POINTS TO BE REMEMBER
Deforestation : The loss or continual degradation of forest habitat due to natural or human activities.
Afforestation : Planting of trees on a large scale to regenerate forest.
Desertification : The process of conversion of fertile land into deserts due to the removal of top layer of soil.
Ecosystem : The basic unit of ecology which consists of the biotic and abiotic components.
Reforestation : It is the restocking of the destroyed forests by planting new trees.
Fauna : The community of animals in a specific region or habitat.
Flora : The plant life of particular area.
Endemic species : The species that are exclusively found in any geographical unit like a state, zone or a country or a habitat type are referred as endemic species.
Sanctuaries : The protected area which is reserved for the conservation of animals only and human activities upto a certain extent are allowed in these areas.
National Park : The large and diverse reserves to protect whole sets of ecosystem including flora, fauna, landscape and historical objects of an area are termed as national park.
Biosphere Reserve : A biosphere reserve is a unique concept which includes one or more protected areas and surrounding lands that are managed to combine both conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
INTRODUCTION
We have read in earliar classes that humans use a number of natural resources for their survival. However, as human population has been increasing at a high rate, the natural resources are also being used in greater quantity than ever before. With recent advances in science and technology, people now have a higher standard of living. As a result, there is a far great demand for the natural resources.
It is for this reason that the natural resources must be 'conserved' so that there will be enough resources available for the future generations.
It must be clearly understood that conservation does not mean that we have to stop the use of these resources completely. It only means that we have to use the resources wisely and judiciously. conservation is the wise and judicious use of resources. The overuse or wastage of resources would lead to imbalanaces among the various components of nature.
Aims of conservation
* To preserve the quality of environment, i.e., maintain a pollution-free environment.
* To ensure a continuous yield of useful plants, animals and materials for generations to come.
Importance of Forests
DEFORESTATION
The loss or continual degradation of forest habitat due to natural or human activities is called deforestation.
OR
Large scale cutting of trees is called deforestation
Causes of Deforestation
Trees are cut in the forest on a large scale to clear the land for some useful purposes listed below.
Natural Causes of deforestation
(i) Forest fire (ii) Drought
Effects of Deforestation
(i) Effect on Soil : Roots of trees help in binding the soil particles together.
When this protective cover of vegetation is destroyed, soil is left loose, and hence, more soil is lost due to erosion by wind and moving water.
Loss of topsoil, which is rich in humus and nutrients, results in reduction in fertility of soil.
(ii) Effect on Wildlife : Forests which are the natural habitat of many species of plants, animals, and birds.
(iii) Effects on recycling of materials : Plants intake CO2 and give out O2 during photosynthesis. This O2 is necessary for human beings to survive.
An increase in the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere causes greeen house effect or global warming.
O2 level in atmosphere become low due to deforestation.
Trees draw ground water up through their roots and release water vapour into the atmosphere by transpiration. If a large number of trees are cut down, transpiration rate will be greatly reduced. this in turn will effect the water cycle.
(iv) Climatic changes : Increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere may lead to an increase in the temperature of the earth as carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, i.e., it allows the sun’s infrared radiations to enter the earth but stops them from going out of the atmosphere. Hence, it results in an increase in temperature which makes the atmosphere drier.
This can lead to reduced rainfall. This could cause droughts.
(v) Landslides and floods : Vegetation helps to absorb the rainwater that falls on the earth.
Excessive falling of trees would mean that a greater proportion of the rain may reach the ground, which could give rise to floods. Loss of vegetation may lead to reduction in binding capacity of soil particles during rainy season which in turn lead to landslides in mountainous regions.
(vi) Desertification : Deforestation is a major cause which leads to the change in soil properties.
Physical properties of the soil get affected by plantation and vegetation. Due to soil erosion the top fertile layer of soil is removed. Gradually the fertile land gets converted into deserts. It is called desertification.
STEPS FOR CONSERVATION OF FORESTS
CONSERVATION OF FORESTS
The maintenance and upkeep of forest is called forest conservation. The following steps should be undertaken to conserve them.
1. Massive afforestation work should be undertaken to cover large areas of land with appropriate trees.
2. Felling of trees in the forest should be banned.
3. Every piece of barren land should be planted with trees.
4. Weeds, damaged trees, crowded trees, diseased trees, etc. should be removed.
5. Forest fire must be prevented.
6. Forest nurseries should be established on a large scale.
THE CHIPKO MOVEMENT
(A) Give answer of following questions :
1. What is soil erosion ?
2. How deforestation affect increasing concentration of CO2 ?
3. How deforestation affect Land-slides and floods ?
4. How increased carbondioxide concentration is responsible for increase in temperature of earth ?
5. Define flora.
6. How building houses and factories affect deforestation ?
7. Mention the effect of overgrazing on biodiversity.
8. What is importance of forests ? Write a short note on it.
9. Mention main causes of deforestation.
10. Write consequences of deforestation.
(B) Fill in the blanks :
1. Restocking of the destroyed forests by planting new trees is called ...................
2. ...................act as saviour from various solar radiations.
3. Forest helps in maintaining oxygen and ................... level.
4. Loss of water in the form of water vapour through stomata of green leaves is called ...................
5. The animals found in a particular area called ...................
(C) Fill out the true and false statements from following :
1. The natural causes for the destruction of forests are draughts, floods, storms and forest fires.
2. About 40% of the wood used in the world every year goes into making paper.
3. The Thar desert in the north west of india is an example of nature made desert.
4. Deforestation is an important cause of increase in global temperature.
5. Forests are natural habitat of wild animals and plants.
Ans. 1. T 2. T 3. F 4. T 5. T
* Biodiversity or Biological Diversity
If you look around yourself, you may get to see several different kinds of plants and animals. A typical neighbourhood park may be home to a variety of flowers, each differing in size, shape, colour, and smell. The kind of trees found here could range from big trees such as the banyan tree to small bushes that may have been planted to border the pavement.
Biodiversity refers to existence of a wide range of different types of organisms in a given place at a given time.
Variety of life on earth and variability among living organisms.
OR
Variety of life forms and habitats found in a particular area.
* Uses of Biodiversity
1. Source of food and improved varieties : Biodiversity is used to modern agriculture in three ways as a source of
(a) New crops (b) Material for breeding improved varieties
(c) New biodegradable pesticides.
2. Drugs & Medicines : e.g. Morphine : Papaver somniferum [Analgesic], Quinine- Chincona ledgeriana [Treatment of malaria], Taxol- Taxus brevifolia [Anticancer drug].
3. Aesthetic and cultural benefits : e.g. Ocimum sanctum- Tulsi, Ficus religiosa- Pipal, Prosopis cineraria- Khejri.
4. Ecosystem services
Project Tiger : 'Project Tiger' is one of the successful operations for conserving wildlife in India. There were about 40,000 Bengal tigers in 1910. There was a sharp decline in their numbers to 1827 in 1972. The main reasons for the extinction of tigers are hunting, deforestation and taming of rivers for human needs. Realizing this decline, a project named 'Project Tiger' was initiated in 01 April 1973. The project was funded by the World Wide Fund for Nature.
The project focussed on protecting tiger habitats by creating sanctuaries and extending the existing ones. Under this project, there are 18 tiger reserves in India.
1. Jim Corbett National Park (Uttaranchal)
2. Periyar National Park (Kerala)
3. Ranthambore National Park (Rajasthan)
4. Kanha National Park (Madhya Pradesh)
5. Sariska National Park (Rajasthan)
6. Sunderban National Park (West Bengal)
Species : A group of population which are capable of interbreeding.
This means that the members of a species can reproduce fertile offspring only with the members of their own species and not with members of other species.
Endemic Species : Those species of plants and animals which are found exclusively in a particular area.
OR
Plant and animal species confined to specific geographic areas are called endemic species.
Sal, Wild mango, Bison, Indian giant squirrel and flying squirrel are endemic species in Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve.
Some Endemic Species of India
1. Lion-tailed Macaque (Western Ghats) 2. Malabar Parakeet (Malabar region)
3. Nilgiri Langur (Nilgiri hills) 4. Nilgiri Tahr (Nilgiri hills)
WHO CONSERVES
Conserving the biodiversity on earth is the duty of every human being. To promote conservation, government and non-government bodies at the international, national, and local levels are constantly organizing awareness programmes and issuing rules and regulations to protect the existing forests and wildlife.
The International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN), now known as the World Conservation Union, works towards assessing the global conservation status of plant and animal species.
IUCN maintains a comprehensive list known as the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Here, species are classified into nine groups, set through criteria such as rate of decline, population size, area of geographic distribution, and degree of population and distribution fragmentation.
Red Data Book : It is a record of animals and plant species which are in danger.
On the basis of degree of threat 9 red list categories have been given :
(i) Extinct (ii) Extinct in the wild (iii) Critically Endangered.
(iv) Endangered (v) Vulnerable (vi) Near Threatened
(vii) Least concern (viii) Data deficient (ix) Not evaluated
· Head office of IUCN - Morges in Switzerland.
· Red Data Book listed about 11096 species in 2000. Animal species - 5485, Plant species - 5611.
CAUSES OF EXTINCTION AND DEPLETION OF WILDLIFE
1. Indiscriminate Hunting : Several species have become extinct due to their hunting by man for food, pleasure and animal products. The examples are disappearance of the bird dodo in Mauritius and the cheetah in India.
2. Destruction of Natural Habitat : Man has destroyed the natural habitats of wildlife for his settlement, cropping, plantation, mining and raising of dams, overgrazing by domestic animals, etc.
3. Introduction of Exotic Species : Man not only destroys the natural habitat, but also sometimes changes the structure of the biotic community of a place by introducing exotic species of his interest. Such species compete with the native species for food and space and may threaten the later will extinction. For example, the introduction of exotic trout and bass fish in the USA is endangering the native species of fish.
4. Forest Fires : Setting the forest on fire not only kills the useful animals but also causes large-scale destruction of the plant life.
5. Overexploitation of Natural Resources : Several animals and plants are valuable sources of food and other materials. Fish, prawns and crabs constitute an important part of human food. Man has, however, over-exploited these resources. Overfishing in sea is causing a grave situatoin and the picture is not encouraging with respect to fresh water fishing. The rate of consumption of fish is greater than its replenishment.
6. International Trade of Animal Products
7. Legal lapse : The failure of enforcement of the existing laws of wildlife management is yet another reason for the rapid depletion of wild life.
8. Human Ignorance : Man is mainly responsible for depletion and extinction of wildlife on the earth. This is largely due to ignorance of common man regarding the value of wildlife and the probable consequences of the disappearance of wildlife to man himself.
Poaching : Illegal hunting of animals is called poaching.
Organized poaching by anti-social elements threatens extinction of a number of species, especially those which have valuable body parts. These include:
(i) Body parts valued as ornaments : Examples include elephants for ivory and turtles for shells.
(ii) Body parts used in traditional medicine (particularly in Asia) : Examples include the rhinoceros for horns and tigers for bones.
(iii) For fur and hides : Animals killed for their hides include deer and cattle for leather, alligators and snakes for their skins, and wild cats, minks, and bears for fur.
(iv) The Tibetan antelope, also known as chiru, is mainly killed for its fine fleece, which is popularly known as shahtoosh. Shahtoosh shawls are very expensive, and considered a fashion statement by many. To check the population of the Tibetan antelope, a ban has been declared in India on the sale and usage of Shahtoosh shawls.
Threatend Species : The living species which have been greatly reduced in their number are called threatend species.
1. Endangered Species : These are the species which face immediate threat of extinction. Their number has been drastically reduced to a critical level either due to their indiscriminate hunting or due to destruction of their habitats. If the same factors continue, these species would soon become extinct. Indian rhino, Asiatic lion & Great Indian bustard.
Endangered species in Satpura National Park : Lion, Elephants, Wild buffaloes and Barasingha.
2. Vulnerable Species : These are species that are declining but still have sufficient number of individuals in their natural habitat. However, in near future they might represent the category of endangered species, in case the causal factors for their decline are not removed. Musk deer, Sambhar, Spotted deer and Black buck.
3. Rare Species : These are localised in certain geographical area and exhibit scattered population considering the global environment. Thus their overall population in the world is small. In future these species may enter into the category of vulnerable or endangered species. Indian elephant, Wild buffalo and Asiatic wild ass.
PROTECTED SPECIES OF INDIAN WILDLIFE
The following wild animals have been enlisted as threatened and protected species in India.
1. Musk deer 2. Bharat Swamp Deer 3. Duck
4. Horned Pheasant 5. Monal Pheasant 6. Great Indian Bustard
7. Indian Gazelle or Chinkara 8. Pea fowl 9. Gharial
10. Marsh crocodile 11. Python 12. Leathery turtle
13. Albino snow leopard
(A) Give answer of following questions :
1. What do you mean by biodiversity ?
2. How biodiversity is useful in Drug and Medicines. ?
3. How biodiversity is useful to modern agriculture ?
4. What is species ?
5. What do you mean by Endemic species ? Give any three example.
6. What is Red Data Book ?
7. What are categories of different species on the basis of degree of threat ?
8. Where is head office of IUCN located ?
9. What are threatened species ? Write their categories.
10. Give definition of Rare species.
(B) Fill in the blanks in following sentences :
1. The rare species are usually localised with in restricted .............................
2. The speices whose populations are abundant at present but they may become endangered in future are called..............................
3. Endangered species in Satpura National park are .......................... and ............................. (write any two)
4. Red Data Book listed about ............................. species in 2000.
5. The ............................. maintains Red Data Book.
6. Head office of IUCN located at ............................. in Switzerland.
7. In Red data book, on the basis of degree of threat ............................. categories have been given.
8. Project tiger running since............................. by central government.
9. A group of population which are capable of ............................. is called species.
10. Those species of plants and animals which are found exclusively in a particular area is called.............................
ANSWERS
1. Geographical area or habitat 2. Valnerable species
3. Lion, Elephants, Wild buffaloes & Barasingha 4. 11096
5. IUCN-International Union for Conservation of Nature & Natural resources
6. Morges 7. Nine 8. 1 April 1973 9. Interbreeding 10. Endemic species.
PROTECTED AREAS IN INDIA
To protect and conserve the wildlife in India the government has passed the Wildlife Protection Act in 1972.
(A) National park : A national park is characterised by an area reserved for the betterment of wildlife where foresting, grassing or cultivation is prohibited. It protects the flora and fauna of the reserved area. Private ownership is not allowed in a national park.
OR
Areas reserved for wild life where they can freely use the habitats and natural resources.
There are 97 national parks in India.
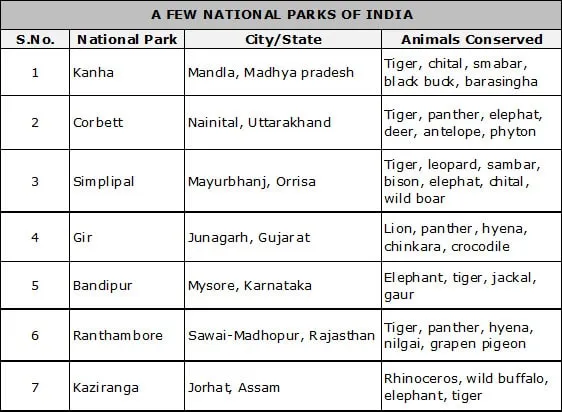
(B) Sanctuaries : A wildlife sanctuary is aimed at protecting the wild animals. In a wildlife sanctuary, cutting of trees for timber and other forest products is permitted to private operators with specific instructions to ensure that the well being of wild animals does not suffer. At present there are 508 santuaries in India.
OR
Areas where animals are protected from any disturbance to them and their habitat.
(C) Biosphere Reserves : A biosphere reserve is designed to provide protection to the wild flora and fauna, the domesticated animals and plants, as well as to the traditional life styles of the tribals of the area.
OR
Large areas of protected land for conservation of wild life, plant and animal resources and traditional life of the tribals living in the area.
At present there are 14 biosphere reserves in India.
This concept was launched by MAB [Man and Biosphere] programme in 1971.
A biosphere reserve is much larger than a national park or a sanctuary.
There are 3 zones of biosphere Reserve.
(1) Core Zone (2) Buffer Zone (3) Manipulating zone or Transition zone.
Important Biosphere Reserves in India
1. Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve 2. Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve
3. Uttarakhand Biosphere Reserve 4. Nokrok Biosphere Reserve 5. Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve
(D) Zoological Park : Zoos are places where animals and birds are protected by keeping them in special cages or enclosures for public exhibition.
(E) Botanical Gardens : Botanical gardens have been established to conserve rare and threatened plants. There are about 1600 botanical gardens all over the world.
CAONSERVATION OF WILD LIFE
(i) Ex-situ Conservation : The protection of wild life in other than their natural habitate e.g., zoos and botanical gardens,
Other examples of Ex-situ conservation are -
(a) Gene banks (b) Germ plasm bank. (c) Seed bank.
(ii) In situ conservation : It is the protection of species (wild life) in their natural habitat e.g., National parks.
Wildlife can be conserved by :
(a) Preventing illegal hunting of animals.
(b) Preventing sale and export of animal products and hunting of rare and endangered animals.
(c) Setting up wildlife sanctuaries and national parks.
(d) Reforestation.
MIGRATION
The movement of animals in large numbers from one place to another and back to their original home is called migration. Animals migrate during winter and breeding seasons. Birds are well known for their long migratory flights.
The Arctic tern is a sea bird which travels from the north pole to the south pole each year. Siberian cranes travel large distances and come to India during winter.
Migration often provides the migrating species with more favourable conditions of temperature, food, or water. For instance, bats of cold and temperate regions are known to migrate to warmer areas during winter.
* Reforestation : Restocking of the destroyed forests by planting new trees is called reforestation.
1. (i) Biosphere Reserve Scheme – 1986
(ii) Wild life protection Act – 1972 [ Revised in 1991]
(iii) World Environment Day – 05th June.
(iv) Forest Act-1927.
(v) National Forest Policy-1988.
2. Silviculture - The branch of science which deals with management and development of forest trees.
3. Chipko Movement : March 1973 Gopeshwar in Chamoli District.
The movement had two leaders :
(i) Sundar lal Bahuguna of Silyara in Tehri
(ii) Chandi Prashad Bhatt of Gopeshwar.
At First – Amrita Devi Bishnoi in Khejarli (Jodhpur)
4. Appiko Movement : Pandurang Hegde in south, in 1983.
5. Silent Valley : Palghat (kerala) , Declared as National Reserve Forest.
6. Green Data Book : A book containing a list of rare plants in a protected area like Botanical gardens.
7. (i) IUCN – International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources.
Heat Quarter – Morges [Switzerland]
(ii) WWF – World Wildlife Fund.
(iii) FAO – Food and Agricultural Organisation.
(iv) UNDP – United Nations Development Programme.
8. (i) Desert National Park, Jaiselmer (Rajasthan) Famous for Great Indian bustard & Black buck.
(ii) Kaziranga National Park, (Assam) Famous for Rhinoceros.
(iii) Keoladeo Ghana Bird Sanctuary, Bharatpur (Rajasthan) famous for migratory birds specially Siberian Crane.
(iv) Hangul- Kashmir Stag [Endangered] found in Dachigam [Srinagar - Jammu & Kashmir]
(v) Smallest tiger reserve in India – Ranthambore National Park [Rajasthan]
NCERT QUESTIONS WITH SOLUTIONS
Q.1 Differentiate between the following
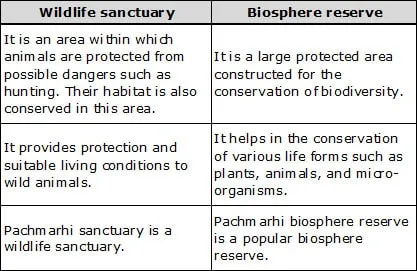
(a) Wildlife sanctuary and biosphere reserve
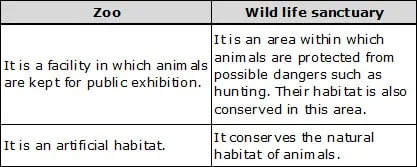
(b) Zoo and wildlife sanctuary
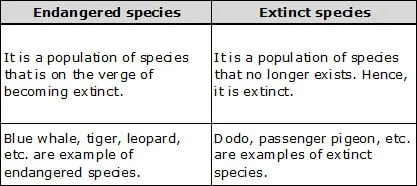
(c) Engangered and extinct species
(d) Flora and fauna
Ans. (a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
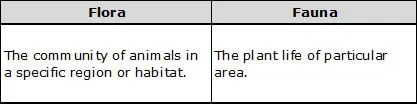
Q.2 Discuss the effects of deforestation on the following.
(a) Wild animals (b) Environment
(c) Villages (Rural areas) (d) Cities (Urban areas)
(e) Earth (f) The next generation
Ans. (a) Effects of deforestation on wild animals: Deforestation is the removal of trees or other vegetation from an area for industrial, agricultural, or other purposes. Trees and other vegetation form the habitat of many animals. Hence, if the habitat of wild animals is destroyed, then their numbers would automatically decline.
(b) Effects of deforestation on the environment: Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere to perform photosynthesis. If plants are destroyed, then the level of CO2 in the atmosphere will rise. As a result, CO2 will trap more heat radiations, thereby adding to global warming. An increase in the temeprature of the Earth will disturb the natural water cycle. As a result, there will be a change n the rainfall pattern. This could lead to floods or droughts.
(c) Effects of deforestation on villages: Roots of plants hold soil particles together, in the absence of plants, the top layer of the soil will be easily remvoed by the action of high speed winds or water flow. Thus, deforestation increases the chances of soil erostion. As a result, soil loses humus and become less fertile. Hence, a fertile land, which is a source of living for farmers in villages, gets converted into a desert.
(d) Effects of deforestation on cities: Deforestation in cities can increase the risk of many natural calamities such as floods and droughts in that area. Also, it can lead to global warming due to an increase in the level of CO2 in the atmosphere as a result of vehicular and industrial pollution. This increase in temperature industrial pollution. This increase in temeprature can disturb the natural water cycle of an area.
(e) Effects of deforestation on the Earth: As a result of deforestation, chances of desertification, droughts, floods, etc. increase Deforestation can also increase the level of CO2 in the Earth, it will lead to an increase in temperature i.e., gloval warming. As a result, the entire natural water cycle will get disrupted. This again increase the risk of natural calamities.
(f) Effects of deforestation on the next generation: Deforestation is slowly changing our environmental conditions. It is responsible for global warming, soil erosion, greenhouse effect, drought, floods, and many other gloval problems. As a result, the next generation will have to face severe consequences of deforestation.
Q.3 What will happen if:
(a) we go on cutting trees
(b) the habitat of an animal is disturbed.
(c) the top layer of soil is exposed.
Ans. (a) If we go on cutting trees, the natural habitat of many animals will get completely destroyed.
As a result, the biodiversity of many areas will be severely affected. Also, there will be an increase in the temperature of the Earth as a result of gloval warming, which can disturb the natural water cycle. As a result, there will be a change in the rainfall pattern. This could lead to floods or droughts. This will also increase the risk of soil erosion, desertification, and natural clalamities.
(b) The habitat of an animal provides it with necessities such as shelter, food, and protection. If the habitat of an animal is disturbed, then it will be forced to go to other places in search of food and shelter. The animal could get killed by other animals in this process.
(c) if the top layer or soil is exposed, then it will gradually expose the lower layer of soil, which is hard and rocky in nature. This type fo soil is less fertile as it contains less humus. Continued soil erosion will make the land barren or infertile.
Q.4 Answer in brief:
(a) Why should we conserve biodiversity?
(b) Protected forests are also not completely safe for wild animals. Why?
(c) Some tribals depend on the jungle. How?
(d) What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
(e) What is Red Data Book?
(f) What do you understand by the term migration?
Ans. (a) Biodiversity refers to the number and variety of various life forms such as plants, animals, and micro-organisms in an area. Plants and animals depend on each other for survival.
This means that the destruction of either of the two will affect the life of the other. Hence, we need to conserve biodiversity to maintain the balance of nature.
(b) Protected forests are not completely safe for wild animals because people who live near or adjacent to forests use resources from forests to fulfil their oWn requirements. In this process, wild animals are killed and sold for lucrative amounts of money.
(c) Tribals gather food, fodder, and fallen branches of trees from forests. Hence, they depend on forests for their daily requirements.
(d) Causes of deforestation:
(i) Forests are cleared for accommodating expanding urban areas and for fulfilling their ever increasing requirements.
(ii) Forests are destroyed to clear land for crops and cattle grazing.
(iii) Tees are cut down to be used for firewood.
Consequences of deforestation:
(i) Soil erosion (ii) Loss of biodiversity (iii) Floods and droughts
(iv) Climate change due to global warming (v) Disruption of water cycle
(e) Red Data Book is a source book that maintains an intemationallist of all endangered animal and plant species: This book is maintained by IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural resorces).
(f) Migration refers to the movement of an organism or a group of organisms from its natural habitat to another place at a particular time every year. Organisms migrate from one place to another to avoid inhabitable climatic conditions or for breeding.
Q.5 In order to meet the ever-increasins demand in factories and for shelter, trees are being continually cut. Is it justified to cut trees for such projects? Discuss and prepare a brief report.
Ans. No. It is not at all justified to cut trees to meet the ever increasing demands of human population. Forests are the habitat of sweral organisms including wild animals. They provide us with good quality air as they give out O2 and absorb the harmful CO2 gas from the atmosphere.
In the process, they prevent the excessive heating of the atmosphere. They prevent soil erosion and natural calamities such as floods and droughts. They increase the fertility Of the soil and help conserve biodiversity. The cutting of forests to meet the demands of growing human population will lead to global warming, soil erosion, greenhouse effect, droughts, floods, and many more problems. Ttw destruction of forests will disturb the balance of nature. Hence, forests must be conserved.
Q.6 How can you contribute to the maintenance of green wealth of your locality? Make a list of actions to be taken by you.
Ans. I can help in maintaining the green wealthy of my locality by taking care of the plants and trees growing in or around my locality. I can plant more and more tees. I can also encourage the people in my locality to plant more trees by informing them about the importance of growing trees. I can make yound children aware of the effects that deforestation has on our environment and on our planet. I can also ask them to water the plants daily, which will take very little of their time. I believe planting new trees is as important as taking care of the existing trees.
Q.7 Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall.
Ans. Deforestation is the removal of trees or other vegetation from an area for industrial, agricultural, or other purposes. Plants or trees abosrob CO2 from the atmosphere. If plants are destropted, then the level of CO2 in the atmosphere will rise. The high levels of CO2 in the atmosphere will trap more heat radiations, leading to global warming. This increase in temperature of the Earth will disturb the natural water cycle. As a result of disruption in the water cycle, there will be a change in the rainfall pattern. The reduced amount of rainwater can cause droughts.
Q.8 Why should paper be saved? Prepare a list of ways by which you can save paper.
Ans. Paper should be saved because it takes around seventeen full grown trees to make one tonne of paper. Trees, as we know, are important to maintain a balance of nature. Therefore, in order to save trees and prevent the impact of their loss on living organisms, we need to save paper.
Ways by which paper can be saved:
(i) Collect used paper and recycle it.
(ii) Use both sides of a paper for writing.
(iii) Spread awarencess about the importance of paper.
(iv) Use paper intelligently.
EXERCISE - I
Q.1 Name some parks and sanctuary.
Q.2 What do you mean by deforestation.
Q.3 Write two natural causes of deforestation.
Q.4 Name some products which we get from forests.
Q.5 What is sanctuary ?
Q.6 What are National Parks.
Q.7 Name any two endangered species protected in our wildlife sanctuaries.
Q.8 When was Project Tiger launched ?
Q.9 What do you mean by endangered animals
Q.10 Write the name of one extinct animal.
Q.11 What is Red Data Book ?
Q.12 Name the term related to the plantation of new plants.
Q.13 What do you know about deforestation ?
Q.14 What are the causes of the deforestation
Q.15 How does deforestation causes to decrease rainfall ?
Q.16 What do you mean by desertification ?
Q.17 Explain the term ecosystem.
Q.18 Make a list of threatened animals. Write cause of becoming endangered.
EXERCISE - II
Q.1 More soil erosion occurs where there is-
(A) No rainfall (B) Low rainfall (C) High rainfall (D) None of the above
Q.2 Which is most suitable soil for plant growth?
(A) Gravel (B) Loam
(C) Sand (D) Clay
Q.3 Frequent floods in plains of Northern India is due to–
(A) Excessive rainfall
(B) Siltation of dams
(C) Deforestation in catchment areas (D) Agriculture
Q.4 Conservation refers to -
(A) Management of natural resources (B) Judicious use of natural resources
(C) Protection of natural ecosystems (D) All of the above
Q.5 Soil conservation is –
(A) Aeration of soil
(B) Erosion of soil
(C) Protection of soil against loss
(D) Conversion of sterile soil into fertile soil
Q.6 Removal of top fertile layer of soil by wind or water is called –
(A) Leaching (B) Erosion
(C) Siltation (D) Weathering
Q.7 Soil erosion can be prevented by–
(A) Increase in bird population
(B) Afforestation
(C) Over-grazing
(D) Removal of vegetation
Q.8 MAB stands for –
(A) Man and Biodiversity
(B) Mammals and Biosphere
(C) Man and Biosphere
(D) Man and Biology
Q.9 What is the main cause of extinction of wild life ?
(A) Urbanisation (B) Poaching
(C) Felling of trees (D) All of the above
Q.10 A National Park provides protection to -
(A) Flora only (B) Fauna only (C) Flora and fauna (D) Entire ecosystem
Q.11 Conservation refers to -
(A) Management of natural resources (B) Protection of natural resources
(C) Proper use of natural resources (D) All of the above
Q.12 Deforestation is the major cause of-
(A) Environmental pollution
(B) Genetic erosion
(C) Desertification of habitat
(D) Depletion of natural resources
Q.13 'Red Data Book' provides information of :
(A) Threatened species
(B) Biota of Red Sea
(C) World flora
(D) World fauna
Q.14 Forests control drought through-
(A) Increasing rainfall
(B) Functioning as water shed
(C) Large trees
(D) Retention of water and prevention of soil erosion
Q.15 Plants and animals are best protected in-
(A) Sanctuaries (B) Botanical gardens (C) Zoos (D) National parks
Q.16 Forests-
(A) Maintain natural balance
(B) Control atmospheric pollution
(C) Prevent soil erosion
(D) All of the above
Q.17 5th June is -
(A) World population day
(B) World health day
(C) World environment day
(D) World animal day
Q.18 'Chipko movement' is connected with-
(A) Project tiger
(B) Plant breeding
(C) Protection of environment including habitat and wild life
(D) Conservation of natural resources
Q.19 A threatened species is-
(A) Rare (B) Endangered (C) Vulnerable (D) All of the above
Q.20 An example of in situ conservation is-
(A) Zoo (B) Pond
(C) Biosphere reserve (D) Seashore
ANSWERS KEYS
1. C 2. B 3. C 4. D
5. C 6. B 7. B 8. C
9. D 10. D 11. D 12. C
13. A 14. A 15. D 16. D
17. C 18. C 19. D 20. C
EXERCISE - III
1. Wildlife refers to :
(A) Any living organism kept in cage
(B) Any living organism present in sanctuary
(C) Any plant species growing in garden
(D) Any living organism in its natural habitat
2. The cause of extinction of species is :
(A) Man made forest fire
(B) Excessive grazing
(C) Inroduction of exotic species
(D) All of the above
3. Aim of conservation is :
(A) To preserve the quality of environment i.e. maintain a pollution - free environment.
(B) To ensure a continuous yield of useful plants, animals and materials for generations to come
(C) 1 and 2 both
(D) None of the above
4. How many megadiversity centres present in all over the world?
(A) 5 (B) 7
(C) 10 (D) 12
5. Asiatic lion protected in :
(A) Gir Forest National Park, Gujarat.
(B) Sunderban National Park, Westbengal.
(C) Kanha National Park, Madhya Pradesh.
(D) All the above
6. Which of the following is endangered species
(A) Indian Rhinoceros
(B) Asiatic lion
(C) Blue whale (D) All the above
7. We can conserve biodiversity by :
(A) Planting of trees should be undertaken
(B) Hunting of animals which is banned should be strictly enforced.
(C) Protected areas like National Parks, Wildlife sanctuaries and biosphere reserves should be established.
(D) All the above
8. Which of the following statement is incorrect
(A) Project tiger was initiated on 1 April 1973
(B) Biosphere reserves are multipurpose protected areas.
(C) Sanctuaries are special protected areas for protection of wild animals.
(D) None of them
9. Which of the following is a biosphere reserve
(A) Bandipure Sanctuary, Karnataka.
(B) Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary, Rajasthan.
(C) Kaziranga National Park, Assam
(D) Sunderban, West Bengal
10. Which of the following is the site of project tiger
(A) Jim Corbett National Park, Uttaranchal. (B) Periyar National Park, Kerala.
(C) Kanha National Park, Madhya Pradesh. (D) All the above.
11. The main object of Man and Biosphere programme is to :
(A) Conserve representative samples of ecosystem
(B) Provide opportunities for education and training
(C) Provide appropriate sustainable managements of the living resources.
(D) All te above
12. Which of the following is killed for oil and blubber?
(A) Tiger (B) Blue whale
(C) Chiru (D) All of them
13. Which of the following is a wildlife sanctuary in Rajasthan?
(A) Ranthambore (B) Periyar
(C) Kaziranga (D) Bandhavgarh
14. Which of the following is a bird sanctuary?
(A) Ranthambore (B) Periyar
(C) Keoladeo (D) All of them
15. The black rhino is killed for its :
(A) Ivory (B) Fur
(C) Horn (D) Meat
ANSWERS KEYS
1. D 2. D 3. C 4. D
5. A 6. D 7. D 8. D
9. C,D 10. D 11. D 12. B
13. A 14. C 15. C
EXERCISE-I
1. What is Red Data Book?
2. Define migration with one example?
3. Abbreviate IUCN?
4. Differentiate between flora and fauna.
5. What is biodiversity?
6. What do you mean by Reforestation?
7. Why should paper be saved?
8. What are endemic species?
EXERCISE-II
1. What is the effect of deforestation on the environment and wild animals?
2. What is the difference between endangered and extinct species?
3 Explain how deforestation leads to reduced rainfall?
4. What will happen if the top layer of soil is exposed?
5. What are the causes and consequences of deforestation?
6. How forest are important for mankind?
7. What is an ecosystem? What are the components of an ecosystem?
8. What are the causes of extinction of the organisms?
9. What is the difference between the zoo and a wildlife sanctuary?
10 Diffrentiate beteen conservation and preservation
11. What is Red Data Book? What is the purpose of this book for conservation?
EXERCISE-III
Section-A
· Fill in the blanks
1. Migratory birds fly to far a way places because of___________ changes.
2. Species found only in a particular area is known as ___________.
3. A place where wild animals are protected in their natural habitat it called ___________.
4. Wise and judicious use of resources is termed as ___________.
5. Biodiversity includes ___________ ___________ & ___________.
6. Corbett National Park is located in ___________.
7. Lions are found in ___________sanctuary located in ___________.
8. In a sanctuary, only ___________are protected
9. A book in which information on threatened species is available is ___________
10. Species existing but can no longer be seen are known as ___________.
Fill in the blanks(Multiple blanks)
Plants and animals are important components of the environment._____ helps to provide the oxygen needed for respiration by performing ______. They also serve as a food source for animals. Certain animals, the herbivores, also depend on plants for food. ________ use plants and animals for numerous purposes; however, with such atrocities as environmental pollution, the killing of animals, and the destruction of their natural habitat, the plant and animal populations have diminished.
Section-B
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. Deforestation generally decreases
(A) Rainfall (B) Soil erosion (C) Drought (D) Biodiversity
2. Species found only in a particular area is known as
(A) Endemic (B) Epidemic (C) Endangered (D) None
3. Migratory birds fly to far away places because of ________changes.
(A) Climatic (B) Mood (C) Both (D) No
4. What are the four requirements of all habitats?
(A) Food (B) Water (C) Space (D) All
5 The number of animals that a given area will support (or “carry”) without damage to the habitat or to the animals is called its:
(A) Biological surplus (B) Renewable resource (C) Carrying capacity (D) All
6. The giant panda, a threatened species, was chosen as a logo by with of the following organisation
(A) IUCN (B) WWF (C) NCC (D) IBP
7 Name the only country in the world where both the Lion (Panthera Leo) and the tiger (Panthera tigris) are found in the wild ?
(A) Uganda (B) India (C) Zaire (D) Pakistan
8. ________ is champion migratory bird
(A) Artic tern (B) Pegion (C) Crow (D) All of these
9. The most probable cause of depleting of tiger population is
(A) Habitat destruction (B) Diseases (C) Poaching (D) Malnutrition
10 Rare species is/are
(A) Golden cat (B) Indian pied hornbill (D) Himalayan porcupine (D) All
Section-C
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) National Park (P) Sariska
(B) Sanctuary (Q) WWF
(C) Biosphere reserve (R) Jim Corbett
(D) Project Tiger (S) Pachmarhi
Section-D
· Match the following (one to many)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. One or more than one entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II may have one or more than one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Pachmarhi (P) Sanctuary
(B) Protected Areas (Q) Biosphere reserve
(C) Conservation project (R) National Park
(D) Hunting Prohibited (S) Project Tiger
Answers
Exercise-III
Section-A
1. Climatic 2. Endemic sp.
3. Sanctuary 4. Conservation
5. Plants, animals & microbes 6. Uttranchal
7. Gir, Gujrat 8. Animals
9. Red Data book 10. Endangered Species Multiple
11. Plant, Photosynthesis, Animals
Section-B
1. (A) 2. (A) 3. (A) 4. (D) 5. (C)
6. (B) 7. (B) 8. (A) 9. (A) 10 (D)
Section-C
1. (A)-(R), (B)-(P), (C)-(S), (D)-(Q)
Section-D
1. (A)-(P,Q,R), (B)-(P,Q,R), (C)-(S), (D)-(P,Q,R)
*****