The materials present in natural environment and useful to living organisms are called natural resources.
A resource satisfies human wants. Water, air, sunshine, land, soil, forests, wildlife, fishes, minerals and power resources all are useful
to man. All basic needs of food,
shelter and clothing are supplied by natural resources on earth. Natural resource includes total natural environment,
that is the entire surface layer of earth, because all parts of earth's surface are of some use to man in they contribute to the production
of necessities and comforts of mankind.
The word resource is use for "means of supplying a material generally held in reserve".
Substances used by man in bulk for survival are called resources and since they are found in nature, they are called natural resources.
The resources available on earth include land [Lithosphere], water [Hydrosphere] and Air [Atmosphere].
Inexhaustible Exhaustible
1. These resources have no chance 1. These resources have every chance of
of getting exhausted. getting exhausted.
2. These resources are unlimited 2. These resources are limited, e.g. coal,
e.g. wind energy, solar energy, petroleum, forests etc.
hydropower, tidal energy etc.
Renewable resources Non-renewable resources
1. Exhaustible resources which can be 1. Exhaustible resources which cannot be
regenerated or recycled within regenerated or recycled in reasonable time.
reasonable time.
2. Can be made to last indefinitely if used 2. Will get exhausted whether or not used
judiciously. judiciously.
3. Availability can be enhanced by 3. Availability can be enhanced by increased
increasing their capability of regeneration extraction but it will cause early depletion
Examples : Ground water, Wildlife, Examples : Minerals, Fossil fuels like coal
Grasslands, Forests & Soil fertility and petroleum.
a Air is a mixture of many gases like nitrogen,
oxygen, carbon dioxide, water vapour and some
others present in the atmosphere.
a Air is an important inexhaustible natural resource.
a Nitrogen and oxygen are the major components of the air.
N2 – 78.9% O2 – 21% Other gases – 1%
Venus and Mars – CO2 ® 95–97% of the atmosphere. That's why no life on these planets.
O2 in Earth atmosphere – 0.03%
Small amount of water vapours, dust, salts, smoke is also found.
To show the possible directions in which hot and cold air move.
Take a candle. Fix it in a beaker and light it as in figure.
Take one incense stick. Light it and bring it to the mouth of beaker.
Note the result with following actions :
(i) Which way smoke flows, when incense stick is brought near
the margin of beaker's mouth ?
(ii) Tell the direction of smoke when incense stick is brought little
above the burning candle.
(iii) Which way smoke flows when incense stick is taken to other areas
Give the possible reasons.
The present day industrial growth has polluted air to a greater extent by releasing SO2, CO2, CO, oxides of nitrogen
, H2S fumes of acids, dust particles of unburnt carbon, lead asbestos and even cement. For example,
the burning of coal and oil to generate electric power, run factories and fuel automobile engines creates oxides of nitrogen
and sulphur that acidify the rain.
Air carries many undesirable substances or impurities which are not good for our health.
The chief constiuents of the impurities of air include (i) carbon dioxide, (ii) carbon monoxide, (iii) oxides of sulphur,
(iv) oxides of nitrogen, (v) fluoride compounds, (vi) metals (e.g. lead nickel, arsenic, cadmum, tin etc.) (vii) hydrocarbons (e.g., benzene),
(viii) particulate matter (dust, grit, fly ash) and
(ix) toxicants. All these impurities are called pollutants. They cause air pollution.
Definition : The presence of harmful gases and suspended particles in the air which have adverse effect on
human beings, animals and vegetation is called air pollution.
Air pollutants can cause respiratory problems, renal problems, high blood pressure, problems in nervous system, eye irritation etc.
in the human beings. Many injurious effects such as falling of leaves, reduced growth, degeneration of chlorophyll etc.
have been reported in plants. Lichens are found to be very sensitive to the levels of contaminants such as sulphur dioxide present in polluted air.
Literally acid rain means the presence of excessive acid in rain water : Acid rain is infact cocktail of mainly H2SO4 and HNO3.
H2SO4 is the major contributor (60–70%) to acid precipitation HNO3 ranks second (30–40%) and HCl third.
Causes of Air Pollution
(i) Increase in human population and rapid industrialization.
(ii) Burning of fossil fuels.
(iii) Oxides of nitrogen and sulphur inhalation adversely affect human health and also causing acid rains.
(iv) During cold weather water vapour get condensed on the suspended particle [Unburnt carbon particles and hydrocarbons]
resulting in smog formation.
Fossil fuels considered as non-renewable resources because it takes millions of the year for recycle.
Differential heating of earth surface [water & land] causes the wind.
Air is a bad conductor of heat, therefore atmosphere maintains the average temperature of the earth.
The atmosphere prevents sudden increase in temperature during day time and during night, it prevents the escape of heat into outer space.
The envelope of air that surrounds our planet earth is called atmosphere. Different layers of atmosphere are :-
(a) Troposphere (b) Stratosphere (c) Mesosphere (d) Thermosphere
Air is inexhaustible natural resource. It is a mixture of gases such as nitrogen, Oxygen and
Carbon dioxide. It also holds water vapours & dust particles. It is essential for life.
World Environment day - 5th June : It was established by UN General Assembly in 1972.
Q.1 How is our atmosphere different from the atmosphere on Venus and Mars ?
Ans. On the planets Venus and Mars carbon dioxide forms the major component constituting upto
95-97% of the atmosphere. No life is known to exist there. On the contrary, on the Earth,
air forms the blanket around the Earth having nitrogen (78.08%), oxygen (20.92%), carbon dioxide (0.03%), argon (0.93%) and
trace components (0.04%). It has life on it.
Q.2 What causes winds ?
Ans.The movement of air from one region to another creates winds. When the solar radiations fall on the Earth,
some are absorbed and majority of these are reflected back or reradiated by the land and water bodies.
These reflected or reradiated solar radiations heat up the atmosphere from below. As a result, convection currents are set up in the air.
But since land gets heated faster than the water, the air above the land gets heated faster than the air over water bodies.
During the day, the air above the land gets heated faster and starts risings, creating a region of low pressure below.
As a result, the air over the sea moves into this region of low pressure and forms the wind.
Give answer of following questions
1. What are the basic needs of life to exists ?
2. How is our atmosphere different from the atmospheres on Venus and mars ?
3. What is biosphere ?
4. What causes winds ?
5 How clouds are formed ?
6. Name any three human activities that causes air pollution.
7. What are the effects of air pollution on human health ?
8. Give the definition of Resources.
9. Give the definition of air pollution.
Fill in the blanks
1. Natural resources are air ........................... and ............................
2. Water covers about .......................... percent of the earth.
3. itrogen form ................ percent part of air where as oxygen form .................. percent part of air.
4. Carbon dioxide constitutes ........................... of the atmosphere of venous planet.
5. During day time air moves from .............. to ..........................
Water is a basic human need.
About 3/4 of the earth surface is occupied by water.
Most of the water on earth's surface (about 97.5%) is found in seas and oceans. It is strongly
alkaline.
The rest (2.5%) is fresh water.
Importance of water to the living organisms - No life can exists without water because of :-
(i) All cellular processes take place in a water medium.
(ii) Water is essential for the process of digestion.
(iii) Water helps in maintaining body temperature.
(iv) All the biochemical reactions that take place within our body and within the cells occur between the substances that are dissolved in water.
(v) Substances are also transported from one part of the body to the other in dissolved form. Hence
, organisms need to maintain the level of water within their bodies in order to stay alive.
(vi) Water is also required for cooking, cleaning, irrigation, in industries and generating electricity.
Terrestrial life-forms require fresh water because their bodies cannot tolerate or get rid of the high amounts of dissolved salts in saline water.
Therefore, water sources must be easily accessible for animals and plants to survive on land.
The addition of undesirable substances or removal of desirable substances in/from the water bodies are a change in the temperature of water,
which degrades the quality of water so that it either becomes health hazard or unfit for use is called water pollution.
(1) Physical water pollutants
These include heat and oil-spills. Specific industries and thermal / nuclear power plants use water for cooling
in various operations and later return this hot water to water bodies. This result in thermal pollution.
Another manner in which the temperature of the water in river can be affected is when water is released from dams.
The water inside the deep reservoir would be colder than the water at the surface which gets heated by the sun. High temperature of water
reduces its dissolved oxygen content.
(2) Chemical water pollutants
These include organic wastes e.g. sewage, detergents, fertilizers, pesticides (e.g. dieldrin, DDT, DDE, BHC, etc.), [polychlorinated biphenyls [PCBs],
inorganic chemicals (e.g. arsenic, cadmium, mercury, lead, phosphates, nitrates, fluorides etc.)] and radioactive wastes.
Common inorganic impurities in water are compounds of calcium and magnesium.
(3) Biological water pollutants
These include pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, fungi, helminths & nematodes etc.
POINT AND NON-POINT SOURCES OF WATER POLLUTION
(1) Point sources
These sources have a specific location for the discharge of water pollutants directly into water bodies.
Therefore, these sources are located near the water bodies i.e. factories, power plants, breweries,
underground coal mines and oil wells. It is always easy to treat the pollution coming out of point sources before their discharge into water bodies.
(2) Non-point sources
These pollution sources are scattered and do not have any specific location for discharging pollutants into particular water bodies.
Example of non-point sources are run-off from fields, lawns and gardens, road and streets, construction sites,
ogging areas etc. Unlike point sources, these sources are difficult to monitor and treat to remove the pollutants.
The term water pollution is used to cover the following effects in water :-
(i) Addition of undesirable substances to water bodies.
Like fertilizers and pesticides used in agriculture or poisonous substances
(ii) Removal of desirable substances from water bodies. i.e. dissolved oxygen.
(iii) hange in temperature.
Eutrophication :- Eutrophication is the process in which dissolved oxygen in water is reduced due to excessive growth of algae as
a result of extra loading of nutrients in the water body. In fact, presence of sewage and fertilizers (nitrates and phosphates) in
polluted water provide a lot of nutrients to the algae (phytoplankton) present in water body.
As a result, excessive growth of algae occurs which is termed algal bloom. The algae subsequently die and aerobic decomposers become active.
They consume rapidly the dissolved oxygen of the water during decomposition of the dead algae. In the absence of dissolved oxygen,
all the aquatic life (including fishes) in the water body dies. Thus, eutrophication deprives us of one of our significant sources of food.
Biomagnification (bioaccumulation) :- Pesticides such as DDT, DDE, dieldrin, etc. are harmful chemicals that are regularly
being used in agriculture to protect crops from the pests (fungi, insects, etc.). Also heavy metals (e.g. mercury, cadmium, tin, lead, arsenic, etc.)
are regularly poured from industries into the water bodies. These chemicals are non-biodegradable, i.e.
unlike the organic sewage wastes they are not broken down by the activity of microorganism. These pesticides / heavy metals,
therefore, enter the soil or washed out by run off water to surface water bodies such as lakes, streams, rivers.
From soil or water these pesticides / heavy metals then enter the food chain via the producers. At each trophic level, their concentration goes on increasing.
This phenomenon of increase in concentration of harmful non-biodegradable chemical substances in the body of living organisms at
each trophic level of the food chain is called bioaccumulation, biological accumulation or biomagnification.
This makes it more likely that predators such as fish-eating birds such as kingfishers become poisoned.
For example, biomagnification of mercury in the fishes through a food chain results in Minimata disease in fish-eating
human populations of the regions.
SOIL
Definition :- Soil is a portion of earth's a surface consisting of disintegrated rock and decaying organic material. It provides
the support for many plants and animals.
Thickness of soil on the earth's surface ranges from a few millimeters to 3–4 meters.
Terrestrial plants depends for their nutrients, water supply and anchorage upon the soil.
Even for the aquatic plants, the solid is important as chief storage of all the nutrients which are made available to the water medium.
Our planet earth has three distinct regions innermost core region (about 2200 miles in thickness),
middle mantle region (about 1800 miles in thickness) and the outermost crust region (about 20–25 miles in thickness)
.The outermost crust region has huge rocks containing variety of bound minerals, some of which become available to us.
About one-fifth of the surface of the earth is exposed solid and distinct from oceans, lakes etc. It is called the land.
The top surface layer of this exposed, solid part of crust capable of supporting plant growth is called soil.
Over millions of years of long periods of time, the rocks at or near the surface of the earth are broken down by various physical,
chemical and some biological processes to form fine soil particles. Soil is a dynamic layer in which many complex physical,
chemical and biological activities are going on constantly. It is and important resource that decides the diversity of life in an area.
The soil is a complex mixture. It consists of five components :
(i) Mineral matter = 45% (ii) Organic matter = 5%
(iii) Water = 25% (iv) Air = 25%
(v) Living organisms.
All these components are essential for proper plant growth. Their percentage is given figure.
Soil profile :
Soil profile shows four distinct layers, called horizons. Horizon A is the topsoil. It is darker and of a looser texture than the
underlying horizon B.
Plant and animal matter collects at the surface of this horizon, forming the litter. Below the
litter is the humus, i.e., organic matter undergoing decay
by microbial action. The rest of horizon is rich in organic and mineral contents.
The horizon B has soil particles smaller and usually more compacted than in the horizon C.
Minerals brought by rain water from the upper horizon accumulate in this horizon.
The horizon C consists of the weathered material derived from the intact parent rock. The parent rock forms the horizon D.
Humus is partially decayed organic matter. It makes the soil porous, there by increasing its air and water holding capacity.
Humus is rich in nutrients that promote plant growth. Being black, it absorbs heat to warm up the soil.
Soil particles differ in their size, look and texture. Mainly four types of soil particles are commonly found in top soil. These are :
(i) Gravels :- These are large particles having size of greater than 2 mm in diameter. These can be easily picked up by hands.
(ii) Sand particles :- These are still smaller in size ranging between 0.005 mm to 2 mm. These are rough to touch and can be seen with naked eye.
(iii) Silt particles :- These are still smaller in size ranging between 0.005 mm to 0.05 mm in diameter.
(iv)Clay particles :- These are the smallest soil particles having size less than 0.005 mm.
Depending upon the presence of relative amounts of soil particles, soils are classified into following three types:
1. Sandy soil :- It contains very large proportion of sand particles and very small quantity of silt and clay.
Since sand particles are relatively larger in size, this soil can not hold much water. It is found in deserts and is unfit for plant growth.
2. Clayey soil :- It contains large proportion of clay particles (40% or more) and small amounts of humus and silt. Clayey soil,
being compact, can hold water. However, it is poorly aerated as it can not trap air. It is also not suitable for plant growth.
3. Loamy soil :- Loamy soil contains relatively larger quantities of clay, silt, sand particles and humus.
In fact, it contains about one part clay, two parts silt and two parts sand.
Therefore, it is porous has very good water holding capacity and also allows aeration of roots.
MAJOR TYPES OF SOILS IN INDIA
The soil is classified on the basis of its composition and nature. The major types of soils found in our country and their
composition are presented in table.
The contamination of soil (or land) with solid waste, chemicals (through industrial wastes or acid rain),
fertilizers and pesticides, reducing its fertility is called soil pollution (or land pollution).
Soil pollution : Soil pollution can be defined as decrease in soil fertility because of addition of some foreign elements.
Soil is polluted with dumping of solid wastes generated in house hold and manufacturing units. Domestic wastes include kitchen garbage,
broken bottles, cloth rags, ash, etc. Industrial wastes include fly ash, metal scraps, dyes, plastics, etc.
Agricultural chemical and fertilizers are also the cause of land pollution. The dumping of human excreta and waste
from cow-sheds and slaughter houses befouls the land. Most important causative pollutant of soil is plastics.
The main sources of soil pollution include :
1. Solid wastes
2. Chemical (directly through industrial wastes or indirectly through acid rain)
3. Excess of fertilizers and pesticides
1. Solid wastes :- These are considered the main source of soil pollution. Solid waste generally comes
from residences, cattle sheds, industries, agricultural fields, and many other places. It includes peelings
of fruits and vegetables, cow dung, human excreta, ash, paper, glass, plastics, leather and rubber articles, brick
, sand worn out clothes, and metal objects. These heaps of solid waste make the surroundings dirty, and pollute the soil.
2. Chemicals :- Industrial wastes are generally dumped in vacant sites along the roads, railway tracks or elsewhere.
These industrial wastes contain a lot of chemicals that pollute the soil.
Chemicals discharged into the air in the form of fumes such as compounds of sulphur and lead,
as well as gases (e.g., SO2 and NOX) eventually come down and settle as dry deposition or as acid rain on the soil and pollute it.
3 Excess of fertilizers and pesticides :- Fertilizers are used in the agricultural fields to increase the crop production.
Also, different kinds of chemicals (pesticides) are sprayed on the crops to kill the pests, weeds, etc.
All these chemicals, when used in excess, get mixed with soil and pollute it. From the soil, many non-biodegradable chemicals (e.g. DDT) even enter the food chains and biomagnify.
1. The industrial pollutants increase the toxicity levels of the soil.
2. Soil pollution due to domestic sewage may cause diseases like giardiasis, tetanus, etc. in human beings.
3. Land pollution may also cause several plant diseases.
4. Weedicides act as metabolic inhibitors or reduce the plant yield.
5. Mine dust causes many types of deformities in animals and human beings. It also destroys the vegetation of that area.
6. Excess of fluorides in land cause fluorosis.
Soil is a complex mixture of non-living materials and living organisms. It provides anchorage (firm support) to plants,
and is also a source of nutrients and water to the plants. Majority of the plants, thus, grow in the soil.
The top layer of soil (commonly called top soil) is very fertile. It is often carried away by environmental agencies i.e., strong winds and fast flowing water.
CAZRI:: is actively engaged in research to suggest measures for controlling wind erosion.
The removal and transportation of top layer of soil from its original position to another place with the help of certain agents such as strong winds
and fast running rain water, is called soil erosion.
Soil erosion normally occurs in bare areas i.e. areas without plant cover. It is so because the bare top-soil is loose and thus can easily be carried
way by strong winds or fast moving water of heavy rains or rivers.
CAUSES OF SOIL EROSION
1. Strong winds
2. Heavy rains
3. Improper farming and suspended cultivation
4. Human actions
5. Dust storms
EFFECTS OF SOIL EROSION
1. Loss of fertility and desertification
2. Landslides in hilly areas
3. Flash floods
4. Famines
PREVENTION OF SOIL EROSION
1. Intensive cropping
2. Sowing grasses and planting xerophytes
3. Terrace farming
4. Proper drainage canals around the field
5. Making strong embankments along the river banks
To show the effect of vegetative cover on ground and soil erosion.
Now answer the following :
(i) How much soil is carried out of trays i.e. 'A' and 'B' ?
(a) When water is poured gently ?
Q.1 How is soil formr rocks into small, fine soil particles is called weathering.ed ?
Ans. Soil is a mixture of small particles of rocks and humus (i.e., organic matter obtained from decaying of living organisms or their wastes).
Temperature variations due to radiations of the sun, rain water, winds and living organisms influence the formation of soil from the rocks
involving two processes ; weathering and paedogenesis.
Breakdown of bigge It may occur due to physical, chemical or biological means. Under the influence of solar radiations, rocks heat up and expand.
At night, these rocks cool down and contract. Since all the parts of rocks do not expand and contract at the same rate,
cracks appear in the rocks and ultimately the large rocks breakdown into smaller pieces. Flow of water through or over the rocks make the cracks bigger.
Flowing / falling water also as erasing effect on the rocks. On freezing the water expands in rock crevices and break the rocks.
Similarly, strong winds continue to rub against hard rocks and erode them. Growth of lichens, mosses and other plants also influence the
formation of soil by eroding the rocks over which they are growing.
Paedogenesis involves the decomposition of organic materials by bacteria and fungi and humification and mineralization of decomposed
organic matter. Earthworms also play an important role in the soil formation.
Q.2 Why is the atmosphere essential for life ?
Ans. The multilayered gaseous envelope (or blanket) surrounding the planet Earth is called atmosphere. Atmosphere filters sunlight reaching the
Earth affect climate and is a reservoir of several elements which are essential for life. Oxygen is required by most living beings for respiration and for
burning (combustion) of materials. Air contains about 21% oxygen and its percentage in air is balanced by the process of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis occurs in chloroplasts of green plants and this metabolic activity requires CO2, water and sunlight but release oxygen gas.
Ozone umbrella of atmosphere does not allow penetration of ultraviolet light of solar radiations to reach the Earth
. These solar radiations otherwise affect organisms adversely (e.g., UV rays may cause skin cancer in human beings).
BIO-GEOCHEMICAL CLYCE
Both non-living (abiotic) and living (biotic) components of the biosphere constantly interact with each other to form a dynamic, but stable system.
The intersection include transfer of matter and energy between the different components of the biosphere.
As far as nutrients are concerned, all living organisms require eight elements as nutrients in relatively larger amounts.
These include carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulphur, phosphorus, potassium and calcium.
The living organisms get the nutrient elements from lithosphere (mainly soil), hydrosphere and atmosphere.
Bio-refers to living, geo-refers to the rocks, soil, air and water of the earth.
The cyclic flow of elements or compounds between non-living environment [Soil, rock, air, water] and living organisms
is known as 'bio-geochemical cycle.
Water, oxygen, carbon and nitrogen cycles are very important in maintaining the balance in our environment
(i) Water is a compound and include two vital elements
hydrogen and oxygen. It forms a very important component of the environment and survival of all living organisms depend on it.
(ii) Ocean is the biggest store house of water which on evaporation form clouds and which after condensation fall down as rain or snow.
(iii) After rain it passes through puddles, ponds and rivers and get collected again in the ocean.
The circulation of water in this manner is known as hydrologic cycle or water cycle.
This cycle is driven by solar power and also performed through living organisms such as
absorption and transpiration of water by plants and drinking by animals. The formation of soil, too depend on water.
(i) Nitrogen is an important chemical on the earth and present in all the living organisms in the form of protein, amino acids and nucleic acid.
(ii) In atmosphere it exists in molecular form (N2) and in form of some oxides [N2O, NO, NO2 , NO3– ].
Nitrogen is the most abundant component of air (78 percent). Atmospheric nitrogen directly cannot be used by living organisms.
(iii) During lightning nitrogen of atmosphere reacts with oxygen and ultimately form dilute nitric acid.
This acid comes down to earth with rainwater. Nitrates are absorbed by plants and utilized for making organic matter (proteins), etc.
(iv) When animals consume plant matter, they break down the plant's nitrogenous compounds and use them to form new animal
proteins and other cell components.
Nitrogen fixation [conversion of atmospheric nitrogen gas into N2-compounds]
(i) Rhizobium [in root nodules of leguminous plants]
(ii) Azotobacter [in soil]
(iii) Blue Green Algae
Ammonification [conversion of nitrogen containing proteins of dead plants and animals into ammonia]
(i) Putrefying bacteria
(ii) Fungi
Nitrification [conversion of ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates]
(i) Nitrosomonas bacteria - Convert NH3 into nitrites ()
(ii) Nitrobacter bacteria - Convert nitrites into nitrates ()
Denitrification [Conversion of nitrate salts into free nitrogen gas]
e.g. Pseudomonas.
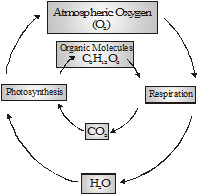
Importance of Oxygen :- Oxygen is also an essential component of biomolecules. It is needed for respiration also.
Main sources :- Oxygen is available in molecular form (O2) in the air, forming about 21% of it. Some oxygen is found dissolved in water.
Oxygen also occurs as a component of water and carbon dioxide.
Use and Release :- The oxygen of the atmosphere is in a state of dynamic equilibrium.
It is taken by animals and plants from the air or as dissolved in water for use in oxidative reactions (respiration).
It is returned to the environment, either in combination with carbon as carbon dioxide or with hydrogen as water.
The carbon dioxide and water are used by plants in photosynthesis, which liberates molecular oxygen into the environment
for reuse in respiration. Thus, the cycle is completed.
The concentrations of oxygen in the air and water are maintained by equal rates of its use in respiration and release in photosynthesis.
Oxygen is also released as a part of CO2 by decay of dead organic matter.
Some oxygen is added to the air as CO2, H2O, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides during burning of fuel (wood, coal, petroleum and natural gas).
Some oxides are formed by microbial oxidation. These oxides release O2 when reduced by chemical and biological processes.
Effect of Human Activity :- Oxygen was not present when the earth was formed.
It was added to the atmosphere later when photosynthesis started with the evolution of photoautotrophs.
Human activity has not affected the oxygen content of the atmosphere because it is replenished by photosynthesis.
Oxygen is essential element required for respiration. It forms about 21% of the air in the atmosphere.
The cyclic flow of carbon between non-living environment and living organisms of biosphere is called carbon cycle in nature.
In abiotic environment, carbon is present in the following forms :
as carbon dioxide in the air or atmosphere.
as dissolved carbon dioxide or carbonic acid and bicarbonates in water bodies or hydrosphere.
as fossil fuels, like coal, petroleum and natural gas, and
as carbonates and graphite in rocks.
In biotic environment, Carbon forms the backbone of complex organic molecules like carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes, hormones etc.
The availability of carbon in the environment is, therefore, a crucial factor in the maintenance of living beings. It is essential that the
carbon 'locked up' within the organisms be returned to the environment for reuse.
Then main reservoir of carbon is the atmosphere.
Processes by which carbon dioxide of atmosphere is consumed :-
The plants use carbon dioxide as one of the raw materials for the process of photosynthesis and prepare carbohydrates.
When animals feed on the plant products, plant carbohydrates change into animal carbohydrates.
Some of the dead plants and animals get buried deep under the earth and change into fossil fuels (coal and petroleum) through slow chemical change.
Some of the dissolved carbon dioxide in oceans and other water bodies gets converted into limestone and other carbonate rocks.
Processes by which carbon is released from biotic world to abiotic world
Both plants and animals release carbon dioxide in the atmosphere as a product of respiration.
When plants and animals die, their bodies are decomposed by decomposers and carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere.
Combustion of fossil fuels like coal, petroleum gas, kerosene, petrol, diesel, etc gives carbon dioxide which goes into atmosphere.
Weathering of carbonate rocks by the action of micro organisms or when acid rain falls on these rocks liberates carbon dioxide.
Volcanic eruptions and hot springs also release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Thus, there is continuous exchange of carbon dioxide between living and non-living world.
Greenhouse effect :
In greenhouse, the heat is trapped by glass, hence the temperature in a glass enclosure is much higher than the surroundings.
Due to higher temperature in glasshouses, the tropical plants can be kept warm and protected from cold temperature during winter.
Some gases, like carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxides also prevent the escape of heat from the earth. With industrialization,
widespread deforestation and burning of more fossil fuels, the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air is increasing with an alarming
rate. Carbon dioxide gas traps heat within the atmosphere preventing its escape into the space.
Therefore increased CO2 concentration in air is the major cause of rise in atmospheric temperature. It causes melting of polar ice. It
also causes submerging of coastal land under water.
CFC is the major compound responsible for ozone depletion.
Green house effect and global warming :-
Earth temperature is maintained by re-radiated infrared (heat) radiation by greenhouse gases which prevent heat from escaping to outer space.
This is comparable to glass panels of a greenhouse which keep CO2 concentration higher and so higher temperature inside i.e. greenhouse.
This effect is called greenhouse effect.
Green house gases - CO2, CH4, NOx. They prevent the escape of heat from the earth.
Increased CO2 concentration in air is the major cause of rise in atmospheric temperature. It causes melting of polar ice. It also causes
submerging of coastal land under water.
Due to higher temperature in glasshouses, the tropical plants can be kept warm and protected from cold temperature during winter.
Ozone Gas :
Ozone is poisonous in nature.
1. Ozone is formed in atmosphere by the action of ultraviolet radiation on oxygen gas.
2. The high energy ultraviolet radiation (UV radiation) coming from the sun splits oxygen gas into free oxygen atoms
O2 2O (oxygen atom) [O]
3. The free oxygen atoms are highly reactive. One oxygen atom reacts with an oxygen molecule to form an ozone molecule.
O2 + O ----> O3 (Ozone molecule)
4. Ozone Layer : It is a layer of the earth's atmosphere ozone is concentrated.
The Ozone layer is very important for the existence of life on earth because it absorbs most of
the harmful ultraviolet radiation coming from the sun and prevents them from reaching the earth.
The thining of ozone layer is commonly called ozone depletion. Ozone is being depleted by air pollutants.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are air pollutants that are mainly responsible for the depletion of ozone layer in the stratosphere.
Besides, methane (CH4) and oxides of nitrogen (NOx) also cause destruction of ozone.
Ozone hole : Decline in thickness of ozone layer a restricted area is called ozone hole.
Ozone hole was first discovered over Antarctica in 1985. Amount of atmospheric ozone is measure by Dobson spectrometer and is expressed in Dobson units (DU).
Q.1 How is our atmosphere different from the atmosphere on Venus and Mars?
Ans. Unlike Earth, which has 0.03% carbondioxide, on planet Venus and Mars, carbon dioxide (CO2)
forms the major component constituting upto 95-975 of the atmosphere. Nitrogen and oxygen are absent on
Mars and Venus but Earth has 78.08% nitrogen and 20.94% oxygen. They also do not have atmospheric water vapour. No life
is knows to exist on Venus and Mars unlike earth.
Q.2 How does atmosphere act as a blanket?
Ans. Atmosphere acts as a blanket which provide protection to the organisms.
It keeps the average temperature of the earth steady during the day and even throughout the year.
The ozone layer of the atmosphere absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiations from the sun thereby protecting humans
and other organisms from their harmful effects.
Q.3 What causes winds?
Ans. Winds are created due to movement of air from one place to the other
. Due to solar radiations the air gets heated up and rises upwards. This creates an area of low pressure
. Now cooler air from adjacent high pressure area passes into this area. This creates breezes and wind.
Various factors affect the wind movements like unevenheating ofland and water, rotation of earth and mountainbarriers.
Q.4 How are clouds formed?
Ans. Clouds are wet air masses that float in the direction of prevailing wind. When the solar radiations heat the water in water bodies,
a large amount of water gets evaporated into the air. The air which carry water vapour also gets heated.
The hot air rises up and carry water vapour along with it. The temperature in the atmosphere is low which causes water vapour to
condense into the water droplets.
These droplets condense around dust particles. Slowly the water droplets grow bigger and bigger. This huge collection of water
droplets is called cloud.
Q.5 List any three human activities that you think would lead to air pollution.
Ans (i) Burning of fossil fuels in automobiles
(ii) Burning of fossil fuels in thermal power plants
(iii) Smoke produced from industries
Q.6 Why do organisms need water?
Ans. Organisms need water because it is major component (60-90%) of living matter.
It plays a vital role in the metabolic reactions taking place within their body.
Water acts as universal solvent and provides a medium for the chemical reactions to occur in body.
Various substances in dissolved form are also transported from one part of body to other.
Water protects the body from sudden changes of temperature. It helps in separation and elimination of metabolic wastes.
Therefore to survive, it is necessary for the organisms to maintain the level of water within their bodies.
Q.7 What is the major source of fresh waterin the city/town/village where you live?
Ans. Major source of fresh water in the city/town/village where we live is underground water.
Q.8 Do you know any activity which may be polluting this underground water source?
Ans. Sewage and industrial tanks are polluting this underground water source.
Q.9 How is soil formed?
Ans. Soil is formed due to weathering of huge rocks by temperature variations, rainwater,
winds and living organisms. Other processes which are involved in the formation of soil a
re decomposition of organic matter and subsequent humification and mineralisation.
Q.10 What are the methods of preventingor reducing soil erosion?
Ans. Soil erosion can be prevented by following methods
(i) Intensive cropping
(ii) Growing grasses and xerophytes
(iii) Terrace farming
(iv) Proper drainage canal around the fields
(v) Making strongembankments along river banks.
Q.11 What is soil erosion?
Ans. The removal of top fertile layer of soil from its original position to another place due to strong winds and running water is called soil erosion.
Q.12 What are differentstates inwhich water is found during the water cycle?
Ans. In water cycle, water is found in liquid (as rain) and vapour form (found in air and ultimately form clouds) and sometimes in the form of snow at mountains.
Q.13 N arne two biologically importantcompounds that contain both oxygen (02) and nitrogen (N2)'
Ans. Nucleic acid (DNA and RNA) and proteins are two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
Q.14 List any three human activities which couldlead to an increase in CO2 content of air.
Ans. (i) Burning of fossil fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) in homes, industries, power plants, etc.
(ii) Deforestation leads to reduced utilisation of CO2 in photosynthesis
(iii) Burning associated with agricultural practices
Q.15 What is the greenhouse effect? Ans. Greenhouse effect is to keep an area warm by allowing
solar radiations to pass into but preventing long wave radiations to escape due to presence of relatively active gases and glass panels.
Carbon dioxide, methane and chlorofluorocarbons present in our atmosphere prevent the escape of heat from the earth.
These are called greenhouse gases. An increase in the percentage of such gases in the atmosphere would cause the average temperature to
increase worldwide and this is called global warming.
Q.16 What are the two forms ofoxygen found inatmosphere?
Ans. Molecular oxygen (O2) and ozone (O3)
Q.17 Howare living organisms dependent on the soil? Are organisms that live inwater totally independent ofsoil as a resource?
Ans. Soil is a complex mixture, comprising of minerals (45%), organic matter (5%), water (25%), air (25%) and livingorganisms
.Itis an important resource which is responsible for the diversity of life in an area. Plants are dependent on soil for obtaining nutrients
and water and all terrestrial organisms depend upon plants for their food and its contained energy. So, all living terrestrial organisms depend upon soil
. Organisms living in water are not totally independent of soil as a resource because some aquatic decomposers present at bottom of water
, decompose dead bodies of plants and animals. The released nutrients from the organic matter get dissolved inwater and are then takenby plants and animals.
Q.18 You have seen weather reports on television and in newspapers. How do you think we are able to predict the weather?
Ans. We see daily weather reports on television and newspapers. The information are actually recorded by meteorological laboratories
of different cities present in our country. Information such as direction and speed of wind, average daily minimum and
maximum temperature are recorded and then displayed on television or published in newspapers.
The meteorological information helps us to predict the weather and to act accordingly. For example,
a farmer can decide his next step in agriculture according to latest weather report and may bebenefitted.
Q.19 We know that many human activities lead to increasing levels of pollution of air,
water bodies and soil. Do you think that isolating these activities to specific and limited areas would help in reducing pollution?
Ans. Many human activities lead to increased level of pollution of air, water bodies and soil.
Isolating such activities to specific and limited areas will notreduce pollution in thatarea. The benefits of suchpractices are
(i) Joint pollution treahnent plants canbe introduced.
(ii) The residential and commercial areas will be comparatively free from pollution.
Q.20 Write a note onhow forests influence the quality of our air, soil andwater resources.
Ans. Forest influence the quali ty of our air, soil and water resources in following ways:
(i) Plants maintain the oxygenand carbon dioxide balance in the atmosphere.
(ii) Roots of plant hold the soiland do notallow its erosion byfast wind orfast moving water.
(iii) By preventing soil erosion, forests maintain the quality ofwater resources as well and control silting.
VERY SHORT SHORT TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Name the substances which are responsible for damaging ozone layer.
Q.2 What are different stages in which water is found during the water cycle?
Q.3 Where ozone hole was first discovered?
Q.4 What are the two forms of oxygen found in the atmosphere?
Q.5 What is the ultimate source of energy for organisms?
Q.6 Give definition of Bio-Geochemical cycle.
Q.7 Name a free-living bacterium which helps in nitrogen fixation.
Q.8 Name the main reservoir of gaseous carbon.
Q.9 Name any two Green house gases.
Q.10 What is green house effect?
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Mention few harmful effects which are caused due to depletion of ozone layer.
Q.2 Write a short note on water cycle.
Q.3 Write a short note on Green house effect.
Q.4 Write a short note on carbon cycle.
Q.5 Name the micro-organisms which are involved in :-
(a) Biological nitrogen fixation
(b) Nitrification
(c) Denitrification
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Draw a labelled diagram to show :
(a) Nitrogen cycle in nature.
(b) Carbon cycle in nature.
(c) Oxygen cycle in nature.
Q.2 Explain nitrogen cycle.
Q.3 Write an essay on ozone layer.
REASONING ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.1 Why ozone layer is important for us?
Q.2 "Increased concentration of carbon-dioxide in air is cause of Global warming" Why?
FILL IN THE BLANKS
Q.1 In some terrestrial ecosystems more than .......... percent of the moisture passes through plants.
Q.2 Water is a compound of two vital elements ...... and ..........
Q.3 Conversion of atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen compounds by living organisms is called ............
Q.4 The process of conversion of ammonia into nitrites and nitrates is called nitrification. It is carried out by the action of ............ and .........
Q.5 Denitrification is carried out by ............ bacteria.
Q.6 The plants use ............ as one of the raw materials for the process of photosynthesis and prepare carbohydrates.
Q.7 Both plants and animals release carbondioxide in the atmosphere by the process of ............
Q.8 Water forms ............ percent of the cell content.
Q.9 In nature, oxygen occurs in the gaseous form constituting ............ percent of the total atmosphere.
Q.10 Ozone layer is about ............ km thick. It absorbs harmful radiations come from the sun.
SUBJECTIVE QUESTION
1. 90 2. Hydrogen, Oxygen
3. Ammonification 4. Fungi & bacteria
5. Pseudomonas 6. Carbondioxide
7. Respiration 8. 60 – 90
9. 21 10. 5
Q.1 A pollutant is any substance, chemical or other factor that changes natural :
(A) geo-chemical cycle
(B) flora of a place
(C) balance of our environment
(D) wild life of a region
Q.2 The pollutant released from motor vehicles :
(A) CO2 (B) CO (C) NO2 (D) None
Q.3 Lichens do not like to grow in cities because of :-
(A) SO2 pollution
(B) Missing natural habitat
(C) Absence of right type of algae and fungi
(D) Lack of moisture
Q.4 Carbon dioxide in atmospheric air amounts to be about :
(A) 0.003% (B) 33% (C) 0.03 % (D) 0.3 %
Q.5 Greenhouse effect is related to :
(A) Green trees on house
(B) Global warming
(C) Grasslands
(D) Greenery in country
Q.6 The greenhouse effect is due to :
(A) impermeability of long wavelength radiations through CO2 of the atmosphere
(B) penetrability of low wavelength raditions through O3 layer
(C) penetrability of low wavelength radiations through CO2
(D) impermeability of long wavelength radiations through O3 layer.
Q.7 Which of the following gases contributes maximum to the 'Greenhouse effect' on earth ?
(A) Carbon dioxide
(B) Methane
(C) Chlorofluorocarbon
(D) Freon
Q.8 Which of the following is not a "Greenhouse gas" ?
(A) SO2 (B) CO2 (C) N2O (D) CH4
Q.9 What are the chief pollutants of the atmosphere which are most likely to deplete the ozone layer ?
(A) Sulphur dioxide (B) Carbon dioxide
(C) Carbon monoxide (D) Nitrogen oxides and chloro fluorocarbons
Q.10 Formation of ozone hole is maximum over :
(A) India (B) Antarctica (C) Europe (D) Africa
Q.11 Which of the following is the main factor of water pollution ?
(A) Pesticides (B) Ammonia
(C) Detergents (D) Industrial wastes
Q.12 Often in water bodies subjected to sewage pollution, fishes die because of the :
(A) pathogens released by sewage
(B) reduction of dissolved oxygen caused by microbial activity
(C) clogging of their gills by solid substances (D) foul smell
Q.13 Spraying of DDT on crops produces pollution of :
(A) Air only
(B) Air and soil only
(C) Air and water only
(D) Air, soil and water
Q.14 Soil pollution is chiefly caused due to indiscriminate use of :
(A) Insecticides (B) Nutrients (C) Wheat crops (D) none of these
Q.15 Which disease is not water borne ?
(A) Cholera (B) Typhoid (C) Dysentery (D) Asthma
Q.16 The supersonic jets cause pollution by thinning of :
(A) CO2 layer (B) SO2 layer (C) O2 layer (D) O3
Q.17 Agricultural chemicals denote :
(A) Pesticides
(B) Fertilizer
(C) Growth regulators
(D) All of these
Q.18 A logical sequence of carbon cycle is :-
(A) Producer - Consumer - Decomposer
(B) Decomposer - Producer - Decomposer
(C) Consumer - Producer - Consumer (D) Producer - Decomposer - Consumer
Q.19 Biogeochemical cycles are also known as :-
(A) Sedimentary Cycles (B) Gaseous Cycles
(C) Material Cycling (D) Cycles of water
Q.20 Which of the following is a free living nitrogen fixing bacterium present in soil ?
(A) Azotobacter (B) Nitrosomonas
(C) Rhizobium (D) Pseudomonas
Q.21 CO2 and O2 balance is atmosphere is due to :-
(A) Photosynthesis
(B) Respiration
(C) Leaf anatomy
(D) Photorespiration
Q.22 Role of bacteria in carbon cycle is ....................
(A) Photosynthesis
(B) Chemosynthesis
(C) Breack down of organic compounds
(D) Assimilation of nitrogen compounds
Q.23 Under anaerobic conditions, denitrifying bacterium Pseudomonas changes .............
(A) Nitrate to molecular nitrogen
(B) Nitrate to ammonia
(C) Nitrate to nitrite (D) Nitrite to nitrate
Q.24 If the plants of world die, all the animals will also die due to the shortage of ...........
(A) Cold (B) Food (C) Oxygen (D) Timber
Q.25 In a natural ecosystem decomposers include:
(A) Bacteria & Fungi (B) Parasitic algae
(C) Macroscopic animals (D) All the above
Q.26 Suppose all consumers of the earth are dead. Then
(A) Producers will not prepare food
(B) Decomposers will die
(C) There will be no sunlight available by photosynthesis.
(D) None of these
Q.27 Why does a goat not eat a tiger?
(A) Because the tiger is more powerful than the goat
(B) Because the goat is not adapted to eat flesh.
(C) Because every goat is taught by its parents to keep away from tigers.
(D) All of these
Q.28 The correct food chain out of the following is
(A) Tiger ® Cat ® Lion ® Goat
(B) Grass ® Insects ® Lizard ® Snake
(C) Grass ® Rabbit ® Lion ® Man
(D) Sun ® Plant ® Insect ® Man
Q.29 Following is an incomplete food chain:
Grass ® ? ® Jackal ® tiger. The choice for the correct answer will be
(A) Lion (B) Deer (C) Rat (D) Cockroach
Q.30 The loss of energy in successive steps of energy transfer is aproximately
(A) 20% (B) 25% (C) 10% (D) 2%
Q.31 Environmental planning will
(A) reduce spoilage by bacteria
(B) cause more wildlife loss
(C) reduce air and water pollution
(D) None of these
Q.32 An example of aerosol spray is
(A) Dichloro difluoro methane
(B) Tetra chloromethane
(C) Trichloro methane
(D) Di-iododibromo methane.
Q.33 The full form of DDT is
(A) Dibromo Dichloro Toluene
(B) Dichloro Diphenyl Trichloroethane
(C) Difluorodichloro Terbutaline
(D) None of these
Q.34 Lichens are found on hillsides under conditions where neither the alga nor the fungus can live alone.
This shows that the relationship between the alga and the fungus is one of
(A) Parasitism (B) Saprophytism
(C) Mutualism (D) Commensalism
Q.35 Organic matter decayed to a relatively stable, amorphous state;
formed when soil microorganisms decompose animal and plant material into elements usable by plants
(A) manure (B) peat (C) humus (D) green manure
Q.36 The species, which are in danger of extinction, are referred to as
(A) endangered species
(B) vulnerable species
(C) threatened species
(D) rare species
Q.37 Minamata disease is a pollution-related disease, which results from
(A) release of human organic waste into drinking water
(B) accumulation of arsenic into atmosphere
(C) release of industrial waste mercury into fishing water
(D) oil spills into sea
Q.38 Eutrophication leads to death of fish due to
(A) increased O2 content
(B) increased algae content
(C) decreased algae content
(D) decreased O2 content
Q.39 The two great industrial tragedies namely, MIC and Chernobyl tragedies respectively occurred where and at which time?
(A) Bhopal 1984, Ukraine 1990
(B) Bhopal 1984, Ukraine 1988
(C) Bhopal 1984, Ukraine 1986
(D) Bhopal 1986, Russia 1988
Q.40 NO2 vapours are harmful to the body because
(A) They produce allergy
(B) They produce respiratory problems
(C) They create blood clots
(D) None of these
Q.41 Why is smoking injurious to health?
(A) It can casue pregnanacy problems in smoking mothers.
(B) It can cause large scale air pollution
(C) It can be responsible for a heart attack
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Q.42 'Decibel' is a unit to measure
(A) Sound depth
(B) Sound intensity
(C) Sound wavelength
(D) All of these
Q.43 An effective method to stop air pollution is
(A) Degradation of wastes causing air pollution
(B) Keeping the river water clean
(C) Keeping factories away from big cities.
(D) None of these
Q.44 The Ganga purification project is controlled by
(A) Central Water Commission
(B) Union Public Service Commission
(C) Central Pollution Control Board
(D) Central Intelligence Agency.
Q.45 Sunder Lal Bahuguna is associated with the
(A) Salt movement
(B) Green revolution
(C) Greenhouse effect
(D) Chipko movement.
1. C 2. B 3. A 4. C
5. B 6. A 7. A 8. A
9. D 10. B 11. D 12. B
13. D 14. D 15. D 16. D
17. D 18. A 19. C 20. A
21. A 22. C 23. A 24. B
25. A 26. B 27. B 28. B
29. B 30. C 31. C 32. A
33. B 34. C 35. C 36. A
37. C 38. D 39. C 40. B
41. D 42. B 43. C 44. C
45. D
1. Suppose all consumers of the earth are dead. Then
(A) Producers will not prepare food
(B) Decomposers will die
(C) There will be no sunlight available by photosynthesis.
(D) None of these
2. Why does a goat not eat a tiger?
(A) Because the tiger is more powerful than the goat
(B) Because the goat is not adapted to eat flesh.
(C) Because every goat is taught by its parents to keep away from tigers.
(D) All of these
3. The correct food chain out of the following is
(A) Tiger ® Cat ® Lion ® Goat (B) Grass ® Insects ® Lizard ® Snake
(C) Grass ® Rabbit ® Lion ® Man (D) Sun ® Plant ® Insect ® Man
4. Following is an incomplete food chain:
Grass ® ? ® Jackal ® tiger. The choice for the correct answer will be
(A) Lion (B) Deer (C) Rat (D) Cockroach
5. The loss of energy in successive steps of energy transfer is aproximately
(A) 20% (B) 25% (C) 10% (D) 2%
6. Environmental planning will
(A) reduce spoilage by bacteria (B) cause more wildlife loss
(C) reduce air and water pollution (D) None of these
7. An example of aerosol spray is
(A) Dichloro difluoro methane (B) Tetra chloromethane
(C) Trichloro methane (D) Di-iododibromo methane.
8. The full form of DDT is
(A) Dibromo Dichloro Toluene (B) Dichloro Diphenyl Trichloroethane
(C) Difluorodichloro Terbutaline (D) None of these
9. Lichens are found on hillsides under conditions where neither the alga nor the fungus can live alone. This shows that the relationship
between the alga and the fungus is one of
(A) Parasitism (B) Saprophytism (C) Mutualism (D) Commensalism
10. Organic matter decayed to a relatively stable, amorphous state; formed when soil microorganisms decompose animal and plant material
into elements usable by plants
(A) manure (B) peat (C) humus (D) green manure
11. The species, which are in danger of extinction, are referred to as
(A) endangered species (B) vulnerable species (C) threatened species (D) rare species
12. Minamata disease is a pollution-related disease, which results from
(A) release of human organic waste into drinking water
(B) accumulation of arsenic into atmosphere
(C) release of industrial waste mercury into fishing water
(D) oil spills into sea
13. Eutrophication leads to death of fish due to
(A) increased O2 content
(B) increased algae content
(C) decreased algae content
(D) decreased O2 content
14. The two great industrial tragedies namely, MIC and Chernobyl tragedies respectively occurred where and at which time?
(A) Bhopal 1984, Ukraine 1990
(B) Bhopal 1984, Ukraine 1988
(C) Bhopal 1984, Ukraine 1986
(D) Bhopal 1986, Russia 1988
15. NO2 vapours are harmful to the body because
(A) They produce allergy (B) They produce respiratory problems
(C) They create blood clots (D) None of these
16. Why is smoking injurious to health?
(A) It can casue pregnanacy problems in smoking mothers.
(B) It can cause large scale air pollution
(C) It can be responsible for a heart attack
(D) Both (A) and (B)
17. 'Decibel' is a unit to measure
(A) Sound depth (B) Sound intensity (C) Sound wavelength (D) All of these
18. An effective method to stop air pollution is
(A) Degradation of wastes causing air pollution (B) Keeping the river water clean
(C) Keeping factories away from big cities. (D) None of these
19. The Ganga purification project is controlled by
(A) Central Water Commission (B) Union Public Service Commission
(C) Central Pollution Control Board (D) Central Intelligence Agency.
20. Sunder Lal Bahuguna is associated with the
(A) Salt movement (B) Green revolution (C) Greenhouse effect (D) Chipko movement.
1. B 2. B 3. B 4. B
5. C 6. C 7. A 8. B
9. C 10. C 11. A 12. C
13. D 14. C 15. B 16. D
17. B 18. C 19. C 20. D