ADOLESCENCE
The period of life, when the our body undergoes changes, leading to reproductive maturity, is called adolescence.
OR
PUBERTY
The start of the time when a boy is biologically ready to become a father, and a girl is biologically ready to become a mother.
Review Questions
1. What is adolescence ?
2. Define puberty.
3. Adolescents are generally called teenagers. Why ?
CHANGES AT PUBERTY
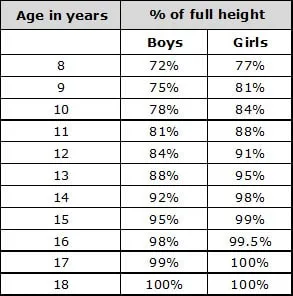
Calculation for full height (cm):
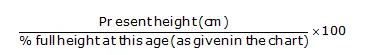
One can use this formula and table to work out how tall he or she is likely to be.
Increase in Height :
Change in Body Shape : 
Voice Change :
* At puberty, the voice box or the larynx begins to grow.
Boys develop larger voice boxes. The growing voice boxes
in boys can be seen as a protruding part of the throat called
Adam's apple.
Increased Activity of Sweat and Sebaceous Gland :
Development of Sex Organs :
Reaching Mental, Intellectual and Emotional Maturity :
Mental growth :- Thinking skill develops. They are able to think in a more flexible, abstract, and logical way. The ability to see others point of view, exploring ideas, developing concepts and memory skills improve.
Emotional growth :- Emotional changes cause the young person to look at friend and family in new ways. They are very happy at one moment and the very next their mood changes. These comes a feeling of giving and of helping people. Interest in the opposite sex and desire for closeness arise.
Social growth :- In includes developing a personal identity, accepting oneself, forming more mature relationships with peers of both sexes, developing independence and preparing for a career.
Review Questions
1. Name the male sex hormone.
2. List the changes which are occur at puberty.
3. What is Adam's apple ?
4. Name the female sex hormone.
SECONDARY SEXUAL CHARACTERS
The reproductive organs are testes and ovaries which produce the gametes, i.e., sperms in males and ova in females. The features which help to distinguish the male from the female, are called secondary sexual characters.
Pubertal Changes (Secondary Sexual Characters) in Male :
Widening of shoulders.
Deepening of voice.
Growth of hairs under chest armpits and around pubic area.
Appearance of beard and moustaches.
Growth of sex organs, [Testes & Penis].
Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands.
Oily skin and appearance of pimples.
Darkening in skin colour of the genital area.
Pubertal Changes (Secondary Sexual Characters) in Female :
Widening of pelvis and hips.
High pitch voice.
Growth of hairs under armpits and around pubic area.
Initiation of menstrual cycle.
Growth of mammary glands (breasts).
Maturation of secondary sex organs like fallopian tubes, uterus.
Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands.
Oily skin and appearance of pimples.
Darkening in skin colour of the genital area.
THE ROLE OF HORMONES IN ADOLESCENCE
During the perod of puberty, the sex hormnes bring about changes in the body. These are called the secondary sexual characteristics, which are as follows:
Boys develop deep voice, beard and moustache and large hands and feet.
Girls develop breasts and begin to menstruate.
Reproductive organs grow and start functioning.
Changes in behaviour and attitude can be seen.
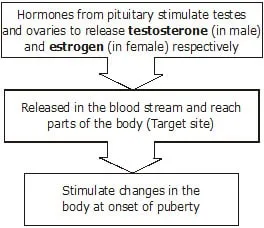
The biological processes associated with puberty include the prominent maturation of several endocrine glands with consequent physical growth and sexual development. It is as if a switch clicks on in the brain and activates asection of the brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus, in turn, triggers the pituitary gland to produce two hormones-follicle sitmulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). The pituitary gland also releases a growth hormone called somatotropin. FSH and LH are released cyclically in females and play a key role in the menstrual cycle. They stimulate the ovaries to secrete oestrogen and progesterone and are responsible for the growth of the egg in the ovary. In the case of males, these hormones laget the testes, which are responsible for hte production of sperms and testosterone.
Role of Hormones in Initiating Reproductive Function :
Review Questions
1. Define secondary sexual characters.
2. Write the secondary sexual characters in boys.
3. Write the secondary sexual characters in girls.
4. Which endocrine gland stimulates testes and ovaries to release sex hormones ?
Reproductive Phase of Life in Humans:-
Adolescents become capable of reproduction when their testes and ovaries begin to produce gametes. The capacity for maturation and production of gametes lasts for a much longer time in males than in females.
In females, the reproductive phase of life begins at puberty (10 to 12 years of age) and generally lasts till the age of approximately 45 to 50 years.
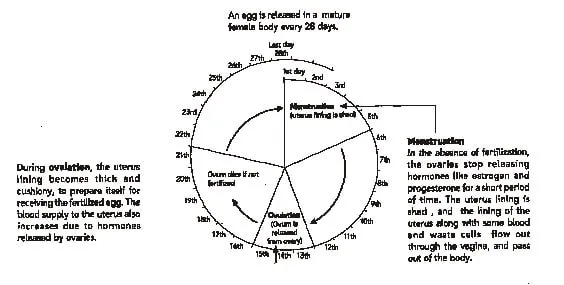
Menstruation occurs once in about 28 to 30 days.
The first menstrual flow begins at puberty and is termed menarche.
At 45 to 50 years of age, the menstrual cycle stops. Stoppage of menstruation is termed menopause.
Menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones. The cycle includes the maturation of the egg, its release, thickening of uterine wall and its breakdown if pregnancy does not occur. In case the egg is fertilised it begins to divide and then gets embedded in the uterus for further development.
MENSTRUAL CYCLE
1. Defintion: Menstrual cycle involves the series of cyclic changes occurring in the ovaries and female reproductive tract during the reprodctive period of female.
2. Introduction: Reproductive period of female extends from puberty and is termed menarchae (i.e. 10-14 years) to menopause (i.e. 45-55 years). During this period, every month a menstrual cycle occurs whose peculiar feature is 'period' - the vaginal bleeding (called menstruation) that lasts for about four days. Primary aim of menstrual cycle is to prepare the female for fertilization and pregnancy.
3. Period: On average a menstrual cycle is completedi n 28 days (mensem means a month) though it may very by 1 or 2 days.
4. Phases: During the menstrual cycle, the wall of the uterus passes through several phases, which are controlled by two hormones, oestrogen and progesterone. The first phase of hte menstrual cycle usually lasts for about 4-6 days. During this period the lining of the uterus, is shed, accompanied by a loss of blood. This duration of the first phase is called a woman's period. This phase is called the menstrual phase or menstruation.
SEX DETERMINATION
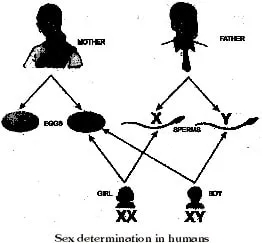
All human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nuclei of their cells. Two chromosomes out of these are the sex chromosomes, named X and Y.
A female has two X chromosomes, while a male has one X and one Y chromosome. The gametes (egg and sperm) have only one set of chromosomes. The unfertilised egg always has one X chromosome. But sperms are of two kinds. One kind has an X chromosome, and the other kind has a Y chromosome.
When a sperm containing X chromosome fertilises the egg, the zygote would have two X chromosomes and develop into a female child. If the sperm contributes a Y chromosome to the egg (ovum) at fertilisation, the zygote would develop into a male child. The sex chromosomes of the father determine the sex of an unborn baby. The belief that the mother is responsible for the sex of her baby is completely wrong and to blame her for this is totally unjustified.
Review Questions
1. How many chromosomes are present in human beings ?
2. Define the term menarche ?
3. Which hormone play main role in menstrual cycle ?
4. What is number of sex chromosomes in human male and female ?
5. Who is the responsible to determine the sex of unborn baby ?
Role of Hormones in Completing the Life History of Insects and Frogs :-
The caterpillar of silk worm has to pass through various stages to become an adult. Similarly, a tadpole also passes through various stages to become a frog.
This process of change from larvae or caterpillar to an adult is called metamorphosis. The process of metamorphosis in insects is controlled by insect hormones.
In a frog the process of metamorphosis is regulated by thyroxine hormone which is produced by thyroid gland. A tadpole cannot become an adult if there is deficiency of iodine in the water where it is growing.
REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH
Health is a state of complete mental, physical and social well being.
· Nutritional Needs of the Adolescents :-
* Personal Hygiene :-
Everyone should have a bath at least once everyday. It is more necessary for teenagers because the increased activity of sweat glands sometimes makes the body smelly. All parts of the body should be washed and cleaned everyday. If cleanliness is not maintained there are chances of catching bacterial infection. Girls should take special care of cleanliness during the time of menstrual cycle.
* Physical exercise :-
Walking and playing in fresh air keeps the body fit and healthy. All young boys and girls should take walks, exercise and play outdoor games.
* Say "NO" to Drugs and Alcohols :-
Adolescence is a period of much activity in the body and mind which is a normal part of growing up. So do not feel confused or insecure. If anybody suggests that you will get relief if you take some drugs, just say 'No' unless prescribed by the doctor. Drugs are addictive. If you take them once, you feel like taking them again and again. They harm the body in the long run. They ruin health and happiness.
Review Questions
1. Define 'balanced diet.'
2. Why physical exercise is essential for adolescents ?
3. How can you achieve a healthy life ?
4. Define metamorphosis.
ADOLESCENCE PREGNANCY
You might be knowing that in our country, the legal age for marriage is 18 years for girls and 21 years for boys. This is because teenage mothers are not prepared mentally or physically for motherhood. Early marriage and motherhood cause health problems in the mother and the child. It also curtails employment opportunities for the young woman and may cause mental agony as she is not ready for responsibilities of motherhood.
AIDS (Acquired immuno deficiency syndrome)
AIDS is a disease which is caused by HIV virus. This virus destroys the natural defence mechanism of the body and makes it susceptible to diseases.
Causes of AIDS
1. Sharing the needle of the syringe for injecting drugs.
2. Unprotected sex with an infected person.
3. Transfusing blood into the body of a healthy person from an infected person.
4. Infected mother can pass HIV virus through milk to an infant.
Symptoms
Include weakness, loss of appetite, loss of weight, fever and swelling of hte lymph nodes. The patient becomes more liable to catch infections diseases. The number of certain lymphocytes in the blood of the patient decreases below average and those which are present do not work property. About 40% of the patients die within a year or two years.
How to Prevent AIDS
1. Use disposable syringes.
2. Get blood from registered blood banks for transfusion.
3. Have safe and protected sex.
4. HIV infected mother should not breast feed her baby
5. Be faithful to your partner.
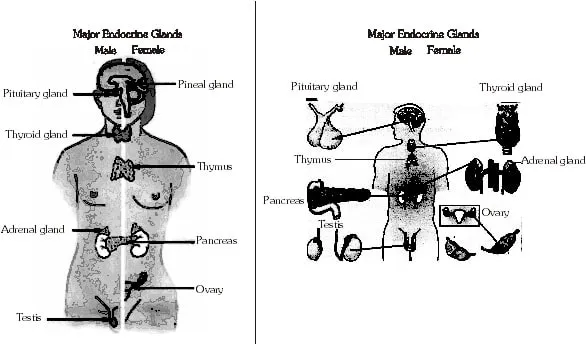
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
· The branch of biology which deals with study of endocrine system and its physiology is known as "endocrinology".
· "Thomas addison" is known as 'Father of Endocrinology'.
· The glands which pour their secretion directly in the blood are called endocrine glands. These glands lack ducts, so these glands are called ductless glands. e.g.– Thyroid gland, parathyroid gland.
· Whereas the glands with duct are called exocrine glands. e.g. – Sweat gland, salivary gland.
· Pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine part, so it is also called mixed gland or common gland or heterocrine gland.
HORMONES
· Substances secreted by endocrine glands are called "Hormones".
· The term hormone was coined by Starling.
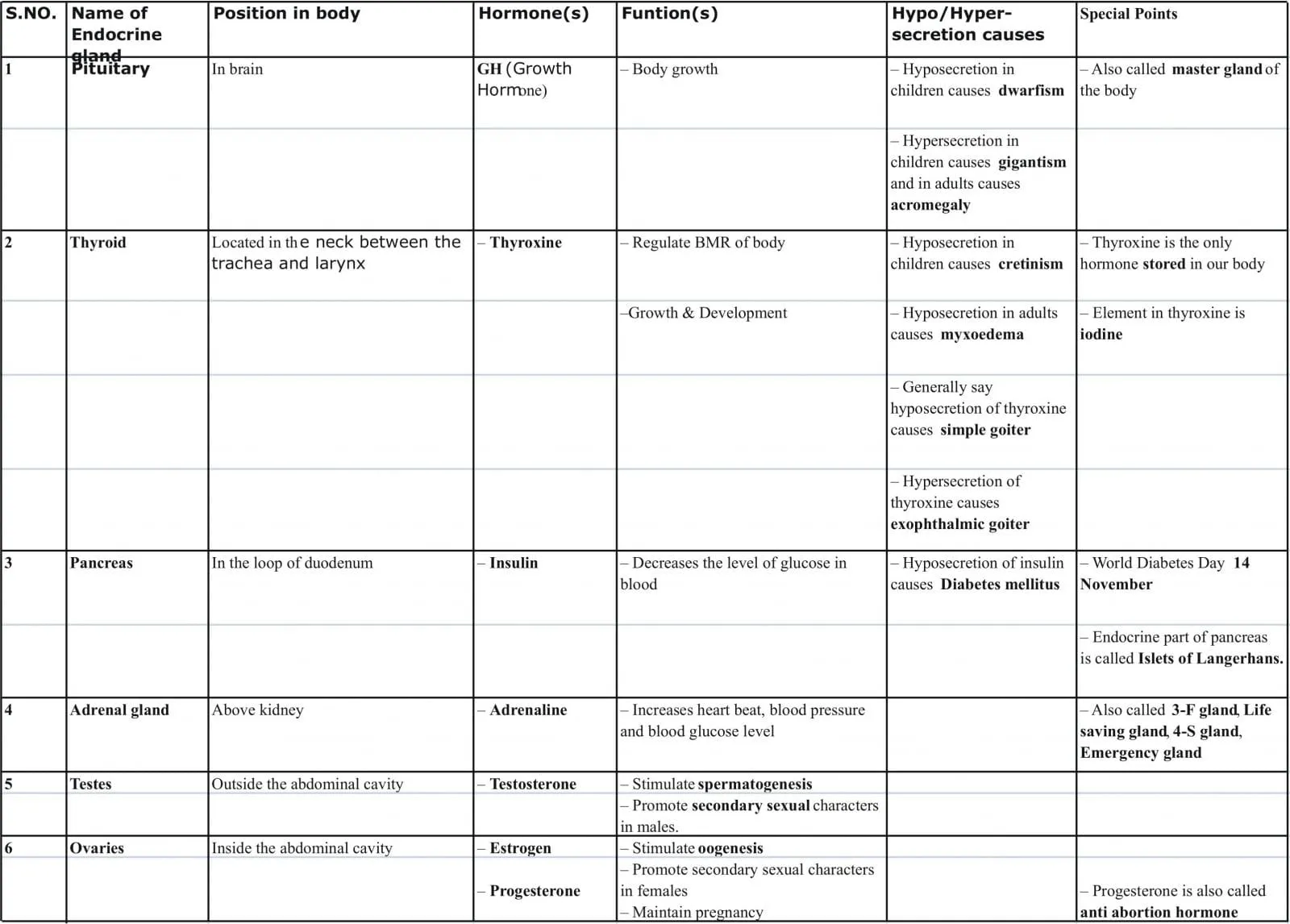
Various endocrine glands present in the human body are:
(i) Pituitary gland (or Hypophysis) (ii) Pineal gland
(iii) Thyroid gland (iv) Parathyroid gland
(v) Thymus gland (vi) Adrenal gland
(vii) Pancreas (viii) Ovaries
(iv) Testes
Review Questions
1. What are hormones?
2. What are endocrine glands?
3. What are the secretions of endocrine glands known as?
4. Distinguish between exocrine and endocrine glands.
5. Term "Hormone" was coined by ?
Q.1 What is the term used for secretions of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body?
Ans. Homones
Q.2 Define adolescence.
Ans. Adolescence is the period of life, when the body undergoes changes, leading to reproductive maturity.
Q.3 What is menstruation? Explain.
Ans. It fertilization does not occur, the released egg, and the thickened lining of the uterus along with its blood vessels are shed off. This causes bleeding in women which is called menstruation.
Q.4 List changes in the body that take place at puberty.
Ans. (i) Increase in height
(ii) Change in body shape
(iii) Change in voice
(iv) Increased activity of seat and sebaceous gland
(v) Reaching mental, intellectual and emotional maturity
(vi) Development of sex organs
(vii) Secondary sexual characters
Q.5 Prepare a table having two columns depicting names of endocrine glands and homones secreted by them.
Ans.
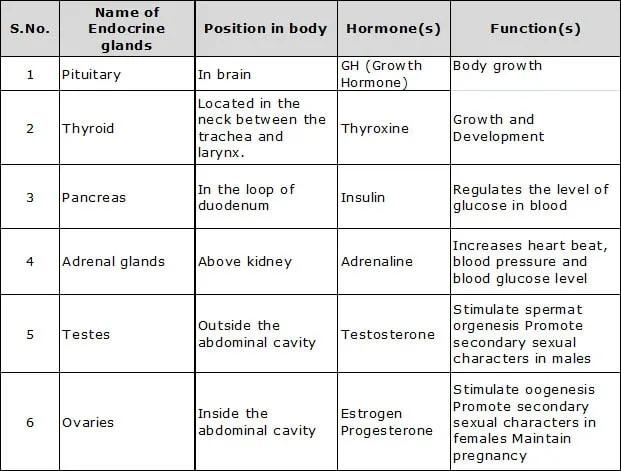
Q.6 Whata're sex hormones? Why are they named so? State their function.
Ans. The testes and ovaries secrete sex hormones. These hormones responsible for the male and female secondary sexual characters.
The male hormone or testosterone begins to be released by the testes at the onset of puberty. This causes changes in boys, for example, the growth of facial hair.
Once puberty is reached in girls, ovaries begin to produce the female hormone or estrogen which makes the breasts develop. Milk secreting glands or mammary glands develop inside the breasts.
Q.7 Write notes on
(a) Adam’s apple.
(b) Secondary sexual charcters.
(c) Sex determination in the unborn baby.
Ans. (a) At puberty, the voice box or the larynx begins to grow. Boys develop larger voice boxes. The growing voice boxes in boys can be seen as a protruding part of the throat called Adam's apple.
(b) Secondary sexual characters
The features which help to distinguish the male from the female, are called secondary sexual characters. The reproductive organs qre testes and ovaries which. produce the gametes, sperm in male and ova in female. Similar secondary sexual characters in male and females are: Growth of hairs under chest armpits and around public area. Increased activity of sweat and sebaceous glands. Oily skin and appearance of pimples. Darkening in skin colour of the genital area.
Secondary sexual characters in male
Widening of shoulders.
Deepening of voice.
Appearance of beard and moustaches.
Growth of sex organs (testes and penis).
Secondary sexual characters in female
Widening of pelvis and hips.
High pitch voice.
Initiation of menstrual cycle.
Growth of mammary glands (breasts).
Maturation of secondary sex organs like)alloplan tubes, uterus.
(c) When a sperm containing X chromosome fertilises the egg, the zygote would have two X chromosomes and develop into a female child. If the sperm contributes a Y chromosome to the egg (ovum) at fertilisation, the zygote would develop into a male child. The sex chromosomes of the father determine the sex of an unborn baby. The belief that the mother is responsible forh te sex of her baby is completely wrong and to blame her for this is totally unjustified.
Q.1 What is the term used for secretions of endocrine glands responsible for changes taking place in the body?
Q.2 How many chromosomes are there in the nuclei of human cell ?
Q.3 What is menstruation ?
Q.4 Name one male sex hormone.
Q.5 List the changes in the body that take place at puberty.
Q.6 Name the female sex hormone that ovaries secrete.
Q.7 What are hormones ?
Q.8 What does AIDS mean ?
Q.9 What do you mean by endocrine system ?
Q.10 What is the most conspicuous change during puberty ?
Q.11 Why is dwarfism caused ?
Q.12 What change in the voice body of the males can be seen during puberty ?
Q.13 What is the function of insulin in human body?
Q.14 Why is the father considered responsible for the sex of a baby ?
Q.15 Explain the secondary sexual characters in male and female individuals.
Q.16 What are sex chromosomes ? How are they different from other chromosomes ?
Q.1 Endocrine glands put their secretions directly into :-
(A) ducts (B) blood (C) both (D) none of these
Q.2 The first hormone to be isolated was :-
(A) thyroxine (B) testosterone (C) epinephrine (D) secretin
Q.3 According to the accepted concept of hormone action, if receptor molecules are removed from target organs :-
(A) the target organ will continue to respond to the hormone without any difference
(B) the target organ will continue to respond to the hormone but will require higher concentration
(C) the target organ will not respond to the hormone
(D) the target organ will continue to respond to the hormone but in the opposite way
Q.4 In an accident the anterior pituitary of a four year old boy was severely damaged but the boy survived. What is likely to happen :-
(A) High levels of thyroxine will be released (B) Spermatogenesis will be released
(C) The boy will not grow much in height (D) The growth of mammary glands will be stimulated
Q.5 A gorilla like man with huge hand and legs. This is due to the abnormal secretion of :-
(A) pituitary FSH (B) pituitary LH (C) pituitary GH (D) thyroid
Q.6 LH and FSH are called :-
(A) antistress hormones (B) gonadotropic hormones
(C) emergency hormone (D) neurohormones
Q.7 FSH is to estrogen as LH is to :-
(A) vasopressin (B) testosterone (C) progesterone (D) LTH
Q.8 In a pregnant woman having prolonged labour pains, its childbirth has to be hastened. It is advisable to administer a hormone that can :-
(A) activate the smooth muscles (B) increase the metabolic rate
(C) release glucose into the blood (D) stimulate the ovary
Q.9 Diabetes insipidus is the syndrome which results due to the :-
(A) failure of neurohypophysial system to inhibit the excess release of ADH
(B) failure of neurohypophysial system to produce or release ADH
(C) inability of pituitary to produce oxytocin
(D) inability of pituitary to release ACTH
Q.10 If a rat was given an injection of sodium iodide with radioactive iodine, then in which one of the following most of the iodine would be incorporated ?
(A) Cartilage (B) Thyroid (C) Lymph nodes (D) Parathyroid
Q.11 Failure of insulin production results in :-
(A) addison's disease
(B) cushing's disease
(C) diabetes insipidus
(D) diabetes mellitus
Q.12 The gland whose hormone affects the functions of many other endocrine glands is :-
(A) thyroid gland (B) pituitary gland (C) pancreas (D) parathyroid
Q.13 Injecting a tadpole with thyroxine would lead to :-
(A) giant but normal tadpoles (B) precocious metamorphosis
(C) stoppage of metamorphosis (D) atrophy of gonads
Q.14 A very high level of calcium in the blood suggests malfunction of the :-
(A) parathyroid (B) thyroid (C) thymus (D) adrenal gland
Q.15 Cortisone is used for the treatment of inflammation, allergy and arthritis. Which of the following endocrine glands produces cortisone:-
(A) Thyroid (B) Pancreas (C) Adrenal (D) Gonads
Q.16 A hormone secreted in a female body only :-
(A) Progesterone (B) Testosterone (C) Thyroxine (D) Adrenalin
Q.17 Sexual maturity in males obtained at the age of :-
(A) 12-13 years (B) 13-14 years (C) 14-15 years (D) 16-17 years
Q.18 Adolescents should be careful about what they eat, because :-
(A) Proper diet develops their brains
(B) Proper diet is needed for the rapid growth taking place in their body
(C) Adolescents feel hungry all the time
(D) Taste buds are well developed in teenagers
Q.19 The stage when the reproductive organs reach sexual maturity is called :-
(A) puberty (B) menstruation (C) gestation (D) fertilization
Q.20 Which of the following is not a part of female reproductive system ?
(A) ovary (B) oviduct (C) uterus (D) embryo
Q.21 Reproductive age in women starts when their:-
(A) Menstruation starts (B) Breasts starts developing
(C) Body weight increases (D) Height increases
Q.22 In a frog the process of metamorphosis is regulated by :-
(A) Insulin (B) Testosterone (C) Growth hormone (D) Thyroxine
Q.23 Sperms in male are produced in :-
(A) testes (B) urethra (C) epididymis (D) penis
Q.24 Which of the following constitutes the right meal for adolescents ?
(A) Chips, noodles, coke (B) Chapatti, dal, vegetables
(C) Rice, noodles and burger (D) vegetable cutlets, chips and lemon drink
Q.25 After fertilization the human embryo grows inside the :-
(A) uterus (B) ovary (C) fallopian tubes (D) zygote
Q.26 Secretions of endocrine glands are called :-
(A) enzymes (B) hormones (C) catalysts (D) sugars
Q.27 The features which help to distinguish the male from the female are called :-
(A) Sex chromosomes (B) Primary sexual characters
(C) Secondary sexual characters (D) All of these
Q.28 If fertilization doesn't occur, the ovum is released out of :-
(A) urine (B) menstrual cycle (C) sweat (D) None of these
Q.29 The fusion of male and female gametes usually takes place inside the :-
(A) uterus (B) ovary (C) fallopian tubes (D) zygote
Q.30 The process of release of ovum by the respective ovary is called as :-
(A) Ovulation (B) Menstruation (C) Menarche (D) Menopause
1. B 2. D 3. C 4. C
5. C 6. B 7. C 8. A
9. B 10. B 11. D 12. B
13. B 14. A 15. C 16. A
17. C 18. B 19. A 20. D
21. A 22. D 23. A 24. B
25. A 26. B 27. C 28. B
29. C 30. A
1. Define Adolescence ?
2. What do you mean by secondary sexual characters ?
3. What are endocrine glands.
4. Which gland is called the master endocrine gland ?
5. What is menarche ?
6. What do you mean by metamorphosis ?
7. What is the difference between menarche and menopause?
8. Name the hormones produced by testis and ovaries ?
9. What is adam’s apple ?
10. How sex of an individual determined ?
11. What is mensturation ?
12. Name the gland whose size gets reduced as the child grows?
13. Apart from Oestrogen, name the other female hormone produced by ovaries?
14. Which hormone causes sweating under fear?
15. What is the difference between the voice of boys and girls during adolescence?
16. Give the right word for:
(b) A gland in the neck, which when swollen causes goitre.
(c) A hormone which helps to balance the sugar in the body.
(d) An element without which thyroxine hormone is not form.
1. What is correct regarding puberty ?
(A) Sexual maturation take place
(B) Puberty includes physical changes
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
2. Largest part of female reproductive system :-
(A) Vagina (B) Uterus (C) Fallopian tubes (D) Ovaries
3. What is correct about testis :-
(A) Is an endocrine gland (B) Is the male gonad
(C) Is the male gamete (D) Both (A) & (B)
4. The formation of frog from tadpole depends on :-
(A) Cell division rate (B) Availibity of nutrients in water
(C) Availability of Iodine in water (D) High temperature
5. Release of ovum from the ovary is called :-
(A) Ovulation (B) Menstruation (C) Reproduction (D) All of these
6. In the male cells, the chromosomes are:-
(A) 22 pairs + XX (B) 22 pairs + XY (C) 23 pairs + XX (D) 23 pairs + XY
7. Hormone which maintain’s Ca+ level in the blood
(A) Growth hormone (B) Thyroid hormone (C) Parathormone (D) Testosterone
8. AIDS can be transmitted through:-
(A) Infected syringes (B) Sexual contact (C) Mother to foetus (D) All of these
9. Pituitary gland is located in :-
(A) Heart (B) Liver (C) Brain (D) Throat
10. Pimples on face at the time of adolescence is due to
(A) Increased activity of the sweat and oil glands on the skin
(B) Increased level of adrenal hormones in the body
(C) Increased Sensitiveness of the skin
(D) Contamination in the blood
· Fill in the blanks
1. Larynx is also called __________
2. Hormones reach there through blood stream __________
3. Term used for changes at adolescent is __________
4. Male sex hormone is _________
5. Protruding voice box in males is called _________
6. Glands without ducts are called ___________
7. Starting of menstruation___________
8. Gland that Secretes thyroxine is _____________
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. The gland which get disappear in old age.
(A) Thymus (B) Thyroid (C) Pancrease (D) Testis
2. Which is the largest gland of the body :-
(A) Liver (B) Thyroid (C) Digestive gland (D) Salivary gland
3. Which is the largest endocrine gland :-
(A) Pituitary (B) Hypothalamus (C) Parathyroid (D) Thyroid
4. Hormone necessary for normal growth of a person :-
(A) Insulin (B) Adrenaline (C) Growth hormone (D) Thyroxine
5. What is correct about Menstrual cycle
(A) Thickening of uterus (B) Maturation of egg
(C) Break down of uterine wall (D) All
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Pituitary gland (P) Testosterone
(B) Thyroid gland (Q) Insulin
(C) Testis (R) Growth hormone
(D) Ovaries (S) Thyroxine
(E) Pancreas (T) Oestrogen
· Comprehension
The human body undergoes several changes during adolescence. These changes marks the onset of puberty. The most important change which marks puberty in boys & girls is that they become capable of reproduction Puberty ends after reaching reproductive maturity.
1. Which of the follwoing is right regarding adolescence :-
(A) Duration from 11 to 19 years (B) Boys and Girls start appearing different
(C) Period of confusion and Hyper activity of body (D) All the above
2. What is wrong regarding adolescence
(A) Covers teens of life (B) Height shoots up
(C) Body shape changes (D)Mind has minimum learning capacity
3. Reproductive maturity means :-
(A) Capability to reproduce
(B) Development of reproductive organs
(C) Production of sex hormones
(D) All of these
· Match the following (one to many)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. One or more than one entries of column-I may have the matching with the some entries of column-II and one entry of column-II may have one or more than one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Pituitary (P) Endocrine gland
(B) Thyroid gland (Q) Stress hormone
(C) Adrenaline (R) Thyroxine
(D) Hormone required for proper growth of body (S) Growth hormone
1. (C) 2. (B) 3. (D) 4. (C) 5. (A)
6. (B) 7. (C) 8. (D) 9. (C) 10 (A)
1. Voice box 2. Target organ
3. Puberty 4. Testosterone
5. Adam’s apple 6. Endocrine glands
7. Menarche 8. Thyroid glands
1. (A) 2. (A) 3. (D) 4. (C) 5. (D)
1. (A-R, B-S, C-P, D-T, E-Q)
1. (D) 2. (D) 3. (D)
1. (A-PS, B-PR, C-PQ, D-S,)