Any fabric (cloth) is made up of yarns arranged together which are further made up of still thinner strands called fibres.
Thread like part in animal and vegetable tissues is called fibres. They are the raw materials that are long,
strong and pliable enough to be spun into yarns and woven into fabrics.
CLASSIFICATION OF FIBRES
Natural, semi-synthetic and artificial (synthetic) fibres:
(a) Natural Fibres:
Fibres obtained from plants are called plant fibres and fibres obtained from animals are called animal fibres.
Plant and animal fibres together are called natural fibres. For example cotton, jute and silk.
(i) Jute: It is a long, soft, shiny plant and is one of the cheapest natural fibres. Jute fibres are composed of cellulose and lignin.
Jute is used to make cloth for wrapping bales of raw cotton, and to make sacks and coarse cloth.
Jute fibres are also woven into curtains, chair coverings, bags, carpets, hessian cloth, etc.
(ii) Wool: It is a fibre obtained from animals like sheep, lambs and goats. It is a form of hair, with a wavy structure characteristic of the breed of sheep.

Wool comes from sheep, llama, alpaca, guanaco and vicuna.
In India, mostly sheep are reared (to bring up) for getting wool.
Sheep hair is sheared off from the body, scoured, sorted, dried, dyed, and woven to yield wool.
Scouring: The fleece of the sheep along with a thin layer of skin is removed from its body. This is called shearing.
Sorting: Separation of hair of different textures is called sorting.
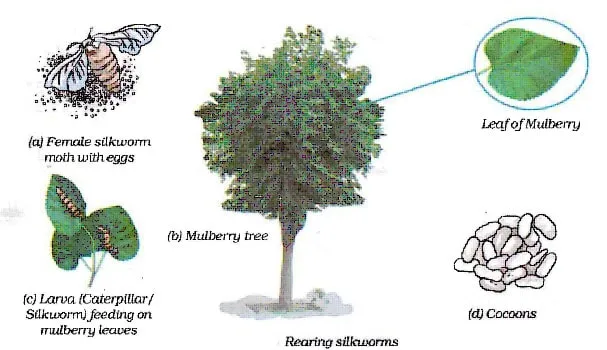
(iii) Silk: It is a natural fibre consisting mainly of two proteins, fibroin and sericin.
Q.1 What is semisynthetic fibre? How it is obtained.
Q.2 Give the type of polymers according to their source of availability.
Q.3 Give the uses of cotton and jute.
Q.4 Explain the followng terms.
(i) Shearing
(ii) Scouring
(iii) Sorting
(iv) Sericulture
Q.5 What is Occupational hazard.
Q.6 Explain selective breeding?
Q.7 Name some Indian breeds of sheep?
Q.8 What is reeling of the silk?
Q.9 Name the different types of silk?
Q.1 Silkworms are _________ of silk moth.
Q.2 Silk fibres are made up of ________.
Q.3 Silk & Wool are ________ .
Q.4 The most common silk moth is the ________.
Q.5 Wool is obtained from the _______ of the sheep or yak.
Q.1 Wool is a/an:
(A) fibre obtained from cocoon
(B) artificial fibre
(C) plant fibre
(D) animal fibre
Q.2 Which fibres are used to make clothes?
(A) Natural (B) Synthetic
(C) Both (D) None of these
Q.3 Which of these is not a plant fibre?
(A) Seed fibre (B) Fruit fibre
(C) Avian fibre (D) None of these
Q.4 _________ is a cellulose fibre:
(A) Cotton (B) Wool
(C) Silk (D) None of these
Q.5 Which of the following is made from coconut fibres?
(A) Seaters (B) Shoes
(C) Mattresses (D) Sarees
Q.6 Wool is graded according to its-
(A) length & texture (B) dyeing capacity
(C) Both (A) & (B) (D) None of these
Q.7 Eri is a type of:
(A) Silk (B) Wool
(C) Cotton (D) None of these
Q.8 Which fibre burns with a yellow flame?
(A) Silk (B) Nylon
(C) Rayon (D) None of these
Q.9 Removing the wool from a sheep is called
(A) sericulture (B) shearing
(C) spuning (D) ginning
Q.10 Removing of silk fibre from cocoons is
(A) shearing (B) reeling
(C) sericulture (D) None of these
Q.11 Silk is a natural animal fibre obtained from silkworms named
(A) Bombyx mori (B) Earthworm
(C) Morus alba (D) None of these
Q.12 The fibre obtained from Angora goat is
(A) Mohair (B) Alpaca
(C) Llama (D) None of these
Q.13 Cotton is obtained from -
(A) larva of silkworm
(B) hairs of sheep
(C) balls of flowers
(D) patsun
Q.14 The wool of Arabia camels is used to make _______.
(A) sweaters (B) carpets
(C) shawls (D) None of these
Q.15 Which disease is most common among the workers of sericulture industry ?
(A) Cancer & Skin (B) Respiratory & Skin
(C) Cancer & T.B . (D) None of these
Q.16 Silk thread woven by silkworm around its larva is made up of
(A) carbohydrates (B) proteins
(C) fat (D) None of these
Q.17 Jute is-obtained from which part of patsun ?
(A) Leaves
(B) Root
(C) Stem
(D) Both leaves and stem.
Q.18 Wool burns with smell of burning hairs
(A) as it is obtained from hairs of sheep and goat.
(B) because it is a natural fibre.
(C) because it is synthetic fibre.
(D) None of these
Q.19 Caterpillars spin their cocoons at which stage?
(A) Pupa Stage (B) Larva Stage
(C) Both (A) & (B) (D) None of these
Q.20 Pashmina shawls are obtained from the skin of which animal?
(A) Kashmiri Goat (B) Camel
(C) Yak (D) None of these
1. D 2. C 3. C 4. A
5. C 6. C 7. A 8. C
9. B 10. B 11. A 12. A
13. C 14. B 15. B 16. B
17. C 18. A 19. A 20. A
A. Fill in the blanks
1. Synthetic fibre is also called _______________ and _______________ fibre.
2. Fabrics are made from _______________.
3. _______________ fibres are made by human beings.
4. The silk fibres are obtained from the _______________ of silk moth.
5. Woollen fabrics are _______________ insulator of heat.
6. The people who do sorting of wool get infected by a bacterium called _______________.
7. The process of drawing woollen fibres in to straight form is called _______________
8. Silk worm feed on _______________ leaves.
9. Tweed and worsted are type of _______________ fabrics.
10. The oily substance found in raw wool is called _______________.
11. The process of removing fleece from the sheep is _______________.
B. State true or false
1. Rayon fibre is also known as natural silk.
2. A large unit of monomer is called polymer.
3. Polythene is an example of plastic.
4. Plastic are corroded easily.
5. Plastic is light, strong and durable.
6. Melamine is a versatile material.
7. Plastics are poor conductor of heat & electricity.
8. Cellulose is made up of a large number of glucose units.
9. Nylon is a natural fibre.
10. Sweaters and shawls are made up of Nylon .
A. Short questions:-
1. What do you mean by natural fibres?
2. What are Synthetic fibres?
3. What are thermoplastics?
4. What are thrmosetting plastics?
5. What do you mean by artificial silk?
6. What are monomers?
7. What are polymers?
8. What is polymerisation?
B. Very long questions
1. Write the characteristics of Synthetic fibres?
2. What are the advantage of Synthetic fibres?
3. Write the uses of Acrylic fibres?
4. Write the advantage and disadvantage of natural fibres?
5. What are the raw materials which are used for synthetic plastics?
6. What do you mean by 4-R principle.
A. MCQs with one correct choice
1. The raw material for making rayon is-
(A) ethene (B) wood pulp (C) ester (D) PVC
2. Synthetic fibre used for making light weight blankets is:
(A) Polyester (B) Koroseal (C) Acrylic (D) Polythene
3. The material which is not biodegradable is:
(A) Card board (B) Cotton guaze (C) dried leaves (D) nylon fishing nets
4. Rayon fibres are used for making:
(A) Undergarments (B) bed sheets (C) Parachutes (D) Sail of boats
5. Synthetic fibres-
(A) have lustre (B) need lot of ironing
(C) do not get electricity charged (D) Absorb moisture
6. Artificial fibre is
(A) Synthitic fibres (B) man made fibres (C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None of these
7. Rayon fibre is not used for:
(A) Carpets (B) Bed sheets (C) Automobile tyres (D) Parachutes
8. Terylene is used for:
(A) Parachutes (B) Sailing boats (C) Conveyor belts (D) Both (B) and (C)
9. Which of the following is not characteristics of synthetic fibres:
(A) High lusture (B) Absorb more sweat(C) Less expensive (D) Easy to clean
10. Which of the following is natural fibre:
(A) Silk (B) Nylon (C) Terylene (D) Polythene
11. Which is the example of thermosetting plastics:
(A) Polythen (B) PVC (C) Bakelite (D) Nylon
12. Which is the examle of thermoplastic:
(A) Electric Switches (B) Water pipes (C) Dinner sets (D) Terylene
13. Which plastic has anti-stick property:
(A) Bakelite (B) Teflon (C) Melamine (D) All of these
14. Which fibre is called regenerated fibre:
(A) Nylon (B) Teflon (C) Rayon (D) Dacron
15. Which of the following is synthetic fibre:
(A) Terene (B) Silk (C) Wool (D) Cotton
B. Write one word answers
1. Name the fabric which is water proof as well as air proof?
2. Name the fibre which is also known as artificial silk?
3. Name the material which do not get decomposed by various natural process?
4. The material which get decomposed by various natural process?
5. Which raw material is used for making rayon?
6. Which synthetic fibre is used for making light weight blankets?
7. Name the simplest molecule of a polymer?
8. What is called the combination of a large number of monomers?
9. Which fibres are good absorber of sweat?
10. Which fibres are used for making hand knit sweaters?
11. Name the fibre which burns vigorously with a smell of burning paper?
Answers
A. Fill in the blanks
1. Man made, artificial 2. Fibres 3. Synthetic 4. Cocoon 5. Good 6. Anthrax
7. Carding 8. Mulberry 9. Woollen 10. Lanolin 11. Shearing
B. State true or false
1. [F] 2. [T] 3. [T] 4. [F] 5. [T]
6. [T] 7. [T] 8. [T] 9. [F] 10. [F]
A. MCQs with one correct choice
1. (B) 2. (C) 3. (D) 4. (B) 5. (A)
6. (C) 7. (D) 8. (D) 9. (B) 10. (A)
11. (C) 12. (D) 13. (B) 14. (C) 15. (A)
B. Write one word answers
1. Koroseal/PTFE 2. Rayon 3. Non biodegradable
4. Biodegradable 5. Wood pulp 6. Acrylic
7. Monomer 8. Polymer 9. Cotton fibres
10. Wool 11. Cotton
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. An expensuve and rare fibre called Cashmere is obtained from
(A) Goat (B) Sheep
(C) Camel (D) Rabbit
2. The small fluffy fibres are
(A) Reels (B) Burrs
(C) Combs (D) Bolls
3. Silk moth feed on
(A) Mulberry leaves (B) Grape leaves
(C) Eucalyptus leaf (D) Neem Leaves
4. Which of thes is a symthetic fibre?
(A) Mobair (B) Alpaca
(C) Vicuna (D) Rayon
5. The life cycle of silkworm is
(A) Eggs, lerva, pupa, adult
(B) Eggs, Pupa, larva, adult
(C) Eggs, larva, adult, pupa
(D) None of these
6. Suitable temperature for eggs of silkworm to hatch is
(A) 20-27°C (B) 22 - 27°C
(C) 25 - 30°C (D) 25 - 31°C
7. Which of the following is the function of hair in animals?
(A) Keeps body cool
(B) Protects internal organs
(C) Trap a lot of hair
(D) Give beauty
8. Removal of fleece of sheep with skin is
(A) Refining (B) Shearing
(C) Shaving (D) None of these
9. .........and........yield wool found in south America.
(A) Yak and sheep (B) Goat and sheep
(C) Hama and alpaca (D) Angora goat
10. Rearing of silk worm is
(A) Silviculture (B) Sericulture
(C) Apculture (D) Horticulture
11. ........wool is common in Ladhak and Tibet.
(A) Yak (B) Sheep
(C) Goat (D) Camel
12. Silk clothes are prepared from
(A) silk sheep (B) silk animals
(C) silk (D) silk worms
13. Which of the following has a great tensile strength?
(A) Wool (B) Cotton
(C) Silk (D) None of these
14. Which of the following is present in silk fibre?
(A) lipids (B) proteins
(C) Fats (D) Carbihydrate
15. Which of the following comes in the empty box in the given steps of processing
fibres into wool Shearing ----?------Sorting
(A) Knitting (B) Scouring
(C) Weaving (D) separating
16. ......shawls are woven from fur of Kashmiri goat.
(A) Pashmina (B) Parse
(C) Kashmiri (D) Shimla
17. Match of following
Column-I Column-II
(A) Scouring (i) Yields silk fibres
(B) Mulberry leaves (ii) Cleaning sheared skin
(C) Sheep (iii) Food of silk worm
(D) Cocoon (iv) Wool yielding animal
(A) A-(iii), B - (i), C - (ii), D - (iv)
(B) A -(ii), B - (iii), C - (iv), D - (i)
(C) A - (iv), B - (iii), C - (ii), D - (i)
(D) A - (i), B - (ii), C - (iii), D - (iv)
18. Which of the following parts swing side to side during
the formation of cocoon around the cat- erpillar?
(A) Abdomen moves
(B) Neck Move
(C) Head moves
(D) Thorax moves
19. Which of the following fibres in spun and woven in to woolen cloth?
(A) shorter fibres (B) Longer fibres
(C) Fluffy fibres (D) None of these
20. In which of the following process threads are taken out from the cocoons?
(A) shearing (B) spinning
(C) scouring (D) Reeling
21. WHich of the following silk fibre is soft, lustrous and elastic?
(A) kosa silk
(B) mulberry silk moth silk
(C) mooga silk
(D) Tassar silk
22. Which of the following breed yield good quality wool?
(A) Lohi (B) Marwari
(C) Patan wadi (D) Nali
23. You do not get hurt when you get a hair cut. Which of the following is the correct reason?
(A) Hair are dead cells
(B) The upper layer of the skin with hair is dead
(C) The roots of hair do not have sensory cells
(D) All of these
24. The larvae of silkworm ae called is
(A) Moth (B) Imago
(C) Numph (D) Caterpillar
25. The eggs of silkworm are stored in
(A) Plastic box (B) Strips of cloth
(C) Metal box (D) Wooden box
ANSWER KEY
1. A 2. B 3. A 4. D
5. A 6. B 7. C 8. B
9. C 10. B 11. A 12. D
13. A 14. B 15. B 16. A
17. B 18. C 19. A 20. D
21. B 22. A 23. B 24. B
25. D 26. B