Before the beginning of the eighteenth century when there are only 30 elements known, it was easier to study and remember their properties.
In later years when number of elements discovered were increased then it became difficult to study them. So scientist fell the need of simple
method to facilitale the study of the properties of various elements and their compounds. After numerous attempts they got success & elements
were arranged in such manner that similar elements were grouped together and different elements were separated. This arrangement of elements
is known as classification of elements which led to the formation of periodic table.
Periodic table may be defined as "the arrangement of all the known elements according to their properties in such way that the elements
of similar properties are grouped together in a tabular form."
Earlier attempts of classification of elements (development of periodic table) :
Earlier attempts to classify the elements resulted in grouping as metals and non-metals. Later on they were classified on the basis of their atomic masses.
In 1817, Johann walfgang dobereiner. A German chemist, arranged the elements as group of three elements and in a manner that the atomic mass of
middle element was roughly the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements of the triad.
Example : Element : Lithium, Sodium and Potassium.
Atomic mass 7 23 39
Average of the atomic masses of Lithium and Potassium is only three triads could be arranged in this manner at that time. They were :
This classification was not found satisfactory as it could be applied to the limited number of elements.
Now a days some more triads have been made they are
(i) Potassium Rubidium Cesium
K Rb Cs
(ii) Phosphorus Arsenic Antimony
P As Sb
(iii) Sulphur Selenium Tellurium
S Se Te
(iv) Hydrogen Fluorine Chlorine
H F Cl
(v) Scandium Yttrium Lanthanum
Sc Y La
For a Debereiner's triad all the three elements should belong to the same group and the difference in atomic number should be 8 or 18.
In 1866, J.A.R. Newlands correlated the chemical properties of the elements with the increasing order of atomic masses. i.e.
to arrange the element having lowest atomic mass (H) firstly and ended to at secondly the element having highest atomic mass.
(Thorium which was 56th known element at that time).
Definition : When the elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic masses, every eighth element has the properties
similar to those of the first elements like the eighth note of an octave in music. Thus according to this law, the physical & chemical
properties are repeated after an interval of eight elements and this is similar to eight notes of an octave on a musical scale shown below:
The properties of Lithium are similar to that of 8th element i.e. Na, Be is similar to Mg and so on.
Limitations :
1. Law of octaves was applicable only up to calcium. It worked well with lighter elements only.
2. At that time only 56 elements were existed in nature, but later several elements were discovered which can not be kept in periodic
table as per this law. Their properties were not in accordance with the law of octaves.
3. (i) In order to fit element in to his table Newlands adjusted two elements in the same column. For example cobalt and nickel were
placed in the same position and in the same column as fluorine, chlorine and bromine.
(ii) Iron which resembles cobalt and nickel in properties were placed far away from these elements.
4. After the discovery of inert gases & included in the periodic table it becomes the eighth element from alkali so this law has to be dropped out.
Q. Did Dobereiner's triads also exist in the columns of Newland's Octaves ? Compare and find out.
Q. What were the limitation of Dobereiner's Classification ?
Q. What were the limitations of Newlands' Law of Octaves ?
In the year 1861, D Mitri Ivanovich Mendeleev arranged all the known elements (63 elements) in the form of a table in which
elements were arranged in the increasing order of their atomic mass and also on the similarities of chemical properties.
r The arrangement of element was based on the physical and chemical properties of the elements and also the formulae of
the compounds they formed with oxygen and hydrogen. He selected hydrogen and oxygen as they are very reactive and
formed compounds with most elements.
The table which classifies the elements in such a way that elements having similar properties are placed in same vertical
column or group is known as periodic table. The term periodic means repetition of elements having similar properties after
a certain regular interval. The periodic table consists of vertical columns which are called as groups and horizontal rows called
as periods. Mendeleev's periodic table had six periods and eight groups as shown in the table, he arranged all the elements
horizontally in the order of their increasing atomic masses and vertically according to their similarities in properties.
Each group was further sub divided into two sub groups A & B.
1. Systematic study of the elements : All the elements in general were arranged systematically in increasing order of their atomic masses.
This arrangement helped to study the properties of various elements. If the nature of the element present in a group is known,
it become easier to predict or guess the expected properties of other elements.
2. Prediction of new elements : Mendeleev predicted the properties of some unknown elements and left gaps for these elements to
be filled as and when discovered. For eg. Scandium, Gallium and Germanium were not known at that time but Mendeleev already
named these elements as eka-boron, eka-aluminium and eka-silicon. When these elements were later on discovered, they were
found to have more or less similar properties as predicted by Mendeleev.
3. Position of Noble gases : When noble gases were discovered they were placed in a new group without disturbing the existing order.
4. Correction of atomic masses : Atomic masses of several elements were corrected on the basis of periodic table. eg. Atomic mass of
Beryllium was corrected from 135 to 9. Mendeleev predicted that atomic mass of gold is incorrect. Later on it was found to be so.
Similarly atomic masses of Indium, Uranium and Platinum were also corrected.
Position of Hydrogen is uncertain becomes it resemble with IA group alkali metals elements and VII A (halogens) group elements.
(i) Isotopes : Isotopes of an element have similar chemical properties but different atomic masses.
(ii) Position of isotopes : Since basis of periodic table was increasing atomic mass. So isotopes should be placed separately but
no separate place was given to isotopes.
(iii) Anamolus pairs of certain elements : Certain elements were not arranged according to their increasing atomic mass eg.
(a) Argon (Atomic mass 39.9) was placed before potassium (atomic mass 39.0)
(b) Cobalt (58.95) before Nickel (58.70)
(c) Tellurium (127.6) before Nickel (126.9)
(d) Thorium (232) before Protactimum (231)
(iv) Similar elements were placed in different groups. eg.
(a) Silver and thallium
(b) Barium and lead
(c) Copper and mercury
(d) Platinum and gold.
(v) Dissimilar elements were placed in same group eg. silver and gold were placed in a same group while there is little
similarity in physical and chemical properties.
(vi) Cause of periodicity : Mendeleev did not explain the cause of periodicity in the physical and chemical properties of the elements.
(vii) Metals have not been separated from non-metals.
(viii) Position for elements of group (VIII) : There is no proper position for the elements of group (VIII) consisting of elements in three triads.
These elements are placed out side the main structure of the periodic table.
In 1913 Henry Moseley showed that properties of the elements are determined by atomic numbers instead of the atomic mass.
It formed the basis of modern periodic law. The law is -
"The physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic function of their atomic numbers". Since atomic mass is a
nuclear property where as atomic number implies for the no. of electrons in neutral atom or no. of protons in nucleus.
Nucleus is deep seated in the atoms and does not take part in chemical reactions. Therefore the physical and chemical
properties depends upon the no. of electrons and their electronic configuration which in turn depends upon atomic number (Z).
So when elements are arranged in the increasing order of atomic numbers, after an regular interval elements have similar no.
of valence electrons therefore chemical properties are repeated i.e. periodicity in the chemical properties of the elements occurs.
Q. Use Mendeleev's periodic table to predict the formulae for the oxides of the following elements :
K, C, AI, Si, Ba
Q. Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his periodic table ? (any two)
Q. What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his periodic table ?
Q. Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group ?

l It is also called as Bohr, Bury & Rang, Werner periodic table
(1) It is based on the Bohr-Bury electronic configuration concept and atomic number.
(2) This model is proposed by Rang and Werner.
This table is based on modern periodic law, the elements are arranged in the increasing order of atomic numbers in such
a way that elements having the same number of valence electrons are placed in the same vertical coloumn.
It consists of 18 vertical colums and seven horizontal rows. Vertical columns of periodic lable are known as groups
while horizontal rows are known as periods.
The co-relation between the groups in long form of periodic table and in modern form of periodic table are given below :-
IA IIA IIIB IVB VB VIB VIIB VIII IB IIB
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8,9, 10 11 12
III A IV A VA VIA VIIA 0
13 14 15 16 17 18
Elements belonging to same group having same number of electrons in the outer most shell so their properties are similar.
Description of periods :-
Description of periods :
Description of Groups :
1st/IA/Alkali metals
H = 1s1
Li = 1s2 , 2s1
Na = 1s2 , 2s2 2p6 , 3s1
K = 1s2 , 2s2 2p6 , 3s2 3p6 , 4s1
General electronic configuration = ns1(n = Number of shell)
Number of valence shell e– = 1
2nd/IIA/Alkali earth metals :
Be = 1s2, 2s2
Mg = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2
Ca = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2
General electronic configuration = ns2
Number of valence shell e– = 2
13th/IIIA/Boron Family :
B = 1s2, 2s2, 2p1
Al = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p1
Ga = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d10,4s2,4p1
General electronic configuration = ns2 np1
Number of valence shell e– s = 3
14th/IVA/Carbon Family :
C = 1s2, 2s2, 2p2
Si = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p2
Ge = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d10, 4p2
General electronic configuration = ns2 np2
Number of valence e– s= 4
15th/VA/Nitrogen family/Pnicogen : (Used in fertilizer as urea)
N = 1s2, 2s2, 2p3
P = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p3
As = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d10, 4p3
General electronic configuration = ns2 np3
Number of valence shell e– = 5
16th/VIA/Oxygen family/Chalcogen : (Ore forming)
O = 1s2, 2s2, 2p4
S = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p4
Se = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6,3d10, 4s2, 4p4
General electronic configuration : ns2 np4
Number of valence shell e– s= 6
17th/VIIA/Fluorine family/Halogens : (Salt forming)
F = 1s2, 2s2, 2p5
Cl = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p5
Br = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d10, 4p5
General electronic configuration = ns2 np5
Number of valence shell e– s= 7
18th/Zero group/Inert gases / Noble gases :
Ne = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6
Ar = 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6
Kr = 1s2, 2s2, 3p6, 3s2, 3p6, 3d10,4s2, 4p6
General electronic configuration = ns2 np6 ( except. He)
Number of valence shell e– = 8
Elements of group 16 are known as chalocogens Elements of group 17 are known as halogens.
Classification on the basis of subshell in which last electron (e–) enters
Characteristics of the elements present in groups are listed.
(i) The elements present in a group are separated by definite gaps of atomic numbers (8, 8, 18, 18, 32).
(ii) There are eighteen (18) independent groups in the Long from of Periodic Table. These are numbered from 1 to 18.
(iii) The elements present in a group have the same number of electrons in the valence shell of their atoms.
(iv) The elements present in a group have the same valence.
(v) The elements present in group have identical chemical properties.
(vi) The physical properties of the elements in group such as melting point, boiling point, density vary gradually.
(vii) Atomic radii of the elements present in a group increase downwards.
Characteristics of the element present in period
(i) In all the elements present in a period the electrons are filled in the valence shell.
(ii) As the number of electrons in the valence shell change, the chemical properties of the elements present in a period also change.
(iii) Atomic radii of the elements in a period decrease from left to the right.
(iv) Along a period, the metallic character of the elements decreases and the non-metallic character increases.
(v) Along a period, the reducing character of the elements decreases and their oxidizing character increases.
1. I period contains ..................and II period contains ......................elements.
2. Group 17 elements are called .............. .
3. Group 18 elements are .....................valent.
4. Which one has the bigger size
Na (11) or Cl (17) ; Cl (17) or F (9) ?
5. Name two elements whose valencies are equal to their group numbers.
6. How many elements are there in the 4th period.
7. Give two examples of elements of Groups 1, 2, 16 and 17.
8. Group 2 elements are known as ................
There are several advantages of long form of periodic table over Mendellev's periodic table. Some of these are as follows:
(i) It is based upon atomic number which is a fundamental property instead of atomic mass.
(ii) The elements have been grouped as s, p, d and f-block elements. Which helps us to understand the electronic configuaration in a bettery way.
(iii) In the long form of periodic table, the elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic number,s therefore,
no separate place is required for isotopes.
(iv) The position of some of the elements which were a misfit on the basis of atomic mass is not because argon has atomic
number 18 which is less than that of potassium which is 19.
(v) Metals, non-metals, metalloids, transition elements, lanthanoids and actinoids and actinoids are now better classified.
The electronic configurations of atoms display a periodic variation with increase in atomic number. Since the properties
of elements depends upon the electronic configurations. So the elements exhibits periodic variation of physical & chemical properties.
Some properties of elements are :-
(A) Valency :- It is defined as the combining capacity of the element. Valency is determined by the number of electrons present in outer most shell.
These electrons are known as valence electrons.
Variation of valency across a period :- The number of valency electrons increases from 1 to 8 on moving across a period.
The valency of an element with respect to hydrogen and halogen increases from 1 to 4 and then decreases from 4 to zero.
With respect to oxygen valency increases from 1 to 7.
Variation of valency along a group :- On moving down a group. The no. of valence electrons remains same so the valence of
all the elements of a group is same.
Group (1) elements have valency - 1
Group (2) elements have valence - 2
Atomic size :- Atomic size means atomic radius of an atom which is defined as the distance between the centre of the nucleus of an
atom and the valence shell containing electrons in an isolated atom since it is very difficult to measure the atomic radius because -
(i) The isolation of single atom is very difficult.
(ii) There is no well defined boundary for the atom.
So the more accurate definition of atomic radius is -
(Half the internuclear distance between the two atoms in a homatomic molecule is known as atomic radius)
This internuclear distance is also known as bond length. It depends upon the type of bond by which two atoms combine.
Based on chemical bonds, atomic radius is divided in to four categories.
(a) Covalent radius (Single bonded covalent radius) For homoatoms
It is half of the internuclear distance between two singly bonded homoatoms.
(b) Covalent radius for hetero atoms.
(i) In case of hetero atomic molecule (A – B), if the electronegativity difference is less. Then covalent
radius of oxygen, nitrogen and carbon is taken from the compound H2O2, N2H4 and C2H6 respectively.
This radii is subtratied from the bond length of A–B molecules.
eg. C–I (electronegativity is almost same 2.5)
Internuclear distance C–I is 2.13Å, covalent radius of carbon in compound C2H6 is 0.77Å covalent radius of I– will be.
dC–I = rC + rI (covalent radius of iodine)
(covalent radius of carbon)
i.e. 2.13 = 0.77 + rI
rI = 2.13 – 0.77 = 1.36Å
(ii) When electronegativity difference is more. Then bond length is determined by the schole maker and Stevenson law –
dA–B = rA + rB – 0.09(XA – XB)
where dA–B = Bond length of dA–B molecule
XA = Electronegativity of A
XB = Electronegativity of B
Example – Bond length of F2 = 1.44 Å
i,e. dF–F = 1.44Å rF = = 0.72Å
dH–H = 0.74Å rH = = 37Å
Electronegativity of Fluorine is 4.0 and Electronegativity of Hydrogen is 2.1
dH–F = rF + rH + 0.09(XF – XH)
= 0.72 + 0.37 – 0.09(4 – 2.1)
= 1.09 – (0.09 × 1.9)
= 1.09 – 0.171 = 0.919
(B) Ionic Radius –
(i) Cationic radius (ii) Anionic radius
(i) Cationic Radius –
Size of cation µ
eq. Fe > Fe+2 > Fe+3
(ii) Anionic radius –
Anionic radius is always greater than atomic radius because in an anion electrons are more than the protons so effective nuclear
charge reduces and inter electronic repulsion increases so size of anion also increases.
(C) Metallic Radius –
Half of the inter nuclear distance between two adjacent metallic atoms.
Metallic radius µ
(D) Vander Waal's radius –
Those atoms which are not bonded with each other experiences a weak attractive force to come nearer. Half of the distance
between the nuclei of adjacently placed atoms in solid state of a noble gas is vander waal's radius.
Variation of Atomic size in a group :
On moving down a group of periodic table, the size of the atom increases.
When we move from top to bottom in a group a new shell of electron is added in each period. This addition increases the size.
Variation of atomic size in period :
In general atomic radii decreases across a period from left to right eg. In IInd period. Cl atom is largest and Fluorine is the smallest
atom because nuclear charge increases with increase in atomic number. Electrons are also increasing but these are added to the same shell.
Þ Atomic Size :- Decreases along the period. Increases down the group.
Þ Metallic and Non-metallic character :
Metallic character is the tendency of atoms of the elements to lose electrons and form positive ions. It can be expressed as
M ¾® M+ + e–
Therefore metals are also called as electropositive elements.
The metallic character increases from top to bottom in a group the metallic character of the element goes on increasing eg.
Li is least metallic element while cesium is most metallic element.
If we use the term electropositive in place of metallic character, we can say that electropositive character goes on increasing
as we move from top to bottom in the periodic table. If we consider the electronegative character, it goes on decreasing as we
move down in a group of the periodic table.
Þ Ionization Enthalpy :
The minimum amount of energy required to remove the most losely bounded electron from an isolated gaseous neutral atom to
form gaseous electropositive ion called Ionization enthalpy. Its unit is kilo joules per mole (kJ/mol)
M(g) + Energy ¾® M+(g) + e–
It is a measure of tendency to lose electrons by atoms. The tendency to lose electron increases from top to bottom in a group
and it decreases on moving left to right in a period.
Þ Electron gain enthalpy :
It is defined as the amount of energy released when an isolated gaseous atom in the ground state accepts an electron to form
gaseous negative ion i.e. and anion. It is a measure of tendency of an atom to accept an extra electron to form an anion.
Its unit is kilo joule mole (kJ/mole). Electron gain enthalpy of elements goes on increasing as we move from left to right in a period.
In group it decreases from top to bottom.
Þ s-Blocks Elements: The elements in which the last electron enters the s-sub-shell of their outermost energy level and electronic
configuration is ns1 or ns2 (I or II group) are called s-block elements are:
(i) They are soft metals.
(ii) They have low ionisation energies.
(iii) They are very reactive and form ionic compounds.
(iv) They show oxidation states of +1 group and +2 group.
(v) They are good reducing agents.
Þ p-Block Elements: The elements in which the last electron enters the p-sub-shell of their outermost energy level are called
p-block elements. The exception is helium (1s2)..?
The general configuaration of their outermost shell is ns2np1-6. These elements are kept in group 13 to 18. Some of the general
characteristics of p-block elements are:
(i) They show variable oxidation states.
(ii) They form ionics as well as covalent compounds.
(iii) Most of them are non-metals.
(iv) Most of them form acidic oxides.
Þ d-Block Elements:
(i) They are hard and having high melting point.
(ii) They show variable oxidation states.
(iii) They form coloured compexes.
(iv) They form ionic as well as covalent compounds.
(v) Most of them exhivit paramagnetism.
(vi) Most of them possess catalytic properties.
f-Block elements: The elements in which the last electron enters the f-block elements.
Their general configuaration is (n-2) f1-14 (n-1)d0-1,ns2. They consist of two series of 28 elements (14 in each) placed at
the bottom of the periodic table.
The elements of first series followed by lanthenum (57La) are called Lanthenides.
The elements of second series followed by actinium (89Ac) are called actinides.
The general Charactertics of f-block elements are:
(i) They show variable oxidation states.
(ii) They have high melting points.
(iii) They have high densities.
(iv) They form coloured compounds.
(v) Most of the elements of actinide series are radioactive.
It may be noted that:
1. The elements of group zero are called inert gases, noble gases, rare gases or aerogens.
2. The elements of p-block (except noble gases) are called representative or main group elements.
The members of this group of elements have all their occupied subshells filled except their outermost electron shell.
• Element are classified on the basis of similarities in their physical and chemical properties.
• Dobereiner grouped elements into triads.
• Newland grouped elements on the basis of law of octaves.
• Mendeleev grouped elements in the increasing order of their atomic masses and the similarity in chemical properties.
• Mendeleev was able to predict the existence of some elements on the basis of gaps in the periodic table.
• Moseley discovered that fundamental property of an element is its atomic number, rather than atomic mass.
He revised Mendeleev Periodic Table on the basis of atomic numbers of elements and removed some of its anomalies.
• Elements in the long form of Modern Periodic Table are arranged in 18 vertical columns called groups and 7 horizontal rows called periods.
• The elements arranged in the long form of periodic table show (i) periodicity of properties (ii) atomic size (iii) valency (iv) metallic and non-metallic character.
Q.1 Did Dobereiner's triads also exist in the columns of Newlands' Octaves? Compare and find out.
Ans. Only one triad of Dobereiner's triads exists in the columns of New lands' octaves. The triad formed by the elements Li,
Na, and K of Dobereiner's triads also occurred in the columns of Newlands' octaves. Dobereiner's triads
Newlands' octaves
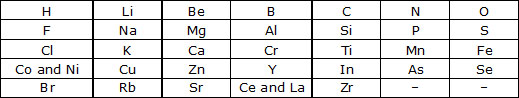
Q.2 What were the limitations of Do be reiner's classification?
Ans. Limitation of Dobereiner's classification: All known elements could not be classified into groups of triads on the basis of their properties.
Q.3 What were the limitations of Newlands' Law of Octaves?
Ans. Limitations of Newlands' law ofoctaves:
(i) It was not applicable throughout the arrangements. It was applicable up to calcium only. The properties of the elements listed after
calcium showed no resemblance to the properties of the elements above them.
(ii) Those elements that were discovered after Newlands' octaves did not follow the law of octaves.
(iii) The position of cobalt and nickel in the group of the elements (F, Cl) of different properties could not be explained.
(iv) Placing of iron far away from cobalt and nickel, which have similar properties as iron, could also not be explained.
Q.4 Use Mendeleev's Periodic Table to predict the formulae for the oxides of the following elements: K, C, Al, Si, Ba.
Ans. K is in group 1. Therefore, the oxide will be K2O.
C is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be CO2.
Al is in group 3. Therefore, the oxide will be Al2O3.
Si is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be SiO2.
Ba is in group 2. Therefore, the oxide will be BaO.
Q.5 Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were left by Mendeleev in his Periodic Table? (any two)
Ans. Scandium and germanium.
Q.6 What were the criteria used by Mendeleev in creating his Periodic Table?
Ans. Mendeleev's periodic table was based on the observation that the properties of elements are a periodic function of their atomic masses.
This means that if elements are arranged in the increasing order of their atomic masses, then their properties get repeated after regular intervals.
Q.7 Why do you think the noble gases are placed in a separate group?
Ans. Noble gases are inert elements. Their properties are different from the all other elements. Therefore, the noble gases are placed in a separate group.
Q.8 How could the Modern Periodic Table remove various anomalies of Mendeleev's Periodic Table?
Ans. Mendeleev was unable to give fixed position to hydrogen and isotopes in the periodic table. In Mendeleev's periodic table, the increasing manner
of atomic mass of the elements is not always regular from one to its next. It was believed that a more fundamental property than atomic mass
could explain periodic properties' in a better manner. It was Henry Moseley who demonstrated that atomic number of an element could explain
periodic properties in a better way than atomic mass of an element and arranged the elements in increasing order of their atomic numbers.
Then it was found that the various anomalies of Mendeleev's periodic table were removed by the modern periodic table.
Q.9 Name two elements you would expect to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium. What is the basis for your choice?
Ans. Calcium (Ca) and strontium (Sr) are expected to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium (Mg). This is because the number of
valence electrons (2) is same in all these three elements. And since chemical properties are due to valence electrons,
they show same chemical reactions.
Q.10 Name
(a) three elements that have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) two elements that have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) three elements with filled outermost shells.
Ans. (a) Lithium (Li), sodium (Na), and potassium (K) have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Magnesium (Mg) and calcium (Ca) have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) Neon (Ne), argon (Ar), and xenon (Xe) have filled outermost shells.
Q.11 (a) Lithium, sodium, potassium are all metals that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas. Is there any similarity in the atoms of these elements?
(b) Helium is an unreactive gas and neon is a gas of extremely low reactivity. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common?
Ans. (a) Yes. The atoms of all the three elements lithium, sodium, and potassium have one electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Both helium (He) and neon (Ne) have filled outermost shells. Helium has a duplet in its K shell, while neon has an octet in its L shell.
Q.12 In the Modern Periodic Table, which are the metals among the first ten elements?
Ans. Among the first ten elements, lithium (Li) and beryllium (Be) are metals.
Q.13 By considering their position in the Periodic Table, which one of the following elements would you expect to have maximum metallic characteristic? Be, B, C
Ans. Since Be lies to the extreme left hand side of the periodic table, Be is the most metallic among the given elements.
Q.14 Which ofthe following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of periodic Table.
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature.
(b) The number of valence electrons increases.
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(d) The oxides become more acidic.
Ans. (c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily.
(On moving from left to right across the periods of the periodic table, the non-metallic character increases. Hence, the tendency to lose electrons decreases.)
Q.15 Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, which is a solid with a high melting point. X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as
(a) Na (b) Mg (c) Al (d)Si
Ans. (b) X would most likely be in the same group of the Periodic Table as magnesium (Mg). .
Q.16 Which element has
(a) two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons?
(b) the electronic configuration 2, 8, 2?
(c) a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell?
(d) a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell?
(e) twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell?
Ans. (a) Neon has two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons (2 electrons in K shell and 8 electrons in L shell).
(b) Magnesium has the electronic configuration 2, 8,2.
(c) Silicon has a total of three shells, with four electrons in its valence shell (2 electrons in K shell, 8 electrons in L shell and 4 electrons in M shell).
(d) Boron has a total of two shells, with three electrons in its valence shell (2 electrons in K shell and 3 electrons in L shell).
(e) Carbon has twice as many electrons in its second shell as in its first shell (2 electrons in K shell and 4 electrons in L shell).
Q.17 (a) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as boron have in common?
(b) What property do all elements in the same column of the Periodic Table as fluorine have in common?
Ans. (a) All the elements in the same column as boron have the same number of valence electrons (3). Hence, they all have valency equal to 3.
(b) All the elements in the same column as fluorine have the same number of valence electrons (7). Hence, they all have valency equal to 1.
Q.18 An atom has electronic configuration 2, 8,7.
(a) What is the atomic number of this element?
(b) To which of the following elements would it be chemically similar? (Atomic numbers are given in parentheses.) N(7) F(9) P(15) Ar(18)
Ans. (a) The atomic number of this element is 17.
(b) It would be chemically similar to F(9) with configuration as 2, 7.
Q.19 The position of three elements A, B and C in the Periodic Table are shown below?
(a) State whether A is a metal or non-metal.
(b) State whether C is more reactive or less reactive than A.
(c) Will C be larger or smaller in size than B?
(d) Which type of ion, cation or anion, will be formed by element A ?
Ans. (a) A is a non-metal.
(b) C is less reactive than A, as reactivity decreases down the group in halogens.
(c) C will be smaller in size than B as moving across a period, the nuclear charge increases and therefore, electrons come closer to the nucleus.
(d) A will form an anion as it accepts an electron to complete its octet.
Q.20 Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to group 15 of the Periodic Table. Write the electronic configuration
of these two elements. Which of these will be more
electronegative? Why?
Ans. 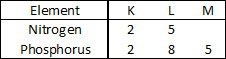
Nitrogen is more electronegative than phosphorus. On moving down a group, the number of shell increases. Therefore, the valence electrons
move away from the nucleus and the effective nuclear charge decreases. This causes the decrease in the tendency to attract electron and
hence electro negativity decreases.
Q.21 How does the electronic configuration of an atom relate to its position in the Modern Periodic Table?
Ans. In the modern periodic table, atoms with similar electronic configurations are placed in the same column. In a group, the number of
valence electrons remains the same. Elements across a period show an increase in the number of valence electrons.
Q.22 In the Modern Periodic Table, calcium (atomic number 20) is surrounded by elements with atomic numbers 12, 19, 21, and 38.
Which of these have physical and chemical properties resembling calcium?
Ans. The element with atomic number 12 has same chemical properties as that of calcium. This is because both of them have same number
of valence electrons (2).
Q.23 Compare and contrast the arrangement of elements in Mendeleev's periodic Table and the Modern Periodic Table.
Ans. 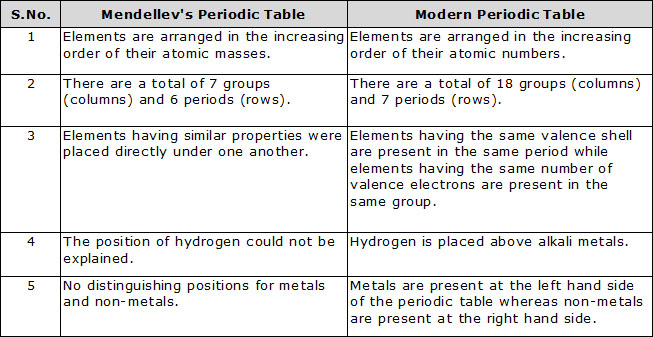
Q.1 Which physical and chemical properties of the elements were used by Mendeleev in creating his periodic table ?
List two observation which posed a challenge of Mendeleev's periodic law. (C.B.S.E. 2008)
Ans. The creation of Mendeleev's periodic table was based upon certain physical and chemical properties.
Physical properties : The atomic masses of the elements was taken into account and the elements were arranged
in order of increasing atomic masses. The influences of their physical properties such as melting points, boiling points, density etc.
Chemical properties : The distribution of the elements into different groups was linked with formation of hydrides by combining
with hydrogen and formation of oxides by combining with oxygen. This is linked with the valency of the elements.
The two main observations which posed challenge to Mendeleev’s periodic table are as follows:
(i) Position of isotopes : Since the isotopes of an element differ in their atomic masses, they must be assigned separate slots or positions in the periodic table.
(ii) Anomalous positions of some elements: In the Mendeleev’s periodic table, certain elements with higher atomic masses precede or
placed before the elements with lower atomic masses. For example, the element Ar (Atomic mass = 39.9) is placed before the element K (Atomic mass = 39.1)
Q.2 Using the part of the periodic table given below, answer the questions that follow.
(i) Na has physical properties similar to which elements and why?
(ii) Write the electronic configuration of N and P
(iii) State one property common to fluorine and chlorine. (C.B.S.E. All India 2008)
Ans. (i) Na has physical properties similar to Li and K. All the three elements have one electron each in the valence of their atoms.
These are known as alkali metals.
(ii) Electronic configuration of N (z = 7) = 2, 5
Electronic configuration of P (z = 15) = 2, 8, 5
(iii) Both the elements have seven electrons in the valence shells as their atoms
Fluorine (z = 19) = 2, 7
Chlorine (z = 17) = 2, 8, 7
Q.3 Table given below shows a part of the periodic Table
Using this table explain why
(a) Li and Na are considered as active metals.
(b) Atomic size of Mg is less than that of Na.
(c) Fluorine is more reactive than chlorine. (C.B.S.E. Foreign 2008)
Ans. (a) Both Li and Na are active elements since their atoms have only one, electron in their valence shells. They readily lose this electron
to have the configuration of the nearest noble gas element.
(b) Mg is placed after Na in the same period (third). As the atomic size decreases along a period, the size of Mg is less than that of Na.
(c) Both F and CI belong to group 17 (halogen family). Since fluorine is more electronegative than chlorine, it is therefore more reactive also.
Q.4 (a) Why do all the elements of the same group have similar properties ?
(b) How will the tendency to gain electrons change as we go from left to right across a period? Why ? (C.B.S.E. All India, 2009)
Ans. (a) The properties of the elements are linked with the valence shell electronic configuration of their atoms. The elements with the
same configuration are expected to have similar properties. In a group, the elements are separated by definite gaps of atomic
numbers and have same number of electrons in the valence shells of their atoms. For example, the alkali metals in group I have one electron each.
They have similar properties. For further details, consult text part.
(b) In moving from left towards the right across a period, the tendency of the elements to gain electrons increases.
Explanation. In general, the atoms of all the elements have a desire or urge to have stable electronic configuration of the nearest noble gas
elements or to have eight electrons in their outermost or valence shells. Now, across a period the valence electrons are added one by one
from left to the right. This is supported by the electronic configuration of the elements present in period 3 or third period.
This clearly shows that the element chlorine needs one electron while oxygen requires two to have to stable electronic configuration.
Thus, tendency to gain electrons increases from left to right across a period.
Q.5 What valency will be shown by an element having atomic number 17?
Q.6 How does the electronic distribution in atoms change in a period from left to right?
Q.7 By which common name are the elements of group I and group-17 called?
Q.8 What is a period in the periodic table? How do atomic structures change in a period with an increase in atomic number?
Q.9 Name three elements whose existance was predicted by Mendeleev?
Q.10 What happens to the metallic character, melting point and boiling points of the elements as we go down in a group of the periodic table.
Q.11 An element (X) is in the third group of the periodic table. What is the formula of its oxide?
Q.12 What is the name and the chemical symbol of the alkaline earth metal with the smallest atomic number?
Q.13 Which element has the highest ionisation energy?
Q.14 Why does the size of the atom increases down the group?
Q.15 Arrange the following atoms in order of decreasing atomic radius:
Na, Al, P, Cl, Mg
Q.16 Arrange the following atoms in order of increasing radius:
P, Si, N
Q.1 According to IUPAC recommondations, the number of groups in the long form of the periodic table is :-
(A) 7
(B) 8
(C) 16
(D) 18
Q.2 The law of modern periodic table was proposed by :-
(A) D.I. mendeleev
(B) Dobereincer
(C) H.G.I moselly
(D) Newlands
Q.3 the least metallic element of group 1 is :-
(A) Lithium
(B) Sodium
(C) Potassium
(D) Cesium
Q.4 Which of the following properties generally increases on moving from top to bottom ?
(A) Ionisation energy
(B) Non-metallic character
(C) Atomic size
(D) Valency
Q.5 Which of the following statement is not correct about the trends when going from left to right across the periodic table ?
(A) The elements become less metallic in nature
(B) The number of valence electrons increases
(C) The atoms lose their electrons more easily
(D) The oxides becomes more acidic
Q.6 The law of octaves was proposed by :-
(A) New lands
(B) Lother Meyer
(C) Dobereiner
(D) Mendeleev
Q.7 The number of periods in the long form of the periodic table is :-
(A) 6
(B) 7
(C) 10
(D) 18
Q.8 Which of the following has the maximum non-metallic character ?
(A) F
(B) Cl
(C) Br
(D) I
Q.9 Which of the following sets of elements do not belong to the same group ?
(A) F, Cl, Br
(B) Na, K, Rb
(C) P, S, Cl
(D) C, Si, Ge
Q.10 Which of the following has lowest number of electrons in the valency shell ?
(A) O
(B) C
(C) N
(D) B
Q.11 Which of the following pairs of elements does not belong to same group ?
(A) Cl, Br
(B) N, P
(C) Mg, Ca
(D) Al, Si
Q.12 Which of the following has largest atomic size ?
(A) Be
(B) C
(C) O
(D) F
Q.13 Which of the following belongs to group 18?
(A) Sr
(B) I
(C) Ar
(D) Rb
Q.14 What is the basis of long form of the periodic table ?
(A) Atomic mass
(B) Atomic number
(C) Atomic size
(D) Metallic and Non-metallic character
Q.15 Which one is more metallic element ?
(A) Na
(B) Mg
(C) Al
(D) Si
Q.16 Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, Which is a solid with a high melting point,
X would most likely be in the same group of the periodic table as :-
(A) Na
(B) Mg
(C) Al
(D) Si
Q.1 The horizontal rows in the periodic table are known as ....................
Q.2 The vertical columns of in the periodic table are known as ...............
Q.3 A very short period contains ........ elements.
Q.4 The element having electronic configuration
(2, 8, 3) belongs to ............ group.
Q.5 In a group atomic radii ............. from top to bottom and in a period atomic radii ............ from left to right.
Q.6 Size of Na+ is ............... than sodium atom.
Q.7 Size of Cl– is .............. than Cl atom.
Q.8 An element 'B' belongs to the second period and group 13, formula of its oxide is ....................
Q.9 Elements in the same group have similar .................
Q.10 Elements in the same group have similar ................ in their outer most shell.
Q.11 The alkaline earth metal with the smallest atomic number is ...................
Q.12 A, B & C are the elements of the Doberiner's triads. If the atomic mass of A is 7 and that of B is 23, then the atomic mass of 'C' will be .................
Q.13 When Mendeleev made the periodic table the number of elements discovered till then were ...........
Q.14 Among alkali metal.....................has the smallest atomic radius.
Q.15 Among halogens.....................has the smallest atomic radius.
Q.16 The amount of energy released when a neutral gaseous atom gains one electron is called .....................
Q.17 The energy required to remove an electron from an isolated gaseous atom is called .....................
Q.18 Non-metallic character ..................... from left to right in a period.
Q.19 Metallic character ..................... down a group.
Q.20 Ionisation energy ..................... down a group and ..................... along a period.
Q.21 Atomic size ..................... from left to right in a period.
Q.1 Explain why the properties of the 8th element are repeated in case of elements arranged in 2nd and
3rd period of the long from of the periodic table.
Q.2 Nitrogen (atomic number 7) and phosphorus (atomic number 15) belong to Group 15 of periodic table.
Write the electronic configuration of these elements. Which of these will be more electronegative ? Why ?
Q.3 Name two element you would expect to show chemical reactions similar to magnesium. What is the basis for your choice ?
Q.4 Name
(a) Three elements that have a single electron in their outermost shells.
(b) Two elements that have two electrons in their outermost shells.
(c) Three elements with filled outermost shells.
Q.5 (a) Lithium, sodium, potassium are all metal that react with water to liberate hydrogen gas is there any similarity in the atoms of these atoms.
(b) Helium is an unreactive gas and neon is a gas of extremely low reactivity. What, if anything, do their atoms have in common ?
Q.6 By considering their position in the periodic table, which one of the following elements would you expect to have maximum metallic characteristic.
Ga Ge As Se Be
Q.7 Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of periodic table.
(a) The elements become less metallic in nature.
(b) The number of valence electrons increase
(c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily
(d) The oxides become more acidic
Q.8 Element X forms a chloride with the formula XCl2, which is a solid with a
high melting point X woud most likely be in the same group of the periodic table
(a) Na
(b) Mg
(c) Al
(d) Si
Q.9 (a) What property do all elements in the same column of the periodic table as boron have in common ?
(b) What property do all elements in the same column of the periodic table as fluorine have in common ?
Q.10 An atom has electronic configuration 2.8.7
(a) What is the atomic number of this element?
(b) To which of the following elements would it be chemically similar ? (Atomic number are given in parenthese)
N(7) F (9) P(15) Ar(18)
1. D 2. A 3. A 4. D
5. C 6. A 7. B 8. A
9. C 10. D 11. B 12. A
13. C 14. B 15. A 16. B
1. Periods 2. Groups
3. 2 4. 13
5. Increases, decreases 6. Smaller
7. Larger 8. B2O3
9. Properties 10. electrons
11. 4 12. 15 13. 63 elements
14. Li 15. F 16. Electron affinity
17. Ionisation energy 18. Increases
19. Increases
20. Decreases, Increases
21. Decreases
Q.1 The element with atomic number 9 resembles with the
element having atomic number
(A) 8
(B) 17
(C) 36
(D) 27
Q.2 The elements of the group 16 are also called ______.
(A) halogens
(B) noble gases
(C) chalcogens
(D) alkaline earth metals
Q.3 The most metallic element in the fifth period is
(A) silver
(B) rubidium
(C) gold
(D) rhodium
Q.4 Two elements that have similar properties because
they have the same number of valence electrons are
(A) C and Cl
(B) Ca and Ga
(C) Si and S
(D) S and O
Q.5 The element with lowest IE1 is
(A) sodium
(B) cesium
(C) barium
(D) magnesium
Q.6 Which amongst the following is not a noble gas?
(A) helium
(B) neon
(C) radium
(D) radon
Q.7 The elements in the middle of the periodic table are called
(A) metalloids
(B) transition elements
(C) rare earth element
(D) noble gases
Q.8 The general name of the elements of 17th group are-
(A) hydrides
(B) halogens
(C) chalcogens
(D) noble gases
Q.9 Which of the following is the lightest metal?
(A) Li
(B) Mg
(C) Na
(D) Ca
Q.10 Elements belonging to the same group have similar chemical properties because
(A) they are all metallic elements
(B) they have similar electronic configuration
(C) atomic number increases on moving down the group
(D) none of these
Q.11 Law of Triad was proposed by
(A) Newland
(B) Gay Lussac
(C) Mendeleev
(D) Dobereiner
Q.12 Which amongst the following are called Magic numbers?
(A) 2,8,8,18
(B) 2,8,8,32
(C) 2,8,18,32
(D) none of these
Q.13 Third period of the periodic table contains the following number elements.
(A) 2
(B) 18
(C) 8
(D) 32
Q.14 An element has electronic configuration 2,8,4. It belong to which
group and period of the Periodic Table
(A) 2,4
(B) 4,3
(C) 4,14
(D) 3,14
Q.15 The element with electronic configuration 2,8,6 is:
(A) metallic with valency 2
(B) non-metallic with valency 2
(C) metalloid with valency 2
(D) none of these
Q.16 The elements belonging which group called representative elements?
(A) gp 1 and 2
(B) gp 3 to 12
(C) gp 13 to 18
(D) Element lying at the bottom of periodic table
Q.17 Modern periodic table by Mosley states that
(A) properties of elements are periodic function of Atomic mass
(B) propoerties of element depend upon number of neutrons
(C) properties of element depend upon number of reactions
(D) properties of elements are periodic function of atomic number
Q.18 Element 'A' has Electronic configuration 2,7 'B' has configuration 2,8,6,
'C' has configuration 2,8,8 while 'D' has 2,8,7. Which element will show
similar chemical properties?
(A) A and C
(B) A and D
(C) B and C
(D) B and D
Q.19 Which amongest the following is highest non-metal?
(A) nitrogen
(B) lithium
(C) oxygen
(D) hydrogen
Q.20 Which amongst the following is not an alkaline earth metal?
(A) Mg
(B) Ba
(C) Fr
(D) Sr
1. D 2. C 3. B 4. D
5. C 6. C 7. B 8. B
9. A 10. B 11. A 12. C
13. C 14. B 15. B 16. A
17. D 18. B 19. D 20. C
1. Dobereiner, in 1829, pointed out that when elements are arranged in the order of increasing relative atomic masses,
in a triad, the relative atomic mass of the middle element was approximatery equal to the mean of the relative atomic
masses of the first and third elements. Name the element which is in between the elements calcium and barium :
(A) Beryllium (B) Magnesium (C) Strontium (D) Iodine
2. The third member of the Dobereiner triad consisting of lithium and sodium is :
(A) Potassium (B) Hydrogen (C) Boron (D) Barium
3. If the two members of a Dobereiner triad are chlorine and iodine, the third member of this triad is :
(A) Fluorine (B) Bromine (C) Sodium (D) Calcium
4. If the two members of a Dobereiner triad are sulphur and selenium, the third member of this triad is :
(A) Calcium (B) Barium (C) Strontium (D) Tellurium
5. If the two members of a Dobereiner triad are phosphorus and antimony, the third member of this triad is :
(A) Arsenic (B) Sulphur (C) Iodine (D) Calcium
6. Who gave the 'law of octaves'?
(A) Dobereiner (B) Lothar meyer (C) Mendeleef (D) Newlands
7. Lothar Meyer obtained the curve for the known elements plotting their atomic volumes against :
(A) Atomic numbers (B) Atomic masses (C) Densities (D) Ionization energies
8. In Lothar Meyer plot, the peaks are occupied by :
(A) Alkali metals (B) Alkaline earth metals (C) Halogens (D) Noble gases
9. According to Mendeleef periodic law, the properties of elements are periodic function of their :
(A) Atomic mass (B) Atomic numbers (C) Atomic volumes (D) Densities
10. Mendeleef periodic table had no place for
(A) Alkali metals (B) Alkaline earth metals (C) Halogens (D) Noble gases
11. The basis of the modern long form of the periodic table is :
(A) Atomic masses (B) Atomic number (C) Atomic size (D) Atomic volume
12. The elements with atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54 and 86 are all :
(A) Halogens (B) Noble gases (C) Noble metals (D) Light metals
13. In the periodic table :
(A) There are two elements in the first period (B) There are eighteen elements in the third period
(C) The horizontal rows are called groups (D) The vertical columns are called periods
14. How many periods are there in the long form of the periodic table?
(A) 6 (B) 7 (C) 8 (D) 9
15. Elements in the vertical group of the periodic table have generally the same :
(A) Atomic size
(B) Electronic configuration
(C) Number of electrons
(D) Number of electrons in the outermost shell of their atoms
16. The elements with atomic numbers 3, 11, 19, 37 and 55 belong to :
(A) Alkali metals (B) Alkaline earth metals (C) Halogens (D) Noble gases
17. The elements with atomic numbers 4, 12, 20, 38 and 56 belong to :
(A) Alkali metals (B) Alkaline earth metals (C) Halogens (D) Noble gases
18. The elements with atomic numbers 9, 17, 35, 53 and 85 belong to :
(A) Alkali metals (B) Alkaline earth metals (C) Halogens (D) Noble gases
19. The atomic number of the element next to 16S in the same group is :
(A) 18 (B) 24 (C) 34 (D) 42
20. The atomic number of the element next to 53I in the same group is :
(A) 55 (B) 61 (C) 85 (D) 93
21. The atomic number of the element next to 2He in the same group is :
(A) 4 (B) 10 (C) 20 (D) 52
22. The elements belonging to IA to VIIA and 0 groups are known as :
(A) Alkali metals (B) Representative elements
(C) Transition elements (D) Inner-transition elements
23. The elements belonging to IIIB to VIII and IB and IIB are known as :
(A) Representative elements (B) Transition elements
(C) Lanthanides (D) Actinides
24. Each transition series contains a total of :
(A) 2 elements (B) 8 elements (C) 10 elements (D) 18 elements
25. The number of elements in each of the inner transition series is :
(A) 2 (B) 8 (C) 10 (D) 14
26. The number of elements in the first period of the periodic table is :
(A) 2 (B) 8 (C) 18 (D) 32
27. The number of elements in the second period of the periodic table is :
(A) 2 (B) 8 (C) 18 (D) 32
28. The number of elements in the third period of the periodic table is :
(A) 2 (B) 8 (C) 18 (D) 32
29. The number of elements in the fourth period of the periodic table is :
(A) 2 (B) 8 (C) 18 (D) 32
30. The number of elements in the fifth period of the periodic table is :
(A) 2 (B) 8 (C) 18 (D) 32
31. The number of elements in the sixth period of the periodic table is :
(A) 2 (B) 8 (C) 18 (D) 32
32. The total number of elements in VIII group of the periodic table is :
(A) 3 (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 9
33. The total number of elements in the zero group of the periodic table is :
(A) 2 (B) 4 (C) 6 (D) 8
34 . The total number of element in the Group III A is :
(A) 3 (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 9
35. The total number of elements in the group IB is :
(A) 3 (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 9
36. Which of the following elements has the least nonmetallic character?
(A) Fluorine (B) Chlorine (C) Bromine (D) Iodine
37. Which of the following elements has the maximum metallic character?
(A) Lithium (B) Sodium (C) Potassium (D) Rubidium
38. Which of the following elements will form acidic oxide ?
(A) Sodium (B) Magnesium (C) Aluminium (D) Sulphur
39. Which of the following elements will form alkaline oxide?
(A) Potassium (B) Phosphorus (C) Sulphur (D) Chlorine
40. Which one of the following is the most electropositive element?
(A) Sodium (B) Calcium (C) Aluminium (D) Silicon
41. Which one of the following is the most electronegative element?
(A) Iodine (B) Bromine (C) Chlorine (D) Fluorine
42. Which one of the following will have the least size?
(A) Lithium (B) Beryllium (C) Sodium (D) Magnesium
43. Which of the following statements is correct?
(A) Electropositive nature of elements increases in a period.
(B) Electropositive nature of elements decreases in a period.
(C) Electropositive nature of elements remains more or less constant in a period.
(D) Electropositive nature of elements first increases followed by the decrease.
44. Which of the following statements is correct ?
(A) Electronegative nature of elements increases in a group.
(B) Electronegative nature of elements decreases in a group.
(C) Electronegative nature of elements remains more or less constant in a group.
(D) Electronegative nature of elements first increases followed by the decrease.
45. Which of the following oxides will be more acidic in nature?
(A) Na2O
(B) MgO
(C) SiO2
(D) Cl2O7
46. Which of the following oxides will be more basic in nature?
(A) Na2O
(B) MgO
(C) SiO2
(D) Cl2O7
47. An element X belongs to Group IVA and 2nd period of the periodic table. Its atomic number will be :
(A) 6
(B) 14
(C) 7
(D) 15
48. In the modern periodic table :
(A) There are eight elements in the third period
(B) There are eight elements in the fourth period
(C) The horizontal rows are termed as groups
(D) The vertical columns are termed as periods
49. An element belongs to Group VA and third period. Its electronic configuration will be :
(A) 2, 5
(B) 2, 8, 5
(C) 2, 4
(D) 2, 8, 4
50. In the periodic table, the metallic character of elements :
(A) Increases, (i) from left to right across a period and (ii) on descending a group
(B) Decreases (i) from left to right across a period and (ii) on descending a group
(C) Increases from left to right across a period and decreases on descending a group
(D) Decreases from left to right across a period and increases on descending a group
51. Atomic sizes of the following elements decrease in the order :
(A) B > Be > Li
(B) Be > Li > B
(C) Li > B > Be
(D) Li > Be > B
52. Which of the following has the largest size?
(A) Cl
(B) Cl–
(C) Br
(D) Br–
53. Which of the following has the smallest size?
(A) Na
(B) Na+
(C) K
(D) K+
54. The element chromium belongs to the
(A) First transition series
(B) Second transition series
(C) Third transition series
(D) Fourth transition series
55. Valency of silicon with respect to hydrogen is :
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
56. Valencies of phosphorus with respect to oxygen are :
(A) 1, 3
(B) 3, 5
(C) 2, 4
(D) 1, 2, 4
57. The nature of bonding of phosphorus with other elements is :
(A) Ionic
(B) Covalent
(C) Both ionic as well as convalent
(D) Coordinate
58. The valence electrons of 9F are
(A) 4
(B) 5
(C) 6
(D) 7
59. An element belongs to Group IIIA and the second period of the periodic table.
Which of the following properties will be shown by the element?
(A) Gaseous, non-metallic
(B) Liquid, metallic
(C) Solid, metallic
(D) Solid, nonmetallic
60. An element belongs to Group VIIA and the fourth period of the periodic table.
Which of the following properties will be shown by the element?
(A) Gaseous, metallic
(B) liquid, nonmetallic
(C) Solid, nonmetallic
(D) Solid, metallic
Question 61 to 64 are based on the following passage -
The long form of the periodic table is outlined below.
In this form, the elements are grouped into different blocks, viz., s-block, p-block, d-block and f-block.
61. The area marked with circles is called :
(A) s-block
(B) p-block
(C) d-block
(D) f-block
62. The area marked with crossed is called :
(A) s-block
(B) p-block
(C) d-block
(D) f-block
63. The area marked with dots is called
(A) s-block
(B) p-block
(C) d-block
(D) f-block
64. The black shaded portion is called
(A) s-block
(B) p-block
(C) d-block
(D) f-block
65. The alkali metals :
(A) Combine directly with hydrogen on heating to form salt-like hydrides
(B) Form salts which are predominantly covalent in nature
(C) Show decreased chemical reactivity with dry oxygen in going from the first to the last element in the
alkali-metal group
(D) Show increasing electronegativity from the first to the last element of alkali-metal group
66. Alkaline earth metals
(A) Are much less dense, softer and have lower melting points than the corresponding alkali metals
(B) Are readily oxidized
(C) Exhibit an oxidation state of +1 in their compounds
(D) Have melting points which increase with increasing atomic number
67. The halogens
(A) Are highly electropositive
(B) Have an electronic configuration ps2np6
(C) Form a volatile, covalent hydride HX in which the halogen (X) shows an oxidation state of +1
(D) Show variable oxidation states –1, +1, +3, +5 and +7 in their various compounds
68. Beryllium bears diagonal relationship with
(A) Magnesium
(B) Boron
(C) Aluminium
(D) Lithium
69. Which of the following elements has the highest electronegativity?
(A) Fluorine
(B) Iodine
(C) Lithium
(D) Caesium
70. Oxidising power of halogens decreases in the order
(A) Cl > Br > I
(B) Br > I > Cl
(C) I > Cl > Br
(D) I > Br > Cl
71. Melting points of alkali metals decrease in the order
(A) Li > Na > K
(B) Na > K > Li
(C) K > Li > Na
(D) K > Na > Li
72. Which of the following elements is expected to have the most metallaic character?
(A) S
(B) P4
(C) Cl2
(D) I2