INTRODUCTION
Throughout the day, we listen the various types of sounds like our father's voice, our mother's voice, our teacher's voice, chirping of birds, ringing of a school bell,
a telephone ringing, a guitar being played, a siren, a jet engine roaring in the sky, buzzing of a mosquito, a gunshot etc. These sounds stimulate the auditory nerve
in thehuman ear and the brain interprets the sound. Now let us define sound.Sound is a form of energy which produces the sensation of hearing in our ears.
PRODUCTION OF SOUND
Perform the following activities to produce sound.
ACTIVITY
1. Take a plastic scale or ruler from your geometry box. Hold it flat on your desk or table with about half its length protruding (stick out from the surface) over the edge.
Now bend it down and release it. It will move up and down rapidly (i.e. it will vibrate) and produce the sound at the same time. The sound will last as long as the vibration
(i.e. rapid up and down motion) of the scale continues.
2. Take a tuning fork. Hold it from its stem and strike it with a rubber pad or hammer. You will observe that the prongs of the tuning fork vibrate and at
the same time sound is produced (Figure).
3. Place your finger lightly on your throat near the vocal cords as shown in figure. Now say "Ah" for few seconds. You will feel the vibration in your
finger as long as you say "Ah".
4. Tie a thin metallic string rigidly at the two ends of a table as shown in figure. Now, pluck the string from the middle and release it.
The string begins to vibrate up and down and at the same time,
sound is heard.
Conclusion: From these activities, we come to the conclusion that the sound is produced by the vibrating objects or bodies.
PRODUCTION OF SOUND IN MUSICAL INSTRUMENTS
When a drum is beaten, then the skin of drum vibrates and sound is produced. When the strings of a guitar are plucked and released, they vibrate
and produce sound. When air is blown into the flute, pipe, clarinet, saxophone etc., it vibrates in the tube of the instrument and hence sound is
produced. Sound isalso produced when the birds flap their wings during the flight.
PROPAGATION OF SOUND
When a person speaks, the molecules in the air near his mouth are disturbed. Due to this, these molecules start vibrating to-and-fro about their mean positions.
These vibrating molecules then disturb the nearby molecules. This process continues until the molecules in the air next to the listener's ear start vibrating. These
vibrating molecules then cause vibrations in the diaphragm of the listener's ear and the sound is heard.
* SOUND NEEDS A MEDIUM TO TRAVEL
We have learnt that sound travels from one place to another place when the energy is transferred from one particle to another particle of a medium like
air or gas, liquid, solid etc. It means, sound needs a material medium for its propagation. In other words, sound cannot travel through vacuum.
* DEMONSTRATION TO SHOW THAT SOUND WAVES CANNOT TRAVEL THROUGH VACCUM
Put an electric bell inside a closed Bell jar connected with a vacuum pump. Initially, air from the jar is not taken out. Connect the electric bell with a battery (Figure). It rings
and the sound produced is heard by us.
Now start evacuating the air from a Bell jar using a vacuum pump, we will hear less and less sound. i.e. the loudness of the sound decreases. When there is no air in the Bell
jar, we do not hear sound. This activity demonstrates that sound waves require material medium (in this case air) for its propagation.
REQUIREMENTS FOR SOUND
To produce sound by vibrations, a mechanical device (the source) must first receive an input of energy. Next, the device must be in contact with a medium that will receive the
sound energy and carry it to a receiver. If the device is not in contact with a medium, the energy will not be transferred to a receiver, and there will be no sound. Thus, three basic
elements for transmission and reception of sound must be present before a sound can be produced they are
(1) the source (or transmitter),
(2) a medium for carrying the sound (air, water, metal, etc.), and
(3) the detector (or receiver).
OSCILLATIONS
In sound producing objects, the vibrations take place very fast...so fast, in fact, that they cannot be seen very clearly with the unaided human eye (slow-motion video is one
practical solution that is routinely used in scientific and industrial applications). We can produce slower vibrations, which are also called oscillations, by an arrangement called
a simple pendulum.
It consists of a ball or any weight, such as a stone, wooden top, steel bolt, etc. which is here called a bob, and which hangs down vertically.
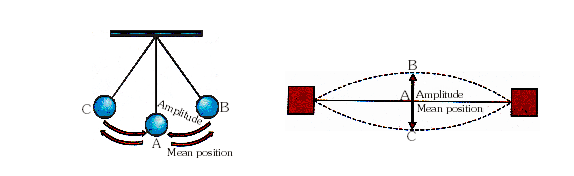
Figures show a oscillating simple pendulum and a vibrating string depicting the mean position and amplitude. By means of a thread. It hangs vertically because of the
force of gravity acting upon it. When the bob is given a small push, it performs a to-and-fro motion for some time and ultimately stops. The position where the bob stops is
called the mean position (A) or the equilibrium position.
* AMPLITUDE
The maximum displacement of the bob from the mean position during oscilations is called amplitude of the oscillation. In the case of a simple pendulum, as show in
the figure, the amplitude is AB (or AC).
* FREQUENCY
The number of oscillations produced by the vibrating body in one second is called its frequency. It is denoted by the letter 'f'. The unit of frequency in SI
system is Hertz (Hz or s–1).
When a vibrating body produces 10 vibrations (oscillations) in one second, its frequency is said to be 10 hertz.
If the frequency of a tuning fork is written as 200 Hz, it means that it produces 200 vibrations in one second.
* TIME PERIOD
When a bob moves from one position and returns to the same position, such that it repeats the motion, it is said to complete on oscillation.
The time taken by a vibrating body to complete one oscillation is called the time period.

CHARACTERISTICS OF A SOUND
(a) Loudness : When the string is plucked softly, it produces a feeble sound and when it is plucked hard, it produces a louder sound. In other words, in the first case
vibrations with small amplitudes are produced and in the second case vibrations with large amplitudes are produced.
This means that the loudness of a sound depends on the amplitude of vibration. It is measured in decibels (dB).
(b) Pitch : The shrillness or flatness of a sound is known as pitch. We can distinguish between a man's voice and woman's voice of the same loudness without even
seeing whether the speaker is a man or a woman. A man's voice is flat and has a low pitch, Whereas a woman's voice shrill and has a high pitch. The pitch of a sound
depends on the frequency of vibration. The higher the frequency of a sound, the higher will be its pitch. In other words, high pitched sounds (such as the shrill whistling
of a kettle or a jet engine) are created at high frequencies. This is obviously why we whistle for our dog; the high pitched sound attracts him. You can get a special 'dog whistle'
that emits a very high pitched sound at a frequency much beyond 20,000 Hz; humans cannot hear it, but your dog will come bounding up to you when he hears the sound (inaudible to you)!
(c) Quality or Timber : The characteristic of sound which enables us to distinguish between two sounds of the same pitch and loudness, produced by two different sources
is called its quality or timber. For example, we can recognize a person by hearing his voice, we can also distinguish the sound of a guitar from that of a sitar or harmonium.
SPEED OF SOUND
Sound waves travel at different speeds in different substances. The speed of sound varies, depending on factors such as temperature, nature of material, physical state
of the substance, etc. For example, the speed of sound in air at 20°C is about 340 m/s, but drops to about 330 m/s 0°C. Sound travels fastest in solids and slowest in gases.
Sound does not travel in vacuum.
Speed of sound in solids is greater than the speed of sound in liquids and the speed of sound in liquids is greater than the speed of sound in gases.
SPEED OF SOUND IN VARIOUS MEDIA
ABSORPTION OF SOUND
It has been found that shining objects like mirrors, metals or hard objects like buildings or stones reflect sound. However, materials with loose texture absorb sound.
For example, curtains; gunny bags; straw; carpets; etc., absorb sound. Big cinema halls or auditoriums are carpeted and their walls are coated with some rough materials,
so that they do not reflect any sound. It is because, such places are very big and therefore, echoes are formed. Thus, the quality of sound heard by people becomes poor.
However, in ordinary rooms in which we live, we do not have this problem. It is because they are seldom 11 m or more long or wide. Thus, the original sound and reflected
sound reach the ears at almost the same time and hence, no echo is formed.
SOUND PRODUCED BY HUMANS
In a human being, sound is produced by a voice box (larynx). Two vocal cords are stretched across the voice box such that a passage for air remain between the
cords. When we speak lungs force air through the passage due to which the cords start vibrating and produce sound. The tightness of the cords are controlled by the
muscles connected to vocal cords.
HOW WE HEAR SOUND THROUGH OUR EARS
* Human Ear : We have learnt that vibrating objects produce sound which is carried in all directions in a medium. How do we hear sound? Our ears help us to
hear sound. Human ear has three important parts. Only one of its parts can be seen and felt by you, which is the outer ear. The rest of the ear remains deep inside the skull.
(i) Outer Ear : The outer ear consists of the pinna and the eartube. The shape of the outer part of the ear is like a funnel. When sound enters the ear, it travels
down a canal at the end of which a thin membrane is stretched tightly. This tightly stretched membrane is called the eardrum, which performs a very important function.
(ii) Middle Ear : It has three very tiny interlocked bones. The innermost bone is joined to the inner ear.
(iii) Inner Ear : It has a coiled organ of hearing semicircular canals and the auditory nerve.
A vibrating body causes air molecules to vibrate. These vibrations reach out ear and are collected by the pinna and then funneled into the ear tube. These vibrations
strike the eardrum that start vibrating with the same frequency. It then forces the interlocked bones to vibrate. The hearing organ passes the vibrations to the auditory nerve,
which takes the signal to the brain. This enables us to hear the sound.
AUDIBLE AND INAUDIBLE SOUND
It has been proved that the human ear is not sensitive to vibrations of all frequencies. In other words, we can only hear sounds that fall within a certain range of
frequencies; any sound outside that frequency range is inaudible to our ears. We can hear sounds within frequencies ranging from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz. This is called
Audible frequency range of sound. Such vibrations are called sonic vibrations or sound vibrations.
Sound frequencies less than 20 Hz are called Infrasonic sound and sound frequencies more than 20,000 Hz (20 k Hz) are called Ultrasonic sound. Human beings
cannot perceive either infrasonic or ultrasonic sounds. Hence, these are called 'Inaudible' sounds, i.e., sounds we cannot hear. Dogs, on the other hand, have much 'sharper'
hearing, since they can hear sounds within the frequency range of 50 Hz to 45000 Hz ! That is why your dog starts braking a welcome long before you have reached
your front door; he has heard your footfalls or recognised the distinctive sound of your car as it enters the gate. Almost all animals have a wide range of hearing. Bats can
detect frequencies as high as 100,000 Hz!
SOUND PRODUCED BY ANIMALS
Most mammals such as dogs, cows, cats, etc. produce sound with the help of their vocal cords. Dogs can be easily trained to respond to a whistle which generates
ultrasonic vibrations and is commonly called Galton's whistle.
Birds produce sound by means of a ring of cartilage called Syrinx, fixed at the beginning of their winds pipe. Some birds have two parts in the syrinx. Thus, they can
produce two different notes. Insects such as bees, houseflies, mosquitoes produce buzzing sound by rapidly flapping their wings. Dolphins are related to the whale family.
They use ultrasonic sound to locate their prey.
* USES OF ULTRASONIC VIBRATIONS BY ANIMALS
1. Dogs can hear upto the frequency of 40,000 Hz as compared to humans who can hear upto 20,000 Hz. Dogs can be specially trained to respond to
a whistle which produces ultrasonic vibrations and is commonly called Galton whistle. The sound of this whistle cannot be heard by humans.
2. Bats produce vibrations in the frequency range of 50 Hz to 80,000 Hz. Bats have very weak eyes. When the bats fly at night, they produce ultrasonic vibrations which
cannot be heard by the humans or the insects. When these vibrations strike the insects, they are reflected back. On receiving the reflected sound, the bat can locate the insect and eat it.
3. Dolphins are related to the whale family. They use ultrasonic sound to locate their prey, in much the same way as the bats.
* USE OF ULTRASONIC VARIATIONS IN INDUSTRY
1. Ultrasonic vibrations are used for homogenising milk, i.e., the milk is agitated with ultrasonic vibrators. These vibrations break down the larger particles of the
fat present in milk to smaller particles.
2. Ultrasonic vibrations are used in dish washing machines. In such machines, water and detergent are vibrated with ultrasonic vibrators. The vibrating detergent
particles rub against the dirty utensils and thus clean them.
3. Ultrasonic vibrations produce a sort of depression in rats and cockroaches. Ultrasonic vibrators are used to drive rats and cockroaches from godowns.
4. Ultrasonic vibrations are used for imaging internal organs of human body. In fact they are even used to study the growth of foetus in mother's womb.
5. Ultrasonic vibrations are used in relieving pain in joints and muscles.
6. Ultrasonic vibrations are used in detecting flaws in articles made from metals. They are also used in finding the thickness of various parts of a metallic component.
NOISE AND MUSIC
A sound which does not have a pleasing sensation on the ears is called noise. Scientifically, a noise is produced by irregular vibrations. Conversely,
a sound which has a pleasant sensation on the ears is called music. Scientifically, a musical sound is produced by regular vibrations. For example, the
prong of a tuning fork or the string of a sitar vibrates at regular intervals and hence, they produce musical sound.
* MEASURE OF LOUDNESS OF SOUND
The loudness of sound is measured in decibels (dB). It signifies the sound pressure level. Human ears can pick up sound from 10 dB to 180 dB. The loudness of
sound is considered normal, if it is between 50 dB to 60 dB. A normal human being can tolerate loudness of 80 dB. The sound above 80 dB is painful and causes
various health problems. The table given below gives the loudness of various sounds in decibels and their effect on human ear.
NOISE POLLUTION
The disturbance produced in the environment by undesirable, loud and harsh sound from various sources is called noise pollution.
Noise pollution is a recent phenomenon of twentieth century. Increasing dependence of the man on various kinds of machines at home, or work place or factories, etc.,
has contributed a lot to the noise pollution.
The noise pollution at a particular place is determined by following factors :
(i) Loudness of the sound (ii) Duration of noise.
SOURCE OF NOISE
1. Noise in homes: Following are the causes of noise in homes. (i) television, (ii) radio,
(iii) power music system, (iv) washing machines, (v) desert cooler, (vi) mixer-cum-grinder,
(vii) vacuum cleaner, (viii) telephone, (ix) typewriter, (x) air conditioner.
2. Noise in surroundings: Following are the causes of noise in surroundings: (i) loud speakers used in marriages and religious places, (ii) exploding crackers on various functions,
(iii) hawkers in the street, (iv) publicity announcements made by trading companies, (v) noise produced in the construction of houses, etc.
3. Noise in factories: All factories, big or small use machines, which invariably produce noise and hence contribute to noise pollution.
4. Noise due to transportation : This noise is produced by (i) trains, (ii) all kinds of petrol and diesel vehicles, (iii) aeroplanes, (iv) pressure horns used in automobiles.
* HARMFUL EFFECTS OF NOISE POLLUTION
1. Noise in the surroundings interferes with conversation with another person.
2. A long exposure, to noise pollution may result in the loss of hearing.
3. Noise pollution reduces concentration and results in the loss of work efficiency.
4. Noise causes anger, tension and interferes with the sleep pattern of individuals.
5. Noise produces headaches, irritability and nervous tension.
6. Noise can cause loss of night vision as well as cause colour blindness.
SOLVED EXAMPLES
Ex.1 Choose the correct answer. Sound can travel through :
(a) gases only (b) solids only (c) liquids only (d) solids, liquids and gases
Sol. (d) solids, liquids and gases
Ex.2 Voice of which of following is likely to have minimum frequency ?
(a) Baby girl (b) Baby boy (c) A man (d) A woman
Sol. (a) Baby girl
Ex.3 In the following statement, tick ‘T’ against those which are true, and ‘F’ against those which are false.
(a) Sound cannot travel in vacuum.
(b) The number of oscillations per second of vibrating object is called its time period.
(c) If the amplitude of vibration is large, sound it feeble.
(d) For human ears, the audible range is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
(e) The lower the frequency of vibration, the higher is the pitch.
(f) Unwanted or unpleasant sound is termed as music
(g) Noise pollution may cause partial hearing impairment.
Sol. (a) True (b) False (c) False (d) True (c) False (f) False (g) true.
Ex.4 Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) Time taken by an object to complete one oscillation is called _____________ .
(b) Loudness is determined by the ________
(c) The unit of frequency is _____________
(d) Unwanted sound is called __________.
(e) Shrillness of a sound is called _____________.
Sol. (a) time period (b) amplitude (c) hertz (d) noise (e) frequency
Ex.5 A pendulum oscillates 40 times is 4 seconds. Find its time period and frequency.
Sol. Number of oscillates = 40
Total time = 4 seconds
Time taken to complete one oscillation
= = 0.1 second
So time period = 0.1 second.
Frequency = = 10 Hz
Ex.6 The sound from a mosquito is produced when it vibrates its wings at an average rate of 500 vibrations per seconds, what is the time period of the vibrations ?
Sol. Total vibrations = 500
Time taken = 1 second
Time taken to complete one vibration
= = 0.002 seconds.
So time period = 0.002 seconds.
Ex.7 Identify the part which vibrates to produces sound in following instruments.
(a) Dholak (b) Sitar (c) Flute.
Sol. (a) Stretched membrane (b) Strings (c) Air column.
Ex.8 What is the difference between noise and music ? Can music become noise sometimes
Sol. The sound which is unpleasant for our ears is called noise while music is the sound which is pleasant for our ears. Music becomes noise sometimes when it
crosses the bearable range of sound for our ears.
Ex.9 List sources of noise pollution in your surroundings.
Sol. Sources of noise pollution. Honking of horns, loud speakers, loud sounds of machines in factories, loud sounds of T.V. radio, domestic appliances etc.
Ex.10 Explain in what why noise pollution is harmful to humans ?
Sol. Harmful effects of noise pollution :
(i) It causes deafness.
(ii) It causes mental illness.
(iii) It causes headache and high blood pressure.
Ex.11 A ship sends on a high frequency sound wave and receives an echo after 1 second. What is the depth of the sea? Speed of sound in water is 1500 m/ s.
Sol. Let,
Depth of the sea = d
So, Total distance travelled by the sound wave = 2d
Time taken by sound to travel both ways = 1 s
As per definition,
Speed of the sound
=
Then, 1500 m s–1 =
or
d = = 750 m
thus the depth of the sea is 750 metres.
Ex.12 A sonar echo takes 2.2 s to return from a whale. How far away is the whale?
Sol. Total time taken by the signal = 2.2 s
So, Time taken the signal to reach the whale
= = 1.1 s
Distance of the whale = d ?
From the literature, speed of sound in sea water at 25°C = 1533 m s–1
So, Distance of the whale, d = Speed of the signal x Time taken
or d = 1533 m s–1 × 1.1 s = 1686.3 m
NCERT QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
Q.1 Choose the correct answer. Sound can travel through
(a) gases only (b) solids only (c) liquids only (d) solids, liquids and gases.
Ans. Option (d) is correct, sound can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. Sound requires a medium to travel through. Solid, liquid and gas provide the
medium for sound. Hence, sound can travel through solids, liquids and gases.
Q.2 Which of the following voices is likely to have minimum frequency?
(a) Baby girl (b) Baby boy (c) A man (d) A woman
Ans. Option (c) is correct i.e., a man. The voice of an adult man is of lower pitch in comparison to the voices of a baby boy, a baby girl and a woman. Since frequency
of a sound is directly proportional to its pitch, man's voice is of minimum frequency in comparison to a boy, a girl, or a woman's voice.
Q.3 In the following statements, tick 'T' against those which are true, and 'F' against those which are false.
(a) Sound cannot travel in vacuum. (T / F)
(b) The number of oscillations per second of a vibrating object is called its time period. (T / F)
(c) If the amplitude of vibration is large, sound is feeble. (T / F)
(d) For human ears, the audible range is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz (T / F)
(e) The lower the frequency of vibration, the higher is the pitch. (T / F)
(f) Unwanted or unpleasant sound is termed as music. (T / F)
(g) Noise pollution may cause partial hearing impairment. (T / F)
Ans. (a) True. Sound requires a medium to travel through. Since vacuum is devoid of any medium, sound cannot travel through it.
(b) False. The number of oscillations per second of a vibrating object is known as its frequency.
Time period is the time required to complete one oscillation.
(c) False. Loudness of a sound is proportional to the square of the amplitude of its vibration.
When the amplitude of vibration of a sound is large, the sound is very loud. The sound is feeble for small amplitude.
(d) True. Humans cannot hear sounds of all frequencies. Humans can hear a sound whose frequency falls in the range of 20 Hz-20,000 Hz. The sound having frequency
out of this range is inaudible to humans.
(e) False. The pitch of a sound is proportional to its frequency. As the frequency of vibration increases, the pitch of the sound also increases and vice-versa. A sound is said
to be high pitched if its frequency of vibration is high, and is low. pitched for a small frequency of vibration.
(f) False. Unwanted or unpleasant sounds are known as noise. Sounds that are melodious and pleasing to ear are known as music.
(g) True. Unwanted or unpleasant sounds are known as noise. If one is subjected to loud unpleasant sound continuously for a long time, then it may cause temporary hearing impairment.
Q.4 Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
(a) Time taken by an object to complete one oscillation is called ______ .
(b) Loudness is determined by the _____ of vibration.
(c) The unit of frequency is ______ .
(d) Unwanted sound is called _______ .
(e) Shrillness of a sound is determined by the _______ of vibration.
Ans. (a) Time period (b) Amplitude (c) Hertz (d) Noise (e) Frequency
Q.5 A pendulum oscillates 40 times in 4 seconds. Find its time period and frequency.
Ans. Frequency of oscillations is defined as the number of oscillations of a vibrating body per second.
It is given by,
f = = = 10Hz
Now, f = or T = = = 0.10s
Q.6 The sound from a mosquito is produced when it vibrates its wings at an average rate of 500 vibrations per second. What is the time period of the vibration ?
Ans. Given, frequency, f = 500 vibrations/sec
Now, Time period, T = =
or T = = s = 0.002 s.
Q.7 Identify the part which vibrates to produce sound in the following instruments.
(a) Dholak (b) Sitar (c) Flute
Ans. (a) Dholak consists of a stretched membrane called its head. When the head is beaten gently, the stretched membrane sets into vibration. Since sound is produced
when an object vibrates, the dholak produces a sound.
(b) Sitar is a musical instrument. It consists of stretched strings. When a string is plucked, it sets into vibration. Since sound is produced when an object vibrates, the sitar produces a sound.
(c) Flute is a hollow pipe. When air is blown over its mouth, the air inside the pipe is set into vibration.
As a result, a pleasant sound is produced.
Q.8 List sources of noise pollution in your surroundings.
Ans. Some sources of noise pollution are as follows :
(i) Televisions and radios running at high volumes.
(ii) Loudspeakers and crackers.
(iii) Horns of buses, cars and trucks
(iv) Appliances such as mixer, desert cooler, etc. used at homes.
(v) Heavy industries, thermal power plants, stone cutting and grinding machines.
Q.9 Explain in what way noise pollution is harmful to humans.
Ans. Noise pollution can lead to a number of health related problems. Some of them are as follows:
(i) Hearing loss (ii) Insomnia i.e., inability to sleep
(iii) Hypertension i.e., high blood pressure (iv) Severe headache
(v) Stress and emotional disturbance.
Q.10 What is the difference between noise and music?
Can music become noise sometimes?
Ans. The sound that is pleasing to the ear is called music. For example, the sound produced by violins, pianos, flutes, etc. The sound that is unpleasing to the ear is called noise.
Some examples of noise are as follows :
(i) Sound produced by horns of buses and trucks
(ii) Sound of electrical generators
(iii) Sound of a gun shot
Yes, music can become noise when played at high volumes.
Q.11 Your parents are going to buy a house. They have been offered one on the roadside and another three lanes away from the roadside. Which house would you suggest
your parents should buy? Explain your answer
Ans. There will be more noise in the house which is along the roadside. This is because noise produced by transportation vehicles may cause trouble to the residents.
The intensity of noise decreases with the distance between the source and the listener. Hence, it is better to take the house that has three lanes away from the roadside.
Q.12 Sketch larynx and explain its function in your own words.
Ans. Inside the larynx, there are two vocal cords. There is a small gap between them. This small gap allows air to pass through. When we speak, air is forced into this small gap
by the lungs. This prompts vocal cords to vibrate. Since vibrating objects produce sound, sound is produced due to the vibration of vocal cords.
Layrnx in humans
Q.13 Lightning and thunder take place in the sky at the same time and at the same distance from us. Lightning is seen earlier and thunder is heard later.
Can you explain?
Ans. The speed of sound is quite less· as compared to the speed of light. Hence, light reaches us before the sound during a lightning, which is accompanied by thundering.
EXERCISE II
Q.1 Sound cannot travel through
(A) air (B) water
(C) iron (D) vacuum
Q.2 The audible range of frequency is
(A) 200-2000 Hz (B) 20-20000 Hz
(C) 20-23000 Hz (D) 220-20000 Hz
Q.3 A tightened string of instrument produces sound of ......... frequency, a
(A) lower (B) higher
(C) same (D) none of these
Q.4 An object produces a sound of 15 Hz. Which of the following is correct ?
(A) this sound can be heard by us
(B) this sound cannot be heard by us
(C) it does not produce sound
(D) this sound can be heard only through solids
Q.5 A mosquito produces sound by vibrating its...
(A) wings (B) vocal cords
(C) legs (D) body
Q.6 Violin is a musical instrument with ........
(A) stretched bow
(B) stretched string
(C) stretched membrane
(D) none of these
Q.7 Loudness is the measure of ......... of a sound.
(A) shrillness (B) heaviness
(C) Length (D) Pitch
Q.8 The level of normal conversation is about..... dB.
(A) 40-60 (B) 100-200
(C) below 60 (D) 60-100
Q.9 Late Ustad Bismillah Khan was a famous.... player.
(A) Flute (B) Table
(C) Guitar (D) Shehnai
Q.10 The frequency of a sound wave is
(A) Directly proportional to time period
(B) Inversely proportional to time period
(C) Equal to the time period
(D) Has no relation with time period
Q.11 The maximum distance of a vibrating body from its mean position is called its –
(A) Frequency (B) Quality
(C) Amplitude (D) Pitch
Q.12 The loudness of a sound depends upon its–
(A) Amplitude (B) Frequency
(C) Pitch (D) None of these
Q.13 The pitch of a sound depends upon its –
(A) Amplitude (B) Frequency
(C) Quality (D) None of these
Q.14 Two wires A and B of equal length differ only in their thickness. A is thinner than B. If both are plucked with same force, then–
(A) A will produce sound of higher pitch than B
(B) A will produce sound of lower pitch tha B
(C) Both will produce sounds of equal pitch
(D) None of these
Q.15 Which of the following are used in dishwasher or to wash the machines ?
(A) Infra-sonic waves
(B) Ultra-sonic waves
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) Neither (A) nor (B)
Q.16 Which of the following sounds has the
greatest frequency ?
(A) man’s voice
(B) woman’s voice
(C) boy’s voice
(D) all have the same frequency
Q.17 The sound waves travel the slowest in –
(A) Dry air (B) Moist air
(C) Liquid water (D) Ice
Q.18 For an echo to be distinguishable from sound, the minimum time difference is –
(A) 1 sec (B) 0.1 sec
(C) 0.01 sec (D) 10 sec
Q.19 Which of the following is the correct group of wind instruments –
(A) Violin, drum, nadaswaram
(B) Shehnai, flute, nadaswaram
(C) Shehnai, flute, cymbals
(D) Gongs, jaltarang, shehnai
Q.20 Sound cannot be associated with
(A) hearing (B) frequency
(C) wave (D) sunlight
Q.21 Sound is caused due to
(A) propagation of light
(B) vibrations
(C) change in physical state
(D) clouds
Q.22 The minimum distance required to produce a distinct echo is
(A) 10 m (B) 11 m
(C) 15 m (D) 17 m
Q.23 Which of the following is not a stringed instrument ?
(A) Sitar (B) Tabla
(C) Violin (D) Guitar
Q.24 Sound travels in air at 0ºC with a velocity of about
(A) 300 m/s (B) 330 m/s
(C) 360 m/s (D) 380 m/s
Q.25 Velocity of sound in water is about
(A) 340 m/s (B) 420 m/s
(C) 1000 m/s (D) 1500 m/s
Q.26 If a pendulum has a time period of 3 second, then its frequency is
(A) 3 Hz (B) 0.5 Hz
(C) 3 s (D) 0.33 Hz
Q.27 Which travel faster through the emptiness of outer space than through the earth's atmosphere?
(A) Light (B) Sound
(C) Both (D) None of these
Q.28 Objects vibrating faster have a ..................... frequency.
(A) Lower (B) Neutral
(C) Higher (D) (A) and (B) both
Q.29 Which sound has a higher frequency?
(A) The music of a tabla
(B) The music of a flute
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
Q.30 Echo is the effect produced due to
(A) Reflection of sound
(B) Refraction of sound
(C) Dispersion of sound
(D) (A) and (B) both
ANSWERS KEY
1 D 2. B 3. B 4. B
5. A 6. B 7. C 8. A
9. D 10. B 11. C 12. A
13. B 14. A 15. B 16. B
17. A 18. B 19. B 20. D
21. B 22. D 23. B 24. B
25. D 26. D 27. A 28. C
29. B 30. A
EXERCISE III
1. If a pendulum is allowed to oscillate into a jar containing water, its time period will
(A) increase (B) decrease (C) remain same (D) none of these
2. If a pendulum is allowed to oscillate in vacuum, its time period will
(A) decrease (B) increase (C) remain same (D) none of these
3. If the mass of a pendulum is doubled, the time period
(A) becomes double (B) becomes half (C) becomes 4 times (D) remains the same
4. The phenomenon in which the amplitude of oscillation of a pendulum decreases gradually is called
(A) decay period of oscillation (B) damping
(C) building up of oscillation (D) maintained oscillation
5. In which of the following media will sound travel the fastest?
(A) Solid (B) Both solid and liquid (C) Liquid (D) Gas
6. Sound waves in air are waves.
(A) longitudinal (B) radio (C) transverse (D) electromagnetic
7. Out of the following, which frequency is not clearly audible to the human ear?
(A) 30 Hz (B) 30,000 Hz (C) 300 Hz (D) 3000 Hz
8. Sound waves are
(A) transverse mechanical waves (B) longitudinal mechanical waves
(C) neither (A) nor (B) (D) none of these
9. The time period of the above wave would be
(A) 1/30 s (B) 30 s (C) 1/24 s (D) none of these
10. The relation between frequency (n) and wavelength (l) is given by (v is velocity, n is frequency and T is time-period)
(A) v = nl (B) n = (C) v = (D) n =
11. A body produces sound only if it is
(A) made of steel (B) made of glass (C) plucked (D) vibrating
12. A crest is the point of
(A) zero displacement (B) maximum displacement
(C) minimum displacement (D) none of these
13. A trough is a point of
(A) zero displacement (B) maximum displacement
(C) minimum displacement (D) none of these
14. Velocity of sound is maximum in
(A) iron (B) mercury (C) water (D) air
15. The vibrating body while playing a violin is
(A) wire (B) the box of the violin (C) both wire and box (D) only air
16. The waves which propagate in metals are
(A) longitudinal (B) transverse (C) both (A) and (B) (D) neither (A) nor (B)
17. Velocity of sound is minimum in
(A) nitrogen (B) hydrogen (C) air (D) carbon dioxide
18. The speed of electromagnetic waves in air is
(A) 3 × 105 km/s (B) 3 × 106 km/s (C) 3 × 107 km/s (D) 3 × 108 km/s
19. Which of the following types of waves is different from others?
(A) waves in the strings of musical instruments (B) water waves
(C) light waves (D) sound waves
20. The SI unit of amplitude of oscillation is
(A) cm (B) m (C) km (D) none of these
21. Echo is produced due to
(A) reflection of sound (B) refraction of sound
(C) resonance (D) none of these
22. SONAR is based on the principle of
(A) echo (B) resonance (C) reverberation (D) anyone of the above
23. The audible range of frequency is
(A) 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz (B) 40 Hz to 40,000 Hz (C) 60 Hz to 60,000 Hz (D) 10 Hz to 20,000 Hz
24. Which of the following frequency of sound can't be heard by human beings?
(A) 40 Hz (B) 400 Hz (C) 4000 Hz (D) 40,000 Hz
25. The depth of the troughs of a wave is called its
(A) amplitude (B) displacement (C) frequency (D) none of these
26. The height of the crests of a wave is called its
(A) amplitude (B) displacement (C) frequency (D) none of these
27. A sound wave is travelling from East to west. In which direction do the molecules in the air move?
(A) East to West (B) West to East (C) North to South (D) South to North
28. The number of crests passing a given point in one second is (where T is time period and v is frequency)
(A) T (B) v (C) 2T (D) 2v
29. The time taken by a crest to travel a distance l. is
(A) (B) (C) (D) T
30. What name has been given to the wave of short duration?
(A) pulse (B) periodic wave (C) elastic wave (D) none of these
31. Sound is caused due to
(A) Vibrations (B) Propagation of light
(C) Change in Physical State (D) (A) and (C) both
32. Sound cannot travel through vacuum because
(A) There are no vibrations (B) There is no medium present in vacuum
(C) Sound travels in straight line (D) None of these
33. The loudness of a sound depends on its __ of vibration.
(A) Oscillations (B) Frequency
(C) Amplitude (D) (B) and (C) both
34. Which figure shows the softer sound and why?
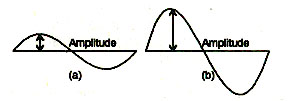
(A) Figure (A) because it has low amplitude wave
(B) Figure (B) because it has high amplitude wave
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
35. The audible frequency range of sound is
(A) 20 HZ to 2000 HZ (B) 40 HZ to 4000 HZ
(C) 20 HZ to 20000 HZ (D) (A) and (B) both
36. The speed of sound wave in air at room temperature is
(A) 364 m/s (B) 346 m/s (C) 3 × 108 m/s (D) None of these
37. In humans, the sound is produced by
(A) Larynx (B) Windpipe (C) Throat (D) (A) and (B) both
38. The intensity of sound decreases with increase in distance.
(A) Because sound needs a medium to travel
(B) Because sound energy is lost during propagation of sound
(C) Because loudness of sound depends upon amplitude of vibration
(D) None of these
39. In the seven notes of Indian music system sa, re, ga, ma, pa, dha, nee the frequency
(A) Increases from nee to sa (B) Decreases from sa to nee
(C) Increases from sa to nee (D) (A) and (B) both
40. If a pendulum has a time period of 3 seconds"then its frequency will be
(A) 3 HZ B) 3 Seconds (C) 0.33 HZ (D) (A) and (C) both
41.
(A) Frequency of wave (A) is greater than wave (B)
(B) Frequency of wave (B) is greater than wave (A)
(C) Cannot be determined (D) None of these
42. What is the relationship between frequency and pitch?
(A) The higher the frequency of a sound, the lower will be its pitch
(B) The higher the frequency of a sound, the higher will be its pitch
(C) The lower the frequency of a sound, the higher will be its pitch
(D) None of these
43. Ultrasonic waves are used in SONAR to
(A) Detect the frequency of the waves (B) Detect the radio waves
(C) Detect objects on sea bed (D) (A) and (C) both
44. Why are percussion instruments are widely used to keep beats in a musical composition?
(A) Because range of frequencies and pitches produced by these instruments is very large
(B) Because range of frequencies and pitches produced by these instruments is limited
(C) Both
(D) None of these
45. The position where the bob stops is
(A) Right extreme position
(B) Left extreme position
(C) Mean position
(D) None of these
46. Echo is the effect produced due to
(A) Reflection of sound (B) Refraction of sound
(C) Dispersion of sound (D) (A) and (B) both
47. Tick the odd one out
(A) Amplitude (B) Frequency
(C) Acceleration due to gravity (D) (A) and (C) both
48. The wall of the auditorium built for musical concerts should ....................
(A) Transmit (B) Absorb (C) Reflect (D) None of these
49. The stethoscope used by doctors works on the principal of
(A) Reflection of sound
(B) Interference of sound
(C) Refraction of sound
(D) (A) and (B) both
50. Bats send out ..................... squeaks that humans cannot hear.
(A) Low frequency
(B) High frequency
(C) Low Pitch
(D) None of these
51. Objects vibrating faster have a ..................... pitch.
(A) Louder (B) Lower (C) Higher (D) (A) and (B) both
52. Which travel faster through the emptiness of outer space than through the earth's atmosphere?
(A) Light (B) Sound (C) Both (D) None of these
53. Objects vibrating faster have a ..................... frequency.
(A) Lower (B) Neutral (C) Higher (D) (A) and (B) both
54. Which sound has a higher frequency?
(A) The music of a tabla
(B) The music of a flute
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these