Any material which cannot be used in the form in which it is produced is called a waste. According to their physical state, waste can be classified into
3 categories – Solid waste, liquid waste & gaseous waste.
The impurities present in waste water are called contaminant. This waste water is called sewage.
1. Domestic Waste Water :
It includes all kinds of wastes like human excreta, food waste, soaps, detergents, oil, animal excreta, urine, etc.
2. Agricultural Waste Water :
The waste water generated from farms and agricultural fields contains harmful pesticides, weedicides and animal wastes.
3. Industrial Waste Water :
The waste water generated from various industries contains harmful chemicals. The discharge of industrial waste water is called Industrial effluent.
4. Petroleum Oil :
The leakage of petroleum oil into the sea during drilling and shipping pollutes sea water. Oil spill is caused due to release of oil into rivers and oceans knowingly or unknowingly.
5. Mining :
Waste water is also generated as a result of mining activities.
6. Construction Activity :
Lot of waste water is generated during various stages of building houses, homes, malls, multiplexes, etc.
There are three processes which are involved in treating waste water before it is discharged into the water reservoirs. These processes are :
1. Primary treatment 2.Secondary treatment
3. Tertiary treatment
A. Primary Treatment :
B. Secondary Treatment :
C. Tertiary Treatment :
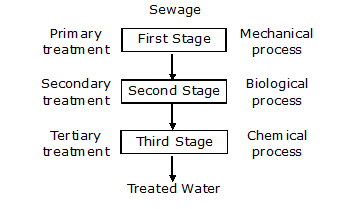
The treated water which is obtained from sewage treatment plant is used for irrigating fields, lawns and for aquaculture. In Kolkata the treated water
is used for fisheries and growing crops and
vegetables. The treated water is finally released in streams and rivers.
Drinking of waste & contaminated water cause many human disease in India
People consuming contaminated water may suffer from diseases like gastroenteritis, dysentry, typhoid, cholera, meningitis and hepatitis.
Q.1 How will you define a waste ?
Q.2 Why are bacteria used in sewage treatment plants ?
Q.3 Name any four water borne diseases.
Q.4 Name two organic impurities present in sewage
Q.5 Name two inorganic impurities present in sewage.
Q.6 Name one disease which are caused by bacteria present in sewage.
Q.7 What problem do we face with open drainage?
Q.8 What is oil spill and how is it harmful for aquatic life ?
Q.9 What are the main constituents of sewage ?
Q.10 What is the function of a treatment plant ?
Q.11 Why butter and oil should not be released in the drainage ?
Q.12 Discuss the stages of waste water treatement process.
Q.13 Why is it harmful to discharge untreated sewage into the rivers ?
Q.14 Discuss the three stages involved in water treatment plant.
Q.15 List five ways to control sewage generation from your home.
Q.1 Waste water containing human excreta is known as -
(A) Sewage (B) Sewer
(C) Sewerage (D) None
Q.2 Discharge of industrial waste is called -
(A) Effluent (B) Sewer
(C) Sewerage (D) Sludge
Q.3 The light materials which float during waste water treatment is -
(A) Sludge (B) Scum
(C) Biogas (D) Sewer
Q.4 Water is disinfected by -
(A) Chlorine (B) Ozone
(C) UV-radiations (D) All of these
Q.5 Primary treatment is a -
(A) Mechanical process
(B) Chemical process
(C) Biological process
(D) None of these
Q.6 The discharge of industrial waste water is called-
(A) Industrial effluents
(B) Oil spill
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
Q.7 Sewage is often processed with the help of -
(A) Septic tank
(B) Over tank
(C) Both (A) and (B)
(D) None of these
Q.8 Contaminated water disease is -
(A) Gastroenteritis (B) Malaria
(C) Flu (D) None of these
Q.9 A feul produced by anaerobic fermentation of sludge is -
(A) Biogas (B) Petrol
(C) Kerosene (D) Wood
ANSWER KEY
1. A 2. A 3. B 4. D
5. A 6. A 7. C 8. D
9. A
EXERCISE-I
SECTION-A
• Fill in the blanks
1. In secondary treatment sewage water is treated with _________________
2. _____________is the solid matter that settles to the bottom of the septing tank.
3. Chlorination is done during ______________ treatment.
4. The sewage is carried by ______________ pipes or sewers
5. The network of pipes which carries waste water to water treatment plant is called ________________
6. The treatment designed to inactivated or kill disease causing bacteria is called _________________
7. Drains get blocked by ______________ and _________________
8. The activated sludge is about _________________water.
9. Waste water released by houses is called ______________
SECTION-B
• True or False
1. Micro-organisms decompose the organic matter present in sewage (T)
2. Sewage consists mainly of human excretion (F)
3. Scum is also called Detritus (F)
4. Pretreatment takes place in the collection system before waste water reaches the treatment plant (F)
5. An aerated arit chamber detention time usually ranges from 3 to 5 minutes (T)
6. Dirty water should be kept in houses (F)
7. Water must be wasted. (F)
8. Sewer system is available in cities and towns (T)
9. All drains must be connected to sewer system (T)
10. Removal of pollutants is known as cleaning of water. (T)
Exercise-II
• Very Short Questions (1 mark each)
1. Which micro-organism decomposes the sludge
2. What is Sewage
3. Organic impurities in the waste water
4. Which process of waste water treatment is commonly known as “Sewage treatment”?
5. Define term ‘Contaminants’
6. Which removes the floatable solid like oil and grease?
7. Name two by products of waste water treatment
8. Two chemicals used to disinfect water
9. Name two inorganic impurities in the waste water.
10. Which process removes the solids like faeces and other substances from the waste water?
• Short Questions (2 marks each)
1. Define sewage treatment
2. What is the reason behind increasing scarcity of fresh water.
3. What is meant by Vermi-compositing toilet?
4. Why should we plant eucalyptes tree all along sewage ponds.
5. (a) Which is a source of water for wells, tubewells, springs and rivers?
(b) Which emits foul smell?
• Long Questions (3 marks each)
1. What type of impurities are present in sewage?
2. Define alternate arrangement for sewage disposal?
3. How ‘bar screen’ and grit and sand removal tank help in clarification of water?
4. Why should Oils and fats not be released in the drain? Explain
• Long Questions (4 marks each)
1. Outline your role as an active citizen in relation to sanitation.
2. Describe the steps involved in getting purified water from waste water.
3. With the help of an activity, explain the various processes that take place on the waste water treatment plant (WWTP)
EXERCISE-III
SECTION-A
• Multiple Choice Questions
1. Grit is composed off
(A) Sand and eggshells (B) Floating woods and paper
(C) Plastics and rubber goods (D) Grease and Scum
2. For disinfection purposes, chlorine is added to the
(A)Secondary clarifier (B) Sludge digester
(C) Trickling filter (D) Aeration tank
3. When waste water remains in the collection system too long. What can develop?
(A) Odors (B) Corrosion of pipes and concrete structures
(C) Production of hydrogen sulphide gas (D) All of the above
4. Which diseases are spread by waste water discharges?
(A) Typhoid (B) Hepatitis (C) Cholera (D) Dysentry
5. The hole at the bottom of sink or the pipe that carries the dirty water away is called
(A)Drain (B) Sewage (C) Sludge (D) None of these
6. The water that is fit for use and very difficult to get is called
(A) Clean water (B) Waste water (C) Ground water (D) None of these
7. The water day is celebrated every year on
(A) 22nd March (B) 25th March (C) 23rd March (D) None of these
8. Small scale sewage treatment is carried out by
(A) Cesspols (B) WWTP (C) Septic tanks (D) A and C
9. Chemical used to disinfect water
(A) Bleaching powder (B) Chlorine
(C) Ozone (D) All
10. Solid waste extracted in sewage treatment
(A) Excreta (B) Compost (C) Sludge (D) NOne
11. Word related to hygine
(A) Disinfection (B) Sanitation (C) Sterilization (D) Cleaning
12. Instrument used to remove floatable solids from waste water
(A) Agitater (B) Skimmer (C) Grit (D) Barscreen
13. Clarified water is cleaned by
(A) Anaerobic bacteria (B) Aerobic bacteria
(C) Both (D) None
14. Different ways of disposing off the sewage to maintain sanitation
(A) Dumping (B) Composting (C) Destruction by fire (D) All
15. Disease causing micro-organism
(A) Bacteria (B) Viruses (C) Both (D) None
(B) Short Questions
1. What is cleaning of water?
2. Name two nutrients present in sewage?
3. Use of chlorine or ozone in treatment plant?
4. How is water in river cleaned up?
5. Why used tea leaves should not be thrown in drains?
6. How sewage is disposed in aeroplane?
7. What do you understand by Sanitation and disease?
ANSWER KEY
EXERCISE-I
SECTION-A
1. Anaerobic Bacteria 2. Sludge
3. Tertiary 4. Drainage, Sewers
5. Sewerage system 6. Disinfection
7. Cooking oils, fats 8. 97%
9. Sewage
SECTION-B
1. T 2. F 3. F 4. F 5. T
6. F 7. F 8. T 9. T 10. T
EXERCISE-II
1. Anaerobic Bacteria 3. Animal waste, human faeces, urine
6. Skimmer 8. Ozone and Chlorine
Exercise-III
Section-A
1. (A) 2. (A) 3. (D) 4. (C) 5. (A)
6. (A) 7. (A) 8. (D) 9. (D) 10. (C)
11.(B) 12. (B) 13. (B) 14. (D) 15. (C)