteristics of particles ofmatter:
(i) The particles of matter are very, very small
(ii) The particles of matter have spaces between them
(iii) The particles of matter are constantly moving
(iv) The particles of matter attract each other
b Classification of matter
On the basis of physical states, all the matter can be classified into three groups.
1. Solids 2. liquids 3 . Gases
c. Properties of solids
(i) Solids have a fixed shape and a fixed volume
(ii) Solids cannot be compressed much.
(iii) Solids have high densities. They are heavy
(iv) Solids do not fill their container completely.
(iv) Solids do not flow.
Ex. Ice, wood, coal, stone, iron, brick
d. Properties of liquid
(i) Liquids have a fixed volume but they have no fixed shape. Liquids take the shape of the vessel in which they are placed.
(ii) Like solids, liquids cannot be compressed much.
(iii) Liquids have moderate to high densities. They are usually less dense than solids.
(iv) Liquids do not fill their container completely.
(v) Liquids generally flow easily.
Ex. Water, milk, fruit juice, ink, groundnut oil, kerosene etc.
e. Properties of gases
(1) Gases have neither a fixed shape nor a fixed volume. Gases acquire the shape and volume of the vessel in which they are kept.
(2) Gases can be compressed easily.
(3) Gases have very low densities. They are very light.
(4) Gases fill their container completely.
(5) Gases flow easily.
Ex. Air, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
f. Comparison of characteristic properties of solids, liquids and gases
2. Change of state of matter : –
(i) A substance may exist in any of the three states of matter (i.e. solid, liquid or gas) depending upon the conditions of temperature and pressure.
(ii) By changing the conditions of temperature and pressure, a substance can be made to exist as solid, liquid or a gas.
(iii) A solid on heating usually changes into a liquid which on further heating changes into gas. Similarly, a gas on cooling condenses into a liquid which on
further cooling changes into a solid.
The most familiar and common example is water. It exists in all the three states:
(a) Solid : ice
(b) Liquid : water and
(c) Gas : water vapour.
Ice is a solid state and may be melted to form water (Liquid) which on further heating changes
into steam (gas). These changes can also be reversed on cooling.
3. Effect of temperature change
By increasing the temperature (by heating), a solid can be converted into liquid state; and the liquid can be converted into gaseous state (or vapour state).
And by decreasing the temperature (by cooling), a gas can be converted into liquid state; and a liquid can be converted into solid state.
Conversion of ice to water and water to water vapour
a. Solid to liquid change : Melting
(i) Definition : The process in which a solid substance changes into a liquid on heating, is called melting (or fusion).
(ii) Melting point : The temperature at which a solid substance melts and changes into a liquid at atmospheric pressure, is called melting point of the substance.
(iii) Ice is a solid. In solids, the particles are tightly packed together. When we heat a solid, its particles become more energetic and kinetic energy of the particles increases
. Due to the increase in kinetic energy, the particles start vibrating more strongly with greater speed. The energy supplied by heat overcomes
the intermolecular forces of attraction between the particles. As a result, the particles leave their mean position and break away from each other.
When this happens, the solid melts and a liquid is formed.
Ex. Melting point of ice = 0ºC
Melting point of wax = 63ºC
Melting point of iron = 1535ºC
The melting point of a solid is a measure of the force of attraction between its particles. Higher the melting point of a solid substance, greater
will be the force of attraction between its particles.
Liquid to gas change : Boiling (or vaporisation)
(i) Definition : The process in which a liquid substance changes into a gas rapidly on heating, is called boiling.
(ii) Boiling point : The temperature at which a liquid boils and changes rapidly into a gas at atmospheric pressure, is called boiling point of the liquid.
(iii) In a liquid most of the particles are close together. When we supply heat energy to the liquid, the particles of water start vibrating even faster.
Some of the particles become so energetic that they can overcome the attractive forces of the particles around them.
Therefore, they become free to move and escape from the liquid. When this happens, the liquid evaporates i.e., starts changing into gas.
Ex. Boiling point of water = 100ºC
Boiling point of alcohol = 78ºC
Boiling point of mercury = 357ºC
The boiling point of a liquid is a measure of the force of attraction between its particles. Higher the boiling point of a liquid, greater will be the
force of attraction between its particles.
When a liquid is heated, the heat energy makes its particles move even faster. At the boiling point the particles of a liquid have sufficient
kinetic energy to overcome
the forces of attraction holding them together and separate into individual particles. And the liquid boils to form a gas.
Gas to liquid change : Condensation
The process of changing a gas to a liquid by cooling, is called
condensation. Condensation is the reverse of boiling.
Liquid to solid change : Freezing
The process of changing a liquid into a solid by cooling, is called freezing. Freezing means solidification. Freezing is the
reverse of melting. So, the freezing point of a liquid is the
same as the melting point of its solid form.
Ex. Melting point of ice = 0ºC
Freezing poing of water = 0ºC
4. Effect of change of pressure
(i) The three states of matter differ in the intermolecular forces and intermolecular distances between the constituent particles.
(ii) Gases are compressible because on applying pressure, the space between the gaseous particles decreases. Therefore, gases can
be compressed readily.
(iii) When we apply pressure and reduce temperature the gases can be converted into liquids i.e., gases will be liquefied.
(iv) The process of conversion of a gas into a liquid by increasing pressure or decreasing temperature is called liquidification.
A substance may exist in any of the three different states of matter depending upon the conditions of temperature and pressure.
(1) If the melting point of a substance is above the room temperature at the atmospheric pressure, it is said to be a solid.
(2) If the boiling point of a substance is above room temperature under atmospheric pressure, it is classified as liquid.
(3) If the boiling point of the substance is below the room temperature at the atmospheric pressure, it is called a gas.
5. Latent heat
(i) Definition : The heat energy which has to be supplied to change the state of a substance is called its latent heat.
(ii) Latent heat does not raise the temperature but latent heat has always to be supplied to change the state of a substance. The word ‘latent’ means ‘hidden’
(iii) Every substance has some forces of attraction between its particles which hold them together. Now, if a substance has to change its state,
then it is necessary to break these forces of attraction between its particles. The latent heat does not increase the kinetic energy of
the particles of the substance,
the temperature of a substance does not rise during the change of state.
(i) Latent heat of fusion : The heat required to convert a solid into the liquid state is called latent heat of fusion. In other words ‘
The latent heat of fusion of a solid is the quantity of heat in joules required to convert 1 kilogram of the solid to liquid, with out any change in temperature.
Ex.16 The latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.34 × 105 J/kg
(i) Latent heat of vaporisation : The heat required to convert a liquid into the vapour state is called latent heat of vaporisation.
(ii) The other words ‘The latent heat of vaporisation of a liquid is the quantity of heat in joules required to convert 1 kilogram of the liquid
to vapour or gas, without any change in temperature.
Ex. Latent heat of vaporisation of water
= 22.5 × 105 J/kg
6. Sublimation
(i) Definition : The changing of a solid directly into vapours on heating, and of vapours into solid on cooling, is known as sublimation.
(ii) Sublimation can be represented as:
Solid Vapour (or Gas)
(iii) The solid substance which undergoes sublimation is said to ‘sublime’. the solid obtained by cooling the vapours of the solid is called a ‘sublimate’.
Ex. When solid ammonium chloride is heated, it directly changes into ammonium chloride vapour. And when hot Ammonium chloride vapour is cooled,
it directly changes into solid ammonium chloride. Ammonium chloride, Iodine, Camphor, Naphthalene and Anthracene.
7. Evaporation
(i) Definition : The process of change of a liquid into vapour at any temperature below its boiling point is called evaporation.
Factors affecting evaporation : –
(i) Temperature : Rate of evaporation increase with increase in temperature. This is because with the increase in temperature more
number of particles get enough kinetic energy to go into the vapour state.
Ex. Drying of clothes take place rapidly in summer than in winter
(ii) Surface Area : The rate of evaporation increases on increasing the surface area of the liquid
Ex. If the same liquid is kept in a test tube and in a china dish, then the liquid kept in the china dish will evaporate more rapidly : Because more
of its surface area is exposed to air.
(iii) Humidity : Humidity is the amount of water vapour present in air. Air around us cannot hold more than a definite quantity of water vapour
at a given temperature.
If the amount of water in air is already large i.e., humidity is more, the rate of evaporation decreases. Thus, the rate of evaporation increases with
decrease in humidity in the atmosphere.
Ex. Clothes do not dry easily during rainy season because rate of evaporation less due to humidity.
(iv) Wind speed : The rate of evaporation also increases with increase in speed of the wind. This is because with increase in speed of wind,
the particles of water vapour move away with wind resulting decrease in the amount of vapour in the atmosphere.
Ex. Clothes dry faster on a windy day.
8. Diffusion
(i) Definition : The spreading out and mixing of a substance with another substance due to the motion of its particles is called diffusion.
(ii) Diffusion is a property of matter which is based on the motion of its particles.
(iii) Diffusion is fastest in gases because the particles in gases move very rapidly. The diffusion is slowest in solids because the particles in
solids do not move much.
(iv) The rate of diffusion increases on increasing the temperature of the diffusing substance.
This is because when the temperature of a substance is increased by heating, its particles gain kinetic energy and move more rapidly and this
increase in the speed of the particles of a substance increases the rate of diffusion.
Diffusion in gases
Diffusion in gases is very fast. This is because the particles in gases move very quickly in all directions.
Ex. When we light an incense stick (agarbatti) in a corner of our room, its fragrance spreads in the whole room very quickly. The fragrance of burning
incense stick spreads all around due to the diffusion of its smoke into the air.
Ex. When someone opens a bottle of perfume in one corner of a room, its smell spreads in the whole room quickly. The smell of perfume spreads
due to the diffusion of perfume vapours into air.
Diffusion in liquids
Diffusion in liquids is slower than that in gases. This is because the particles in liquids move slower as compared to the particles in gases.
Ex. The spreading of purple colour of potassium permanganate into water, on its own, is due to the diffusion of potassium permanaganate particles into water
Ex. The spreading of blue colour of copper sulphate into water, on its own, is due to the diffusion of copper sulphate particles into water.
The rate of diffustion in liquids is much faster than that in solids because the patricles in a liquid move much more freely, and have greater
paces between them as compared to particles in the solids.
Diffusion in solids
Diffusion in solids in a very, very slow process.
Ex. If we write something on a blackboard and leave it uncleaned for a considerable period of time we will find that it
becomes quite difficult to clean the blackboard afterwards
. This is due to the fact that some of the a particles of chalk have diffused into the surface of blackboard.
Ex. If two metal blocks are bound together tightly and kept undisturbed for a few years, then the particles of one metal are found to have
diffused into the other metal.
IMPORTANT DEFINITION
1. Melting or Fusion : The process due to which a solid changes into liquid state at constant temperature, by absorbing heat energy, is known as melting or fusion.
2. Freezing or Solidification : The process due to which a liquid changes into solid state at constant temperature, by giving out heat energy, is known as freezing or solidification.
3. Melting point : The constant temperature at which a solid changes into liquid state by absorbing heat energy, is called melting point.
4. Freezing point : The constant temperature at which a liquid changes into solid state by giving out heat energy, is called freezing point.
Note : The numerical value of melting point and freezing point is the same. For example, if melting point of ice is 0°C (273 K), then the
freezing point ofwater is 0°C (273 K).
(a) Liquid to gas change (Boiling or vaporizations) :–
In a liquid most of the particles are close together. When we supply heat energy to the liquid, the particles of water start vibrating even faster.
Some of the particles become so energetic that they can overcome the attractive forces of the particles around them. Therefore, they become
free to move and escape from the liquid. Thus the liquid evaporates i.e., starts changing into gas.
"The temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas or vapour at the atmospheric pressure is called its boiling point".
"Boiling" is a bulk phenomenon.
Example – For water, the boiling point is 100°C or 373 K. The particles in steam i.e., water vapour at 373 K have more energy than water at the same temperature.
Reason :– This is because the particle in steam have absorbed extra energy in the form of latent heat of vaporization.
(b) Latent heat of vaporization :– The latent heat of vaporization of a liquid is the quantity of heat in joules required to convert 1 kilogram of
the liquid (at its boiling point) to vapour or gas,
without any change in temperature. The latent heat of vaporization of water is 22.5 × 105 joules per kilogram(or 22.5 × 105 J/kg).
Density :– The mass of a substance per unit of volume.
Formula –
In SI unit it is measured in kgm–3
Volume :– All solids occupy a fixed volume the shape occupied by a substance is called volume.
The unit of volume is m3 (cubic meter). The common unit of volume is litre. (L)
1m3 = 1000 dm3 = 1000 L
1 L = 1 dm3
1 L = 1000 ml = 1000 cm3
Note: –
Pressure :– In the gaseous state the particle move about randomly at high speed. Due to their random movement, the particles hit each
other and also the walls of the container.
The pressure exerted by the gas is because of this force exerted by gas particles per unit area on the walls of the container.
The atmospheric pressure at sea level is 1 atm, and is taken as the normal atmospheric pressure.
p= Pressure, F = Force, A = Area
It is measured in "pascals" (Pa) in SI units and other unit is atm. these two units are related as–
1 atm = 1.01 × 105 Pa
1 bar = 1 × 105 Pa
1 bar = 1.01 atm.
Ex.1 What do you observe when force is applied and then removed on the plunger of the syringe containing air ? Give a reason for your answer.
Sol. The plunger moves downward on the application of force to a considerable length. When the force is removed, the plunger moves backward
and takes its original position.
Ex.2 Give reasons :
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel, in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Sol. (a) The molecules of a gas have large intermolecular spaces and kinetic energy, but extermely small intermolecular forces. Thus,
the molecules of the gas spread in the entire space of the containing vessel on account of high kinetic energy and practically to
intermolecular forces, hence fill entire space of the vessel.
(b) The molecules of a gas have very large kinetic energy. When these molecules strike against the walls of containing vessel, they exert
certain average force per unit area.
As the force per unit area is known as pressure, therefore, the gases exert pressure on the sides of the containing vessel.
(c) Solids are rigid, incompressible and have definite shape and volume. Since the table has all the above mentioned properties, therefore, it it solid.
(d) The intermolecular forces between the molecules of a gas are almost negligible and intermolecular spaces are very large. Thus, we can
easily move our hand in air, without any appreciable force.
The intermolecular forces between the molecules of a solid are very large and intermolecular spaces are very small. Thus, a lot of force
is required to separate the molecules of a solid. It is for the same reasons that we need karate expert to break a block of wood.
Ex.3 The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. (Density = Mass / Volume). Arrange the following in the order of increasing density :
air, exhaust from chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Sol. Exhaust from chimneys, air, cotton, water, honey and iron.
e.g..
(i) CNG (compressed Natural gas) is used as fuel in internal combustion engines.
(ii) Oxygen in compressed form is supplied to hospitals for serious patients in cylinders.
(iii) LPG (Liquefied petroleum gas) which is used in home for cooking.
(iv) The gases exhibit the property of diffusing very fast into other gases.
Ex.4 We can easily move our hand in the air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a karate expert.
Sol. In air the interparticle attractive forces are negligible and hence, it is easy to separate the particles in air and we can easily move our hand through it.
In a solid block of wood, the interparticle forces are very strong and hence, it is not easy to separate the particles.
Therefore it is not easy to move our hand through a solid block of wood (only a karate expert can do it). Dut to this property large
volume of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder and transported easily.
Ex.5 Arrange the following substances in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles -water, sugar, oxygen.
Sol. Oxygen < water < Sugar
Ex.6 The diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool.
Sol. Explanation :– The diver is able to cut through water in the swimming pool because matter is not continuous, but it is made up of
particles which have vacant spaces between them moreover
, the attractive forces between molecules of water are not very strong. The diver can easily cut through water by applying force to
displace water and occupy its place.
Ex.7 Why ice floats on water?
Sol. Solids generally have higher density than the liquids but ice due to its specific structure has larger interparticle spaces and hence has
lower density than liquid water. As a result ice floats on water.
Temperature and pressure are the two factors which decide whether a given substance would be in a solid, liquid or gaseous state.
Ex.8 Convert the following temperatures to the celsius scale.
(a) 300 K (b) 573 K
Sol. (a) (300 – 273) = 27°C. Temperature in °C = Temperature in K – 273
(b) (573 – 273) = 300°C. Temperature in °C = Temperature in K – 273
Ex.9 Convert the following temperature to the Kelvin scale.
(a) 25°C (b) 373°C
Sol. (a) 25 + 273 = 298 K (b) 373 + 273 = 646 K
Ex.10 What is the physical state of water at –
(a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C
Sol. (a) 25°C – Water is in liquid state.
(b) 0°C – Water is in solid state.
(c) 100°C – Water is in gaseous state.
Convert the following temperature to the Celsius scale-
Q.1 (i) 293 K (ii) 410 K
Ans. (i) 293 – 273 = 20°C
(ii) 470 – 273 = 197°C
Q.2 Convert the following temperature to the kelvin scale.
(i) 25°C (ii) 373°C
Ans. (i) 25 + 273 = 298K
(ii) 373 + 273 = 646K
Q.3 Arrange the following substances in the increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles water, sugar and oxygen.
Ans. Oxygen, water and sugar.
Q.5 What is the physical state of water at
(a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C?
Ans. (a) At 25°C, water is in liquid state.
(b) At 0°C, water is in solid state, provided heat is removed from it.
(c) At 100°C, water is in gaseous state, provided heat is supplied to it.
Q.6 Give two reasons to justify –
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is solid at room temperature.
Sol. (a)
(i) Intermolecular forces are less.
(ii) Intermolecular spaces and kinetic energy is more.
Thus, the molecule of water can interchange their spaces and hence water is in liquid
state at room temperature.
(b)
(i) Intermolecular forces are very large.
(ii) Intermolecular spaces, as well as, kinetic energy are very small.
Q.7 Ice is at 273 K more effective in cooling, than water at the same temperature, why?
Sol. One kilogram of ice at 273 K, needs 3, 36000 J of heat energy in order to form water at 273 K. As the ice can extract out large amount
of heat energy on melting to form water at the same temperature, therefore, it is more effective in cooling.
Q.8 What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Sol. Steam will produce more severe burns than boiling water. It is because, 1 g of steam at 373 K (100°C) contains 2260 J of heat energy
more in the form of latent heat of vaporization as compared to water at 373 K(100° ). Thus steam produces more severe burns.
Q.9 Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid why?
Sol. Naphthalene is volatile solid and has a tendency to sublime, therefore, it changes into vapours completely which disappear into the air and no solid is left.
Q.10 We cna get the smell of perfume sitting several metere away.
Ans. This is because perfumes contain volatile solvent which carries pleasent smelling vapour. They diffuse quite fast and can reach
to people sitting several metere away.
Q.1 Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Q.2 Give reasons :
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a karate expert.
Q.3 Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Q.4 Convert the following temperatures to the Celsius scale.
Q.5 What produce more sever burns boiling water or steam?
Q.6 Define matter.
Q.7 What is plasma?
Q.8 What is Bose-Einstein condensate [BEC]?
Q.9 Why do we see water droplets on the outer surface of a glass container of ice cold water?
Q.10 Define specific heat of substance.
Q.11 Define latent heat of a substance.
Q.12 Why gases are compressible but not liquids?
Q.13 Give two factors which determine the rate of diffusion of a liquid in another liquid.
Q.14 Arrange the solids, liquids and gases in order of :
(A) increasing intermolecular space
(b) lncreasing intermolecular force
Q.15 Which phenomenon occurs during the following changes :
(a) Formation of clouds
(b) Drying of wet clothes
(c) Was melts in the sun
(d) Size of naphthalene balled decreases
Q.16 Why does a wet khus-khus screen hung at the door keep the room cool?
Q.17 What is mean by evaporation? How is this process different from boiling?
Q.18 Why can you smell the perfume of incense stick
Q.19 Why cannot you smell its perfume at a short distance when incense stick is not lighted ?
Q.20 Why is the smell of the perfume of incense stick filled the whole room in few minutes, when lighted ?
Q.21 A rubber band is a solid, but it can change its shape. Why ?
Q.22 When salt or sugar are poured into different kinds of vessels, why do they take the shape of vessel ?
Q.23 Sponge is a solid, yet we are able to compress it. Why ?
Q.24 Arrange the following substances in the increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles – water, sugar and oxygen.
Q.25 What is the physical state of water at :
(a) 25°C (b) 0°C (c) 100°C
Q.26 Give two reason to justify.
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is solid at room temperature.
Q.27 State your observation immediately after adding the blue ink drop.
Q.28 State your observation immediately after adding the honey drop.
Q.29 How much time does it take for the colour of ink to spread evenly ?
Q.30 How does the diffusion of honey varies with the diffusion of ink and why ?
Q.31 What happens around each crystal of solid on introducing in water ?
Q.32 What happens as the time passes, and why ?
Q.33 Does the rate of diffusion change with temperature ? If so, why ?
Q.1 When salt is dissolved in water :-
(A) Boiling point increases (B) Boiling point does not change
(C) Boiling point decreases (D) None of the above
Q.2 Mixture of butane, ethane and propane is called:-
(A) Coal gas (B) Oil gas (C) Petroleum gas (D) Producer gas
Q.3 In the kinetic theory of gases, it is assumed that molecular collisions are :-
(A) Inelastic (B) Short in duration
(C) One-dimensional (D) Not able to exert mutual forces
Q.4 Triple point of water is :-
(A) 373.16 K (B) 273.16° F (C) 273.16 K (D) 273.16 F
Q.5 Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) Same sugar can be added to a full glass of water without causing overflow.
(2) A liquid is continuous even-though space is present between the molecules.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1) (B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain (1)
(C) Only (1) is true (D) Only (2) is true
Q.6 Vanderwaal's forces are also known as :-
(A) Intermolecular forces (B) Intramolecular forces
(C) Atomic forces (D) Molecular forces
Q.7 Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) If we increase the temperature of a gas inside a container, its pressure also increases.
(2) Upon heating, the rate of collisions of the gas molecules increase and increases the impact of force onthe walls of the container.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1) (B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain(1)
(C) Only (1) is true (D) Only (2) is true
Q.8 Match the following and choose the correct answer :-
(i) Solid (a) Super energetic particles
(ii) Liquid (b) No shape nor fixed volume at a given pressure
(iii) Gas (c) Has definite shape
(iv) Plasma (d) Define shape with less molecular forces than that in solids
(A) (i) – a, (ii) – b, (iii) – c, (iv) – d (B) (i) – c, (ii) – d, (iii) – b, (iv) – a
(C) (i) – c, (ii) – d, (iii) – a, (iv) – b (D) (i) – a, (ii) – d, (iii) – b, (iv) – c
Q.9 The process for the change of a solid directly into its vapour is called –
(A) Evaporation (B) Ebullition
(C) Condensation (D) Sublimation
Q.10 When water particles condenses on air on dust, it forms :-
(A) mist (B) fog (C) frost (D) Vapour
Q.11 Which is more effective in cooling ?
(A) Water at 0°C (B) Water at 100°C (C) Ice at 0°C (D) All of these
Q.12 The temperature at which Celsius and Fahrenheit scales show the same reading is:-
(A) 40° K (B) 100° F (C) – 40° C (D) – 100°C
Q.13 Latent heat of fusion for ice is :-
(A) 80 gm cal–1 (B) 80 cal / gm (C) 19 J cal–1 (D) None of these
Q.14 Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) In polar regions aquatic life is safe in water under frozen ice.
(2) Water has a high latent heat of fusion and the upper portion of ice does not allow the heat of the waterto escape to the surroundings.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1)
(B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain (1)
(C) Only (1) is true
(D) Only (2) is true
Q.15 Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) Boiling point of a liquid increases with increase in temperature.
(2) The volume of liquids increases on boiling and the vaporisation curve shows the variation of the boilingpoint of a liquid with pressure
and expands the equilibrium state between liquid and vapour phase.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1) (B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain(1)
(C) Only (1) is true (D) Only (2) is true
Q.16 In an experiment of conversion of ice into water and water into vapour, observations were recorded and a graph plotted for
temperature against time as shown below. From the graph it can be concluded that :-
(A) Ice takes time to heat up to 0°C
(B) During melting and boiling temperature does not rise
(C) Process of boiling takes longer time than the process of melting
(D) All the above
Q.17 The SI unit of temperature is :-
(A) °C (B) °F (C) K (D) All of the above
Q.18 Study the graph given below and select the correct statement :-
(A) When water is cooled to 4°C it contracts
(B) At 0°C water freezes (C) The volume of ice is more than that of water
(D) All of these
Q.19 The solid state of CO2 is called :-
(A) Tear gas (B) Cooking gas (C) Dry ice (D) Laughing gas
Q.20 Corresponding temperature in the Kelvin scale for 104°C F is :-
(A) 313 K (B) 203 (C) 308 K (D) 377 K
Q.21 When the vapour pressure of a liquid is equal to its atmospheric pressure, then it :-
(A) Freezes
(B) Evaporates
(C) Boils (D) Does not undergo any change
Q.22 When ice is converted into water :-
(A) Heat is absorbed
(B) Heat is released
(C) Temperature increases
(D) Temperature decreases
Q.23 Which of the following has the strongest interparticle force at the room temperature?
(A) Nitrogen (B) Mercury
(C) Iron (D) Chalk
Q.24 What is volume of gases?
(A) Definite
(B) Almost Nil
(C) Large
(D) Take the volume of container
Q.25 The change of state from solid to liquid known as –
(A) Fusion (B) Boiling
(C) Melting (D) None of these
Q.26 Dry ice is –
(A) Water in solid state
(B) Water in gaseous state
(C) CO2 in liquid state
(D) CO2 in solid state
Q.27 The boiling point of water on kelvin scale is–
(A) 573 K (B) 273 K
(C) 373 K (D) 100 K
Q.28 The process of change of a liquid into vapour at any temperature is called –
(A) Diffusion (B) Evaporation (C) Cooling (D) Heating
Q.29 Which factor affecting Evaporation –
(A) Temperature (B) Surface area (C) Both (A) & (B) (D) None of these
Q.30 On increasing the temperature of the liquid the rate of evaporation is –
(A) Increase (B) Decreases (C) No change (D) None of these
Q.31 Fluids are –
(A) Liquids and gases
(B) Solids and gases
(C) Liquids and solids
(D) Only solids
Q.32 Which substance undergo sublimation process–
(A) Naphthalene (B) CO2
(C) Ice (D) N2
Q.33 Condensation process is –
(A) Change of state from gas to liquid (B) Change of state from liquid to gas
(C) Change of state from gas to solid (D) Change of state from solid to liquid
Q.34 The temperature at which liquid starts boiling at atmospheric pressure known as –
(A) Melting point (B) Boiling point (C) Latent heat (D) Condensation
Q.35 The melting point of ice is –
(A) 0°C (B) 4°C
(C) 5°C (D) None of these
Q.36 The physical state of matter which can be easily compressed –
(A) Liquid (B) Gas
(C) Solid (D) None of these
Q.37 Name the process by which a drop of ink spreads in a beaker of water –
(A) Diffusion (B) Vaporization (C) Condensation (D) Sublimation
Q.38 The temperature at which a solid changes into liquid at atmospheric pressure is called –
(A) Melting point (B) Boiling point (C) Diffusion (D) Evaporation
Q.39 Convert the temperature of 373°C to the kelvin scale ?
(A) 646 K (B) 546 K
(C) 300 K (D) 500 K
Q.40 Conver t the temperature of 270 K to the celsius scale –
(A) – 3°C (B) – 4°C
(C) 2°C (D) 5°C
Q.41 Plasma is the.......... state of matter –
(A) First (B) Second
(C) Third (D) Fourth
ANSWER KEY
1. C 2. C 3. B 4. C
5. A 6. A 7. A 8. B
9. D 10. A 11. C 12. C
13. B 14. A 15. A 16. D
17. C 18. D 19. C 20. A
21. C 22. A 23. C 24. D
25. C 26. D 27. C 28. B 29. C
30. A 31. A 32. A 33. A 34. B
35. A 36. B 37. A 38. A 39. A
40. A 41. D
Section-A
· Fill in the blanks
1. The best evidence that the particles of matter are constantily moving comes from the studies of __________ and __________.
2. When ice melts there is a __________ in volume.
3. The stars and sun glow because of the presence of __________in them.
4. Anything that occupies space and has mass is called__________
5. The intermixing of particles of two substances on their own is called __________
6. Solid, liquid and gas are called the __________ of matter.
7. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called __________
8. The smell of perfume gradually spreads across a room due to __________
9. Increase in pressure __________the boiling point of water.
10. When steam condense to form water, heat is __________.
Section-B
Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. According to ancient philosphers matter consists of
(A) three constituents (B) four constituents (C) five constituents (D) six constituents
2. Which of the following is not matter?
(A) air (B) feeling of cold (C) dust (D) humidity
3. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(A) Matter is continuous in nature
(B) Interparticle spaces are maximum in the gaseous state of a substance
(C) Particles which constitute the matter follow a zig-zag path
(D) Solid state is the most compact state of a substance
4. The mass per unit volume of a substance is called :
(A) density (B) valency (C) solubility (D) none of above
5. A gas can be best liquefied
(A) by increasing the temperature
(B) by lowering the pressure
(C) by increasing the pressure and reducing the temperature
(D) none of these is correct
6. Evaporation of a material takes place :
(A) above its boiling point (B) below its boiling point
(C) at its melting point only (D) below its melting point
7. Which of the following exists as gas?
(A) Petrol (B) Helium (C) Sodium (D) Iodine
8. 10°C temperature is equal to
(A) 163 K (B) 10 K (C) 183 K (D) 283 K
9. Which of the following will respond to sublimation?
(A) Common salt (B) Sugar (C) Camphor (D) Potassium nitrate
10. Which of the following statements do not go with the liquid state?
(A) Particles are loosly packed in the liquid state
(B) Fluidity is the maximum in the liquid state
(C) Liquids cannot be compressed
(D) Liquids take up the shape of any container in which they are placed
Section-C
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II.
Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only
one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Spread sweet odour into the atmosphere (P) Sublimation
(B) Change of liquid state to gaseous state (Q) Diffusion
(C) Change of solid state directly to gaseous state (R) Condensation
(D) The gas changing to a liquid (S) Vaporization
Section-A
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. The physical state of water at 100°C is
(A) Solid (B) Liquid (C) Gas (D) None of these
2. The state of matter that can be easily compressed is
(A) Solid (B) Liquid
(C) Gas (D) Super cooled solid
3. A substance which has a definite volume but no definite shape is
(A) Solid (B) Liquid (C) Gas (D) None of these
4. Evaporation of a liquid occurs at
(A) Boiling point (B) Fixed temperature lower than the boiling point
(C) All temperatures (D) None of these
5. The change from vapour to liquid is called
(A) Condensation (B) Fusion (C) Sublimation (D) None of these
6. The melting point of ice is
(A) 273.16 K (B) 373.16 K (C) 283.16 K (D) 263.16 K
7. The change from solid to gas directly is called
(A) Vaporization (B) Sublimation (C) Condensation (D) None of these
8. Diffusion is a property of matter, based on
(A) Motion of its particles (B) Size of its particles (C) Pressure (D) Temperature
9. The SI unit of temperature is
(A) Celsius (B) Kelvin (C) Farenhiet (D) None of these
10. The process of changing liquid into solid is called
(A) Evaporation (B) Freezing (C) Condensation (D) Sublimation
11. The state of which 99% matter of the universe is
(A) Plasma (B) Solid (C) Gaseous (D) Liquid
12. The tendency of non-reacting gases to mix with each other is called as
(A) Chemical reaction (B) Diffusion (C) Effusion (D) Explosion
Section-B
· Multiple choice question with one or more than one correct answers
1. Which of the following are states of matter?
(A) Solid (B) Liquid (C) Gas (D) Plasma
2. Physical state of matter can be changed by
(A) change of pressure (B) change of volume
(C) change of temperature (D) change of composition.
3. Solids have/can
(A) Fixed shape (B) Fixed volume (C) Flow easily (D) Low densities
4. The particles of matter are
(A) Very, very small (B) Constanty moving
(C) Repelled by each other (D) Tightly packed
5. In which of the following states, water can exist
(A) Solid (B) Liquid (C) Gas (D) Plasma
6. Which of the following will undergo sublimation?
(A) Ammonium chloride (B) Sodium chloride (C) Iodine (D) Methanol
7. Evaporation of a liquid mainly depends upon
(A) Temperature (B) Pressure (C) Surface area (D) Wind speed
8. Which of the following factors are responsible for change in state of solid carbon dioxide when kept exposed to air?
(A) Increase in pressure (B) Decrease in pressure
(C) Decrease in temperature (D) Increase in temperature
9. The best evidence that the particles of matter are constantly moving comes from the studies of :
(A) Diffusion (B) Fusion (C) Brownion motion (D) Tyndall effect
10. Which state of matter does not consists of superenergetic and super excited particles in the form of ionised gases ?
(A) Super cooled (B) Solid (C) Liquid (D) Plasma
11. The factors which effects the diffusion are:-
(A) Density (B) Temperature (C) Physical state (D) None of these
12. A soild sphere is immersed in a fluid.The magnitude of buoyant force experienced by the sphere depends on the
(A) Density of the fluid (B) Density of the solid
(C) Volume of the fluid (D) Volume of the solid immersed in the fluid
13. Which of the following is/are characteristics of liquids ?
(A) Fixed volume (B) Definite shape
(C) Flow easily (D) Moderate compressibility
Section-C
· Comprehension
We use celsius scale of temperature for measuring temperature in our everyday life. But the S.I. Unit of measuring temperature is
Kelvin which is denoted by symbol K.
The melting point of ice on kelvin scale is 273 K and the boiling point of water on kelvin scale is 373 K.
Temperature on kelvin scale = Temperature on celsius scale +273
Now answer the following questions
1. The kelvin temperature is 270 K. What is the corresponding celsius scale temperature?
(A) 373°C (B) 543°C (C) –3°C (D) –1°C
2. Convert the temperature of 573 K to the celsius scale
(A) 300°C (B) 400°C (C) 500°C (D) 600°C
3. Convert the temperature of 373°C into the kelvin scale
(A) 546 K (B) 646 K (C) 351 K (D) None
4. The kelvin scale temperature is 0 K. What is the corresponding celsius scale temperature?
(A) –273°C (B) 273°C (C) 373°C (D) None of these
Section-D
· Match the following (one to many)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II.
One or more than one entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II may
have one or more than one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Solid (P) Have a fixed volume
(B) Liquid (Q) Mixture of free electrons and ions
(C) Gas (R) Do not have fixed shape
(D) Plasma (S) Flow easily
Section-A
1. Diffusion and Brownian motion. 2. Decrease
3. Plasma 4. Matter 5. Diffusion
6. Three states 7. Density 8. Diffusion
9. Increase 10. Evolved
Section-B
1. (C) 2. (B) 3. (A) 4. (A) 5. (C)
6. (B) 7. (B) 8. (D) 9. (C) 10. (B)
Section-C
1. (A)-(Q), (B)-(S), (C)-(P), (D)-(R)
Section-A
1. (C) 2. (C) 3. (B) 4. (C) 5. (A)
6. (A) 7. (B) 8. (A) 9. (B) 10. (B)
11. (A) 12. (B)
Section-B
1. (A,B,C,D) 2. (A,C) 3. (A,B) 4. (A,B) 5. (A,B,C)
6. (A,C) 7. (A,C,D) 8. (B,D) 9. (AC) 10. (A,B,C)
11. (A,B,C) 12. (A,D) 13. (A,C,D)
Section-C
1. (C) 2. (A) 3. (B) 4. (A)
Section-D
1. (A)-(P), (B)-(P,R,S), (C)-(R,S), (D)-(Q)
1. When salt is dissolved in water :-
(A) Boiling point increases (B) Boiling point does not change
(C) Boiling point decreases (D) None of the above
2. Mixture of butane, ethane and propane is called :-
(A) Coal gas (B) Oil gas (C) Petroleum gas (D) Producer gas
3. In the kinetic theory of gases, it is assumed that molecular collisions are :-
(A) Inelastic (B) Short in duration
(C) One-dimensional (D) Not able to exert mutual forces
4. Triple point of water is :-
(A) 373.16 K (B) 273.16° F (C) 273.16 K (D) 273.16 F
5. Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) Same sugar can be added to a full glass of water without causing overflow.
(2) A liquid is contianuous even-though space is present between the molecules.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1)
(B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain (1)
(C) Only (1) is true (D) Only (2) is true
6. Vanderwaal's forces are also known as :-
(A) Intermolecular forces (B) Intramolecular forces
(C) Atomic forces (D) Molecular forces
7. Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) If we increase the temperature of a gas inside a container, its pressure also increases.
(2) Upon heating, the rate of collisions of the gas molecules increase and increases the impact of force on the walls of the container.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1)
(B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain (1)
(C) Only (1) is true (D) Only (2) is true
8. Match the following and choose the correct answer :-
(i) Solid (a) Super energetic particles
(ii) Liquid (b) No shape nor fixed volume at a given pressure
(iii) Gas (c) Has definite shape
(iv) Plasma (d) Define shape with less molecular forces than that in solids
(A) (i) – a, (ii) – b, (iii) – c, (iv) – d (B) (i) – c, (ii) – d, (iii) – b, (iv) – a
(C) (i) – c, (ii) – d, (iii) – a, (iv) – b (D) (i) – a, (ii) – d, (iii) – b, (iv) – c
9. Match the following and choose the correct answer.
(i) Evaporation (a) Liquid to gas at a fixed temperature
(ii) Vaporisation (b) Solid to gas
(iii) Sublimation (c) Gas to solid
(iv) Hoar frost (d) Liquid into gas at any temperature
(A) (i) – a, (ii) – b, (iii) – c, (iv) – d (B) (i) – c, (ii) – d, (iii) – b, (iv) – a
(C) (i) – c, (ii) – d, (iii) – a, (iv) – b (D) (i) – a, (ii) – d, (iii) – b, (iv) – c
10. When water particles condenses on air on dust, it forms :-
(A) mist (B) fog (C) frost (D) Vapour
11. Which is more effective in cooling ?
(A) Water at 0°C (B) Water at 100°C (C) Ice at 0°C (D) All of these
12. The temperature at which Celsius and Fahrenheit scales show the same reading is :-
(A) 40° K (B) 100° F (C) – 40° C (D) – 100°C
13. Latent heat of fusion for ice is :-
(A) 80 gm cal–1 (B) 80 cal / gm (C) 19 J cal–1 (D) None of these
14. Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) In polar regions aquatic life is safe in water under frozen ice.
(2) Water has a high latent heat of fusion and the upper portion of ice does not allow the heat of the water to escape to the surroundings.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1)
(B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain (1)
(C) Only (1) is true
(D) Only (2) is true
15. Based on the statements given here choose the correct answer.
(1) Boiling point of a liquid increases with increase in temperature.
(2) The volume of liquids increases on boiling and the vaporisation curve shows the variation of the boiling point of a liquid with
pressure and expands the equilibrium state between liquid and vapour phase.
(A) (1) and (2) are true and (2) explains (1)
(B) (1) and (2) are true but (2) does not explain (1)
(C) Only (1) is true (D) Only (2) is true
16. In an experiment of conversion of ice into water and water into vapour, observations were recorded and a graph plotted for
temperature against time as shown below. From the graph it can be concluded that :-
(A) Ice takes time to heat up to 0°C
(B) During melting and boiling temperature does not rise
(C) Process of boiling takes longer time than the process of melting
(D) All the above
17. The SI unit of temperature is :-
(A) °C
(B) °F
(C) K
(D) All of the above
18. Study the graph given below and select the correct statement :-
(A) When water is cooled to 4°C it contracts
(B) At 0°C water freezes
(C) The volume of ice is more than that of water
(D) All of these
19. The solid state of CO2 is called :-
(A) Tear gas (B) Cooking gas (C) Dry ice (D) Laughing gas
20. Corresponding temperature in the Kelvin scale for 104°C F is :-
(A) 313 K (B) 203 (C) 308 K (D) 377 K
21. When the vapour pressure of a liquid is equal to its atmospheric pressure, then it :-
(A) Freezes (B) Evaporates
(C) Boils (D) Does not undergo any change
22. When ice is converted into water :-
(A) Heat is absorbed (B) Heat is released
(C) Temperature increases (D) Temperature decreases