(a) Aquatic adaptations:
(i) In Animals: Animals that live in water are called aquatic animals.
· They have a streamlined body that makes it easier for them to move in water. They have gills for breathing in water.
Fins and the tail help them to swim. The scales on their body provide protection. Bony fishes have air spaces in their bodies to help them float.
Common aquatic animals are fishes, whales, crabs, octopus, etc.
(ii) In plants : Aquatic habitat can be present as marine (oceanic) and fresh water (ponds & lakes) habitat.
Aquatic plants can be present as floating or submerged or amphibious plant. Usually they have narrow and thin ribbon
shape leaves and less developed roots. Plant body is also covered by mucus layer to reduce friction & having
inactive stomata (in submerged plants) and active stomata at upper surface only (in floating plants).
Fig. Hydrilla
(b) Amphibious adaptations
(i) In Animals: Animals which live both on land and water are called amphibious animals.
(ii) In Plants : In amphibian plants root system is more develop than other hydrophytes. They are heterophyllous in nature, e.g. Ceretophylium.
(c) Aerial adaptations :
(d) Terrestrial adaptations
(A) Desert Adaptation or Xeric Adaptation: Desert is a water deeplete area so basically plants and animals are adapted for little loss of water.
(I) In Animals : Camels are desert animals which are well adjusted to the dry hot climate. They store water in all the cells of their body.
· Their urine is very concenttrated. Their nostrils have long hairs to prevent the entry of sand and dust. They have no sweat glands in their skin.
B. Head C. Foot showing adaptations to hc. (Camelus dromedarius)
(ii) In Plants : Desert plants are known as xerophtic plants. They lose very little water through transpiration.
The leaves in desert plants are either absent, very small or they are present in the shape of spines.
This helps in reducing loss of the water from the leaves through transpiration.
· Stem of modified for retaining of water and for photosynthasis. Roots are deeper to absorb water.
(B) Polar regions adaptation :
· Polar regions are charaterized by heavy and snowy winters.
(i) In Animals : The animals seen here are while or light in colour. This enables them to match. the colour of the background (camouflage);
and also to regulate the temperature of the body (thermal regulation).

(ii) In Plants: Usually plants are absent in polar area but some lichens & mosses are found there.
(C) Tropical rainforest's adaptation:
(i) In Animals: Animals in the tropical rainforests are adapted such that they eat different kinds of
food to overcome the competition for food and shelter.
(ii) In Plants: In tropical rain forest diverse flora is found which is present as evergreen forest.
It Is the sum total of all bi otic and abiotic components, substances and conditions that surround & influence the organisms.
The various components of environment are interlinked as well as interdependent.
It consists of 2 major components :
(a) Non living Components: Also called as abiotic components.
(i) Climate: It is the average weather of an area including general patterns of atmosphere and seasonal variations.
(ii) Light
(iii) Temperature
(iv) Water
(v) Soil
(b) Biotic or Living Components :
The living components consist of 3 types of organisms
(i) Producers: Organisms which can prepare their own food from simple inorganic substances like CO2 and Hp in presence of sunlight.
e.g. Green plants, photosynthetic algae, photosynthetic bacteria etc.
(ii) Consumers: Those organisms which consume food prepared by producers are called as consumers. They can be :
(iii) Decomposers: The microorganisms which break down the complex organic compounds present in dead orga nisms (plants and animals) e.g. fungi, bacteria etc.
1. Weather affects our lives.
2. Bad weather may cause ship wrecks, destory crops and may even lead to droughts and floods.
3. Weather may be pleasant, cloudy, rainy, humid cold, sunny or windy.
4. The study of weather is called meteorology.
5. People who study and record weather are called meteorologists.
6. The amount of water vapour present in the air is called humidity.
7. Weather is the state(or condition) of the atmosphere of a particular place at a particular time is terms of humidity, cloudiness, temperature, wind etc.
8. Predicting or estimating the weather in advance is called weather forecasting.
9. Climate of a place is defined as the average weather conditions at a particular place over a long period of time. It varies from place to place.
10. Animals are adapted to the environment in which they live.
11. Deserts, polar regions and tropical rainforests present three extremes of climatic conditions.
12. The climate is warmer at places closer to the equator than the places closer tot he poles.
Q.1 Define adaptation?
Q.2 What Is the difference between climate and weathers? Which of these two changes frequently?
Q.3 Explain the aquatic adaptation.
Q.4 Which features adapt polar bear to live in extremely cold climate?
Q.5 Explain, with examples, why we find animals of certain kind living in particular climatic conditions.
Q.1 During extreme aridity, Desert rat
(A) stores water
(B) uses metabolic water
(C) saves water
(D) does not use water
Q.2 Which trait is not helpful to a fish in adaptation?
(A) Streamlined body
(B) Large pupils of the eyes
(C) Gills
(D) Beautiful colour of the body
Q.3 Hibernation, migration of suitable places and insulation of the body
by fur or feathers are characteristics of
(A) polar animals
(B) animals of temperate regions
(C) animals of tropical regions
(D) animals of equatorial regions.
Q.4 The organism that lives on land but requires aquatic habitat to lay eggs is
(A) frog
(B) camel
(C) Hydra
(D) snake
Q.5 Camel is best adapted to desert habitat as
(A) it can drink 50 liters of water at a time which is evenly distributed in all its tissues.
(B) it excretes very small amount of water during urination .
(C) it can regulate its body temperature at a wider range
(D) all are correct
Q.6 Change in colour of some organisms according to the background, to protect themselves is called
(A) mimicry
(B) moulting
(C) camouflage
(D) none of these
Q.7 In aerial animals the forelimbs are modified into
(A) wings
(B) hind limbs
(C) body
(D) air -chambers
Q.8 Which features adapt polar bears to live in extremely cold climate?
(A) A white fur, fat below skin, keen sense of smell.
(B) Thin skin, large eyes, a white fur.
(C) A long tail, strong claws, white large paws.
(D) White body, paws for swimming, gills for respiration.
Q.9 Xeric environment is characterised by
(A) preCipitation
(B) low atmospheric humidity
(C) extremes of temperature
(D) high rate of vapourisation
Q.10 The xerophytic plants do not have
(A) sunken stomata
(B) needle like leaves or no leaves
(C) air cavities in stems
(D) very long roots.
Q.11 Root system in hydrophytes is
(A) Fully Developed
(B) Partially Developed
(C) Absent
(D) None of above
Q.12 Hibernation means
(A) Long sleep during winter
(B) Short sleep during winter
(C) Short sleep during summer
(D) long sleep during summer
Q.13 The delicate, flexible and thin stem is the characteristic feature of:
(A) mesophytes
(B) hydrophytes
(C) halophytes
(D) Xerophytes
Q.14 Animal not found in polar region is :
(A) Polar bear
(B) Penguin
(C) Seal
(D) Elephant
Q.15 Plants grow on burnt soil called as:
(A) Pyrophilous
(B) Sciophytes
(C) Lithophytes
(D) Heliophytes
Q.16 Negative geotropic breathing roots present in:
(A) Halophytes
(B) Hydrophytes
(C) Xerophytes
(D) Mesophytes
ANSWER KEY
1. A 2. D 3. A 4. A
5. D 6. C 7. A 8. A
9. C 10. C 11. B 12. A
13. B 14. A 15. A 16. A
1. Climate of a place is affected by by
(A) Altitude of a place
(B) Distance from the sea
(C) Location of a place
(D) All of these
2. The trunk of an elephant is a modification of the
(A) Lower lip and nose
(B) Upper lip and nose
(C) Lower jaw and hose
(D) Upper jaw and hose
3. Adjustment of plants and animals to environ mental changes is called
(A) mimicry
(B) aestivation
(C) adaptation
(D) hibernation
4. A student identified the following characteris tics in an animal
(i) Ability to climb the trees
(ii) Spines to prevent fro slipping
(iii) strong claws and broad hip girdles.
Which of the following titles best suits the above animal?
(A) amohibian
(B) arboreal animal
(C) aquatic animal
(D) Terrestrial animal
5. Earth's position in solar system is
(A) 1st nearest to the sun
(B) 2nd nearest to the sun
(C) 3rd nearest to the sun
(D) 4th nearest to the sun
6. Which of the following animals have long sticky tongues?
(A) Cagles
(B) Penguins
(C) Cheetahs
(D) Cows
7. Which of the following statements is false?
(A) In cold regions plants grow new leaves during winter.
(B) Some desert plants do not have leaves.
(C) Thick skin protects the animals from the blazing heat of the sun.
(D) Bears have thick fur as a protection against the cold.
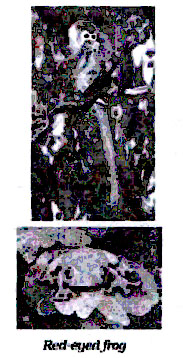
8. Red eyed frog and new world monkey are animals of
(A) Forest
(B) desert
(C) Tropical forest
(D) Tropical rainforest
9. Which of the following penguins adapt to live in extremely cold conditons?
(A) A white colour thick skin less fat
(B) White body, paws for swimmings, gills for respiration.
(C) Thin skin, large eyes, white fur
(D) White colour, thick skin and a lot of fat
10. Presence of sharp claws and powerful feet in the fishing eagle is an adaptation to
(A) Climate
(B) Self protection
(C) Available food
(D) Changing environment
11. Match the following
(P) Toucan bird (I) Modified teeth
(Q) Siberian bird (II) Silver white mane
(R) Trunk of elephant (III)Long beak
(S) Macaque (IV)migrate to India during winter
(A) P-I, Q-II, R- III, S-IV
(B) P-IV, Q-III, R-II, S-I
(C) P-III, Q-IV, R-I, S-II
(D) P-III, Q-I, R-II, S-IV
12. Which of the following animals have sticky padson its feet?
(A) Green eyed frog
(B) Blue eyed frog
(C) Red eyed frog
(D) Yellow eyed frog
13. The rain gauge is used to measure
(A) Rain water
(B) Rainfall
(C) Rain region
(D) Rain speed
14. The side of morning sun is
(A) small
(B) very small
(C) Big
(D) Very big in comparison to day sun
15. An adaptation to arboreal life (tree living) is
(A) Camouflage
(B) Opposable thumb
(C) Hibernation
(D) thick skin
16. Which of the following departments prepare weather reports?
(A) Health department
(B) Environment department
(C) Pollution department
(D) Meteorological department
17. Weather is predicted by considering
(A) Amount of water vapour
(B) The movement of air
(C) Temperature
(D) All the above
18. ........maintains balance in a monkey
(A) Legs
(B) Tail
(C) Hands
(D) none
19. Sheep.......region have thicker fur than than sheep living in ........region.
(A) Cold, warm
(B) Warm, Hot
(C) Hot, Warm
(D) Warm, Cold
20. The scaly skin of snakes
(A) helps them to crawl
(B) makes them beautiful
(C) scares human beings
(D) protects them from drying
21. An animal is taken to polar region. Which of the following adaptive
characteristics may help it to survive in the new environment?
(A) sheep beaks and strong claws
(B) growth of thick fur on its skin.
(C) light weight wings to fly.
(D) growth of thick and less hairy skin
22. The adaptation mechanism of chameleon is ......
(A) to develop scaly skin on its body to main-tain moisture.
(B) to migrate to long distance in the winter
(C) changing colours to suit on its body to maintain moisture.
(D) to hibernate in the winter
ANSWER KEY
1. D 2. B 3. C 4. B
5. C 6. B 7. A 8. D
9. D 10. C 11. C 12. C
13. B 14. C 15. B 16. D
17. D 18. B 19. A 20. D
21. B 22. C
EXERCISE III
1. The characteristic weather pattern over a long period of time is called -
(A) weather
(B) climate
(C) season
(D) atmosphere
2. The climate of a place depends on its
(A) latitude
(B) altitude
(C) distance from the sea
(D) all of these
3. The cause for the occurrence of seasons on the earth is
(A) the inclination of the earth’s axis with the plane of its orbit
(B) its distance from the sun
(C) latitude
(D) all of these
4. ‘Albedo’ refers to
(A) the carbon dixodie content of the atmosphere
(B) the constitution of the atmosphere
(C) the percentage of radiation reflected by a planet
(D) the temperature differences on a planet
5. Camels adapt to the desert climate with the help of
(A) long eyelashes
(B) hump
(C) body temperature changes
(D) all of these
6. The hump of the camel is a reservoir of
(A) fatty tissue
(B) water
(C) milk
(D) all of these
7. Which of these animals possesses blubber under its skin?
(A) camel
(B) African elephant
(C) fennec
(D) polar bear
8. During extreme aridity, Desert rat
(A) stores water
(B) uses metabolic water
(C) saves water
(D) does not use water
9. Which trait is not helpful to a fish in adaptation?
(A) Streamlined body
(B) Large pupils of the eyes
(C) Gills
(D) Beautiful colour of the body
10. Hibernation, migration of suitable places and insulation of the
body by fur or feathers are characteristics of
(A) polar animals
(B) animals of temperate regions
(C) animals of tropical regions
(D) animals of equatorial regions
11. The organism that lives on land but requires aquatic habitat to lay eggs is -
(A) frog
(B) camel
(C) Hydra
(D) snake
12. Camel is best adapted to desert habitat as
(A) it can drink 50 liters of water at a time which is evenly distributed in all its tissues
(B) it excretes very small amount of water during urination
(C) it can regulate its body temperature at a wider range
(D) all are correct
13. Change in colour of some organisms according to the background,
to protect themselves is called
(A) mimicry
(B) moulting
(C) camouflage
(D) none of these
14. In aerial animals the forelimbs are modified into -
(A) wings
(B) hind limbs
(C) body
(D) air - chambers
15. Which features adapt polar bears to live in extremely cold climate?
(A) A white fur, fat below skin, keen sense of smell
(B) Thin skin, large eyes, a white fur
(C) A long tail, strong claws, white large paws
(D) White body, paws for swimming, gills for respiration
16. Xeric environment is characterised by
(A) precipitation
(B) low atmospheric humidity
(C) extremes of temperature
(D) high rate of vapourisation
17. Hibernation occurring in certain animals is
(A) occasional
(B) intermittent
(C) rhythmic
(D) periodic
18. The earth is the ________ closest planet to the sun
(A) second
(B) third
(C) fourth
(D) fifth
19. The aproximate distance of the earth from the sun is __________
(A) 149.6 × 106 km
(B) 19.6 × 106 km
(C) 14.96 × 106 km
(D) 1.94 × 106 km
20. Seasons occur due to the earth’s _______ to the plane of its orbit around the sun
(A) movement
(B) tilt
(C) axis
(D) surface
21. The percentage of radiation reflected by a planet is called
(A) aldeco
(B) alnino
(C) albedo
(D) climatic
22. The study of the climate over thousands of years is called
(A) ecology
(B) dendraclimatology
(C) weather forcasting
(D) paleoclimatology
23. Animals have certain special characteristics that enable them to live
in a particular climate successfully, which are called
(A) adaptations
(B) adoptions
(C) habit
(D) albedo
24. In dry and hot climates, animals need modifications to _______ water
(A) evaporate
(B) conserve
(C) waste
(D) absorb
25. Some animals in extremely hot climates go off to a state of dormancy called ______ during the summer season
(A) hibernation
(B) blubber
(C) aestivation
(D) acclimatization
ANSWER KEY
EXERCISE I
Section - A
Fill in the blanks:
1. ____________ is used to measure temperature.
2. ____________ and ____________ are two regions having extreme climatic conditions.
3. ____________ India receives rain for a major part of the year.
4. Hot and dry climatic conditions used as ____________.
5. Besides birds, ____________ and ____________ also show migration.
6. The average weather taken over a long time is called ____________.
7. Animals shows ____________ to surrounding in which they live.
8. All the changes in the weather occurs due to ____________.
9. ____________ helps in measuring humidity.
10. Maximum bio-diversity is observed in the ____________.
Section - B
True or False
1. The weather reports are prepared by the various news papers.
2. Rainfall in any area is measured by rain gauge.
3. Humidity is amount of water vapours present in air.
4. Hot and wet climate is found in desert.
5. Over earth major source of light and heat is Sun.
6. Adaptation to surrounding in animals causes evolution.
7. Presence of different life forms in biosphere is called variations.
8. Part of earth where life exist called biosphere.
9. In western region of India, the temperature is high during most part of the year.
EXERCISE II
Section - A
Each question carry one mark
1. Define bio-diversity.
2. What do you mean by hibernation?
3. Name the organisms showing migration.
4. To which places of India Siberian Cranes shows migration?
5. Name the butterfly showing migration.
6. Where tropical rainforests are found in India?
7. What are hot-spot areas?
8. Which type of climatic conditions, are most suitable for supporting maximum bio-diversity?
9. What do you mean by climate?
10. When are the maximum and minimum temperature occurs during the day?
Section - B
Each question carry two marks
1. Give difference between weather and climate.
2. The tropical rainforest has a large population of animals. Why?
3. What is migration and why it occurs?
4. Organisms shows adaptations to surrounding, why?
5. Where an extreme climate is found and why?
Section - C
Each question carry 3 marks
1. Write down about the climate of western and north-eastern region of India.
2. What is the role of sun in controlling weather of any place?
3. During summer we feel so miserable in the afternoon as compared to morning, why?
4. Define environment.
5. Discuss types of inactivity shown by animals to low and high temperature conditions.
Section - D
Each question carry 5 marks
1. Discuss the climatic conditions of polar and tropical rain forest regions.
2. What is tropical habitat? Write down the adaptation found in animals of tropical rain forest to live in such habitat.
3. Write down the various adaptations found in Lion - tailed macaque and elephant living in tropical rain forest.
4. Which kind of climatic conditions are found in polar regions? Give adaptations of polar bear.
5. What do you understand by term weather and climate? Why these factors shows variations in different regions?
EXERCISE III
Section - A
Multiple choice questions with one option is correct
1. The average weather taken over a long time is called:
(A) Climate
(B) Atmosphere
(C) Environment
(D) (A) & (B) both
2. Extreme climatic conditions found in:
(A) Tropical rain forest
(B) Polar region
(C) Both of these
(D) None of these
3. A tropical region is:
(A) Hot & humid
(B) Moderate temperature, heavy rainfall
(C) Cold & humid
(D) Hot and dry
4. Factors connected with form and behaviour of earth’s surface are:
(A) Edaphic
(B) Topographic
(C) Geological
(D) Geographic
5. Xeric environment is characterised by:
(A) Light precipitation
(B) low atmospheric humidity
(C) Extremes of temperature
(D) Light rate of vapourisation
6. Under bright light animals become:
(A) Tanned
(B) Light coloured
(C) dark coloured
(D) blue coloured
7. Choose the correct adaptation of polar bears:
(A) fat layer below skin
(B) two thick layer of fur
(C) strong sense of smell
(D) all of these
8. Typical desert climate is:
(A) Hot and dry
(B) wet
(C) cool
(D) none of these
9. Habitat for Red-eye frog is:
(A) Water
(B) Ice-cooled areas
(C) Trees
(D) Desert
10. Maximum plants and animals varieties are found in:
(A) Desert
(B) Polar area
(C) Tropical rain forest
(D) (A) (C) both
11. In India, Siberian crane comes to:
(A) Bharatpur, Rajasthan
(B) Sultanpur, Haryana
(C) Wetlands of North east
(D) All of these
12. Ghana bird Sanctuary is situated in:
(A) Rajasthan
(B) Gujarat
(C) MP
(D) UP
13. Length of day and night is equal in:
(A) Desert
(B) Tropical rain forest
(C) Polar region
(D) None of these
14. Tropical rainforest are found in:
(A) Western ghat of India
(B) Assam of India
(C) North Africa
(D) (A) & (B) both
15. Blending of animals with the surroundings is called:
(A) Camouflage
(B) Autotomy
(C) Hibernation
(D) None of these
16. Lion tailed macaque also called
(A) long tailed age
(B) Beard ape
(C) Hanuman monkey
(D) All of these
17. Trunk of elephant helps in
(A) Smelling
(B) Picking up food
(C) Both (A) & (B)
(D) None of these
18. Large ears of the elephant provide
(A) Strong sense to sound
(B) Cooling effects on body
(C) Both (A) & (B)
(D) Ability to hold objects
19. Desert conditions are also called
(A) Xeric
(B) Lotic
(C) Lentic
(D) None of these
20. Migratory birds detect direction of travel with the help of
(A) Land marks
(B) Sun during day
(C) Stars during night
(D) All of these
SECTION - B
One word or one sentence.
1. What is camouflage?
2. Name the aquatic organism showing adaptation surrounding.
3. Name the animals found in polar region and are good swimmer.
4. Name the region of earth which is most favourable for most of the animals and plants.
5. Red-eyed frogs are characteristics of which region?
6. Which part of India received rain for a major part of the year?
7. Define Weather.
8. What is habitat?
9. Write the function of Meteorological Department.
10.Write the major abiotic factors of environment.
ANSWER KEY
EXERCISE I
Section - A
1. Thermometer 2. North and South poles
3. North-eastern 4. Desert
5. Fishes, Butterflies 6. Climate
7. Adaptation 8. Sun
9. Hygrometer 10. Tropical rainforests
Section - B
1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True
6. True 7. False 8. True 9. True
EXERCISE II
Section - A
1. (A) 2. (B) 3. (B) 4. (B) 5. (B)
6. (B) 7. (D) 8. (A) 9. (C) 10. (C)
11. (D) 12. (A) 13. (B) 14. (D) 15. (A)
16. (B) 17. (C) 18. (C) 19. (A) 20. (D)