An electric cell is a device which converts chemical energy into electric energy.
The cell has two different metal plates – one is the positive terminal and the other is the negative terminal.
These plates are kept inside a chemical called electrolyte. The cell is a source of electric current. Electric current is the flow of electrons or charge.
An electric circuit is the closed path along which electric current flows from the positive terminal to the negative terminal of the cell.
A circuit generally has:
(a) a source of electric current - a cell or battery.
(b) connecting wires for carrying current.
(c) a device which uses the electricity - a bulb etc.
(d) a key or a switch – This may be connected anywhere along the circuit to stop or allow the
flow of current
.
(A) Battery :
The positive terminal of one cell is connected to the negative terminal of the next cell. Such a combination of two
or more cells is called a battery. Many devices such as torches, transistors, toys, TV remote controls, use batteries.
Connecting two cells together to make a battery
(B) Bulb :
In the bulb there is a thin wire, called the filament, which glows when an electric current passes through it.
When the bulb gets fused, its filament is broken.
(C) Electric switch :
An electric switch is a device that opens or closes an electric circuit.
When the switch (key) K is closed, the circuit is complete; current flows through the circuit and the bulb glows.
When the switch (key) K is open, the circuit is not complete; current does not flow through the circuit and the bulb does not glow.
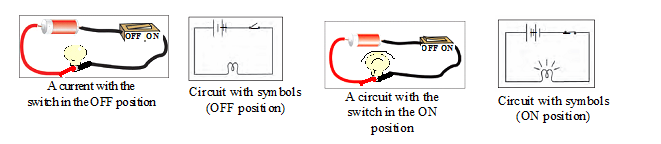

Some common electric components can be represented by symbols.
CONDUCTORS : The materials which allow electric current to pass through them.
Ex. All metals like Copper, Iron, Silver and Human body.
INSULATORS : The materials which do not allow electric current to pass through them.
Ex. Plastic, Wood, Rubber and Glass.
(A) Heating effect of current :
The wire which are not very good conductors gets hot when an electric current passes through it.
This is the heating effect of the electric current.
Ex.
(i) Electric Heater :
(ii) Electric Iron :
The amount of heat produced in a wire depends on its material, length and thickness. Thus, for different requirements,
the wires of different materials and different lengths and thickness are used.
(iii) Electric bulb :
The filament of an electric bulb gets heated to such a high temperature that it starts glowing.
(B) CHEMICAL EFFECT OF ELECTRIC CURRENT (ELECTROPLATING)
The method of plating one type of over another by means of electricity is called electroplating.
Ex. To electroplate a stainless steel razor blade with copper.
Materials required : Glass beaker, copper sulphate solution, two pieces of connecting wire (50 cm long), a cell, stainless steel razor blade.
Method : Remove the insulation from the ends of both wires. Tie one end of a wire to the stainless steel razor blade and tape
the other bare end to the negative terminal of the cell. Tape one end of the other wire to the positive terminal of the cell and dip
its other end into the copper scrub the razor blade clean and dip it in the solution.
After electricity passes through the circuit for some time you will find a reddish-brown deposit on the blade. This is the coating of copper.
(C) MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT :
The needle of a compass is a tiny magnet, which points in north-south direction. When we bring a magnet close to it, the needle gets deflected.
Similarly we can also seen that compass needle gets deflected when the current flows in a nearby wire. Hans Christian Oersted was the
first person who noticed the deflection of compass needle every time the current was passed through the wire. So, when electric current passes
through a wire, it behaves like a magnet. This is the magnetic effect of the electric current. In fact, an electric current can be used to make magnets.
Factors which effect the strength of magnetic effect by current :
(i) Magnetic effect of current depends on number of turns.
(ii) Magnetic effect of current depends the value of current.
(iii) Magnetic effect of current depends on the nature of core inside the coil.
APPLICATION OF HEATING & MAGNETIC EFFECT OF CURRENT
Electric Fuse :
Wires made from some special materials melt quickly and break when large electric currents are passed through them.
These wires are used for making electric fuses,(figure). In all buildings fuses are inserted in all electrical circuits.
There is a maximum limit on the current which can safely flow through a circuit. If by accident the current exceeds
this safe limit, the wires may become overheated and may cause fire. If a proper fuse is there in the circuit,
it will blow off and break the circuit. A fuse is thus a safety device which prevents damages to electrical circuits and possible fires.
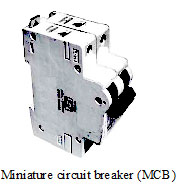
MCB :
These days Miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) are increasingly being used in place of fuses. These are switches which automatically
turn off when current in a circuit exceeds the safe limit. You turn them on and the circuit is once again complete.
Electromagnet :
Wind the wire tightly around the nail in the form of a coil. Connect the free ends of the wire to the terminals of a cell through a switch as shown in Fig.
The coil behaves like a magnet when electric current flows through it. When the electric current is switched off, the coil generally loses its magnetism.
Such coils are called electromagnets. The electromagnets can be made very strong and can lift very heavy loads. The electromagnets are also used
to separate magnetic material from the junk. Doctors use tiny electromagnets to take out small pieces of magnetic material that have accidentally
fallen in the eye. Many toys also have electromagnets inside them.
Electric bell :
It consists of a coil of wire wound on an iron piece. The coil acts as an electromagnet. An iron strip with a hammer at one end
is kept close to the electromagnet. There is a contact screw near the iron strip.
When the iron strip is in contact with the screw, the current flows through the coil which becomes an electromagnet. It, then,
pulls the iron strip. In the process, the hammer at the end of the strip strikes the gong of the bell to produce a sound. However,
when the electromagnet pulls the iron strip, it also breaks the circuit & the current through the coil stops flowing. The coil is no longer
an electromagnet & it no longer attracts the iron strip. The iron strip comes back to its original position and touches the contact screw again.
This completes the circuit. The current flows in the coil and the hammer strikes the gong again.
This process is repeated in quick succession. The hammer strikes the gong every time the circuit is completed. This is how the bell rings.
If a wire is stretched to n times of it's original length, its new resistance will be n2 times.
If a wire is stretched such that it's radius is reduced to of it's original values, then resistance will increases n4 times similarly
resistance will decrease n4 time if radius is increased n times by contraction.
If x% change is brought in length of a wire, its resistance will change by 2x%.
If n resistance (each R) are connected in series there resultant will be nR.
If n resistance (each R) are connected in parallel then their resultant will be .
The equivalent resistance of parallel combination is lower than the value of lowest resistance in the combination.
Ohm's law is not a fundamental law of nature. As it is possible that for an element :-
(i) V depends on I nonlinearly (e.g. vacuum tubes)
(ii) Relation between V and I depends on the sign of V for the same value [forward and reverse Bias in diode]
(iii) The relation between V and I is non unique. That is for the same I there is more then one value of V.
In general :
(i) Resistivity of alloys is greater than their metals.
(ii) Temperature coefficient of alloys is lower than pure metals.
(iii) Resistance of most of non metals decreases with increase in temperature. (e.g.carbon)
(iv) The resistivity of an insulator (e.g. amber) is greater then the metal by a factor of 1022
Temperature coefficient (a) of semi conductor including carbon (graphite), insulator and electroytes is negative.
At the time of charging a cell. When current is supplied to the cell, the terminal voltage is greater than the e.m.f. E
V = E + Ir
Series combination is useful when internal resistance is less than external resistance of the cell.
Parallel combination is useful when internal resistance is greater than external resistance of the cell.
Power in R (given resistance) is maximum, if its value is equal to net resistance of remaining circuit.
Internal resistance of ideal cell = 0
.png)
.png)
Magnetic field produced by solenoid does not depends on its radius of cross section (or average diameter)
Maxwell’s solenoid rule :– This rule is used to find out polarity of solenoid.
Magnetic field produced by solenoid is directed along its axis.
Magnetic field inside the solenoid is uniform.
Magnetic field outside the volume of the solenoid approaches to zero.
When a charge particle projected in uniform magnetic field neither perpendicular nor parallel then
trajectory of charge is called 'helix'.
Axis of helix :- It is a straight line along external magnetic field which joins all the centres of circular turns, called axis of helix.
Radius of circular path :- Centripetal force required to move the charge in a circle is provided by the magnetic force Fm = Fcp
q (vsinq) Bsin90° =
Magnetic force on per unit length of each infinite length wire is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction.
According to Flemming left hand rule or Right hand palm rule, like currents attracts to each other while unlike currents repels to each other.
Q.1 A magnetic needle gets deflected when brought near a current-carrying conductor. What does this show?
Q.2 Why does a bulb get warmer than the wires that connect it to a battery?
Q.3 What do you need to apply across a bulb to cause a current to flow through it?
Q.4 What happens when you place an iron nail in a current-carrying coil?
Q.5 Why do we use a soft iron core in an electromagnet?
Q.6 What is a fuse? How does it work?
Q.7 Mention four applications of electromagnets
Q.8 What is a circuit diagram? Draw the circuit diagram of a torch which works on three cells.
Q.9 Identify the following symbols. Also mark the positive and negative terminals in the symbol for the cell.
Q.10 How is the heat produced by an electric current related to resistance and the magnitude of the current?
Q.11 Why is a long and thin tungsten filament used in a bulb?
Q.12 Mention two problems associated with the heating effect of electric current.
Q.13 What is an electromagnet? Mention two properties of an electromagnet.
Q.14 What is electrical resistance? On what does the resistance of a piece of material depend? How does resistance affect current?
Q.15 Name four devices that use the heating effect of electric current.
Q.16 Explain with the help of a diagram the
construction and working of an electric bell.
Q.1 A moving charge produces -
(A) neither electric field nor magnetic field
(B) electrostatic field only
(C) magnetic field only
(D) both magnetic and electrostatic field
Q.2 Strength of an electromagnet increases by -
(A) increasing the number of turns of the coil
(B) increasing the current flowing through the coil
(C) using soft iron core for the coil
(D) all of the above
Q.3 An electric current produces -
(A) Magnetic effect
(B) Chemical effect
(C) Heating effect
(D) All of the above
Q.4 The process by which chemical change takes place in a substance
when electric current is passed through it is called -
(A) electrolysis
(B) electroplating
(C) electrodes
(D) thermionic conduction
Q.5 An electrolyte is -
(A) a light electric cell
(B) a liquid that conducts electricity
(C) a metal
(D) non of the above
Q.6 Cathode is -
(A) positively charged electrode
(B) negatively charged electrode
(C) a positively charged ion formed in the electrolyte
(D) a negatively charged ion formed in the electrolyte.
Q.7 Electric bell works on the principle of -
(A) chemical effect of current
(B) magnetic effect of current
(C) heating effect of current
(D) all of the above
Q.8 Which is the false statement ?
(A) Fuse wire has low resistance and melting point
(B) Heater wire has high specific resistance and melting point
(C) In these day M.C.B. is used in place of fuse wire
(D) Current does not flow in close circuit.
Q.9 An electric bell when ringing-
(A) carries no electric current
(B) carries continuous current
(C) carries intermittent current
(D) has a permanent magnet to make it work
Q.10 Which is the best conductor ?
(A) carbon (B) Copper
(C) Iron (D) Aluminium
Q.11 The magnitude of a current flowing through a device depends
(A) only on the voltage across it
(B) only on its resistance
(C) on its resistance and the voltage across it
(D) none of these
Q.12 Nichrome is used for making
(A) the filaments of bulbs
(B) fuse wires
(C) heater elements
(D) coils for electromagnets
Q.13 To make a battery of 9 volts. how many 1.5 V cells are needed?
(A) 6 (B) 5
(C) 4 (D) 3
1. D 2. D 3. D 4. A 5. B 6. B
7. B 8. D 9. C 10. B 11. C 12. A
13. A
Q.1 Potential difference between a live wire and the neutral wire is :
(A) 200 volt (B) 150 volt (C) 210 volt (D) 220 volt
Q.2 A rectangular coil of copper wires is rotated in a magnetic field.
The direction of the induced current changes once in each :
(A) One revolution (B)One-fourth revolution (C) Half revolution (D) Two revolutions.
Q.3 Magnetic field inside a long solenoid carrying current is :
(A) Same at all points
(B) Minimum in the middle
(C) More at the ends than at the centre
(D) Found to increase from one end to the other.
Q.4 At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit :
(A) Vary continuously (B)Reduces considerably (C) Increases heavily (D) does not change.
Q.5 The frequency of direct current is :
(A) Zero (B) 50 Hz (C) 60 Hz (D) 100 Hz.
Q.6 The frequency of household supply of a.c. in India is :
(A) Zero (B) 50 Hz (C) 60 Hz (D) 100 Hz.
Q.7 The most important safety device method used for protecting electrical
appliances from short circuiting or overloading is :
(A) Earthing (B) Use of stabilizers
(C) Use of electric meter (D) Use of fuse
Q.8 Current flowing in conductor A is 2A and current flowing in conductor B is 4A. The ratio of magnetic field produced
around conductor A to the magnetic field produced around conductor B at a distance 10 cm from both the conductors is
(A) 2 : 1 (B) 1 : 2 (C) 4 : 1 (D) : 1
Q.9 Current flowing in conductors A and B is same, what is the ratio of the magnetic field produced around the conductor
A at a distance of 5 cm from the conductor to the magnetic field produced around the conductor B at a distance of
2 cm from this conductor is
(A) 0.04 (B) 0.4 (C) 4.0 (D) 10
Q.10 Same amount of current flows in the same direction .long the two parallel conductors separated by a small distance :
(A) Both conductors attract each other
(B) Both conductors repel each other
(C) Conductors neither attract each other nor repel each other
(D) Both conductors rotates about their axis.
Q.11 When an electric current flows through a long solenoid, magnetic field is set up in and around the solenoid :
(A) Magnetic field inside the solenoid is non-uniform and weak
(B) Magnetic field outside the solenoid is uniform and strong
(C) Magnetic field inside the solenoid increases as we move towards the ends of the solenoid
(D) Magnetic field of solenoid resembles the magnetic field of the bar magnet.
Q.12 Magnetic field produced at the centre of a current carrying circular wire is :
(A) Directly proportional to the square of the radius of the circular wire
(B) Directly proportional to the radius of the circular wire
(C) Inversely proportional to the square of the radius of the circular wire
(D) Inversely proportional to the radius of the circular wire.
Q.13 The direction of the magnetic field at a point P above the current carrying wire is
(A) Down the page (B) Up the page (C) Into the page (D) Out of the page.
Q.14 Which of the following properties of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field ?
(A) Mass (B) Speed (C) Velocity (D) Momentum
Q.15 A positively charged particle say an alpha particle projected towards west is deflected
towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is :
(A) Upward (B) Downward (C) Towards south (D) Towards east
Q.16 Magnitude of magnetic field intensity at a point around a current carrying conductor is B.
If the strength of current in the conductor becomes double, then the magnitude of magnetic
field intensity at the point around the conductor is :
(A) (B) B (C) (D) 2B
Q.17 Two parallel conductor carrying current in the same directions
(A) Repel each other
(B) Attract each other
(C) Sometimes attract and sometimes repel each other
(D) None of these
Q.18 Two parallel conductor carrying current in the opposite directions
(A) Repel each other
(B) Attract each other
(C) Sometimes attract and sometimes repel each other
(D) None of these
Q.19 Force acting on a stationary charge Q in the magnetic field B is :
(A) B Q u (B) BQ/u (C) Bu/Q (D) Zero
Q.20 If the plug of the key is taken out (i.e. the circuit is made open) and magnetic
field lines are drawn over the horizontal plane white sheet of paper, the lines are :
(A) Concentric circles (B) Elliptical in shape
(C) Straight lines parallel to each other (D) Parabolic in shape
Q.21 When current passes through a long straight solenoid, N and S poles are created at the two ends of the solenoid. Which of the following statemtns is incorrect ?
(A) The field lines inside the solenoid are in the form of straight lines indicating that magnetic field is same at all the points inside the solenoid.
(B) The pattern of the magnetic field lines associated with the solenoid is different from the pattern of the magnetic field lines around a bar magnet.
(C) N-and S-poles exchange portions when the direction of the current through the solenoid is reversed.
(D) Magnetic field produced inside the solenoid can be used to magnetise a bar of magnetic material like soft iron, when placed inside the solenoid.
In these type of Questions, two statements are given. Choose the correct option by following directions given below :
(Q. 22 to 24)
(A) Statement I is correct and Statement II is correct explanation of the statement I.
(B) Statement I is correct but Statement II is not the correct explanation of the statement I.
(C) Statement I is true but statement II is not true.
(D) Statement I is not true but statement II is true.
Q.22 Statement I : A soft iron bar placed inside a solenoid carrying current is magnetised.
Statemet II : Magnetic field inside a long solenoid carrying current is non-uniform.
(A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D
Q.23 Statement I : The strength of magnetic field of a permanent magnet decreases with the increase in temperature.
Statemet II : A permanent magnet can be demagnetised by heating it.
(A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D
Q.24 Statement I : A charged particle moving parallel to the direction of magnetic field experiences a force.
Statemet II : A charged particle moving at right angle to the direction of magnetic field experiences maximum force.
(A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D
Q.25 A current carrying conductor placed perpendicular to the magnetic field experience a force.
The displacement of this conductor in the magnetic field can be increased by.
(A) Decreasing the magnetic field (B) Decreasing the current in the conductor
(C) Increasing the magnetic field (D) Decreasing the length of the conductor.
Q.26 A conductor of length 50 cm, carrying current of 0.1 A, when placed perpendicular
to direction of magneitc field 0.2 T experience force :
(A) 1.0 N (B) 0.1 N (C)0.01N (D) 0.01 N.
Q.27 A charged particle having charge 3.2 × 10–19 C is travelling with a speed of 1.0 × 106 ms–1.
When it passes perpendicular to the magneitc field 0.4 T, then the force experienced by it is :
(A) 12.8 × 10–13 N (B) 1.28 × 10–13 N
(C) 19.2 × 10–15 N (D) 1.92 × 10–15 N.
Q.28 A charged particle having charge 1.6 × 10–19 C travels with a speed of 3.2 × 106 ms–1 in
a direction parallel to the direction of magnetic field 0.04 T. The force experienced by the particle is :
(A) 2.0 × 10–14 N (B) 0.2 × 10–14 N
(C) Zero (D) 4.0 × 10–14 N
Q.29 A magnetic compass is placed near a current carrying wire. The deflection of the needle of the magnetic compass increases. It shows that
(A) Current in the wire is decreasing
(B) Current in the wire is increasing
(C) Current in the wire has nothing to do with the deflection of the needle of the magnetic compass
(D) Magnetic compass has been disturbed by some one.
Q.30 A charged particle moving in a magnetic field experience a maximum force, when it moves at right angle to the direction of magnetic field.
However, a student observes that a chraged particle moving in the region of a magnetic field experiences no
force and continues to move in a straight line. The observation of the student is correct only if :
(A) Charged particle moves at an angle of 30° with the magnetic field
(B) Charged particle moves at an angle of 60° with the magnetic field
(C) Charged particle either moves parallel or anti-parallel to the magnetic field
(D) Charged particle can never move in a straight line in the magnetic field.
Q.31 A soft iron rod can be made an electro-magnet. Which of the following procedures would be
adopted to test that the soft iron rod had become a magnet ?
(A) Place the iron rod near a bar magnet and observe if it attracts iron pins
(B) Place the iron rod near a current carrying wire and observe if it attracts iron pins
(C) Place the iron rod inside a currrent carrying solenoid and observe if it attacts iron pins
(D) None of these.
Q.32 Current can be made to flow through a coil without connecting the coil with a battery.
Which of the following procedures would be most suited to test this fact ?
(A) Connect a galvanometer across the ends of the coil and observe if galvanometer
shows a deflection, when a bar magnet is placed near the one end of the coil.
(B) Connect a galvanometer across the ends of the coil and observe if galvanometer
shows a deflection, when a bar magnet is placed inside the coil.
(C) Connect the galvanometer across the ends of the coil and observe if galvanometer
shows a deflection, when a bar magnet is moved towards or away from the coil and along the axis of the coil.
(D) Connect the galvanometer across the ends of the coil and observe if galvanometer
shows a deflection, when a bar magnet is moved at right to the axis of the coil.
Q.33 Two coil A and B placed close to each other. If current in the coil A is changed, some current will
be induced in the coil B. This is because of electromagnetic induction. In this statement :
(A) Inference is correct but reasoning is not correct
(B) Inference is incorrect but reasong is correct
(C) Inference as well as reasoning are correct
(D) Neither inference nor reasoning is correct.
1. D 2. C 3. A 4. C 5. A 6. B 7. D
8. B 9. B 10. A 11. D 12. D 13. D 14. C
15. D 16. D 17. B 18. A 19. D 20. C 21. B
22. C 23. A 24. D 25. C 26. C 27. B 28. C
29. B 30. C 31. C 32. C
33. C
SECTION-A
• Fill in the blanks
1. In a cell, the longer line represents the _____________terminal
2. In a cell, the thicker, shorter line represents the _____________terminal
3. The bulb glows, when the switch is in _____________position.
4. The circuit is said to be _____________, when no current flows through any part of the circuit.
5. The wire gets _____________when an electric currernt passes through it
6. The electric heater contain a coil of wire, which is called _____________
7. A _____________is a safely device, which prevents damages to electrical circuits.
8. When _____________passes through a wire it behaves like a magnet.
9. The _____________are used to separate magnetic material from the junk.
10. An electric bell has _____________in it.
SECTION-B
• True or False
1. In a closed electric circuit, bulb will glow.
2. Metals are the good conductor of electricity
3. The combination of batteries is called cell.
4. Ammeter is used for measuring the magnitude of current in an electric circuit.
5. Voltmeter is used for measuring potential difference between two known points in an electric current.
6. The filament of bulb is made of Tungsten and of healer is made of Nichrom.
7. The evacuated bulb containing argon gas prevents the tugnsten filament from heating.
8. The electric fires due to overloading can be prevented by resistors.
9. The fuse wire is always placed in the neutral wire of an electric circuit.
10. Whenever current is passed through a straight conductor, it behaves like a magnet.
Exercise-II
SECTION-A
• Subjective Questions
Very Short Questions (1 mark each)
1. Who is responsible for current in a circuit?
2. What will happen to a man, when an electric current is passed through a nerve?
3. What is open electric circuit?
4. What are bad conductors of electricity.
5. What for the following symbols are used
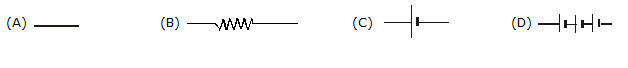
6. Name the material used to make the element of a heater.
7. Name the material used to make the filament of an electric bulb.
8. Which gas is used in the bulb?
9. What is a fuse?
10. Magnetic field is associated with current, who observed it first time?
Short Questions (2 marks each)
1. Draw the symbols of the following electric component.
(a) Switch in on position (b) Battery (c) Bulb (d) cell
2. What for a cell holder is used?
3. Draw a circuit diagram consists of a bulb, cell and switch.
4. Explain, how does a fuse work?
5. What are electromagnets?
6. Why are miniature circuit breakers increasingly being used in place of fuses.
7. Why some special materials made wires are used for making electric fuses.
8. What are the factors on which the amount of heat produced in a wire depends.
9. Name any two effects of electric current.
10. What is the SI unit of current?
Long Questions (3 marks each)
1. An electrician is doing repairs in a house. He wants to replace a fuse by a piece of wire. Would you agree? If not why?
2. In the circuit shown in figure given below:
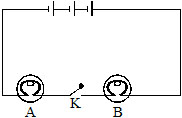

(a) Would any of the bulb glow, when the switch is in the ‘OFF’ state.
3. Why does a glowing electric bulb become warm?
4. To what use are the following put in an electric circuit.
(i) Single key (ii) Connecting wire (iii) Cell (iv) Rheostat
5. Why does an overloaded electric circuit catch fire?
Long Questions (4 marks each)
1. Why do elements of electric heater becomes red hot, when connected to electric supply?
2. With the help of labelled diagram explain the construction and working of electric bell.
3. How the cells can be arranged in a circuit to give maximum current.
4. What is the full form of MCBs and CFL.
5. Give one activity by which, we can say that magnetic effect is associated with current.
Exercise-III
SECTION-A
• Multiple Choice Questions
1. Two electric path which starts from the positive terminal of a cell ends at negative terminal, without any break is called.
(A) Open circuit (B) Closed circuit (C) Both (A) & (B) (D) None of these
2. The material which allows the electric current to flow through it is called
(A) Conductor (B) Insulator (C) Element (D) None of these
3. A coil with a core of iron nail, which acts as a magnet only when electric current flows through it is
(A) Conductor (B) Insulator (C) Electromagnet (D) None of these
4. What we call it, when in a circuit more current is passing than it can tolerate.
(A) Open circuit (B) Closed circuit (C) Overloading (D) Short circuit
5. What that state is called, when a live wire connects to a neutral wire or the earth wire,
by passing an electric current in the device?
(A) Fuse (B) Electromagnet (C) Overloading (D) Short circuit
6. Vacuum is a good conductor of electricity
(A) Yes (B) No (C) Don’t know (D) May be
7. Ammeter is used to measure the flowing in a circuit
(A) Volt (B) Current (C) Resistance (D) All
8. To protect very sensitive devices which one is used?
(A) Resistor (B) Cartridge fuse (C) Fuse (D) None
9. Voltmeter measures the potential difference across the given points
(A) Yes (B) No (C) May be (D) All
10. Which device detect the flow of electric current in the circuit?
(A) Ammeter (B) Voltmeter (C) Galvanometer (D) All
SECTION-B
• One Word Subjective Questions
1. Define current.
2. What is necessary for the flow of charge from one place to another?
3. The electric current is measured in ampere. Can it be written in another unit.
4. In which unit charge is measured.
5. In which unit resistance to the flow of electricity is measured.
6. The electromotic force is measured in which unit.
7. What we study in electrodynamic?
8. Name the material which conduct electricity under certain circumtances.
9. Name the device which is used to change the magnitude of current in the circuit.
10. Who invented electricity.
ANSWERS KEY
EXERCISE - I
SECTION-A
1. Positive 2. Negative 3. ON 4. OFF
5. Hot 6. Element 7. Fuse 8. Current
9. Electromagnets 10. Electromagnet
SECTION-B
1. True 2. True 3. False 4. True
5. True 6. True 7. False 8. False
9. False 10. True
EXERCISE - III
SECTION-A
1. (B) 2. (A) 3. (C) 4. (C) 5. (D)
6. (A) 7. (B) 8. (B) 9. (A) 10. (C)