STRUCTURE OF THE EARTH
Initially earth was considered to be a uniform solid but it consists of different concentric shells, like a boiled egg. These shells or layers are divided into three parts,
crust, mantle and core. The core is further divided into two layers the outer core and the inner core.
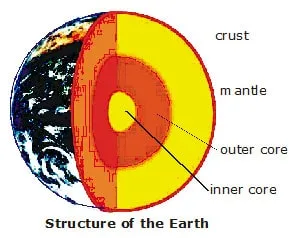
(a) Crust: It is the outer layer of earth on which our continents and ocean basins rest. It is thickest in the continental regions where it has an average thickness of 40 kilometres
and thinnest in the oceans where it may have maximum thickness of 10 to 12 km.
(b) Mantle: The layer beneath the earth's crust is called the mantle. Mantle, is important because it accounts for nearly half of the radius of the earth (2900 km).
The dynamic processes which determine the movements of the crust plates are powered by the mantle. The mantle is a shell of red hot rock and separates the earth's
metallic and partly melted rock (both the inner and the outer rocks) form the cooler rocks of the earth's crust. It consists of silicate minerals rich in magnesium and iron.
The density of mantle increases with depth from about 3.5 grams per cubic centimetre to around 5.5 grams per cubic centimetre, near the outer core.
(c) Outer Core: The outer core is around 2300 km thick. The outer core appears to be in molten state. It contains iron and nickel in molten state. It also contains sulphur.
(d) Inner Core: The inner core is about 1300 km thick and is surrounded by outer core . It is a solid ball and is composed of iron.
EARTHQUAKE
An earthquake is a sudden movement or a fracture in the crust and the upper layer of the mantle (together called the lithosphere). This causes a series of
shocks (movements). An earthquake may range from a mild tremor, which will result in the vibrations of the ground to a large-scale movement of earth causing a
widespread damage over a large area.
The branch of science which deals with the earthquakes and related phenomena is called seismology. All the phenomena related to the emergence and manifestations of
earthquakes are called seismic.
PLATE TECTONICS
The surface of the earth is broken into many large pieces called plates. Tectonics means the study of rock structures involved in earth movements. The world is divided into
seven large plates and several smaller plates. Due to slow movement inside the earth, these plates move with respect to each other by about a few inches in a year. The energy developed
by this 'small movement is very large. The boundaries of the plates are prone to rigorous geological activity and the result of these movements with respect to each other are earthquakes,
volcanoes, mountain formation, etc.
The theory that the surface of earth is made of lithospheric plates which move, is called plate tectonics. This theory explain the locations of earthquakes, volcanic
eruptions and newly forming mountains.
NOTE: The mountain system of the Himalayas is believed to have been formed by the collision of two continental plates, the Eurasian Plate and the Indian Plate.
OCCURRENCE OF EARTHQUAKE
Earthquakes generally occur at plate boundaries as follows:
(i) As the plates move, they rub against each other. At the edges of the plates where the earth's crust" is moving in different directions faults are found.

(ii) Sometimes, the rocks of the plates get locked to each other because the jagged edges of the two plates get locked and prevent the plates from moving,
As a result, pressure builds up against these rough edges.
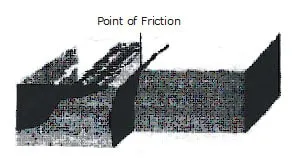
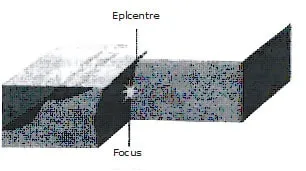
(iii) As the build-up pressure continues, a point is reached when the rocks (which are locked to each other preventing the plates from moving) give way. The plates start rolling
in the direction in which they were moving. This results in earthquake, Focus is the point where the rocks give way. The point vertically above the focus on the surface of the earth
is called the epicentre.
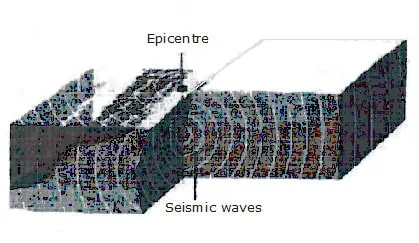
(iv) Vibrations caused by an earthquake travel in the form of a wave within the earth or along the surface of the earth. These waves are called seismic waves.
NOTE:
San Andreas fault: This is one of the world's most famous faults and is in California. It is about 1,000 km long and is about 9 m deep.
The San Andreas Fault marks a boundary between the Pacific Plate and the North American Plate. This fault is known for producing large and devastating earthquakes.
SEISMOGRAPH
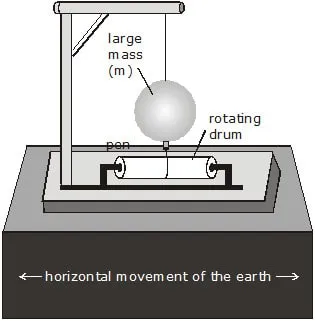
Seismograph or seismometer is an instrument used to measure earthquake waves or seismic waves. It consists of a ball having pen attached to it, suspended with a string.
Such that the tip of the pen touches a sheet of paper (like a graph sheet) placed on a fixed base, The shaking of the earth shakes the fixed base (as it is fixed on the ground) and
the suspended ball moves with respect to the fixed base. The pen tip records this movement on the sheet of paper. This is the output of the seismometer. The seismological output,
looks like a series of waves and is called as seismogram.
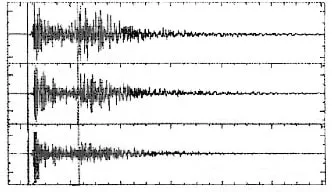
SEISMOGRAM
The graphical record of the intensity of seismic waves is called seismogram.
MAGNITUDE (OR INTENSITY) OF AN EARTHQUAKE
The data recorded by seismograph can be used to determine the magnitude of an earthquake. The scale used to measure the magnitude of an earthquake is the Richter scale.
The amount of damage cause to human being by earthquake can be determined by the location of earthquake, that is if it is in highly populated area or in a remote area.
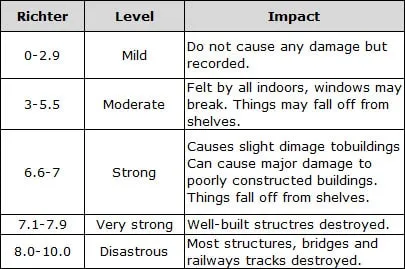
Note: Each increases of 1 on Richter scale means a 30-fold increase in energy. This means a magnitude of 6 on this scale represents 30 times more energy than a magnitude of 5.
HAZARDS OF EARTHQUAKE
Many places in India have been victims of earthquakes besides other major earthquakes. The damage due to the major earthquakes are:
(i) On the morning of 8 October 2005, a major earthquake struck the Indo-Pakistan border with a magnitude of 7.6. It felt severely in Pakistan, northern India and eastern Afghanistan.
Due to this earthquake more than 50,000 people lost their lives.
(ii) On 26 January 2001 , there was a major earthquake in Gujarat. More than 90,000 people lost their lives in this earthquake.
(iii) A powerful earthquake occur on Latur, Osmanabad (Maharashtra) on 30 September 1933 during midnight. In this earthquake more than 10,000 people lost their lives.
EARTHQUAKE PREPAREDNESS
(i) Buildings should be designed and built to withstand ground shaking. When a building is built, the first factor to be considered is the type of soil on which it is being built. Landfills
and reclaimed areas are more dangerous.
(ii) Architectural and engineering input should be out together to improve building design and building practices.
(iii) Intensive analysis of soils must be done before starting construction, no construction of buildings should be done on soft soil.
(iv) Building norms should be followed as far as quality of the material used is concern.
(v) Existing big buildings such as hospitals, schools and fire stations should be upgraded by retrofitting techniques.
(vi) Construction of the buildings should be avoided in the areas prone to fires, floods, landslides, earthquakes and cyclones.
Note: We should make sure that ceiling fans and fixtures, air conditioners and air coolers are firmly secured, otherwise they can cause a lot of harm.
SAFETY MEASURES AT THE TIME OF EARTHQUAKE
Here are some things you should do to prevent injury to yourself in case there is an earthquake.
(i) During an earthquake, if you are indoors, take cover under a heavy table or cot. Keep away from heavy objects that might fall.
(ii) If you are indoors in a public place, you should try to take cover under a sturdy object. Running to the exit may cause a stampede and this could be very dangerous.
(iii) If you are outdoors, move away from buildings, electric poles and trees, which could come down crashing.
(iv) If you are driving, stop if it is safe but stay inside your car. Stay away from bridges, overpasses and tunnels, If possible avoid stopping under trees, light posts, power lines or sign boards.
(v) After earthquakes, look. out for loose overhanging electric wires. Inform an adult so that these could be taken care of.
Important point: Earthquakes are generally followed by aftershocks. Aftershocks are additional low intensity quakes that follow an initial earthquake. They can continue over a period of weeks,
months or even years.
RAIN
Water from the water bodies on the surface of the earth get converted into water vapour by evaporation goes into the atmosphere and then rises up in the air.
The water vapour then condenses on dust particles to form tiny water droplets, which floating the air in the form of clouds. These water droplets by colliding against
each other and stick together to form bigger water droplets. When these water droplets become too heavy to float, they come down as rain.
CHARGED CLOUDS
Clouds contain tiny crystals of ice and droplets of water, which move against each other. This can cause huge amounts of charge to build up in clouds. Ordinarily, nothing
happens due to this charge build-up because air does not conduct the charge from the clouds. But when the accumulation of the charge is great enough and the wind brings
the cloud close together, the charge can jump from one cloud to another through the air .This huge amount of charges makes the insulation property of air gets breakdown
and the nearby air molecules get apart. By this, the air molecules are charged and the air containing charged particles become a conductor of electricity. The ripping apart
of the air molecules occur in steps. The successive layers of air are made conductive in zig-zag or step like path.
Step leader is the path of conductive air which extends from the thunder cloud. Step leader form the conductive path in the air, from the cloud to the ground or to a
neighbouring cloud. This step leader is not as bright as the flash of light.
The sudden rush of electrical charge heats up the air to about 30,000 °C producing a bright glow of lightning .During this process, a huge amount of energy is released
in the form of light and heat.
Due to the heat produced at the time of lightning. The air gets heated up and expands suddenly. This rapid expansion of air sends a disturbance in the form of vibrations
through the air producing a loud sound. This loud sound produced during lightning is called thunder. A rapid flow of electric charges through the air between two oppositely
charged clouds seen as an intense spark of electricity in the sky is called lightning. This is the lightning we see and the thunder we hear during a thunderstorm.
An electric discharge or lightning can occur not only between two clouds but also between a charged cloud and the Earth.
A cloud has the negative charges concentrated at the base and positive charges concentrated at the upper regions. When a charged cloud passes over a tall building or a tall tree,
it induces an opposite charge on them. The negative charges at the base of clouds pull the positive charges. from the tall buildings upwards at a tremendous speed. As soon as the
negative and positive charges connect a continuous path is formed from the cloud to the tall building or a tree on the ground. The large amount of negative charges accumulated in
the clouds rush down this path, give rise to an electric discharge in the form of lightning strike. When electric charge flows between tremendously charged cloud and a tall
building (on the earth), we say lightning has struck in the form of a lightning strike.
LIGHTNING
We know that sometimes during rain, thunder and lightning also take; place. During rain over the sky flashes of light are also observe. This natural phenomenon is
called lightning. During lightning strike, ten to twenty thousand amperes of electric current flows. The air in the path of lightning heats up and gets hotter than the
surface of the sun (about 30,000°C). This causes the flash of lightning.
The thunder that we hear during rain is due to the wave of vibrations (shock wave) which occur due to enormous amount of heat produced and make
the air expand suddenly.
Therefore, a lightning is a high-energy electric discharge accompanied by a large amount of heat and light. This can happen between a charged cloud and the
ground, between two charged clouds or even between two oppositely charged portions of the same cloud.

(a) Lightning & Thunder:
During a thunderstorm, thunder and lightning occur together. But we see a flash of lightning first and hear the number of thunder after few seconds. The time difference that
we sense is due to the speed at which sound and light trave. Light travels so quickly (about 300,000 kilometers in one second) that we see a bright flash of lightning instantly.
Sound, on the other hand, travels much more slowly than light - at about 340 m/s through air. Therefore, we can see light in an instant, but it takes a while to hear thunder.
During a storm, wait until we see a flash of lightning, then start to count slowly. For every count of three, the storm is roughly one kilometre away. If we see lightning
and hear thunder at just about the same moment, watch out. The storm could be right above us, only a few hundred feet away.
(b) Electric Sparks:
An electric spark is an electric discharge (Le. flow of electric charges) through air, vacuum or any other gas. We would have seen these sparks at electric switches.
Switch off all the lights at night and then observe the switch closely when we switch off the fan switch. We will most likely see a small flash of light. This is an electric
spark. This is due to the charges jumping across the small gap formed when the switch is being turned off. Lighting is one example of a huge electric spark in the atmosphere.
The flash of light that we see is due to the air molecules being heated up to very high temperatures.
NOTE : The saying that lightning never strikes the same place twice is wrong. Once the step leader forms the conducting path, charges flow through this path many times,
in rapid succession. So lightning strikes again and again at the same place, with intervals of a few tens of a millisecond. It has even struck more than 40 times at the same spot.
It is so quick that it is difficult for the eye to detect, but if we observe the lightning very closely, we will notice a brightening and dimming. This is called the ‘strobe effect’,
some what like the lights at a disco.
LIGHTNING CONDUCTORS
Lightning always follows: the easiest path. Lightning strikes buildings or projecting objects such as trees, poles, wires or building than larger, flatter surfaces
because the material in them provide easier paths to the ground than the our. The primary target of lightning are lone buildings. The idea behind the lightning protection
is to provide a direct, easy path for the lightning bolt to enter the earth without passing through a building. A lightning conductor runs from the top to the bottom, along
the outer wall of the building to be protected. The lower end of the lightning conductor is connected to a metal plate, which is buried deep inside the earth. When a
lightning strikes, the lightning conductor provides an easy path for the charge to pass through to the earth, thus protecting the building.
Safety Measures Against Lightning Strikes:
Lightning strikes tall buildings and trees. When lightning strikes the earth it can be extremely dangerous.
If we caught in thunderstorm then the safety measures to be taken are:
(i) Do not take shelter under a tree. Even if the tree gets struck by lightning, it could catch fire and cause great harm to us.
(ii) Do take shelter go to indoor.
(iii) We can take shelter inside a car or a bigger vehicle, like a truck.
(iv) We can also sit down in a low-laying place.
(v) We should not run across a large open field or high ground.
Lightning conductors are used to protect buildings from the damaging effects of lightning.
NCERT QUESTIONS WITH SOLUTIONS
Q.1 Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction ?
(A) A plastic scale (B) A copper rod (C) An inflated balloon (D) A woolen cloth
Ans. (B) is correct. Insulating materials can be easily charged by friction. Copper is a highly conducting materials. Therefore, a copper rod cannot be charged easily by friction.
Q.2 When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth the rod
(A) and the cloth both acquire positive charge.
(B) becomes positively charged while the cloth has a negative charge.
(C) and the cloth both acquire negative charge.
(D) becomes negatively charged while the cloth has a positive charge.
Ans. (B) is correct.
The glass rod becomes positively charged, while the silk cloth has a negative charge. When an object is charged by rubbing it against another object, the two objects get
oppositely charged. By convention, it is considered that the charged acquired by the glass rod is positive and charged acquired by the cloth is negative.
Q.3 Write T against true and F against false in the following statements:
(a) Like charges attract each other (T/F)
(b) A charged glass rod attract a charged plastic straw (T/F)
(c) lightning conductor cannot protect a building from lightning (T/F)
(d) Earthquakes can be predicted in advance (T/F)
Ans. (a) False
Like charges repel each other, unlike charges attract each other.
(b) True
A charged glass rod has a positive charge while a charged plastic straw has a negative charge thus, they attract each other as unlike charge attract each other.
(c) False
Lightning conductor is a device to protect a building against lightning.
(d) False
Although the causes of earthquakes is known, but no instrument could be invented to detect it till now. Hence, earthquakes cannot be predicted in advance.
Q.4 Sometime, a crackling sound is heard while taking off sweater during winters. Explain.
Ans. When a sweater is taken off, the woolen sweater gets charged because of the friction between the sweater and the body. Thus, an electric discharge (spark) is takes place
between the body and the sweater. This produced a crackling sound; even a spark (light) can be seen when sweater is taken off in a dark room.
Q.5 Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Ans. When we touch a charged object, our body conducts its charges to the earth. That is why a charged body loses its charge, if we touch it with our hand.
Q.6 Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph ?
Is It likely to cause much damage?
Ans. The Richter scale has the readings from 1 to 10. The reading of magnitude 3 on the Richter scale would be recorded by a seismograph. If the Richter
scale gives a reading of magnitude 3, then the earthquake is not likely to cause much damage. Generally, earthquake of magnitude higher than 7 is considered destructive in natue.
Q.7 Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Ans. (1) If you hear thunder, rush to a safer place like a house or a building. If you are travelling by car or by bus, you are safe inside with windows and doors of the vehicle shut.
(2) Lightning can strike telephone cords, electrical wires and metal pipes. During a thunderstorm contact with these should be avoided.
(3) Bathing should be avoided during thunderstorms to avoid contact with running water.
Q.8 Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged balloon ?
Ans. The nature of charges present on the surface of charged balloons are similar. Since like charges repel each other, two charged balloons repel each other.
When a charged body is brought near an uncharged body, the near end of the uncharged body acquires opposite charge and far end acquires similar charge due to
process of induction. Since the opposite charge is near as compared to the similar charge, there is a net attractive force between them. Hence, an uncharged balloon
is attracted by another charged balloon.
Q.9 Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
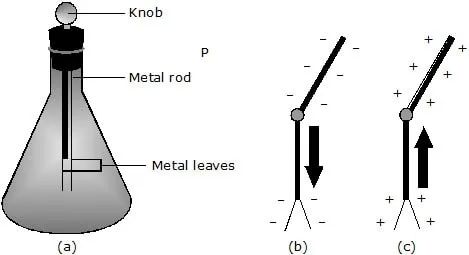
Ans. The leaf electroscope is an instrument used to detect. the presence of electric charge on a body.
It contains a vertical metal rod, with a round metal ball or knob on top, housed in a box. The metal rod and the box are insulated with each other by hard rubber or amber.
Two very thin leaves of gold
(or aluminium) are attached. to bottom end of the rod.
Detection of presence of charge on a body using electroscope: When the electroscope is uncharged, the two leaves hang parallel and vertically downwards due
to its own weight [see fig.(a)]. Suppose a negatively charged rod touches, the knob. Because the metal is a good conductor, electrons travel down the rod into the ,
leaves. Both leaves become negatively charged as they gain electrons [see fig.(b)]. Because the leaves have similar charges, they repel each other. When the positively
charged glass rod is brought into contact wlth the metal knob of an uncharged electroscope, electrons flow out of the metal leaves and onto the rod. The leaves repel
each other because each leaf becomes positively charged as it loses electrons [see fig. (c)]
Q.10 List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Ans. Jammu and Kashmir, Gujrat, and Uttaranchal.
Q.11 Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake strikes. What precaution would you take to protect yourself ?
Ans. (1) Try to find a clear spot, away from buildings, trees and overhead power lines. Drop to the ground.
(2) If you are in a car or a bus, do not come out. Ask the driver to drive slowly to a clear spot.
Do not come out tin. the tremors stop
Q.12 The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella ? Explain.
Ans. Carrying umbrella is not a good idea at all during thunderstorms.
As a lightning flash travels toward the ground from a nearby cloud, it looks for the tallest object.
This is because all the objects attached to the ground acts as ground or earthed objects. So lightning takes the shortest path to travel and thus, falls on the tallest object. If you're
holding an umbrella in an area surrounded by taller buildings, it's not so risky. But if you are the only tall object in the place surrounding you, the lightning flash will fall on you.
Thus, carrying umbrella is not a good idea at all during thunderstorms.
EXERCISE - I
Q.1 Give one important property of electric charge.
Q.2 Sometime, a crackling sound is heard while taking off sweater during winters. Explain.
Q.3 Explain why a charged body loses its charge if we touch it with our hand.
Q.4 Name the scale on which the destructive energy of an earthquake is measured. An earthquake measures 3 on this scale. Would it be recorded by a seismograph?
Is it likely to cause much damage ?
Q.5 Suggest three measures to protect ourselves from lightning.
Q.6 Explain why a charged balloon is repelled by another charged balloon whereas an uncharged balloon is attracted by another charged
balloon ?
Q.7 Describe with the help of a diagram an instrument which can be used to detect a charged body.
Q.8 List three states in India where earthquakes are more likely to strike.
Q.9 Suppose you are outside your home and an earthquake strikes. What precaution would you take to protect yourself ?
Q.10 The weather department has predicted that a thunderstorm is likely to occur on a certain day. Suppose you have to go out on that day. Would you carry an umbrella? Explain.
Q.11 What is the use of step leader ?
Q.12 What to do mean by lightning conductor ? Write their importance.
Q.13 Why do we hear a thunder after lightning ? Explain.
Q.14 Give one importance property of electric charge.
Q.15 Explain the working of seismograph with the help of a diagram.
Q.16 Write the process of occurring of earthquake.
Q.17 Explain the following terms with respect to earthquakes :
(i) Focus (ii) Epicentre
Q.18 Write a note on the precautions we should take while designing buildings to reduce loss of life and property due to an earthquake.
Q.19 Explain the working of seismograph with the help of a diagram.
Q.20 Define seismology.
Q.21 Write the process of occurring of earthquake.
Q.22 Explain the following terms with respect to earthquakes:
(i) Focus (ii) Epicentre
Q.23 Write a note on the precautions we should take while designing buildings to reduce loss of life and property due to an earthquake.
Q.24 What is the use of step leader?
Q.25 What do you mean by lightning conductor? Write their importance.
Q.26 Write the safety measures against lightning strike.
Q.27 Why do we hear a thunder after lightning? Explain.
EXERCISE - II
Q.1 Which instrument is used to measure earthquake waves?
(A) Seismogram (B) Seismograph
(C) Seismic wave (D) Seismology
Q.2 The point at which the rocks on either side of the plate give way is called:
(A) focus (B) epicentre
(C) aftershock (D) fault
Q.3 The outermost layer of the earth is called:
(A) Mantle (B) Core
(C) Crust (D) Centre
Q.4 The branch of science concerned with earthquakes and related phenomena is called:
(A) Electrostatics (B) Optics
(C) Seismology (D) Geology
Q.5 Earthquakes are generally followed by:
(A) rain (B) after shocks
(C) thunder (D) lightning
Q.6 In which of the following state earthquake is most likely to occur:
(A) Gujarat (B) Chhattisgarh
(C) Chennai (D) Kerala
Q.7 Which of the following event can cause earthquake:
(A) Volcanic eruption
(B) Meteor heating earth
(C) Underground nuclear explosion (D) All of the above
Q.8 Earthquake can cause:
(A) flood (B) land slide
(C) tsunami (D) All of the above
Q.9 The fragmented outermost layers of earth are known as:
(A) plates (B) cores
(C) crusts (D) zones
Q.10 Generally lower part of clouds has :
(A) positive charge (B) negative charge
(C) zero charge (D) any type of charge
Q.11 Electric charges are:
(A) only positive
(B) only negative
(C) either positive or negative
(D) insulators
Q.12 In the air the path of lightning goes up to a temperature of about :
(A) 300°C (B) 3,000°C
(C) 300,000°C (D) 30,000°C
Q.13 In a neutral object, there are :
(A) equal number of atoms
(B) more positive charges than negative charges
(C) more negative charge than positive charge
(D) equal number of positive and negative charges
Q.14 A lightning conductor :
(A) conducts light
(B) stops lightning
(C) protects buildings from the damaging effects of lightning
(D) prevents clouds from coming near a building and thus protects it
Q.15 If you are caught in a thunderstorm you should:
(A) go and stand on a high ground (B) stand under a tree
(C) take shelter indoors
(D) all of the above
Q.16 Charged objects exert a .... ...... on each other:
(A) cloud (B) lightning
(C) force (D) power
Q.17 We hear a thunder because:
(A) a lot of charge goes in lightning (B) because lightning is very bright
(C) because the air heats up and expands all of a sudden
(D) clouds band against each other
Q.18 The correct relation between speed of light (C) and speed of sound (Vs) is:
(A) C < Vs (B) C > Vs
(C) C >> Vs (D) C = Vs
Q.19 Lightning occurs because of:
(A) rain (B) electric discharge
(C) wind (D) angry Gods
ANSWER KEY
1. B 2. A 3. C 4. C
5. B 6. A 7. D 8. D
9. A 10. B 11. C 12. D
13. D 14. C 15. C 16. C
17. C 18. C 19. B
EXERCISE - III
Section-A
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1 Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction?
(A) Plastic scale (B) Woolen cloth
(C) Copper rod (D) Inflated balloon
2 When a glass rod is rubbed with a piece of silk cloth. The rod
(A) And the cloth both acquire positive charge
(B) Becomes positively charged while cloth has a negative charge
(C) Both acquire negative charge
(D) Becomes negatively charged while the cloth has a positive charge.
4 Charge can be produced on a body by
(A) Induction (B) Heating (C) Presuring (D) Cooling
5 A body is positively charged means
(A) Having axcess of electron (B) Deficiency of electron
(C) Excess of mass (D) Deficeincy of mass
6 A body is negatively charged means
(A) Excess of electron (B) Deficieny of electron
(C) Extra mass on body (D) Excess of neutrons
7 During thunderstorms lightning which will be seen/heard first-
(A) Light (B) Sound (C) Both same time (D) None
8 During lightning, you should come out from building
(A) Yes (B) No (C) Makes no difference (D) None of these
Section-B
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
Cases Result
(A) Gaining electrons (P) Positively charged body
(B) Losing electrons (Q) Negatively charged body
(C) Using lightning conductors in building (R) Magnitude on Richter scale > 7.
(D) Destructive earthquakes (S) Safety of building
Answers
Section-A
1. (C) 2. (B) 4. (A) 5. (B) 6. (A)
7. (A) 8. (B)
Section-B
1. (A-Q), (B-P), (C-S), (D-R)
EXERCISE - IV
1. Charges are of :
(A) Two types (B) One types (C) Many types (D) *
2. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, silk attains a :
(A) Positive charge (B) Negative charge
(C) Remains neutral (D) Either positive or negative
3. The safest place during a thunderstorm is :
(A) Under a tree
(B) Near electricity poles (C) Inside a car
(D) Lying on the ground
4. An earthquake measuring 9.0 on the Richter scale causes :
(A) No damage
(B) Little damage
(C) Tremendous damage (D) Devastation
5. Lightning ocurs because of :
(A) Rain (B) Electric discharge (C) Wind (D) Angry Gods
6. Electric charges are :
(A) Only positive (B) Only negative
(C) Either positive or negative (D) Insulators
7. In a neutral object, there are :
(A) Equal number of atoms (B) More positive charges than negative charge
(C) Both (A) and (B) (D) Wind
8. The air in the path of lightning goes up to a temperature of about :
(A) 300°C (B) 3,000°C (C) 300,000°C (D) 30,000°C
9. A lightning conductor :
(A) Conducts light
(B) Stops lightning
(C) Protects buildings from the damagking effects of lightning
(D) Prevents clouds from coming near a building and thus protects it
10. If you are caught in a thunderstorm you should :
(A) Go and stand on a high ground (B) Stand under a tree
(C) Take shelter indoors (D) All of the above
11. Charged objects exert a ________ on each other :
(A) Cloud (B) Lightning (C) Force (D) Power
12. We hear a thunder because :
(A) A lot of charge goes in lightning
(B) Because lightning is very bright
(C) Because the air heats up and expands all of a sudden
(D) Clouds bang against each other
13. Lightning always follows :
(A) A straight path (B) The easiest path (C) A thunder (D) Rain
14. Two objects rubbed against each other :
(A) Will lose electrons (B) Will repal each other
(C) Will attract each other (D) A thunder
15. The gold leaf electroscope can be used to :
(A) Detect charge only (B) Detect or measure charge only
(C) Detect, measure and find the nature of charge
(D) Stand under a tree
16. Which of the following can be used to find out whether a body is charged or uncharged?
(A) Lightning conductor
(B) Gold leaf electroscope
(C) Turning fork
(D) The easiest path
17. Atmospheric electricity was discovered by :
(A) Hertz (B) Benjamin Franklin (C) William Gilbert (D) All of these
18. When a glass rod is rubbed with a silk piece, then the glass rod :
(A) Loses electrons (B) Gains electrons
(C) Neither loses nor gains electrons (D) None of these
19. When an ebonite rod is rubbed with flannel, then the ebonite rod :
(A) Loses electrons (B) Gains electrons
(C) Neither loses nor gains electrons (D) All of these
20. The gold leaf electroscope has two strips of foils made of _______ which are fixed to the inside of the glass jar.
(A) Gold (B) Silver (C) Tin (D) Steel
21. The lightning conductor is :
(A) Erected on the building (B) Buried inside the earth
(C) Installed near the window (D) All of these
22. The study of earthquakes is called :
(A) Seimology (B) Phonology (C) Richter scale (D) Both (A) & (B)
23. Magnitude of destructive earthquake generally measures ________on Richter scale :
(A) > 7 (B) < 7 (C) = 7 (D) ± 7
24. When two bodies P and Q are rubbed against each other and P acquires a charge +q, then the charge on Q is :
(A) Greater than + q (B) – q (C) Less than – q (D) More than +q
25. Bodies can be charged by :
(A) Conduction only (B) Induction only
(C) Both conduction and induction (D) None of these
26. When a body is charged by induction, the end farther away from the charged body acquires the :
(A) Positive charge (B) Negative charge (C) Same charge (D) All of these
27. Which of the following is a very good conductor of electricity?
(A) Wood (B) Rubber (C) Graphite (D) None of these
28. Lightning is a heavy flow of charges between two oppositively charged :
(A) Clouds (B) Particles (C) Atoms (D) Graphite
29. Which of the following cannot be charged easily by friction?
(A) Plastic scale (B) Inflated balloon (C) Woollen cloth (D) All of these
30. Earthquake is major :
(A) Richter scale (B) Seismology (C) Phonology (D) None of these
ANSWER KEY
1. A 2. B 3. C 4. D
5. B 6. C 7. A 8. B
9. C 10. C 11. B 12. C
13. C 14. A 15. C 16. B
17. B 18. A 19. B 20. A
21. A 22. C 23. A 24. B
25. C 26. C 27. D 28. A
29. B 30. A