WHAT IS LIGHT?
If we enter a dark room, the objects present in the room are not visible. However, if we switch on a bulb, everything in the room becomes visible. Why?
The bulb gives out an invisible energy called light. When this energy falls on the objects in the room, it bounces off from the surface of objects. When this energy enters our eyes, the eyes sense it and send a message to the brain. It is finally, the brain which really sees the objects. Eyes are only an aid in seeing the objects around us.
Why do we say that light is invisible ? Well, when light energy falls on the objects, we really do not see it. When energy bounces off from the surface of objects and enters our eyes, the sensation produced by this energy, helps our brain to see. Thus, to sum up we can say :
Light is an invisible energy, which causes in us the sensation of vision. When the light falls on any object, it bounces off from the surface of the object in all directions. This is called scattering of light.
DEFINITION
Light is form of energy which enables us to see objects which emit or reflect light.
Light is a type of (form of) energy which can produce sensation in our eyes. So we can experience the sensation of vision.
It travel in straight line in form of particles and waves. With the help of light we see all colours of nature.
Our eyes are mostly sensitive for yellow colour and least sensitive for violet and red colour. Due to this reason commercial vehicles are painted with yellow colour, sodium lamps are used in road lights.
OPTICS
It is a branch of physics which deals with the study of light. It is mainly divided into three parts :
(a) Geometrical optics or ray optics: It deals with the reflection and refraction of light.
(b) Wave or physical optics : It is concerned with nature of light and deals with interference, diffraction and polarisation.
(c) Quantum optics: It deals with the interaction of light with the atomic entities of matter such as photo electric effect, atomic exitation etc.
NATURE OF LIGHT
Theories about nature of light :
(a) Particle Nature of Light (Newton's corpuscular theory) :
According to Newton light travels in space with a great speed as a stream of very small particles called corpuscles.
According to this theory reflection and refraction of light are explained while this theory was failed to explain interference of light and diffraction of light. So wave theory of light was discovered.
(b) Wave Nature of Light:
Huygen consider the light remains in the form of mechanical rays and he consider a hypothetical medium like ether for propagation of light waves:
So, light waves are declared electromagnetic waves so there is no need of medium for the propagation of these waves. They can travel in vacuum also. The speed of these waves in air or in vacuum is maximum i.e., 3 × 108 m/s.
Photoelectric effect was not explained with the help of wave theory, so Planck gave a new theory which was known as quantum theory of light.
This theory is failed to explain photo electric effect.
(c) Quantum Theory of Light:
According to 'Planck' light travels in the form of energy packets or quanta's of energy called photons. The rest mass of photon is zero . Each quanta carries energy E =hv.
h --> Planck's constant = 6.6 x 10-34 J-s.
v --> frequency of light
Some phenomenon's like interference of light, diffraction of light are explained with the help of wave theory but wave theory was failed to explain the photo electric effect of light. It was explained with the help of quantum theory. So, light has dual nature.
(d) Dual Nature of Light:
De Broglie explained the dual nature of light, i.e wave nature and particle nature.
(i) wave nature: Light is electromagnetic waves it is transverse in nature and propagate in vacuum
(ii) Particle or Photon Nature : With the help of this theory Einstein explained the photo electric effect.
SOURCE OF LIGHT
A body which emits light or reflect the light falling on it in all possible direction is said to be the source of light. The source can be point one or an extended one. The sources of light are of two types :
(a) Luminous Source :
Any object which by itself emits light is called as a luminous source.
e.g.: Sun and stars (natural luminous sources), electric lamps, candles and lanterns (artificial luminous sources).
(b) Non-luminous Source :
Those objects which do not emit light but become visible only when light from luminous objects falls on them. They are called non-luminous sources.
e.g.: Moon, planets (natural non-luminous sources), wood, table (artificial non-luminous sources).
Substance through which light propagates or tends to propagate is called medium of light.
(i) Transparent Object :
Bodies that allow light to be pass through them i.e. transmit light through them, are called transparent bodies.
e.g.: Glass, water, air etc.
(ii) Translucent Object :
Bodies that can transmit only a part of light through them are called translucent objects.
e.g.: Frosted or ground glass, greased paper, paraffin wax.
(iii) Opaque Object :
Bodies that do not allow light to pass through them at all are said to be opaque object.
Eg. Chair, desk etc.
Note : Depending on composition optical medium are divided into two type.
(i) Homogeneous medium : An optical medium which has a uniform composition throughout is called homogeneous medium.
E.g. Vacuum, distilled water, pure alcohol, glass, plastics, diamond, etc.
(ii) Heterogeneous medium : An optical medium which has different composition at different points is called heterogeneous medium.
Eg. Air, muddy water, fog, mist, etc.
BEHAVIOUR OF LIGHT ATTHE INTERFACE OF TWO MEDIA
When light travelling in one medium falls on the surface of a second medium the following three effects may occur :
(i) A part of the incident light is turned back into the first medium. This is called reflection of light.
(ii) A part of the incident light is transmitted into the second medium along a changed direction. This is called refraction of light.
(iii) The remaining third part of light energy is absorbed by the second medium. This is called absorption of light.
CHARACTERISTICS OF LIGHT
Some common characteristics of light are given below :
(i) Light has dual nature i.e both wave and particle, nature.
(ii) Light is an electromagnetic wave.
(iii) Light does not require material medium for its propagation i.e. light can travel through vacuum.
(iv) The speed of light in free space (vacuum) is 3 × 108 m/s. lts speed is marginally less in air. lts speed decreases considerably in glass or water.
(v) Light undergoes reflection from polished surfaces such as mirrors, etc.
(vi) Light undergoes refraction when it goes from one medium to another.
RAY OPTICS
Ray optics treats propagation of light in terms of rays and is valid only if the size of the obstacle is much greater than the wavelength of light. It concern with the image formation and
deals with the study of the simply facts such as rectilinear propagation, laws of reflection and refraction by geometrical methods.
Ray :
A ray can be defined as an imaginary line drawn in the direction in which light is travelling. Light behaves as a stream of energy propagated along the direction
of rays. The rays are directed outward from the source of light in straight lines.
Beam of Light :
A beam of light is a collection of these rays. There are mainly three types of beams.
(i) Parallel beam of Light :
A search light and the headlight of a vehicle emit a parallel beam of light. The source of light at a very large distance like sun effectively gives a parallel beam.
(ii) Divergent beam of Light :
The rays going out from a point source generally form a divergent beam.
(iii) Convergent beam of Light :
A beam of light that is going to meet (or converge) at a point is known as a convergent beam. A parallel beam of light after passing through a convex lens becomes a convergent beam.
HOW WE SEE ?
When a light ray is falling (strike) on the surface of any object which reflect and reached to our eyes. Due to this our eyes feel a sensation then we see the object.
REFLECTION OF LIGHT
When rays of light falls on any object it return back in the same medium from the surface this phenomenon is called reflection of light. Due to reflection of light we can see all the nature.
1) Incident ray
The ray of light which falls on a polished surface (or a mirror) is called the incident ray of light.
2) Reflected ray
The ray of light which gets reflected from a polished surface (or a mirror) is called the reflected ray of light.
3) Normal
The normal is a line at right angle to the reflecting surface.
LAWS OF REFLECTION
(i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal to the surface at the point of incidence all lie in the same plane.
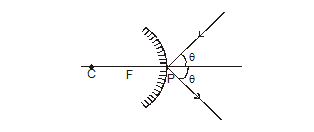
(ii) The angle of incidence (i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (r) i.e. i = r
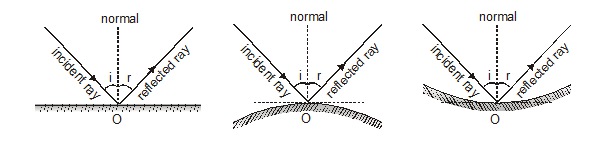
When a ray of light falls on a mirror normally or at right angle it gets reflected back along the same path.
(i) A ray of light striking the surface normally retraces its path.
Explanation
When a ray of light strikes a surface normally, then angle of incidence is zero i.e. Ði = 0. According to the law of reflection, Ðr = Ði, Ðr = 0 i.e. the reflected ray is
also perpendicular to the surface. Thus an incident ray normal to the surface (i.e. perpendicular to the surface) retraces its path as shown in figure.
(ii) Laws of reflection are also obeyed when light is reflected from the spherical or curved surface as shown in figure (a) and (b)
Depending on the nature of the reflecting surface there are two types of reflection :-
(i) Regular (specular) reflection (ii) Irregular (diffused) reflection
* Regular reflection :
The phenomenon due to which a parallel beam of light travelling through a certain medium, on striking become parallel beam, in some other fixed direction is called Regular reflection.
Regular reflection takes place from the objects like looking glass, still water, oil, highly polished metals etc.
Regular reflection is useful in the formation of images, e.g., we can see our face in a mirror only on account of regular reflection. However, it causes a very strong glare in our eyes.
* Irregular reflection or Diffused reflection :
The phenomenon due to which a parallel beam of light, travelling through some medium, gets reflected in various possible directions, on striking some rough surface is
called irregular reflection or diffused reflection.
The reflection which takes places from ground, walls, trees, suspended particles in air, and a variety of other objects, which are not very smooth, is irregular reflection.
Irregular reflection helps in spreading light energy over a vast region and also decreases its intensity. Thus, it helps in the general illumination of places and helps us to see things around us.
NOTE : Laws of reflection are always valid no matter whether reflection is regular or irregular.
RECTILINEAR PROPAGATION OF LIGHT
Definition :
In simplest terms, rectilinear propagation of light means that light energy travels in straight lines.
Examples of rectilinear propagation of light in everyday life :
(i) When the sunlight enters through a small hole in a dark room, it appears to travel in straight lines.
(ii) The light emitted by the head light of a scooter at night appears to travel in straight lines.
(iii) lf we almost close our eyes and try to look towards a lighted bulb, it appears to give light in the form of straight lines, which travel in various direction.
Experiment to prove rectilinear propagation of light :
Take three wooden upright A, B and C having a small hole in the middle, such that the holes are at the same height from the base. Arrange the uprights along the edge
of a table, such that holes are in the same straight line. Place a lighted candle towards the upright A, such that it is facing the hole. Look through the hole of upright C. The
candle flame is clearly visible.Now displace upright B, slightly towards right or left. It is seen that candle flame is no longer visible. This shows that light travels in straight lines.
Reflecting material
The material or matter which reflect the light rays is called reflecting material. There are two types of reflecting material.
(i) Good reflector (ii) Deem reflector
(i) Good reflector : The material which reflect all the incident light rays is called good reflector.
OR
This types of reflectors are reflected maximum incident light rays these type of reflector makes regular reflection like mirror.
(ii) Deem (Medium) Reflector : In this type of reflector, mostly part of incident rays are reflected. But some part is observed or transmitted by them irregular or
diffused reflection are made by them like rough surface.
For making a reflector, a glass plate is polished one side by silver or nickel type material.
MIRROR
A smooth, highly polished reflecting surface is called a mirror.
When a glass plate is polished on one sided with reflecting material such silver or nickel then is becomes a mirror.
From the reflecting surface of mirror there are two types of mirror.
Mirror at the hair dresser shop
From the reflecting surface of mirror there are two types of mirror.
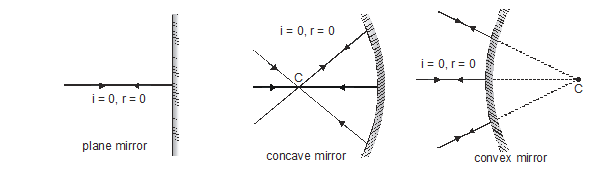
(i) Plane mirror (ii) Spherical or curved mirror
(i) Plane mirror : A highly polished plane surface is called a plane mirror or if a flat (totally plane) surface of a glass plate is polished one side of reflecting material is called plane mirror.
(ii) Spherical mirror : A mirror whose polished, reflecting surface is a part of hollow sphere of glass is called a spherical mirror. For a spherical mirror, one of the two curved
surfaces is coated with a thin layer of silver followed by a coating of red lead oxide paint. Thus one side of the spherical mirror is made opaque and the other side acts as a
reflecting surface. For the polishing side there are two type of spherical mirror.
(A) Convex mirror (B) Concave mirror
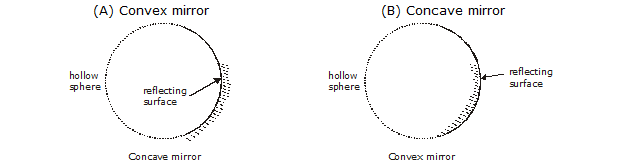
(A) Concave (Converging) mirror : A spherical mirror whose inner hollow surface is the reflecting surface.
(B) Convex (diverging) mirror : A spherical mirror whose outer bulging out surface is the reflecting surface.
* Formation of Image in a plane mirror
P is an object which is placed in front of a plane mirror AB as shown in fig. Rays PO and PO' starting from P falls on mirror
then these rays are reflected in OR and O'R' directions respectively. When the reflected rays enter the eye then they appear to diverge
from P'. P' is called the image of object P.
Following are the properties of the image formed by a plane mirror
(i) Image is always virtual (ii) Image lies as far behind the mirror as the object is infront of it.
(iii) The size of image is the same as the object. The only difference is that the right side of an object appears to be left in the image and vice versa. This effect
is known as lateral inversion. Lateral inversion is shown in fig.
* Uses of plane mirrors
(i) They are used as looking glass.
(ii) They are used by barbers to show the customer the back side of his head.
(iii) They are used for signaling by the scouts and the army personnel.
(iv) They are used by the opticians to provide false dimension, when their place of work is very small.
(v) They are used for providing false dimensions in show cases, displaying jewellery, wrist watches, etc. Two plane mirrors are fixed to the opposite sides of the show case, such that their reflecting surfaces face each other. This leads to the formation of multiple images.
(vi) They are used for reflecting the rays of the sun inside the solar cooker.
(vii) They are used for making toys like kaleidoscope. In this toy, three plain mirrors are inclined at an angle of 60°, and fixed in a tube. Some broken bangles are placed
inside the tube. When the tube is turned, the image of bangles form beautiful hexagonal patterns.
(a) Aperture : The effective width of a spherical mirror from which reflection can take place is called its aperture AA' & BB'.
The line joining the end points of a spherical mirror is called the aperture or linear aperture.

(b) Pole (Vertex) : The centre of a spherical mirror is called its pole it is denoted by letter P.
(c) Centre of curvature : The centre of the hollow sphere of which the spherical mirror is a part is called centre of curvature. It is denoted by letter C.
(d) Radius of curvature : The radius of the hollow sphere of which the spherical mirror is a part called the radius of curvature (R).
(e) Principal axis : The straight line passing through the centre of curvature C and the pole P of the spherical mirror.

(f) Normal : The normal at any point of the spherical mirror is the straight line obtained by joining that point with the centre of curvature C of the mirror.
(g) Principal focus or focus : The point on the principal axis where all the rays coming from infinity (parallel rays) after reflection either actually meets or appears
to meet is called the focus (or focal point) of the mirror. It is denoted by letter F.
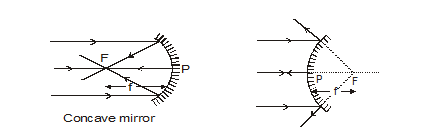
(h) Focal length :– The distance between the pole (P) and the focus (F) is called focal length (f) and
(i) Focal plane :- An imaginary plane passing through the focus and at right angles to the principal axis.
(j) Real Image :- When the rays of light after getting reflected from a mirror (or after getting refracted from a lens) – actually meet at a point, a real image
is formed. A real image can be obtained on a screen.
(k) Virtual image : When the rays of light after getting reflected from a mirror (or after getting refracted from a lens) appear to meet at a point, a virtual image
is formed. Such an image can only be seen through a mirror (or a lens) but cannot be obtained on a screen.
(l) paraxial Rays : The ray which have very small angle of incidence are known as paraxial rays.
The reflection of light rays and formation of images are shown with the help of ray diagrams. Some typical incident rays and the corresponding reflected rays are shown below.
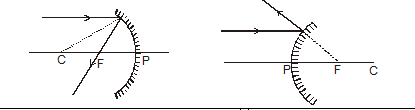
(i) A ray passing parallel to the principal axis, after reflection from the spherical mirror passes or appears to pass through its focus (by the definition of focus)

(ii) A ray passing through or directed towards focus, after reflection from the spherical mirror becomes parallel to the principal axis (by the principal of reversibility of light).
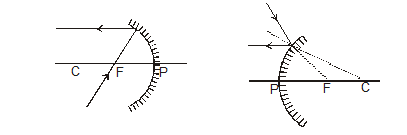
(iii) A ray passing through or directed towards the centre of curvature, after reflection from the spherical mirror, retraces its path (as for it Ði = 0 and so Ð r = 0)
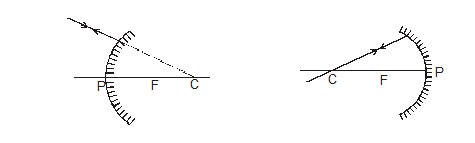
(iv) It is easy to make the ray tracing of a ray incident at the pole as shown in below.
Use of Concave mirror
(i) It is used as a shaving mirror.
(ii) It is used as a reflector in the head light of vehicles.
(iii) It is used by doctor to focus a parallel beam of light on a small area.
Uses of Convex mirror
(i) It is used as a rear view mirror in automobile.
(ii) It is used as a reflector for street light.
Note : A plane mirror is not useful as a rear view mirror, because its field of view is very small.
A plane mirror forms an image of an object placed before it. This is the result of a single reflection of light.
What happens if the object is placed between two mirrors that are at an angle to each other ? Let us find out.
Each of the mirrors will form an image due to reflection. Each of these images is formed by a single reflection.
These images are laterally inverted. In addition, an image is formed at the edge where the mirrors meet.
This image is formed by rays that get reflected twice. As a result, this image is not laterally inverted. So,
the left and right sides of the arrow and the word 'left' appear the correct way round in this image.
NOTE : The number of images of an object placed between two mirrors can be found from the following formula.
When the angle between the mirrors is 90°, the number of images is (360°/90°) – 1 = 4 – 1 = 3. Similarly, when the angle is 60°, the number of images is (360°/60°) – 1 = 6 – 1 = 5.
KALEIDOSCOPE
The kaleidoscope is a device that uses reflections to produce patterns. It consists of mirrors inclined to each other. The mirrors form multiple images
of objects in front of them. This creates beautiful patterns, which change when the kaleidoscope is rotated or shaken.
PERISCOPE
The working of a periscope is based on the principle of successive reflections from two plane mirrors. It consists of two plane mirrors M1 and M2 facing each other fixed
at 45° to the framework of a tube which is bent twice at right angle (fig a). A beam of light from some object is turned through one right angle by the mirror M1. In the
same way the light is deviated through another right angle by the mirror M2. Therefore, the object is seen by the eye in spite of the obstacle. This arrangement can be used
by a person to see a match over the heads of a few people while standing at the back of the crowd.
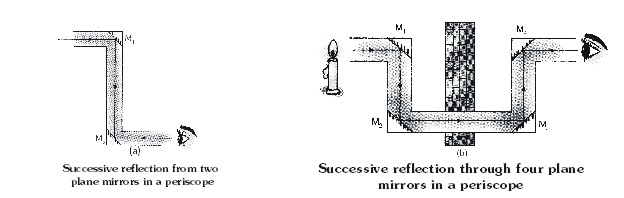
Even an object can be seen through a wall as well by an arrangement as shown in fig.(b) In this case, light from the candle is reflected by four
mirrors M1, M2, M3 and M4 before reaching the eye. Therefore, the candle is seen through the wall.
LATERAL INVERSION IN A PLANE MIRROR
When we place any object in front of a plane mirror, its image is such that its left hand side is seen on the right hand side and the right side is seen on the left.
Fig (a) shows a boy as you will see him when he stands before you. Now, make him stand in front of a mirror and see his image fig (b). Note that the
flower on the coat now appears to be on the right side, and when you see him directly the flower on the coat is on the left side. Similarly, if you write with
your right hand, the image in the mirror shows as if you are writing with your left hand.
This phenomenon of left appearing right and right appearing left on reflection in a plane mirror is called the lateral inversion
Fig. (c) illustrates another example of a lateral inversion. If you write letters 'ABC' on a piece of paper, they will look like . When see in the mirror.
You can see that the letter A has gone from the left side to the right side in the mirror. Not only this, but each letter has gone through a lateral inversion.
Letter 'B' becomes and 'C' has become . Can you now tell why 'A' remains as 'A', when seen in the mirror?
Characteristics of an image formed by a plane mirror :
Thus, we summarize that the image formed in a plane mirror has the following characteristics :
1. The image is virtual and erect.
2. The image is laterally inverted.
3. The image is formed behind the mirror and has the same size as that of the object.
4. The image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it.
I. Definition :
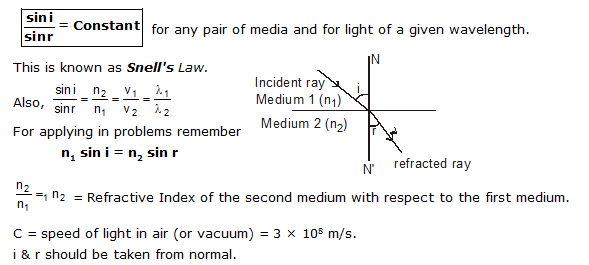
When light rays travelling in one medium are incident on a transparent surface (medium), they are bent as they travel in second medium.
Fig. Refraction of light from a plane transparent denser surface.
II. Definitions of some associated terms
1. Transparent surface : The plane surface which refracts light, is called transparent surface. In diagram, XY is the section of a plane transparent surface.
2. Point of incidence : The point on transparent surface, where the ray of light meets it, is called point of incidence. In diagram, Q is the point of incidence.
3. Normal : Perpendicular drawn on the transparent surface at the point of incidence, is called normal. In diagram, N1QN2 is the normal on surface XY.
4. Incident ray : The ray of light which strikes the transparent surface at the point of incidence, is called incident ray in diagram PQ is the incident ray.
5. Refracted ray : The ray of light which travels from the point of incidence into the other medium, is called refracted ray. In diagram, QR is the refracted ray.
6. Angle of incidence : The angle between the incident ray and the normal on the transparent surface at the point of incidence, is called the angle of incidence.
It is represented by the symbol i. In diagram, angle PQN1 is the angle of incidence.
7. Angle of refraction : The angle between the refracted ray and the normal on the transparent surface at the point of incidence, is called angle of refraction.
It is represented by symbol r. In diagram angle RQN2 is the angle of refraction.
(a) The incident ray, the normal to any refracting surface at the point of incidence and the refracted ray all lie in the same plane called the plane of incidence or plane of refraction.
(b) for any pair of media and for light of a given wavelength.
* Refractive index in terms of wave nature of light
1. Introduction : Light has a wave nature. The waves have a definite velocity. In air (strictly vacuum) light has velocity 3 × 108 m/s. It is represented by the symbol c. It is a universal constant.
2. Expression :
Velocity of light in air = c
Velocity of light in denser medium = n
Then, µ = is called the refractive index of the denser medium with respect to air.
3. Successive refraction : For light going from air to water to glass and to air finally.

SPHERICAL LENS
1. Definition : A piece of a transparent medium bounded by atleast one spherical surface, is called a spherical lens.
2. Types : There are two types of spherical lenses:
(i) Convex or Converging Lenses : These are thick in the middle and thin at the edges.
(ii) Concave or Diverging Lenses : These are thin in the middle and thick at the edges.
There are three types of convex lenses :
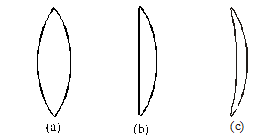
(a) Double Convex Lens : It has both the surfaces convex.
(b) Plano–Convex Lens : It has one surface plane and the other surface convex.
(c) Concavo–Convex Lens : It has one surface concave and the other surface convex.
* Different types of concave lenses
There are three types of concave lenses :
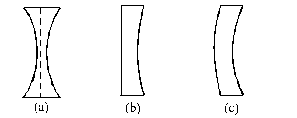
Fig. Three types of concave lenses
(a) Double Concave Lens : It has both the surfaces concave. (Fig.)
(b) Plano–Concave Lens : It has one surface plane and the other surface concave. (fig.)
(c) Convexo–Concave Lens : It has one surface convex and the other surface concave. (fig.)
IMAGE FORMATION
I. Rules
1. Incident on the lens parallel to principal axis : After refraction from the lens, it actually passes through second principal focus F2 (in case of a convex lens) or appears to come from the second principal focus F2 (in case of a concave lens).
2. Incident on the lens through first principal focus : F1 (in case of a convex lens) in direction of first principal focus F1 (in case of a concave lens)
After reflection from the lens it goes parallel to the principal axis.
3. Incident on the lens in direction of optical centre : It passes undeviated through the lens.
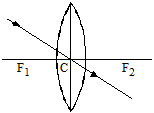
II. Three Special rays for convex lens
1. When light ray incident parallel to principal axis.
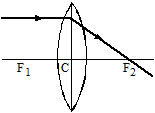
2. When light ray incident from focus.
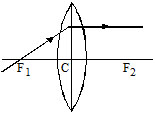
3. When light ray incident on the pole.
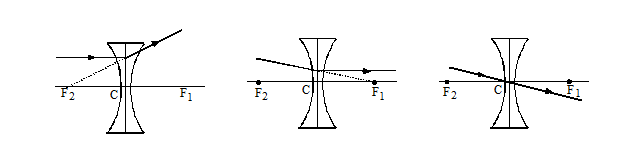
III. Three Special rays for concave lens
1. When light ray incident parallel to principal axis.
POWER OF A LENS
* Definition : It is the capacity or the ability of a lens to deviate (converge or diverge) the path of rays passing through it. A lens producing more converging
or more diverging, is said to have more power
* Relation with focal length : A lens of less focal length, focuses a parallel beam of light at near point. It produces more converging or more diverging.
It is said to have more power.
Hence, power µ i.e., P µ
We have, P =
* Unit : Units of power is Dioptre (D). One Dioptre is the power of a lens of focal length 1 m.
In general, P (Dioptre) = =
CRITICAL ANGLE
The angle of incidence in denser medium for which angle of refraction is 90º, is called the critical angle. It is represented by the symbol C.
In diagram, i3 = C because r3 = 90º.
Angle C µ
[Note: More is the value of µ, lesser will be angle C, more are the changes of total internal reflection.]
* Condition
(i) Light must travel from denser to rarer medium.
(ii) Light must be incident at an angle more than the critical angle for the denser medium.
Merit : In total internal reflection 100% light is reflected, hence images formed are more bright.
in ordinary reflection from mirrors, only 85% light is reflected, rest 15% is either absorbed by mirror glass or transmitted due to poor polish. Images formed by ordinary reflection are less bright.
TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION
1. Definition : When light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium and is incident at an angle more than the critical angle for that medium, it is
completely returned inwardly in the denser medium. This complete inward return of light is called total (complete) internal (inward) reflection (return).
Fig. Total internal reflection
DISPERSION OF LIGHT BY A PRISM
* Definition : When a ray of white light (sunlight) enters a glass prism (denser medium). It emerges out from it broken into seven colours.
This phenomenon, due to which different components of a white light are separated by a denser medium, is called dispersion (separation).
* Explanation : It is due to different velocities of different components of white light in the denser medium.
White light has seven colours, namely, violet indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red (remembered by the word VIBGYOR). In air (strictly in vacuum)
light waves of all colours have same velocity (3 × 108 m/s).
But in a denser medium, their velocities become less and different. Red light waves, being longest in length, travel fastest and have maximum velocity.
Violet light waves, being shortest in length, travel slowest and have minimum velocity in the denser medium.
The refractive index (m)of a medium for a wave is given by the relation.
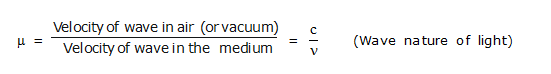
Since n is maximum for red light waves and minimum for violet light waves. m is minimum for red light and maximum for violet light.
The prism produces deviation (change in direction) in a light wave. The angle of deviation ‘D’ produced by a prism of angle ‘A’ is given
by D = (m – 1) A. Red light waves suffer least deviation, whereas violet light waves suffer maximum deviation. [Fig.]
Due to difference in deviation, waves of different colours emerge out from the prism indifferent directions and are said to have been dispersed (separated).
When the dispersed white light is made to fall on a white screen, we get a seven coloured band or light. This coloured band is called spectrum.
HUMAN EYE
* Introduction : It is the most delicate and complicated natural optical instrument.
* Construction
Diagram shows the section of a human eye by a horizontal plane. It is a spherical ball of diameter about 2.5 cm. Its essential parts are described below :
* Sclerotic : It is the outermost coating of the eye ball. It is tough, white and opaque and forms white of the eye. It keeps eye ball in spherical shape and protects it from shocks and injury. It becomes transparent at the front projected part of eye ball, called cornea.
* Choroid : It is the second coat under the sclerotic. It is a black membrane and forms black of the eye. Its function is to keep interior of the eye dark by absorbing diffused light falling on it. It forms coloured portion, called iris, behind the cornea.
* Retina : It forms innermost coat in the interior of the eye. It consists of a thin membrane which is rich in nerve fibres, containing two kinds of vision cells called rods and cones and blood vessels. It is sensitive to light, for it is a continuation of the optic nerves. It serves the purpose of a sensitive screen for the reception of the image formed by the lens system of the eye.
[The rods are responsible for vision in dim light (Scotopic vision). The cones are responsible for vision under ordinary day light (Photopic vision).
The retina possesses following two important spots :
(a) Yellow spot : The yellow spot Y. It is situated at the centre of the retina. It is a slightly raised spot with a minute depression in its peak. It is yellow in colour and most sensitive to light. The central region of the yellow spot is called the fovea centralis.
(b) Blind spot : The blind spot B. It is the spot where the optic nerves enter the eye. It is also slightly raised and insensitive to light, because it is not covered with choroid and retina.
* Cornea : It is the front bulged out part of eye ball covered by transparent sclerotic.
Cornea of the eye-front view.
* Iris : It is the coloured region under cornea formed by choroid. Its colour differs from person to person and country to country. It is this colour which is given to the eye of a person.
* Pupil : It is central circular aperture in the iris. Its normal diameter is 1 mm but it can contract in excess light and expand in dim light, by means of two sets of involuntary muscular fibres.
* Crystalline lens : It is a double convex lens L immediately behind iris. Its back (inner) surface is more convex (R2 = 6mm) than front (outer) surface (R1 = 10 mm). This is made of transparent concentric layers whose optical density increases towards the centre of the lens. The average refractive index of crystalline lens is 1.437.
The crystalline lens divides the interior of the eye ball into two spaces called chambers. The front chamber (towards cornea), is called the anterior chamber (A). The back chamber (towards retina) is called the posterior chamber (P).
* Ciliary muscles : The lens is connected of the sclerotic by the ciliary muscles. These muscles change thickness of the lens by relaxing and exerting pressure. The lens thickness is minimum (3.6 mm) when muscles are relaxed. The thickness becomes maximum (4 mm), when muscles exert maximum pressure (within elastic limit).
* Aqueous humour : Anterior chamber is filled with a transparent liquid of refractive index. The liquid is called the aqueous humour.
* Vitreous humour : Posterior chamber is filled with a transparent watery liquid with little common salt having some refractive index. The liquid is called the vitreous humour.
* Optic axis : The straight line passing through the centre of the cornea and the lens, is called optic axis of the eye.
* Visual axis : The line passing through centre of the lens and fovea centralize is called
visual axis of the eye. When an object is to be seen more minutely, it is brought on the visual axis to get its image on yellow spot which is most sensitive part of the retina.
* Working (Action of the eye)
The cornea and the aqueous humour both having same refractive index, form a single homogeneous medium. Rays of light entering the eye suffer first refraction in this region.
The crystalline lens of mean refractive index. produces second refraction. The vitreous humour of refractive index produces third refraction.
After these three refractions, light rays fall on retina forming a real and inverted image of object seen. The sensation produced on the eye is communicated to the brain by the optic nerves. The brain interprets this inverted image as erect.
* Focusing by eye lens
When seeing objects at infinity, ciliary muscles are perfectly relaxed and lens has least thickness of 3.6 mm. The image is formed at retina. The eye has its far point (F) at infinity.
The distance between the near point and the far point is called range of vision of the eye. Within the range of vision, there is one point where object placed are most distinctly visible. The distance of this point, from the eye, is called least distance of distinct vision. For normal eye this least distance is 25 cm.
The power (ability) of the eye to change the focal length of the eye lens with the change in the distance of the object, is called power of accommodation of the eye.
* Power of accommodation
(Range of variation of power) the power of accommodation is 4 Dioptres. PA = 4D.
Defects of vision, symptoms and remedy (correction)
The major defects of vision are :
1. Short sightedness or myopia.
2. Long sightedness or hypermetropia.
3. Presbyopia
4. Astigmatism.
1. Short sightedness or myopia
* Symptoms : This defect is a born defect. With this defect, the eye can see near very clearly and distinctly, but distance objects are not clearly visible. The defective eye
cannot see clearly beyond a certain distance. It means that the far point of the defective eye has shifted from infinity to a finite distance ahead.
* Reasons : It is so because the image of distant objects is formed in front of the retina. It is shown in fig.
(a) seeing objects at its far point (b) seeing objects at normal eye far point F

Fig. Myopic eye vision
* Causes : It may be due to any one or both of the following two factors.
(i) The lens may be thicker (more converging) that the normal eye lens.
(ii) The eye ball may be elongated, as shown in fig. Due to elongation, distance between lens and retina becomes more than that for normal eye.
Elongated eye
* Correction : The extra converging power of eye lens in compensated by using a concave (diverging) lens of proper power (focal length) as shown in fig.
Myopia corrected by a concave lens
* Explanation : The concave lens kept just in front of the eye, receives distant parallel rays and diverges them. On eye lens the rays fall as if coming from far point F’ of the defective eye. The eye lens focuses them at retina. In a way, the concave lens used makes a virtual image of distant (out of range) object within range of vision.
The lens used must have focal length equal to the distance of the far point from the eye
(–ve sign means concave lens).
2. Long sightedness or hypermetropia
* Symptoms : This defect is a born defect. With this defect, the eye can see distant objects very clearly and distinctly, but near objects are not clearly visible.
The defective eye cannot see clearly within a certain distance. It means that the near point of the defective eye has shifted from 25 cm to some more distance behind (away).
* Reason : It is so because the image of near objects is formed behind the retina. It is shown in fig.
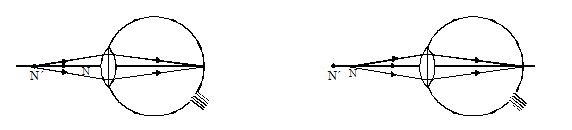
(a) seeing objects at its near point N’ (b) seeing objects at normal eye near point N
Hypermetropic eye vision
* Causes : It may be due to any one or both of the following two factors :
(i) The eye lens may be thinner (less converging) than the normal eye lens.
(ii) The eye ball may be oval as shown in fig. Due to oval shape, distance between lens and retina becomes less than that for normal eye.
* Correction. The deficiency in converging power of eye lens is compensated by using a convex (Converging) lens of proper power (focal length) as shown in fig.
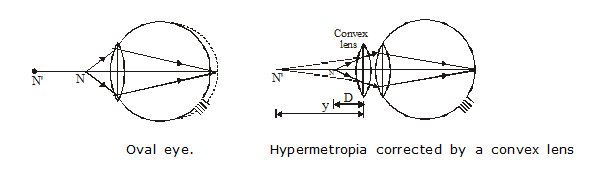
Oval eye. Hypermetropia corrected by a convex lens
3. Presbyopia
The power of accommodation of the eye usually decreases with ageing. For most people, the near point gradually recedes away. They find it difficult to see nearby objects comfortably and distinctly without corrective eye-glasses. This defect is called Presbyopia.
It arises due to the gradual weakening of the ciliary muscles and diminishing flexibility of the eye lens. Sometimes, a person may suffer from both myopia and hypermetropia.
Such people often require bi-focal lenses. A common type of bi-focal lenses consists of both concave and convex lenses. The upper portion consists of a concave lens. It facilitates distant vision. The lower part is a convex lens. It facilitates near vision. These days, it is possible to correct the refractive defects with contact lenses or through surgical interventions.
4. Astigmation
A person suffering from this defect cannot simultaneously focus on both horizontal and vertical lines of a wire gauze.
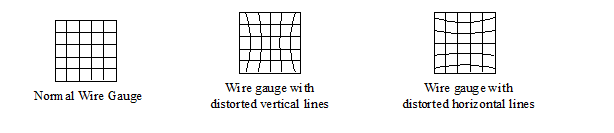
This defect arises due to the fact that the cornea is not perfectly spherical
This defect can be corrected by using cylindrical lens
REFRACTION IN NATURE
(A) FORMATION OF RAINBOW
A rainbow is a natural spectrum appearing in the sky after a rain shower. It is caused by dispersion of sunlight by tiny water droplets, present in the atmosphere. A rainbow is always formed in a direction opposite to that of the Sun. The water droplets act like small prisms. They refract and disperse the incident sunlight, then reflect it internally, and finally refract it again when it comes out of the raindrop. Due to the dispersion of light and internal reflection, different colours reach the observer’s eye.
(B) ATMOSPHERIC REFRACTION
We can observe the apparent random wavering or flickering of objects seen through a turbulent stream of hot air rising above a fire or a radiator. The air just above the fire becomes hotter than the air further up. The hotter air is lighter (less dense) than the cooler air above it, and has a refractive index slightly less than that of the cooler air. Since the physical conditions of the refracting medium (air) are not stationary, the apparent position of the object, as seen through the hot air, fluctuates. This wavering is thus an effect of atmospheric refraction (refraction of light by the earth’s atmosphere) on a small scale in our local environment. The twinkling of stars is a similar phenomenon on a much larger scale.
(a) Twinkling of stars :
The twinkling of a star is due to atmospheric refraction of starlight. The starlight, on entering the earth’s atmosphere, undergoes refraction continuously before it reaches the earth. The atmospheric refraction occurs in a medium of gradually changing refractive index.
Since the stars are very distant, they approximate point-sized sources of light. As the path of rays of light coming from the star goes on varying slightly, the apparent position of the star fluctuates and the amount of starlight entering the eye flickers – the star sometimes appears brighter, and at some other time, fainter, which is the twinkling effect.
(b) Why don’t the planets twinkle?
The planets are much closer to the earth, and are thus seen as extended sources. If we consider a planet as a collection of a large number of point-sized sources of light, the total variation in the amount of light entering our eye from all the individual point-sized sources will average out to zero, thereby nullifying the twinkling effect.
(C) Advance sunrise and delayed sunset :
Advance sunrise and delayed sunset The Sun is visible to us about 2 minutes before the actual sunrise, and about 2 minutes after the actual sunset because of atmospheric refraction. By actual sunrise, we mean the actual crossing of the horizon by the Sun. figure shows the actual and apparent positions of the Sun with respect to the horizon. The time difference between actual sunset and the apparent sunset is about 2 minutes. The apparent flattening of the Sun’s disc at sunrise and sunset is also due to the same phenomenon.
Ex.1 Distinguish between real and virtual image.
Sol. Differences :
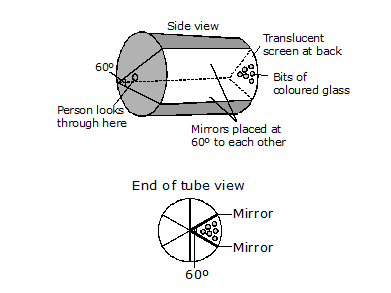
Ex.2 How many plane mirror strips do we use in a kaleidoscope. At what angle are they inclined with respect to each other?
Sol. The kaleidoscope uses a set of three equal size plane mirror strips. The three strips are inclined to each other at angles of 60° each.
Ex.3 What is short sightedness? How is it corrected?
Sol. A person with shorts sight can see nearly objects but not far away objects. It can be corrected by using a concave lens.
Ex.4 What is long sightedness? How is it corrected?
Sol. A person with long sight can see far away objects clearly but cannot see nearby object clearly. It can be corrected by using a convex lens.
Ex.5 Why should children take milk and eat carrots?
Sol. Milk, carrots and yellow fruits are rich in vitamin A, which is very essential for the eyes to maintain good vision.
Ex.6 Is the moon a luminous body? How are we able to see the moon?
Sol. The moon is non-luminous. We are able to see the moon because it reflects the sunlight falling on it.
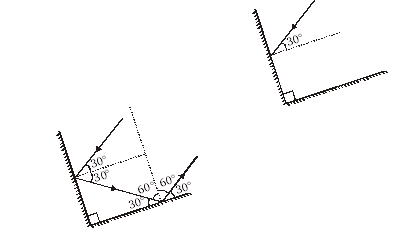
Ex.7 Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30° as shown in fig. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
Ex.8 How are we able to see objects?
Sol. The lens focuses the light on the back of the eye on the retina. Retina contains several nerve cells which transmit the sensations to brain through the optic nerve. We are then able to see the objects.
Ex.9 What are cones and rods? What are their function?
Sol. Cones are the nerve endings which are sensitive to colour light. They help us to distinguish between colours. Rods are the nerve ending which are sensitive to bright light.
Ex.10 (i) In a periscope two mirrors are arranged parallel to each other but they do not form multiple images. Why?
(ii) What is the use of periscope?
Sol. (i) In a periscope two mirrors are placed parallel and facing each other but are in an inclined position at an angle of 45°. So that do not form multiple images.
(ii) Uses of periscope – In submarines to view the happening on the surface of water.
– to view objects behind the wall.
Ex.11 Draw a diagram to show dispersion of light.
Sol. 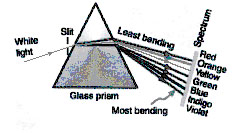
Ex.12 (i) What is spectrum?
(ii) What is the meaning of VIBGYOR?
Sol. (i) Spectrum is the band of seven colours obtained on the screen when white light splits on passing through a prism.
(ii) VIBGYOR represents the seven colours of the spectrum, i.e. violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red.
Ex.13 How is a rainbow formed ?
Sol. The water droplets suspended in the air after the rain act as prisms. When the sun is towards the horizon the inclined rays pass through the water drops to disperse into the seven colours of the spectrum.
Ex.14 Why does white light disperse when it passes through a glass prism?
Sol. White light is a combination of seven colours of light. The speed of each colour is different. So, while passing through the glass prism each colour deviates by different amounts. Therefore, dispersion of light into a spectrum takes place.
Ex.15 (i) Which part of the human eye makes a person 'blue eyed' ?
(ii) What role is played by ciliary muscles?
(iii) What is the importance of retina in the eye?
Sol. (i) Iris is responsible for making the person blue eyed.
(ii) Ciliary muscles help to adjust the focal length of the lens to view all objects clearly.
(iii) The image of the object is formed on the retinal of the eye.
Ex.16 What is the difference between the eye of the night birds and day birds?
Sol. The day birds can see clearly during the day but not at night. The day birds have more cones and less rods. The cones are sensitive to bright light and can sense colours. Night birds can see clearly at night but not during the day. Their eyes have a large cornea and pupil to allow more light to pass. Also their retinal has mostly rods and few cones. Rods are more sensitive to dim light.
Ex.17 How can you compare human eye with a photographic camera?
Sol.
Ex.18 Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Sol. To make a kaleidoscope, get three rectangular strips of glass 15 cm long and 4 cm wide each. Join them together to form a prism. Fix them with a few thick chart papers in a slightly long circular tube. Close one end of the tube by a cardboard disc having a hole in centre. At the other end touching the mirrors fix a circular plane glass sheet. Invert the tube and place some broken small pieces of coloured bangles on the glass plate. Close this end of the tube by a ground glass plate.
Ex.19 Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Sol. We can take care of our eyes in the following ways –
(a) have a regular check up. (b) if advised, use suitable spectacles.
(c) avoid too much or too little sight. (d) wash your eyes frequently with clean water.
(e) always read at the normal distance for vision.
Ex.20 Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in figure. Can he see himself in the mirror? Also can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q and R?
Sol. Yes, Boojho can see his image. Yes, he can see the objects situated at P, Q and R.
Ex.21 (i) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (fig).
(ii) Can Paheli at B see this image? (iii) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(iv) When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?
Sol. (i) 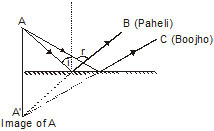
(ii) Yes Paheli can see the image of A.
(iii) Yes, Boojho can see this image.
(iv) When Paheli moves from B to C, the image of A will move from B to C.
Q.1 Suppose you are in a dark room. Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects outside the room. Explain.
Ans. We can see an object if light reflected or emitted by it reaches our eyes. If we are in a dark room, no light will enter into our eyes. Thus, it is not possible for us to.see objects in the room. But, objects outside the room may be visible to us. If there is a light present outside the room or an object is emitting its own light, then we can see the objects that are present outside the room.
Q.2 Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection ?
Ans. The light falling on a flat, smooth, reflecting surface, such as a mirror, undergoes regular reflection. In regular reflection, a parallel beam incident on a smooth surface like mirror remains parallel after the reflection. For example, in the case of the smooth lake, the crisp, clear images that form are the result of many parallel incident rays that reflect as parallel reflected rays.
Regular reflection)
The light failing on a rough surface undergoes diffused reflection. When all the parallel rays reflected from a plane surface are not parallel, the reflection Is known as diffused or irregular reflection.
For example, in the case of the rough lake, the . blurred images that form are the result of many parallel incident rays that are scattered after reflecting in many different directions. This behaviour is called diffuse or irregular reflection.
(Diffused or irregular reflection)
The light rays strike the rough surface at many different angles of incidence. This is because all the normals are not parallel to each other on the rough surface. Thus, the light rays get reflected at many different angles. That is why, the rays of reflected beam become non-parallel to each other. Thus, laws of reflections are not violated in diffused reflections.
Q.3 Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes. Justify your answer in each case.
(a) Polished wooden table (b) Chalk powder
(c) Cardboard surface (d) Marble floor with water spread over'it
(e) Mirror (f) Piece of paper
Ans. (a) Polished wooden table ® Regular reflection
A polished surface is an example of a smooth surface. A polished wooden table has a smooth surface. Hence, reflections from the polished table will be regular.
(b) Chalk powder ® Diffused reflection
Chalk power spread on a surface is an example of an irregular surface. It is not smooth. Therefore, diffused reflection will take place from chalk powder.
(c) Cardboard surface ® Diffused reflection
Cardboard surface is also an example of an irregular surface. Hence, diffused reflection will take place from a cardboard surface.
(d) Marble floor with water spread over it ® Regular reflection
Marble floor with water spread over it is or example of a regular surface. This is because water makes the marble surface smooth. Hence, regular reflection will take place from this surface.
(e) Mirror ® Regular reflection
Mirror has a smooth surface. Therefore, it will give a regular reflection.
(f) Piece of paper ® Diffused reflection
Although a piece of paper may look smooth, but it has many irregularities on its surface. Due to this reason, it will give a diffused reflection.
Q.4 State the laws of reflection.
Ans. (1) The Incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(2) The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
Ð i = Ð r
Q.5 Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.
Ans. Take a chart paper and fix it on a table such that the chart paper project a little beyond the edge of the table. Cut the projecting portion of the chart paper in the middle. Take a paper sheet and make a small cut at the bottom in the middle of the sheet. Hold the sheet perpendicular to the chart paper. Throw light from a torch through the opening of the comb from one side. With slight adjustment of the torch and the sheet you will see a ray of light along the chart paper on the other side of the sheet. Keep the sheet and the torch steady. Place a plane mirror in the path of the light ray. You will observe that the light ray that fallsion the plane mirror is reflected. Make sure that the reflected ray extends ray extends to the projected portion of the paper [fig.(a)]
Now, bend that part of the projected portion on which the reflected ray falls. You will not see the reflected ray on the paper [see fig.(b)]. Bring the paper back to the original position. You can see the reflected ray again. When the whole sheet of paper is spread on the table, it represents one plane. The incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray are all in this plane. When you bend the paper you create a plane different from the plane in which the incident ray and the normal lie. Then you do not see the reflected ray.
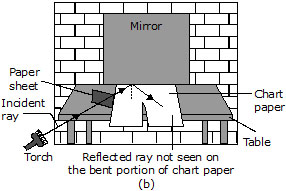
Thus, we can conclude that 'the incident ray, the normal at the point of incidence and the reflected ray all lie in the same plane'. This is another law of reflection.
Q.6 Fill in the blanks in the following :
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be _________ m from his image.
(b) If you touch your ________ ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with _________ .
(c) The size of the pupil becomes _________ when you see in dim light.
(d) Night birds have _________ cones than rods in their eyes.
Ans. (a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be 2 m from his image.
Object distance and image distance are the same from a plane mirror. The image of a person 1 m in front of a mirror is 1 m back to the mirror. Hence, the image is 1 + 1 = 2 m away from the person.
(b) If you touch your left ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with left hand.
This is because of lateral inversion of images formed in a plane mirror.
(c) The size of the pupil becomes large when you see in dim light.
In dim light, the amount of light entering the eye is very little. To increase the amount of light, the pupil expands.
(d) Night birds have less cones than rods in their eyes.
Night birds can see in the night, but not in the day. They have on their retina a large number of rod cells and only a few cones.
Direction: Choose the correct option in Questions 7 - 8
Q.7 Angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
(a) Always (b) Sometimes
(c) Under special conditions (d) Never
Ans. Option (a) is correct. According to law of reflection, 'the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection'.
Q.8 Image formed by a plane mirror is
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object
(c) real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged
(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Ans. Option (b) is correct.
Image formed by plane mirror is always virtual and of same size.
Q.9 Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.
Ans. Kaleidoscope :
This child's toy is a visual delight of changing colours as the toy is rotated. The effects are produced by multi-coloured glass pieces that tumble around when the toy is turned (see. fig.) Here, two (or three) mirrors are positioned 60º to each other and five image of the object are produced for the this orientation.
Q.10 Draw a labeled sketch of the human eye.
Ans.
Q.11 Gurmit wanted to perform Activity 6.5 using a laser torch. Her teacher advised her not to do so. Can you explain the basis of the teachers advise?
Ans. Laser light is harmful for the human eyes, because its intensity is very high. It can cause damage to the retina and lead to blindness. Hence, it is advisable not to look at a laser beam directly.
Q.12 Explain how you can take care of your eyes.
Ans. To protect our eyes, the given points should be taken into account :
(1) Visit an eye specialist regularly.
(2) Avoid reading in dim light and very bright light.
(3) Avoid direct exposure of sunlight to the eye.
(4) Clean your eyes with cold water quickly if dust particles or small insects enter your eye. Do not rub your eyes.
(5) Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm between the book and your eyes while reading.
Q.13 What is the angle of incidence of a ray if the reflected ray is at an angle of 90º to the incident ray ?
Ans. By law of reflection,
Q.14 How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm ?
Ans. Infinite (very large) images of the candle will be formed because of multiple reflections between the mirrors.
Q.15 Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is incident on one at an angle of 30º as shown in fig. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror

Ans. Incident ray 1 makes an angle of incidence of 30º with the mirror 1, thus the angle of reflection in also 30º. The ray 2 is reflected from mirror 1 and it acts as incident ray for the mirror 2. By geometry, we can find that angle of incidence that ray 2 makes at mirror 2 is 60º, thus, the angle of reflection is also 60º. The ray 3 is the reflected ray from the mirror 2.
Q.16 Boojho stands at A just on the side of a plane mirror as shown in fig. Can he see himself in the mirror? Also can he see the image of objects situated at P, Q and R?
Ans. A plane mirror forms a virtual image behind the mirror. The image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. A cannot see his image because the length of the mirror is too short on his side. However, he can see the objects placed at points P and Q, but cannot see the object placed at point R (as show in the given figure).
Q.17 (a) Find out the position of the image of an object situated at A in the plane mirror (see fig.).
(b) Can Paheli at B see this image?
(c) Can Boojho at C see this image?
(d) When Paheli moves from B to C, where does the image of A move?
Ans. (a) Image of the object placed at A is formed behind the mirror. The distance of the image from the mirror is equal to the distance of A from the mirror. Image of A is shown in the given figure.
(b) Yes, Paheli at B can see this image (see fig.).
The rays from A after reflection reaches to Paheli.
(c) Yes. Boojho at C can see this image (see fig.).
The rays from A after reflection reaches to Boojho.
(d) Image of the object at A will not move. It will remain at the same position (A') when Paheli moves from B to C. This is because image of an object does not depend on the position of an observer.
Q.1 What is a luminous object?
Q.2 Define angle of incidence.
Q.3 Define angle of reflection.
Q.4 What is meant by normal to the surface?
Q.5 Can a real image be obtained on a screen?
Q.6 Is a virtual image inverted?
Q.7 An incident ray makes an angle of 30° with the mirror. What is the angle of incidence?
Q.8 An incident ray makes an angle of 20° with the normal. What is the angle of reflection?
Q.9 Who had invented Braille system for visually impaired people?
Q.10 Who controls the amount of light entering the eye?
Q.11 What is the blind spot? Where is it located?
Q.12 Which mirror is used in solar cookers?
Q.13 When is a person unable to see?
Q.14 How is a rainbow formed?
Q.15 When in the eye will you find nerve fibres sensitive to light?
Q.16 Will red light passing through a prism result in a spectrum?
Q.17 Why does eye lens become cloudy in case of old people?
Q.18 What is reflection of light?
Q.19 What are angle of incidence and angle of reflection?
Q.20 What type of image is formed by a plane mirror?
Q.21 What type of reflection forms an image?
Q.22 What is a kaleidoscope?
Q.23 What is persistence of vision?
Q.24 What is cataract?
Q.25 Who invented the Braille system?
Q.26 What do you mean by reflection?
Q.27 State the laws of reflection.
Q.28 Write two uses of plane mirrors.
Q.29 What is power of accommodation?
Q.30 What is lateral inversion?
Q.31 Define dispersion of light through a prism.
Q.32 What will be the value of angle refraction if light ray is incident normally on the glass slab?
Q.33 A light ray is incident at 45° on a plane mirror then what is the angle between incident ray and reflected ray?
Q.34 What type of lens is used in a simple microscope?
Q.35 Name the lens which diverges the light rays.
Q.36 With the help of diagrams, explain the difference between regular and irregular reflection.
Q.37 What do you mean by a spectrum? Why is a spectrum formed by a prism and not by a glass slab?
Q.38 Draw a labeled diagram to show the working of a kaleidoscope. What are the uses of a kaleidoscope?
Q.39 What do you mean by reflection of light? State the laws of reflection of light. With the help of an experiment prove the laws of reflection in case of a plane mirror.
Q.40 What are the properties of the image formed by a plane mirror? Explain the phenomenon of lateral inversion with the help of a diagram.
Q.41 With the help of a labeled diagram, show the essential parts of the human eye. How do we see objects? Briefly explain the common defect of eye.
Q.42 Draw a labeled diagram of the human eye and
explain its various parts.
Q.1 A child walks towards a fixed plane mirror at a speed of 5 km h–1. The velocity of the image with respect to mirror is -
(A) 5 km h–1 (B) –5 km h–1
(C) 10 km h–1 (D) –10 km h–1
Q.2 Cataract is the condition that affects the
(A) lens (B) pupil
(C) retina (D) macula
Q.3 In a plane mirror, an object is 0.5 m in front of the mirror. The distance between object and image is -
(A) 0.5 m (B) 1 m
(C) 0.25 m (D) 0.75 m
Q.4 An object 0.5 m tall is in front of a plane mirror at a distance of 0.2 m. The size of the image formed is-
(A) 0.2 m (B) 0.5 m
(C) 0.1 m (D) 1 m
Q.5 A plane mirror is approaching you at
10 cm s–1. Your image shall approach you with a speed of-
(A) + 10 cm s–1 (B) – 10 cm s–1
(C) + 20 cm s–1 (D) – 20 cm s–1
Q.6 A ray of light is incident on a plane mirror at an angle of incidence of 30°. The deviation produced by the mirror is-
(A) 30° (B) 60°
(C) 90° (D) 120°
Q.7 A plane mirror reflects a pencil of light to form a real image. Then the pencil of light incident on the mirror is-
(A) parallel (B) convergent
(C) divergent (D) any of these
Q.8 Which of the following cannot produce a virtual image?
(A) Plane mirror
(B) Concave mirror
(C) Convex lens
(D) All of the above can produce a virtual image.
Q.9 How many images of himself does an observer see if two adjacent walls of rectangular room are mirror surfaced?
(A) 3 (B) 5
(C) 7 (D) 9
Q.10 The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal at the point of incidence lie on the same
(A) line (B) point
(C) circle (D) plane
Q.11 Diffused reflection occurs if a ray of light is reflected by a
(A) concave mirror (B) plane mirror
(C) convex mirror (D) rough surface
Q.12 Sources of light are also called
(A) luminous objects
(B) non-luminous objects
(C) mirrors
(D) reflections
Q.13 When two plane mirrors are kept at 90º, we get
(A) only one image
(B) two images
(C) three images
(D) infinite number of images
Q.14 If two plane mirrors are placed parallel to each other and facing each other, then we get
(A) only one image
(B) two images
(C) three images
(D) infinite number of images
Q.15 The beautiful patterns that we obtain in a kaleidoscopes are because of
(A) dispersion
(B) spectrum
(C) multiple reflection
(D) diffused reflection
Q.16 Which of the following types of mirror is used in the solar cooker ?
(A) plane mirror (B) convex mirror
(C) concave mirror (D) None of these
Q.17 An incident ray makes an angle of 30º with a plane mirror. Then the angle of reflection is
(A) 30º (B) 60º
(C) 45º (D) None of these
Q.18 The reflection taking place from the walls of a building is called
(A) regular reflection
(B) diffused reflection
(C) multiple reflection
(D) None of these
Q.19 The reflection in which reflected rays travel as parallel beam is called
(A) regular reflection
(B) scattering
(C) multiple reflection
(D) None of these
Q.20 A ray of light which bounces off the surface of mirror is called
(A) normal (B) incident ray
(C) reflected ray (D) None of these
Refraction
Q.21 How will the image formed by a convex lens be affected, if the central portion of the lens is wrapped in black paper, as shown
in the fig .
(A) No image will be formed
(B) Full image will be formed but it is less bright
(C) Full image will be formed but without the central portion
(D) Two images will be formed, one due to each exposed half.
Q.22 An endoscope is employed by a physician to view the internal parts of a body organ. If is based on the principle of:
(A) refraction
(B) reflection
(C) total internal reflection
(D) dispersion
Q.23 The sun is visible to us a little before the actual sunrise and a little after the actual sunset. This is because of atmospheric.
(A) reflection (B) refraction
(C) scattering (D) diffraction
Q.24 Light of different colours propagates through air–
(A) With the velocity of air
(B) With different velocities
(C) With the velocity of sound
(D) Having the equal velocities
Q.25 A monochromatic beam of light passes from a denser medium into a rarer medium. As a result–
(A) Its velocity increases
(B) Its velocity decreases
(C) Its frequency decreases
(D) Its wavelength decreases
Q.26 When light passes from water to olive oil. The ray –
(A) Bends away from the normal
(B) Bends towards the normal
(C) Emerges undeviated
(D) Bends either away or toward the normal depending one whether, the surface separating the two media is plane or spherical.
Q.27 The wavelength of yellow light of sodium (D) in diamond, as compared to that in sugar is –
(A) Same (B) More
(C) Less (D) None
Q.28 The bending of light ray when passing from two optically different mediums is called
(A) Reflection (B) Refraction
(C) Polarization (D) Effervescence
Q.29 The twinkling of stars at night is caused by
(A) Reflection of light (B) Refraction of light
(C) Dispersion of light (D) Polarization of light
Q.30 The rainbow that appears in sky after the rains is caused by the ........... of light by water droplets present in upper atmosphere.
(A) Reflection of light
(B) Refraction of light
(C) Dispersion of light
(D) Polarization of light
Q.31 When an object is at infinity, the image by convex lens is formed at
(A) Focus
(B) Centre of curvature
(C) Beyond the centre of curvature
(D) Optical centre
Q.32 In visible spectrum, the ray of light with maximum wavelength is
(A) Violet rays (B) Green ray
(C) Blue ray (D) Red ray
Q.33 When a ray of light passes from a rare into a denser medium, its velocity
(A) Increases
(B) Decreases
(C) Remains the same
(D) None of these
Q.34 Dispersion is
(A)splitting of light into its constituent colours
(B) formation of many images
(C) formation of only two images
(D) a rainbow
Q.35 The difference in the colour of the eye is due to difference in
(A) retina (B) pupil
(C) iris (D) sclera
Q.36 The image of the object is always formed at the
(A) iris (B) retina
(C) pupil (D) lens
1. B 2. A 3. B 4. B
5. C 6. D 7. B 8. D
9. A 10. D 11. D 12. A
13. C 14. D 15. C 16. A
17. B 18. B 19. A 20. C
21. B 22. C 23. B 24. D
25. A 26. B 27. C 28. B
29. B 30. C 31. A 32. D
33. B 34. A 35. C 36. B
1. Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection. Does diffused reflection mean the failure of laws of reflection?
2. State laws of reflection.
3. Fill in the blanks in the following :
(a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be .............. m from his image.
(b) If you touch your ................... ear with right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with ...........................
(c) The size of the pupil becomes ................... when you see in dim light.
(d) Night birds have ................ cones then rods in their eyes.
(e) The most popular resource for visually challanged person is ............
4. How many images of a candle will be formed if it is placed between two parallel plane mirrors separated by 40 cm?
5. Two mirrors meet at right angles. A ray of light is inclident on one mirror at an angle of 30º as shown in figure. Draw the reflected ray from the second mirror.
6. Up to how much time an image persists on retina?
Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. Two mirrors are kept at 60º to each other and a body is placed at the middle. The total number of images formed is :
(A) Three (B) Four (C) Five (D) Six
2. When a ray of light is incident on a plane mirror, with reflection it is deviated through angle q . If the angle made by incident ray with the mirror is i. then angle of deviation q will be :
(a) 1 i (B) 2i (C) 180 - 2i (D) 80 - i
3. A mirror is rotated through angle q about an axis passing through the point of incident and lying in the plane of the mirror. The reflected ray will be rotated through.
(a) q/2 (B) q (C) 2q (D) 3q
4. A car is moving towards a plane mirror at a speed of 30 m/s. Then the relative speed of its image with respect to car will be :
(A) 30 m/sec. (B) 60 m/sec (C) 15 m/sec (D) 45 m/sec
5. The mirrors are perpendicular at each other as shown in the figure. A light ray AB is incident on the mirror M1. Then the reflected ray will also suffer a reflection from the mirror M2. Then the final ray after reflection from M2 will be parallel to the incident ray if.
(A) i = 45º (B) i = 60º
(C) i < 30º (D) for any i between 0º and 90°
6. Two mirrors make an angle of 90º with each other. If a ray of light is incident on the first mirror at an angle of incident i, the relfected ray from the second mirror will make an angle of reflection.
(A) 0º (B) i (C) 90 – i (D) 45 - i
7. The radious and magnification of a plane mirror are :
(A) R= , m= 0 (B) R= 0 , m= 1 (C) R=, m= 1 (D) R=0 , m=0
8. Which of the following are used in Kaleido scope?
(A) Plane mirror (B) Cocave mirrors (C) Convex mirrors (D) all above
9. An ray incidents on a mirror as shown in Figure angle of reflection would be :
(A) i (B) 2i (C) 90 - i (D) 180 - 2i
1. For an object at infintiy, a concave mirror produces an image at its focus which is
(A) enlarged (B) virtual
(C) erect (D) real, inverted and diminished
2. The mirror used in automobiles to see the rear field of view is
(A) concave (B) convex (C) plane (D) none of these
3. The mirror used in search lights is
(A) concave (B) convex (C) plane (D) none of these
4. A real image, equal in size to the object, is obtained when the object is placed at the centre of curvature in front of a
(A) concave mirror (B) plane mirror (C) convex mirror (D) none of these
5. If we say that the focal length of a spherical mirror is n times its radius of curvature, then n must be
(A) 2.0 (B) 1.5 (C) 0.2 (D) none of these
6. Which is the wrong statement out of the following ?
(A) A concave mirror can give a virtual image.
(B) A convex mirror can give a virtual image.
(C) A concave mirror can give a diminished virtual image.
(D) A convex mirror cannot give a real image.
7. An inverted image can be seen in a convex mirror,
(A) under no circumstances
(B) when the object is very far from the mirror
(C) when the object is at a distance equal to the radius of curvarture of the mirror
(D) when the distance of the object from the mirror is equal to the focal length of the mirror
8. A virtual image is one which
(A) can be taken on a screen
(B) cannot be taken on a screen
(C) sometimes can be and sometimes cannot be taken on a screen
(D) is formed only by a concave mirror
9. When an object is placed between the focus and the pole of a concave mirror, the image formed is
(A) real, inverted and small (B) real, inverted and same size
(C) real, inverted and enlarged (D) virtual, erect and enlarged
10. The line joining the pole and the centre of curvature of a mirror is called the
(A) aperture (B) principal section (C) principal axis (D) pole
11. In order to get a diminished virtual image, the object can be placed anywhere in front of a
(A) concave mirror (B) plane mirror (C) convex mirror (D) none of these
12. The mirror used by dentists to concentrate light on the tooth to be examined is a ___________ mirror.
(A) concave (B) plane or concave (C) convex (D) plane
13. When an object is at infinity from a concave mirror, the image formed is
(A) at the focus (B) virtual and erect (C) highly enlarged (D) none of these
14. When the object is at focus of a concave mirror, the image is formed at
(A) focus (B) centre of curvature (C) within focus (D) infinity
15. Which of the following ray diagrams is not correct ?
16. When an object is kept within the focus of a concave mirror, an enlarged image is formed behind the mirror. The nature of the image is
(A) real (B) inverted (C) virtual and inverted (D) virtual and erect
17. The centre of curvature of a __________ mirrror is behind it.
(A) convex (B) concave (C) convex or concave (D) none of these
18. A ray, emerging from a point on the object, passing through the centre of curvature C strikes the mirror normally i.e. at 90°. Then, then angle of incidence is equal to
(A) 0° (B) 45° (C) 90° (D) 180°
19. Which of the following mirror is used to concentrate light on a given spot ?
(A) Concave mirror (B) Convex mirror (C) Plane mirror (D) None of these
20. What is the value of in the following ray diagram ?
(A) 25° (B) 35° (C) 50° (D) none of these
1. The unit of power of a lens is
(A) metre (B) dyne (C) dioptre (D) None of these
2. The focal length of a lens is 50 cm. Its power would be
(A) 50 dioptres (B) 2 dioptres (C) 20 dioptres (D) None of these
3. A simple magnifying glass consists of a
(A) concave lens (B) convex lens of large focal length
(C) convex lens of small focal length (D) plane mirror only
4. The power of a lens being +4 dioptres suggests it is a
(A) convex lens (B) plano-convex lens (C) concave lens (D) none of these
5. When an object moves towards a convex lens, the size of the image
(A) decreases (B) increases
(C) first decreases then increases (D) remains the same
6. When an object approaches a convex lens from infinity, the image formed by it shifts
(A) away from the lens (B) towards the lens
(C) first away and then towards the lens (D) none of these
7. If the power of a lens is 0.1 D, its focal length is
(A) 1 m (B) 10 m (C) 100 m (D) –10 m
8. The refraction of light is commonly known as
(A) bending (B) scattering (C) reflection (D) interference
9. Which of the following shows the bending of light from rarer (R) into denser (D) medium?
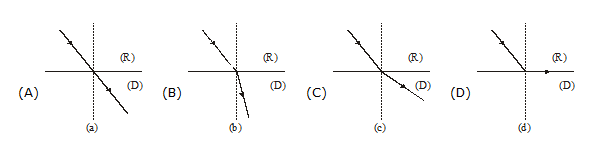
10. Which of the following shows the bending of light from denser (D) medium into a rarer (R) medium?
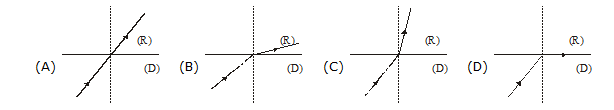
11. How will the image formed by a convex lens be affected if the upper half of the lens is wrapped with a black paper?
(A) The size of the image is reduced to one-half (B) The upper half of the image will be absent
(C) The brightness of the image is reduced (D) There will be no effect
12. Which of the following term is not associated with a lens?
(A) Aperture (B) Focal length (C) Principal focus (D) Efficiency
13. To construct a ray diagram, you need at least __________whose path(s) after refraction through the lens are known
(A) one ray (B) two ray (C) three rays (D) none of these
14. Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of same size is obtained using a convex lens?
(A) Between the lens and its focus (B) At the focus
(C) At twice the focal length (D) At infinity
15. The focal length of a lens is –0.4 m. The lens is
(A) convex (B) concave (C) cylindrical (D) none of these
16. The focal length of a lens is 0.1 m. Then the lens must be
(A) convex (B) concave (C) cylindrical (D) none of these
1. The screen behind the eye lens is called the
(A) iris (B) ciliary muscle (C) retina (D) pupil
2. Cornea is a transparent spherical structure which
(A) reflects light (B) scatters light (C) refracts light (D) none of these
3. The amount of light entering the eye is controlled by the
(A) iris (B) cornea (C) pupil (D) crystalline lens
4. The eye lens contains a watery liquid called the
(A) aqueous humour (B) peroxide (C) vitreous humour (D) none of these
5. Long-sightedness is caused by the eyeball being too short. It can be corrected by the use of a
(A) convergent lens (B) plane mirror (C) divergent lens (D) none of these
6. Hypermetropia is due to the __________of the eye.
(A) low converging power (B) low diverging power
(C) high converging power (D) high diverging power
7. Which of the following lens is used to minimise myopia?
(A) Convex lens (B) Conave lens (C) Cylindrical lens (D) none of these
8. The hyman eye forms the image of an object at its
(A) cornea (B) iris (C) pupil (D) retina
9. Figure shows the eye suffering from
(A) hypermetropia (B) myopia (C) astigmatism (D) none of these
10. Figure shows the eye suffering from
(A)hypermetropia (B)myopia (C)astigmatism (D) none of these
11. When the light is very bright?
(A) the iris makes the pupil expand (B) the iris makes the pupil contract
(C) the iris and the pupil remain as they are (D) none of these
Exercise-II
3. (a) 2 m (b) left , left hand (c) larger (d) lesser (e) Braille system
4. Infinite 5.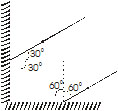
Exercise-III
1. (C) 2. (B) 3. (C) 4 . (B) 5. (D) 6. (C)
7. (C) 8. (A) 9. (C)
Exercise-IV
1. (D) 2. (B) 3. (A) 4. (A) 5. (D) 6. (C)
7. (A) 8. (B) 9. (D) 10. (C) 11. (C) 12. (A)
13. (A) 14. (D) 15. (B) 16. (D) 17. (A) 18. (A)
19. (A) 20. (C)
Exercise-V
1. (C) 2. (B) 3. (C) 4. (A) 5. (B) 6. (A)
7. (B) 8. (A) 9. (B) 10. (B) 11. (C) 12. (D)
13. (B) 14. (C) 15. (B) 16. (A)
Exercise-VI
1. (C) 2. (C) 3. (C) 4. (A) 5. (A) 6. (A)
7. (B) 8. (D) 9. (A) 10. (B) 11. (B)