We observe many chemical changes taking place in our daily life. The milk turns sour if kept for a long time at room temperature, milk changes to curd, rusting of iron, digestion of food in our body are examples of chemical changes.
In such changes, the nature and the properties of the substances change and we say a chemical reaction has taken place.
A chemical reaction is represented by a chemical equation which is a convenient way of describing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols of elements and formulae of chemical compounds.
In this chapter, we shall discuss about chemical formulae, chemical equations, balancing of chemical equations and types of chemical reactions.
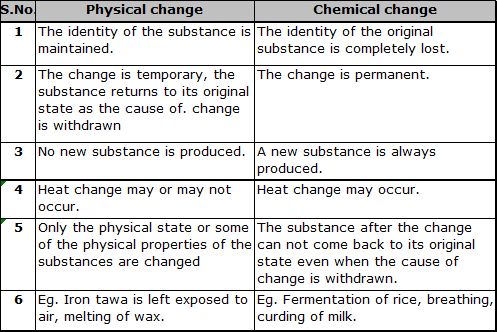
² Physical change :– A change in which the physical properties of the substance changes but the chemical composition does not change. The substance is restored to its original state as soon as the cause of change is withdrawn.
² Chemical change :– In a chemical change, at least one of the reacting substance changes into a new substances with a different composition. The new substances can not be changed back to the original substance even if the cause of change is withdrawn.
Difference between physical & chemical change
The processes, in which a substance or substances undergo a chemical change to produce new substance or substances, with entire new properties, are known as chemical reaction.
The nature and identity of products totally changes from the reactants.
Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are:
(i) Change in state: The physical state of the substances normally changes.
e.g (a) Formation of solid MgO from solid Mg and gaseous O2.
(b) Formation of solid Pbl(ppt) from liquid solutions of PbNO3 and Kl.
(c) Formation of H2 gas from the reaction of solid Zn with liquid H2SO4.
(ii) Change in colour : In some of the chemical reactions change in colour can be observed.
e.g. (a) Formation of brown rust on black iron nails.
(b) Formation of yellow ppt. of lead iodide from colourless solution of PbNO3 and Kl.
(iii) Evolution on a gas: In some cases, a gas may be evolved.
e.g. (a) Evolution of H2 gas, in the reaction between Zn and dil HCL
(b) Evolution of CO2 gas, during burning of any fuel, which contains carbon.
(iv) Change in temperature: Most of the reactions are accompanied by temperature change. i.e.
increase or decrease in temperature.
e.g. (a) In the reaction between Zn and H2SO4, flask was found to be warm. Thus rise in
temperature has taken place.
(b) If a reaction between barium hydroxide, Ba(OH)2 and ammonium chloride, NH4Cl is carried out in a test tube, it is observed that bottom of test tube becomes cooler.
Q. Check Your Concepts
From the given exaples, identify the chemical changes.
(a) Fermentation of grapes.
(b) Burning of a candle.
(c) Evaporation of alcohol.
(d) Freezing of water.
(e) Turning brown of a freshly cut apple in the air.
(f) Growth of a plant.
(g) Dissolution of sugar in water.
(h) Fading of coloured clothes in the sun.
A chemical equation which represents a chemical reaction briefly in words is called word equation.
Example : For the example the word equation is
Sodium + water ¾® Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen

In the above reaction sodium & water are reactants and sodium hydroxide & hydrogen are products.
² Rules for writing a word equation
(i) The substances taking part in chemical reaction, reactants are always written on the left hand side of arrow.
(ii) The substances formed after the chemical reaction, products are always written on the right hand side of arrow.
(iii) A plus sign (+) is put in between the reactants or between the products. If their number is two or more.
(iv) An arrow (¾®) is put between the reactants and products, the arrow shows the direction of the reaction in which the reaction proceeds. The arrow is read as "to yield" or "to form".
In the word equation when symbols and chemical formulae of the reactants and products are
used then it is called as chemical equation.
Example : Na + H2O ¾® NaOH + H2
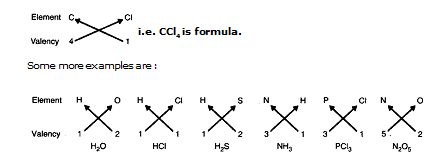
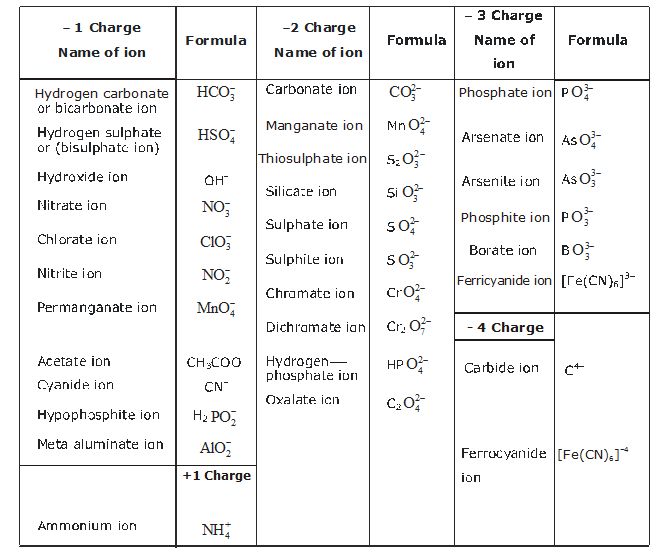
1. Valency. The number of electrons shared by an atom is called its valency. It is also called the combining capacity of an atom, e.g., Cl atom can share one valence electron, its valency is 1, Oxygen can share two valence electrons, its valency is 2. Nitrogen can share 3 valence electrons, its valency is 3, Carbon can share 4 valence electrons, therefore its valency is 4 and so on.
It means if Carbon combines with Chlorine, Carbon will share four valence electrons with four Chlorine atoms, therefore the molecular formula of the covalent compound will be
i.e. CCl4 is formula.
Some more examples are :
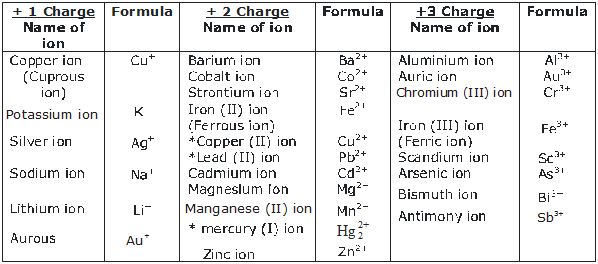
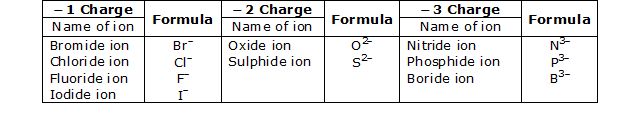
*The elements show more than one valency. So a Roman numeral shows theft valency in a bracket.
2. Chemical Equations. “A chemical equation is a symbolic notation that uses formulae of compounds and symbols of elements to represent a chemical reaction”, e.g., Copper oxide reacts with Carbon to form Copper and Carbon monoxide. The reaction may be represented as
CuO + C Cu + Co
3. Writing of a Chemical Equation.
(i) The symbols of elements and the formulae of reacting substances (reactants) are written on the left hand side and plus (+) sign is written between them.
(ii) The symbols and formulae of the substances formed (products) are written on the right hand side with a plus sign (+) between them.
(iii) An arrow () sign in put between the reactants and products, e. g.,
Mg + H2SO4 MgSO4 + H2
(iv) The physical states of the reactants and products are also mentioned in a chemical equation.
The notations g, l, s, aq. are written in brackets along with symbols/formulae of reactants and products.
These symbols stand for gaseous, liquid, solid and aqueous solution respectively, e.g.,
Mg (s) + H2SO4(aq) MgSO4(aq) + H2 (g)
Zn (s) + H2SO4 (aq) ZnSO4(aq) + H2
The symbol () may also be used to represent a gaseous product. The symbol (¯) is used to represent the formation of a precipitate (water insoluble) or a sparingly soluble substance formed during the reaction which settles down mostly, e.g.,
NaCl (aq) + AgNO3 (aq) AgCl (¯) + NaNO3 (aq)
(v) Sometimes, the temperature, pressure and catalyst of the reaction are indicated above and or below the arrow in the equation, e.g.,
CO (g) + 2H2 (g) CH3OH (g)
(vi) A chemical equation represents an actual chemical reaction in which the reactants and products are known, e.g.,
2 KMnO4 (s) K2MnO4 (s) + MnO2 (s) + O2 (g)
2 KClO3 (s) 2 KCl (s) + 3 O2 (g)
4. Balancing of chemical equation. Observe the following two chemical equations :
Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 + H2 ……(i)
Na + H2O NaOH + H2 …….(ii)
In equation (i), the number of atoms of Zn, H, S, and O are equal on both sides, i.e., the equation is balanced.
5. Balanced Equations. The equations in which atoms of various elements on the reactant’s and the product’s side are equal.
Equation (ii) is not balanced because the number of hydrogen atoms is not equal on both sides. It is called a skeleton chemical equation.
6. Reason of Balancing Equations. The number of atoms of elements on both sides of a chemical equation should be equal in accordance with the law of conservation of mass.
7. Balancing. The process of making atoms of various elements equal in an equation on either side is called balancing.
8. Steps in Balancing of Chemical Equations. A number of steps are involved in balancing a chemical equation, e.g.,
Na + H2O NaOH + H2
Step 1: Examine the number of atoms of different elements present in unbalanced equation.
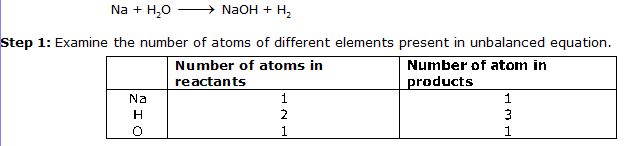
Step 2: Pick an element to balance the equation. In the above equation Na and O are balanced, Hydrogen is not.
Step : To balance Hydrogen on both sides we need to multiply H2O by 2 which makes Hydrogen atoms equal to 4 on the reactants’ side. To make Hydrogen 4 on the products’ side, multiply NaOH by 2. Now oxygen has become 2 on both sides. But Sodium atom has become two on the product’s side. Multiply Na by 2 on the reactant’s side so that they become equal on both sides. The steps are as follows :
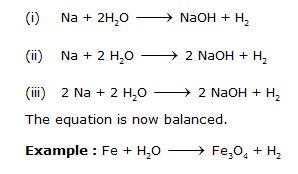
Step 1 :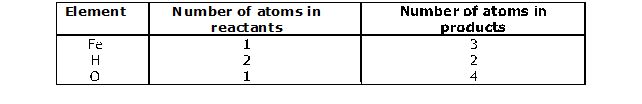
Step 2 : Pick up the compound which has the maximum number of atoms whether a reactant or a product, and in that compound select the element which has the highest number of atoms, e.g., we select Fe3O4 in the above equation :
To balance oxygen atoms,
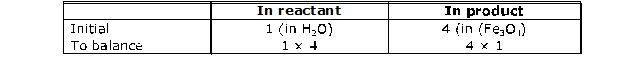
To equalise the number of atoms, we put the coefficient on the left side of the formula. A coefficient is a small whole number, like coefficients used in algebraic equations. You must keep in mind that we can put coefficients but we cannot change the subscripts in the formula, i.e., to balance Oxygen atoms, we can put the coefficient 4 as 4 H2O and not H2O4 or (H2O)4. Now the partly balanced equation becomes as follows :
![]()
Step 3 : Pick up the second element to balance this partly balanced equation. Let us try to balance hydrogen atoms. bIn partly balanced equation. Atoms of Hydrogen
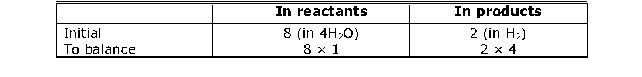
To equalise the number of Hydrogen atoms, we use 4 as the coefficient of H2 in the products.
Fe (s) + 4H2O (g) Fe3O4 (s) 4H2
Step 4 : Pick up the third element to be balanced. The element which is left to be balanced is Fe.

To equalise iron, we use 3 as coefficient of Fe in reactants.
3 Fe + 4 H2O Fe3O4 + 4H2
Step 5 : Check the correctness of the balanced equation.

The equation is balanced because atoms of all the elements are equal on both sides. This method of balancing equation is known as hit and trial method.
9. Balancing of Ionic Equations. In these equations, charge balancing is also done along with balancing of atoms on both sides of the equation, e.g.,

The chemical reactions are classified into various categories depending upon the types of changes taking place. The different types of reactions are as follows :
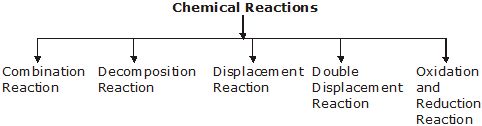
(i) Combination Reaction. The reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a single new substance are called combination reaction.
Combination may take place,
(i) Between two or more elements.
(ii) Between two or more compounds.
(iii) Between elements and compounds.
(a) Between two elements
(i) Burning of Coal
C(s) + O2(g) ¾® CO2(g)
Carbon Oxygen Carbon dioxide
(ii) Formation of Water
2H2(g) + O2(g) ¾® 2H2O(l)
Hydrogen Oxygen Water
(iii) Burning of Magnesium in air
2Mg(s) + O2(s) ¾® 2MgO(s)
Magnesium Oxygen Magnesium oxide
(iv) Formation of Iron sulphide
Fe(s) + S(s) FeS(s)
Iron Sulphur Iron sulphide
(b) Between 2 compounds
(i) Formation of Ammonium chloride
NH3(g) + HCl(g) ¾® NH4Cl(s)
Ammonia Hydrogen Ammonium
Chloride Chloride
(ii) Formation of Calcium Carbonate
CaO(s) + CO2(g) ¾® CaCO3(s)
Calcium oxide Carbon Calcium
(Quick lime) dioxide carbonate
(c) Between an element and a compound
(i) Reaction of carbon monoxide with oxygen
2CO(g) + O2(g) ¾® 2CO2(g)
This is also an exothermic reactions.

Þ Aim : To show the combination reaction between calcium oxide and water is an exothermic process.
Þ Materials Required: Quicklime (calcium oxide), water, beaker.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take 5 g of calcium oxide in a beaker.
2. Add water to it slowly.
3. Touch the beaker.
4. Note down the observations.
Þ Observation : Calcium oxide reacts with water vigorously
to form calcium hydroxide with the evolution of heat.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
CaO (s) + H2O (l) Ca(OH)2 (aq) + Heat

Þ Conclusion : The reaction between CaO (Calcium oxide) and
H2O is a combination reaction. It is an exothermic process because heat is evolved.
Þ Aim: To show burning of magnesium ribbon in air is a combination reaction.
Þ Materials Required: Magnesium wire, tongs, burner.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take a strip of magnesium ribbon and hold it with the
help of tongs.
2. Introduce it in the flame of the burner.
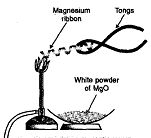
Þ Observation : Magnesium ribbon bums with dazzling light
and white substance is formed which is magnesium oxide.
This happens due to following chemical reaction.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
![]()
Þ Conclusion : Burning of magnesium in presence of oxygen to form magnesium oxide is a combination reaction.
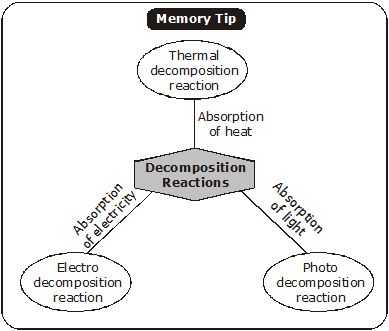
(ii) Decomposition Reaction. A reaction in which a single compound breaks down to produce two or more simpler substances. i.e., a compound decomposes into simpler substances.
It is opposite to combination reactions.
There are three ways in which decomposition reactions can be carried out, i.e., energy required in decomposition reaction can be supplied in the following ways:
(i) Heat (ii) Electricity (iii) Light
(1) Electrolysis. When decomposition reaction is carried out with the help of electric current, the process is called electrolysis (‘electro’ means electric, ‘lysis’ means break down), e.g., when electric current is passed through acidified water (water mixed with a few drops of acid so as to make it a good conductor), it decomposes into Hydrogen and Oxygen gases.
2 H2O (l) 2 H2 (g) + O2 (g)
Þ Aim : To demonstrate electrolysis of water.
Þ Materials Required : Plastic mug, drilling machine or screw driver, carbon electrodes, 6 volt battery, dil. H2SO4, water
Þ Procedure :
1. Take a plastic mug.
2. Drill two holes at the base and insert carbon electrodes as shown in figure.
3. Fill the mug with water to its half and add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid.
4. Fill a graduated measuring cylinder with water and invert it in the apparatus so that one of the two electrodes is enclosed within it.
5. Fill another graduated cylinder with water and invert it over the second electrode.
6. Allow the current to pass through the voltameter and leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
7. The bubble formation starts at both the electrodes.
8. Observe the volume of gases collected in the inverted measuring cylinders.
9. Collect the gases in respective cylinders and test them separately.
10. Bring a match stick near each of the gases in the cylinders and note down the observation and write conclusion about the gas.
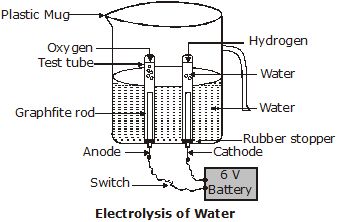
Þ Observation : The volume of one of the gases is twice the volume of other gas. One of the gases catches fire and burns with ‘pop’ sound whereas in other gas match stick burns brightly.
Þ Conclusion : Water, on electrolysis decomposes to hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Hydrogen gas burns explosively whereas oxygen gas helps in burning, i.e., hydrogen is highly combustible and oxygen is supporter of combustion.
(2) Thermal Decomposition. When decomposition reaction is carried out by heating, it is called thermal decomposition reaction, e.g.,
CaCO3 (s) CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
[Limestone] [Quick lime]
FeSO4 (S) Fe2O3 + SO2(g) + SO3(g)
[Ferric oxide]
2Pb(NO3)2(S) 2PbO + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
Zn CO3 (s) ZnO (s) + CO2 (g)
The process of heating ZnCO3 (Calamine), an ore of zinc in absence of air to form Zinc oxide (ZnO) and CO (g) is also called calcination.
Þ Aim : To show heating of lead nitrate is decomposition reaction.
Þ Materials Required : A test tube, lead nitrate solid.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take lead nitrate (white powder) in a test tube and hold
it in tongs.
2. Heat it over flame of burner slowly as shown in diagram.
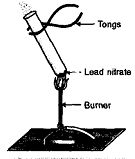
Þ Observation : Pungent smelling brown fumes are evolved and
brownish residue is left.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
2 Pb(NO3)2 2PbO (s) + 4 NO2 (g) + O2 (g)
Þ Explanation : Lead nitrate on heating decomposes to lead monoxide (brown), brown gas nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and oxygen gas are evolved.
Þ Conclusion : It is an example of decomposition reaction.
Þ Aim : To show decomposition reaction of ferrous sulphate.
Þ Materials Required : Ferrous sulphate crystals, dry test tube, burner.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry test tube.
2. Observe the colour of ferrous sulphate crystals.
3. Heat the crystals of ferrous sulphate over the flameof a
burner for some time.
4. Observe the crystals after heating for 5 minutes.
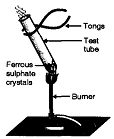
Þ Observation : The green colour of ferrous sulphate crystals
changes to brownish black ferric oxide and smell of burning sulphur is observed.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
2 FeSO4 (s) Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)
Þ Explanation : Ferrous sulphate decomposes to form ferric oxide along with evolution of SO2 and SO3 gases.
Þ Conclusion : Heating of ferrous sulphate is a thermal decomposition reaction because ferrous sulphate breaks down into simpler compounds Fe2O3, SO2 and SO3.
(3) Photochemical Decomposition :
Chemical reaction in which a compound decomposes into simpler substances on the absorption of light energy is called photo-decomposition reaction.

The Decomposition of a Compound with light is called “Photolysis.”
All Decomposition reaction requires energy i.e. these reactions are “Endothermic reactions.”
These reactions are used in extractions of metals.
Þ Aim : To show photochemical decomposition of silver chloride.
Þ Materials Required : AgNO3 (aq), NaCl (aq), test tubes.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take 5 ml of silver nitrate solution in a test tube.
2. Prepare sodium chloride solution in another test tube.
3. Add sodium chloride solution into test tube containing
silver nitrate solution.
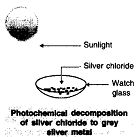
4. Observe the colour of silver chloride formed. Dry it with the
help of filter papers and place it on the watch glass.
5. Place the watch glass under sunlight for some time.
6. Observe the colour of the silver chloride after some time.
Þ Observation : White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight because silver metal is formed.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
![]()
Þ Explanation : Silver chloride is photo-sensitive. It decomposes in presence of sunlight to form silver metal and chlorine gas.
Þ Conclusion : Decomposition of silver chloride in presence of sunlight is photochemical decomposition reaction.
Þ Other examples of photochemical reactions : Silver bromide and silver iodide also decompose in the same manner.

These reactions are photochemical reactions which are used in black and white photography. Another important example of decomposition reaction in our body is digestion of food. When we eat rice, wheat or potatoes, the starch gets decomposed to simple sugar and proteins get converted into simple substances called amino acids in our body.
(C6H10O5)n + H2O C12H22O11
C12H22O11 + H2O 2C6H12O6
Proteins Amino acids
We have observed all the decomposition reactions require energy either in form of heat, light or electricity for breaking down of reactants. Therefore, they are endothermic reactions.
Endothermic Reactions: Those reactions in which heat is absorbed are called endothermic reactions.

(iii) Displacement Reactions. Those reactions in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound are called displacement reactions.
These reactions mostly occur in solution form, e.g.,

It shows magnesium is more reactive than Cu because it can displace Copper from Copper sulphate solution.
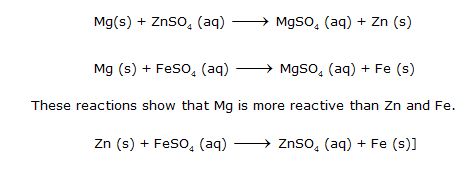
It shows Zn is more reactive than Fe.
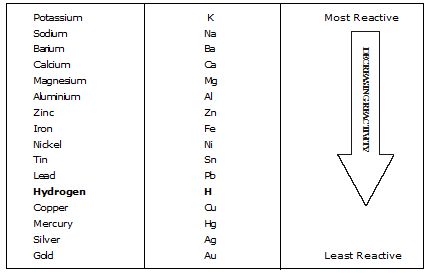
On the basis of the above reactions, we can conclude Mg > Zn >Fe > Pb > Cu > Ag is the order of reactivity.
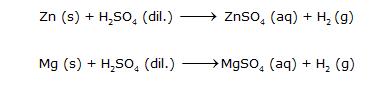
These reactions show that Zn and Mg are more reactive than Hydrogen because they displace Hydrogen from dilute acids. These are also examples of displacement reactions.
Þ Aim: To show iron is more reactive than copper.
Þ Materials Required : Iron nails, copper sulphate
solution, test tubes.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take blue coloured copper sulphate solution
in a test tube.
2. Put iron nails in it. 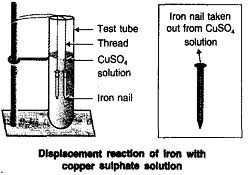
Þ Observation : Colour of solution slowly changes to
light green and brown coloured copper metal gets
deposited over iron nails.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
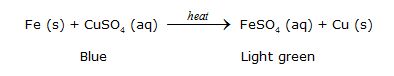
Þ Conclusion : Iron is more reactive than copper because iron can displace copper from copper sulphate solution. It is an example of displacement reaction.
\ Þ Aim : To show the displacement reaction between zinc granules
and dilute hydrochloric ac id or dilute sulphuric acid.
Þ Materials Required : Zinc granules, conical flask,
dil. HCl or dil. H2SO4.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take 5-6 zinc granules in a conical flask.
2. Set the apparatus as shown in figure.
3. Add dil. HCl or dil. H2SO4 over it.
4. Observe the reaction.
5. Touch the conical flask and observe the change in
temperature.
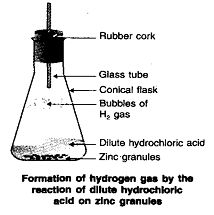
Þ Observation: The bubbles of hydrogen gas are observed.
The conical flask becomes hot showing that the process is exothermic.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
![]()
Þ Conclusion : The reaction between Zn and dil. HCl or dil. H2SO4 is a displacement reaction.
It is exothermic process. It shows zinc is more reactive than hydrogen, therefore it can displace hydrogen from dilute acids like HCl and H2SO4.
(iv) Double Decomposition Reactions (Double Displacement Reactions). Those reactions in which two different atoms or groups of atoms are displaced by other atoms or groups of atoms, i.e., two compounds exchange their ions and one of the products formed is insoluble, e.g.,
![]()
Here, S ions are displacing Cl- ions and Cl- ions are displacing Sions. Since it involves displacement of two species, therefore, is called double displacement reactions.
² If one of the products formed in the reaction is insoluble, it is also called double decomposition reaction.
² These reactions usually occur in between ionic compounds when they are dissolved in water i.e., in aqueous solution.
² These reactions are fast reactions and take place within fraction of a second.
Other examples of double displacement reactions are

Þ Aim : To show reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution is double displacement reaction (precipitation reaction).
Þ Materials Required : Barium chloride solution, sodium sulphate solution, two test tubes.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take sodium sulphate solution in a test tube.
2. Add few drops of solution of barium chloride.
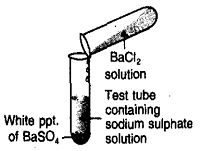
Þ Observation : White precipitate is formed.
Þ Chemical Reaction :
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) BaSO4 ¯ + 2NaCl (aq)
Þ Conclusion : Reaction between sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution is double displacement reaction.
Þ Aim : To show the reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide is double decomposition reaction (precipitation reaction).
Þ Materials Required : Test tubes, lead nitrate solution, potassium iodide solution.
Þ Procedure :
1. Take lead nitrate solution in a test tube.
2. Add potassium iodide solution to it.
3. Observe the changes taking place in the solution.
Þ Observation : Yellow precipitate is formed.
Þ Chemical Reaction and Explanation : Lead nitrate reacts with potassium iodide to form lead iodide which is insoluble in water and yellow in colour. It is called precipitate. The reaction is also called precipitation reaction.
![]()
Þ Conclusion : The reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide is double decomposition reaction. Since Pb is insoluble called precipitate, therefore, this reaction is also called precipitation reaction.
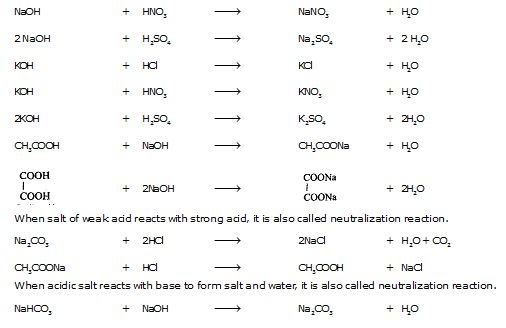
(v) Neutralization Reactions. Those reactions in which acid or acidic oxide reacts with base or basic oxide to form salt and water are called neutralization reactions, e.g.,
(vi) Oxidation and Reduction
(1) Oxidation.
(a) It is a process in which Oxygen or an electronegative element is added.
(b) It can also be defined as a process in which Hydrogen or an electropositive element is removed.
(c) In terms of electronic concept, oxidation is a process in which loss of electrons takes place.
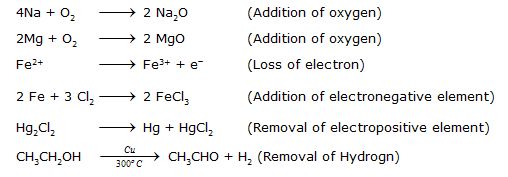
(2) Reduction.
(a) It is a process in which addition of Hydrogen or an electropositive element takes place.
(b) It is also defined as a process in which Oxygen or an electronegative element is removed.
(c) In electronic concept, reduction process involves gain of electrons.

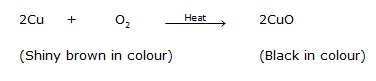
Þ Aim: To study oxidation of copper to copper (II) oxide.
Þ Method: Heat a china dish containing about 1 9 copper powder .
Þ Now answer: What do you observe?
Þ Discussion: It is observed that the brown copper powder gets coated with black copper (II) oxide.
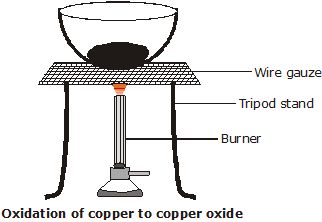
Þ Conclusion:
Copper (brown in colour) on heating combines with oxygen to form black copper (II) oxide.

Here, we can say that copper oxide is being reducing, as it is loosing oxygen and hydrogen is being oxidised.
Those reactions in which oxidation and reduction take place simultaneously are called redox reactions, e.g.,
(i) 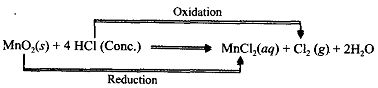


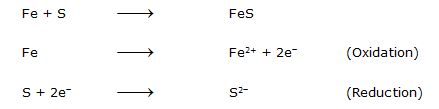
Fe is losing electrons, therefore, it acts as a Reducing agent.
S is gaining electrons, therefore, it acts as an Oxidising agent.
Fe is getting oxidised to Fe2+ (Ferrous ion) whereas S gets reduced to S2- (Sulphide ion)
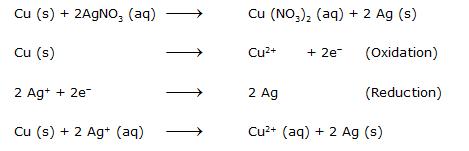
Cu is a reducing agent because it is losing electrons whereas Ag+ is an oxidising agent.
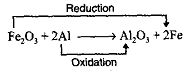
Fe2O3 is an oxidizing agent whereas Al is a readucing agent.
Zn + CuSO4 ZnSO4 + Cu
Zn is a reducing agent whereas Cu2+ is an oxidizing agent
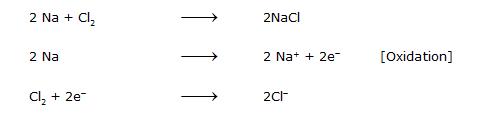
Na is a reducing agent whereas Cl2 is an oxidizing agent.
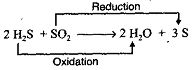
H2S is a reducing agent whereas SO2 is an oxidizing agent.
Oxidation has damaging effect on metals as well as on food. The damaging effect of oxidation on metals is studied as corrosion and that on food is studied as rancidity.
Thus there are two common effects of oxidation reactions are as
(I) Corrosion of metals (II) Rancidity of food
(I) Corrosion of metals :– Corrosion is the process of deterioration of metals as a result of its reaction with air, moisture and acids. (Present in environment) surrounding it.
The corrosion causes damage to buildings, bridges, ships and many other articles especially made of iron.
Rust : Iron corrode readily when exposed to moisture and gets covered with a brown flaky substance called rust. It is called rusting of iron, Rust is a hydrated Iron (III) oxide. [Fe2O3 · 2H2O]
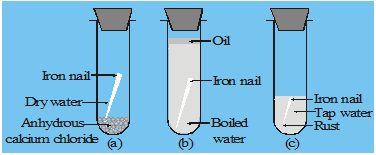
(a) Presence of air (or oxygen)
(b) Presence of water (or moisture) It has been observed that
(c) Presence of impurities in the metal speed up the rusting process. Pure iron does not rust.
(d) Presence of electrolytes in water also speeds up the process of rusting
(e) The position of the metal in the electrochemical series determines the extent of corrosion. More the reactivity of the metal, there will be more possibility of the metal getting corroded.
(i) Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in the air and slowly loses its shiny brown surface and acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate.
(ii) Silver articles become black after sometime when exposed to air because it reacts with sulphur to form a coating of silver sulphide.
(iii) Lead or stainless steel lose their lusture due to corrosion.
(iv) Unreactive metals such as Gold, Platinum, Palladium, Titanium etc. do not corrode.
Prevention of Rusting.
1. The iron articles should be painted.
2. The machine parts should be oiled and greased.
3. Galvanised iron pipes are used for water supply.
4. Iron can be coated with chromium to prevent rusting.
(II) Rancidity. The oxidation of oils or fats in food, resulting into a bad taste and bad smell is called rancidity. It is caused due to prolonged exposure of food in air. Oxygen present in air oxidise fats/oil present in food and form volatile substances, which have bad odour.

(i) Rancidity can be prevented by adding antioxidants to foods containing fats and oils. Antioxidants are reducing agents so when they are added to food it do not get oxidised easily and hence do not turn rancid. The two common anti oxidants are –
(a) BHA (Butylated Hydroxy Anisole)
(b) BHT (Butylated Hydroxy Toluene)
(ii) Rancidity can be prevented by packaging fat and oil containing foods in nitrogen gas.
(iii) It can be retarted by keeping food in refrigerator.
(iv) It can also be retarded by storing food in air tight containers.
(v) It can be retarded by storing foods away from light.
Ex.1 Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
(A) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia
(B) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(C) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(D) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Sol.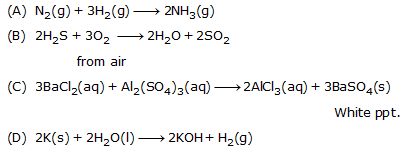
Ex.2 Balance the following chemical equations.
(A) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 ¾® Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(B) NaOH + H2SO4 ¾® Na2SO4 + H2O
Sol. (A) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 ¾® Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(B) 2NaOH + H2SO4 ¾® Na2SO4 + 2H2O
Ex.3 Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(A) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide ¾® Calcium carbonate + water
(B) Zinc + Silver nitrate ¾® Zinc nitrate + Silver
(C) Aluminium + copper chloride ¾® Aluminium chloride + Copper
(D) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate ¾® Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride.
Sol. (A) Ca(OH)2 + CO2 ¾® CaCO3 + H2O
calcium carbon calcium
hydroxide dioxide carbonate
(B) Zn + 2AgNO3 ¾® Zn(NO3)2 + 2Ag
zinc silver nitrate zinc nitrate silver
(C) 2Al + 3CuCl2 ¾® 2AlCl3 + 3Cu
aluminium copper aluminium copper
chloride chloride
(B) BaCl2 + K2SO4 ¾® BaSO4 + 2KCl
barium potassium barium potassium
chloride sulphate sulphate chloride
Ex.4 Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case
(A) Potassium bromide(aq) + Barium iodide(aq) ¾® Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium bromide(s)
(B) Zinc carbonate (s) ¾® Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide(g)
(C) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g) ¾® Hydrogen chloride(g)
(D) Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloridc acid(aq) ¾® Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(g)
Sol. (A) 2KBr(aq) + BaI2(aq) ¾® 2KI(aq) + BaBr2(aq)
This reaction is a double-displacement reaction.
(B) ZnCO3(s) ¾® ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
This reaction is a decomposition reaction
(C) H2(g) + Cl2(g) ¾® 2HCl(g) [Combination Reaction]
(D) Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq.) ¾® MgCl2(aq.) + H2(g) [Displacement Reaction]
Ex.5 Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Sol. Magnesium reacts with the constituent gases of the atmosphere to form various compounds which get deposited over its surface. The ribbon is cleaned before burning to remove the layer of these compounds so that pure magnesium can burn in air.
Ex.6 In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Sol. 2AgNO3(aq) + Cu(s) ¾® 2Ag(s) + Cu(NO3)2(aq)
(silver nitrate) (copper) (silver metal) (copper(II) nitrate)
Ex.7 A shiny brown coloured element 'X' on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element 'X' and the black coloured compound formed.
Sol. An element on heating in air changes in its oxide. The brownish element which forms black oxide is copper. So,
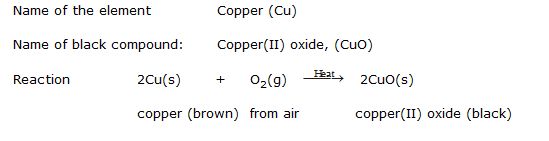
Ex.8 What happens chemically when quick lime is added or water ?
Sol. Calcium hydroxide (or slaked lime) is formed accompanied by a hissing sound. So much heat is evolved during the reaction that the reaction mixture starts boiling. The chemical equation for the reaction is :
CaO(s) + H2O(aq) Ca(OH)2(s) + heat
(Quick lime) (Slaked lime)
Ex.9 What is an oxidation reaction ? Identify in the following reactions :
(i) the substance oxidised (ii) the substance reduced.
ZnO + C Zn + CO
Sol. Oxidation involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen in a chemical reaction while reduction involves the addition of hydrogen or removal of organ.
In the given reaction :
(i) Carbon (C) is oxidised to carbon monoxide (CO).
(ii) Zinc oxide (ZnO) is reduced to zinc (Zn)
Ex.10 Which gas is evolved when dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with zinc ? Write the molecular formula of the gas.
Sol. Hydrogen gas is evolved. Its molecular formula is H2.
Ex.11 State any two observation in an activity which may suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. Give examples in support of your answer.
Sol. (i) In a tube take small amount of solid sodium carbonate (Na2CO3). To this add a few drops of hydrocloric acid.
(ii) A colourless and odourless gas will evolve which shows that a chemical reaction has taken place. The gas will turn lime water milky when passed through it.
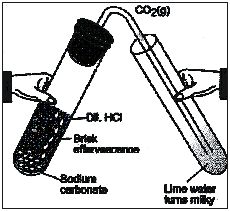
Ex.12 Identify the type of reaction in the following examples :
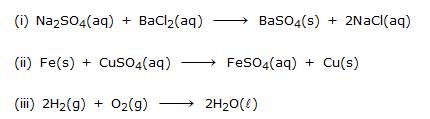
Sol. (i) It is an example of double displacement reaction.
(ii) It is an example of displacement reaction.
(iii) It is an example of combination reaction.
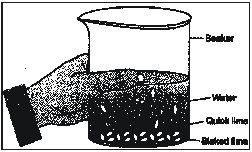
Ex.13 Solid calcium oxide was taken in a container and water was added slowly to it
(i) State two observations made in the experiment.
(ii) Write the name of the chemical formula of the product.
Sol. (i) Water will start boiling and hissing noise will be produced.
(ii) Calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) will be formed.
CaO(s) + H2O(aq) Ca(OH)2(s) + heat
Calcium oxide Calcium hydroxide
Ex.14 A house wife wanted her house to be white washed. She bought 10 kg of quick lime from the market and dissolved in 30 litres of water. On adding lime to water, she noticed that the water started boiling even when it was not being heated. Give reason for her observation. Write the corresponding equation and name the product formed.
Sol. A supension of slaked lime also called calcium hydroxide is formed when water is added to quick lime.
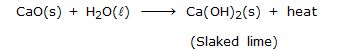 -
-
Since the reaction is highly exothermic, the solution started although it was not being heated.
The suspension of slaked lime is allowed to cool for sometime, preferably overnight. It is then decanted and the liquid obtained is used for white washing.
Q.1 Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before it is burnt in air?
Ans. Magnesium is an extremely reactive metal. When stored, it reacts with oxygen to form a layer of magnesium oxide on its surface. This layer of magnesium oxide is quite stable and prevents further reaction of magnesium with oxygen. The magnesium ribbon is cleaned by sand paper for removing this layer so that the underlying metal can be exposed to air.
Q.2 Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactios.
(i) Hydrogen + Chlorine ¾® Hydrogen chloride
(ii) Berium chloride + Aluminium sulphate ¾® Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium + Water ¾® Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Ans. (i) H2(g) + Cl2(g) ¾® 2HCl(g)
(ii) 3BaCl2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3(aq) ¾® 3BaSO3(s) + 2AlCl3(aq)
(iii) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) ¾® 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Q.3 Write a balanced chemical equation with state symbols for the following reactions.
(i) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(ii) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Ans. (i) BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) ¾® BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
(ii) NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) ¾® NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Q.4 A solution of a substance 'X' is used for white washing.
(i) Name the substance 'X' and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance 'X' with water.
Ans. (i) The substance 'X' is calcium oxide. Its chemical foluma is CaO.
(ii) Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water to form calcium hydroxide (slaked lime).
CaO(s) + H2O(l) ¾® Ca(OH)2(aq)
Calcium oxide Water Calcium hydroxide
(Quick lime) (Slaked lime)
Q.5 Why is the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes is double of the amount collected in the other? Name this gas.
Ans. Water (H2O) contains two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen. Therefore, the amount of hydrogen and oxygen produced during electrolysis of water is in a 2 : 1 ratio. During electrolysis, since hydrogen goes to one test tube and oxygen goes to another, the amount of gas collected in one of the test tubes is double of the amount collected in the other.
Q.6 Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change when an iron nail is dipped in it?
Ans. When an iron nail is placed in a copper sulphate solution, iron displaces copper from copper sulphate solution forming iron sulphate, which is green in colour.
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) ¾® FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
Iron Copper sulphate Iron sulphate Copper
(Blue colour) (Green colour)
Therefore, the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades and green colour appears.
Q.7 Give an example of a double displacement reaction other than the one given in Activity 1.10.
Ans. Sodium carbonate reacts with calcium chloride to form calcium carbonate and sodium chloride.
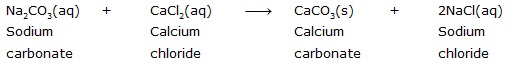
In this reaction, sodium carbonate and calcium chloride exchange ions to form two new compounds. Hence, it is a double displacement reaction.
Q.8 Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the followiing reactions.
![]()
Ans. (i) Sodium (Na) is oxidised as it gains oxygen and oxygen gets reduced.
(ii) Copper oxide (CuO) is reduced to copper (Cu) while hydrogen (H2) gets oxidised to water (H2O).Q.9 Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
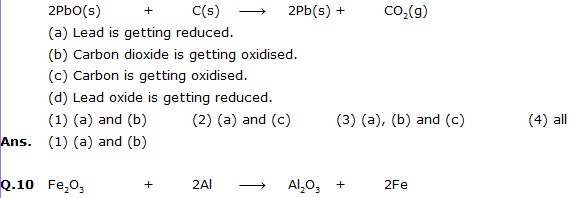
The above reaction is an example of a
(1) Combination reaction. (2) Double displacement reaction.
(3) Decomposition reaction. (4) Displacement reaction.
Ans. (4) The given reaction is an example of a displacement reaction.
Q.11 What happens when dilute hydrochloric add is added to iron filings? Tick the correct answer.
(1) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
(2) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(3) No reaction takes place.
(4) Iron salt and water are produced.
Ans. (1) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced. The reaction is as follows:
![]()
Q.12 What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced ?
Ans. A reaction which has an equal number of atoms of all the elements on both sides of the chemical equation is called a balanced chemical equation. The law of conservation of mass states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed. Hence, in a chemical reaction, the total mass of reactants should, be equal to the total mass of the products. It means that the total number of atoms of each element should be equal on both sides of a chemical equation. Hence, it is for this reason that chemical equations should be balanced.
Q.13 Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them.
(a) Hydrogen gas combines with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassium metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Ans. 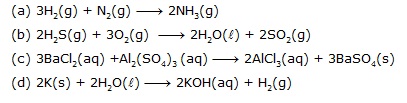
Q.14 Balance the following chemical equations.
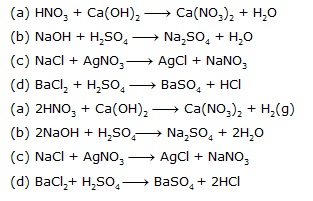
Q.15 Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions.
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide ¾® Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate ¾® Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride ¾® Alumiium chloride + Copper
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulhate ¾® Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Ans. 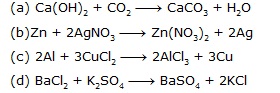
Q.16 Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case.
(a) Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium iodide(aq) ¾® Carbon dioxide(g)
(b) Zinc carbonate(s) ¾® Zinc oxide(s) + Carbon dioxide(g)
(c) Hydrogen(g) + Chlorine(g) ¾® Hydrogen chloride(g)
(d) Magnesium(s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) ¾® Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(g)
Ans. (a) 2KBr(aq) + BaIz(aq) ¾® 2KI(aq) + BaBr2(s); Double displacement reaction
(b) ZnCO3(s) ¾®ZnO(s) + CO2(g) ; Decomposition reaction
(c) H2(g) + Cl2(g) ¾® 2HCl(g) ; Combination reaction
(d) Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) ¾® MgCl2(aq) + H2(g) ; Displacement reaction
Q.17 What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Ans. Chemical'reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound are called exothermic reaction.
Example: Mixture of sodium and chlorine to yield table salt
![]()
In other words, combination reactions are exothermic.
Reactions that absorb energy or require energy in order to proceed are called endothermic reactions. For example: In the process of photosynthesis, plants use the energy from the sun to convert carbon dioxide and water to glucose and oxygen.

Q.18 Why is respiration considerd an exothermic reaction ? Explain.
Ans. Energy is required to support life. Energy in our body is obtained from the food we eat. During digestion, large molecules of food are broken down into simpler substances such as glucose. Glucose combines with oxygen in the cells and provides energy. The special name of this combustion reaction is respiration. Since energy is released in the whole process, it is an exothermic process.
![]()
Q.19 Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans. Decomposition reactions are those in which a compound breaks down to form two or more substances. These reactions require a source of energy to proceed. Thus, they are the exact opposite of combination reactions in which two or more substances combine to give a new substance with the release of energy.
Decomposition reaction: AB + Energy ¾® A + B
2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Combination reaction: A + B ¾® AB + Energy
2H2(g) + O2(g) ¾® 2H2O(l) + Energy
Q.20 Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Ans. 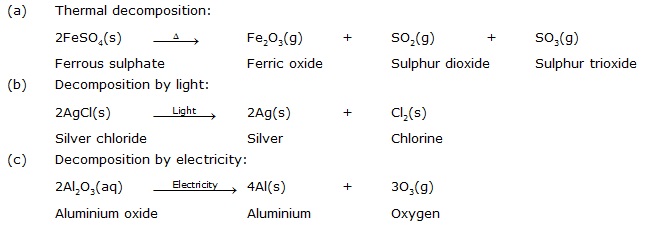
Q.21 What is the difference betuJeen dispiacemen[ and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Ans. In a displacement reaction, a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element from a
compound.
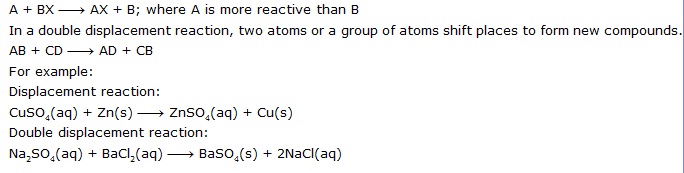
Q.22 In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solutior. involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Ans. ![]()
Q.23 What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Ans. A reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed is called a precipitation reaction.
For example:

Q.24 Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
(a) Oxidation (b) Reduction
Ans.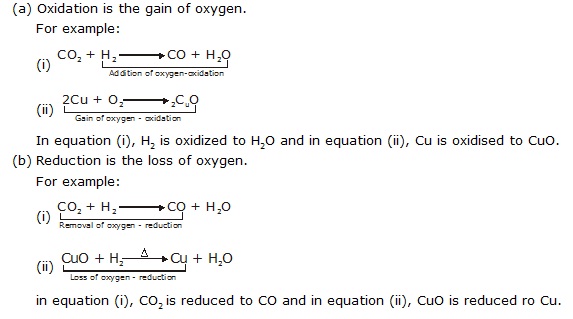
Q.25 A shiny brown-cloured element 'X' on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element 'X' and the black coloured compound formed.
Ans. ‘X’ is copper (Cu) and the black-coloured ocmpound formed is copper oxide (CuO). The equation of the reaction involved on heating copper is given below.
Q.26 Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Ans. Iron articles are painted because it prevents them from rusting. When painted, the contact of iron articles from moisture and air is cut off. Hence, rusting is prevented. Their presence is essential for rusting to take place.
Q.27 Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Ans. Nitrogen is an inert gas and does not easily read with these substances. On the other hand, oxygen reacts with food substances and makes them rancid. Thus, bags used in packing food items are flushed with nitrogen gas to remove oxygen inside the pack. When oxygen is not present inside the pack, rancidity of oil and fat containing food items is avoided.
Q.28 Explain the following terms with one example each.
(a) Corrosion (b) Rancidity
Ans. (a) Corrosion: Corrosion is defined as a process where materials, usually metals, deteriorate as a result of a chemical reaction with air, mOisture, chemicals, etc.
For example, iron, in the presence of moisture, reacts with oxygen to form hydrated iron oxide.
4Fe + 3O2 + nH2O ¾® 2Fe2O3.nH2O
Hydrated iron oxide
This hydrated iron oxide is rust.
(b) Rancidity: The process of oxidation of fats and oils that can be easily noticed by the change in taste and smell is known as rancidity.
For example, the taste and smell of butter changes when kept for long.
Rancidity can be avoided by:
(1) Storing fooo in air tight containers
(2) Storing fooo in refrigerators
(3) Adding antioxidants
(4) Storing food in an environment of nitrogen
Type I- Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1 Why does not a wall immediately acquire a white colour when a coating of slaked lime is applied on it? [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.2 What is ruet?
Q.3 What is the difference b/w the following 2 reactions? [C.B.S.E. 2011]
![]()
Q.4 Suggest 2 ways to check the rancidity of food articles. [C.B.S.E. 2011, 2012]
Q.5 What is the role of oxidising agent in a reaction?
[C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.6 What is meant by a skeletal chemical equation?
[C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.7 On what basis is a chemical equation balanced?
[C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.8 Balance following chemical equation:-
![]()
Q.9 Write a balanced chemical equation to represent the following equation:- Iron reacts with stream to form Iron (II, III) oxide and Hydrogen gas.[C.B.S.E. Sample paper 2011]
Q.10 Balance the following chemical equation.
![]()
Q.11 What happens chemically when Quick lime is added to water? [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.12 Give one example of each exothermic reaction and endothermic reaction? [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.13 What is the brown coloured gas evolved when lead nitrate crystals are heated in a dry test tube? [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.14 In the reaction MnO2 + 4HCl ¾® MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2. Identify which one is reduced and which one is oxidized? [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Q.15 Complete the equation:- [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Fe2O3 + 2Al ¾®
Q.16 Take a small amount of calcium oxide or quick lime in a beaker and slowly add water to this. Is there any change in temperature?
[C.B.S.E. 2010, 2011]
Q.17 Which chemical process is used for obtaining a metal from its oxide? [C.B.S.E. 2010]
Type II - Short Answer Type Questions
Q.18 Write balance chemical equation “during respiration combustion of glucose takes place producing carbon dioxide water and energy”.
Q.19 A zinc rod is left for nearly 20 minutes in a copper sulphate solution. What change would you observe in zinc rod?
Q.20 Name a reducing agent that can be used to obtain manganese from manganese dioxide. Write balanced chemical equation for the reaction? [C.B.S.E. Delhi 2009]
Q.21 Give reason, silver articles become black after sometime when exposed to air?
[C.B.S.E. 2008]
Q.22 What is the role of catalyest in a chemical reaction? [C.B.S.E. 2007]
Q.23 Name 2 salts which are used in black and white photography? [C.B.S.E. 2010, 11]
Q.24 State the essential requriement for rusting?
[C.B.S.E. 2013]
Type III- Long Answer Type Questions
Q.25 When a water insoluble substance “X” is added to dil. Hydrochloric acid, a colourless, odourless gas is evolved. When the gas is passed through lime water, it turns milky. Write the formula of gas evolved and balanced chemical equation of the reaction.
Q.26 (a) Write one equation each for decomposition reaction when energy is supplied in the form of (i) Heat (ii) Light.
(b) Account for following:-
(i) Paint is applied on Iron articles.
(ii) Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. [C.B.S.E. 2011]
Q.27 A green coloured hydrated salt of Iron loses its water of crystallisation and smell of burning sulphur is given. Identify the salt and write chemical equation. [C.B.S.E. 2011]
Q.28 (a) Why cannot a chemical change be normally reversed?
(b) Why is it always essential to balance a chemical equation?
(c) Why do diamond and graphite, 2 forms of carbon evolve different amounts heat on combustion?
(d) Why does milkness disappear when CO2 is passed throug lime water in excess?
(e) Can rusting of Iron take place in distilled water?
Q.29 X + YSO4 ¾® XSO4 + Y
Y + XSO4 ¾® No reaction
and of the 2 elements “X” and “Y” which is more reactive and why? [C.B.S.E. 2011]
Q.30 (a) Can a combination reaction be an oxidation reaction? [C.B.S.E. 2011]
(b) How will you test whether the gas evolved in a reaction is hydrogen?
(c) Why does copper not evolve hydrogen on reacting with dilute sulphuric acid?
Q.31 A brown substance “X” on heating in air forms a substance “Y”. When hydrogen gas is passed over heated “Y”. It again changes back into “X”. [C.B.S.E. 2010]
(i) Name the substance X and Y.
(ii) Name the chemical processes occuring during both changes.
(iii) Write chemical equations?
Q.32 Explain why:- [C.B.S.E. 2011]
(i) Respiration is an Exothermic reaction.
(ii) When blue salt of CuSO4 is heated it becomes colourless?
Q.33 In electrolysis of water [C.B.S.E. 2012]
(i) Name the gas collected at the cathod and anode respectively.
(ii) Why is the volume of one gas collected at one electrode double that at the other? Name this gas?
(iii) How will you test the evolved gases?
Q.34 Identify the type of reaction[C.B.S.E. 2012]
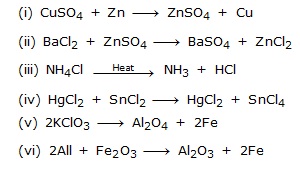
Q.35 Balance the following equation [C.B.S.E. 2008]
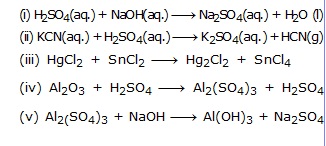
Q.36 Identify the type of reaction
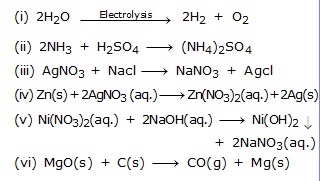
Type IV- Thinking Based/Skill Based Questions
Q.37 The marble statues slowly get carroded when kept in open for a long time. Give suitable explanation?
Q.38 (a) Based on reactions given below, arrange the metals invloved in these reactions in decreasing order of reactivity. Give suitable explanation.

Q.39 A, B and C are 3 elements which undergo chemical reactions according to following equations:-
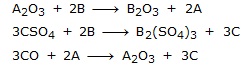
Ans. Following Questions
(a) Which element is more reactive?
(b) Which element is least reactive?
Q.40 You are given following materials:-
(i) Marble chips (ii) Dil. HCl acid (iii) zinc granules
Identify type of reaction when marble chips and zinc granules are added separately to acid taken in two tubes. Write chemical equation in each case.
Q.41 2gm of FeSO4 Crystals were heated in a hard glass test tube and observations recorded.
(a) What was the successive colour change?
(b) Identify liquid droplets collected on cooler part of test tube.
(c) What type of odour is observed on heating FeSO4 Crystals?
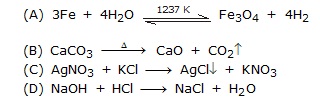
1. Fill in the blanks
1. The compound YBa2Cu3O7, which shows superconductivity, has copper in oxidation state __________ assume that the rare earth element yttrium is in its usual +3 oxidation state.
2. The oxidation number of carbon in CH2O is ______________.
3. The brown ring complex compound in formulated as [Fe(H2O)5(NO)+]SO4. The oxidation number of iron is __________.
4. The oxidation number of phosphorus in Ba(H2PO2)2 is: _______________.
5. The oxidation number of sulphur in S8, S2F2, H2S respectively are ________________.
2. Balance the following equation by ion-electron method.
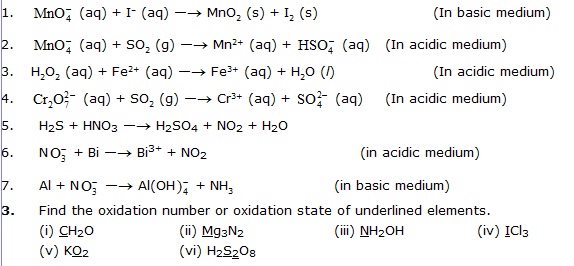
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. A reaction in which, under equilibrium conditions, both the reactants and products are present is called,
(A) reversible (B) Irreversible (C) endothermic (D) exothermic
2. The reaction, H2 + Cl2 —® 2HCl is,
(A) an oxidation reaction (B) a reduction reaction
(C) a combination reaction (D) an isomoerisation reaction
3. When sodium metal is dropped into water, it gets
(A) oxidised (B) reduced (C) remain unchanged (D) hydrolysed
4. Fatty foods become rancid because of which one of the following?
(A) Oxidation (B) Reduction (C) Hydrogenation (D) Corrosion
5. Which one of the following reactions is an example of thermal decomposition?
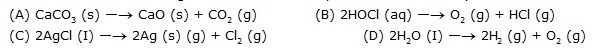
6. In the reaction 2Al + Fe2O3 —® Al2O3 + 2Fe which one is oxidized?
(A) Al (B) Fe (C) Fe2O3 (D) none
7. Oily and fatty food items are flushed with nitrogen gas because of which one of the following reasons?
(A) Nitrogen reacts with oils and fats and thus prevents oxidation
(B) Nitrogen is inert and excludes a direct contact of air with oily and fatty food items
(C) Nitrogen helps in the decomposition of food items and makes them tasty.
(D) The given statements is wrong.
8. Which one of the following is used in the white washing of walls?
(A) Calcium oxide mixed with water (B) Calcium carbonate mixed with water
(C) Calcium sulphate mixed with water (D) Sodium chloride mixed with water
9. Dissolving sugar in water is an example of:
(A) Physical change (B) Chemical change (C) Redox reaction (D) None of these
10. Heat is evolved during:
(A) Endothermic reaction (B) Displacement reaction
(C) Combustion reaction (D) Combination reaction
11. In an electroytic cell where electrolysis is carried, anode has:
(A) Positive charge
(B) Negative charge
(C) Connected to negative terminal of the battery
(D) None of these is correct
12. A change is said to be a chemical change when:
(A) energy change occurs (B) new substances are formed
(C) the change cannot be easily reversed (D) all statements are correct
13. Copper displaces which of the following metals from its salt solution:
(A) ZnSO4 (B) FeSO4 (C) AgNO3 (D) NiSO4
14. Which of the following is an example of displacement reaction?
![]()
15. A redox reaction is one in which :
(A) both the substances are reduced
(B) both are the substances are oxidised
(C) an acid is neutraliesd by the base
(D) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced
· Assertion & Reason
Instructions: In the following questions as Assertion (A) is given followed by a Reason (R). Mark your responses from the following options.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(C) Assertion is true but Reason is false
(D) Assertion is false but Reason is true
1. Assertion: In HClO3 oxidation number of Cl is -1.
Reason: Oxygen is more electropositive then fluorine.
2. Assertion: Oxidation state of carbon in its compounds is some time +4.
Reason: An element has a fixed oxidation state.
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only one matching with entries of column-I.
(Match the oxidation state of the underlined elements.)

· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
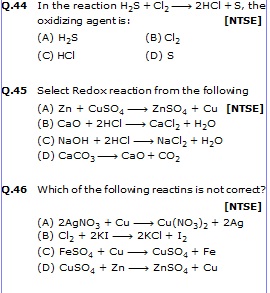
1. In the reaction, H2S + Cl2 —® 2HCl + S, the electrons are transfered from,

6. A substance which oxidises itself and reduces other is known as:
(A) Oxidising agent (B) Reducing agent (C) Both of these (D) None of these
7. The reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide present in aqueous solutions is an example
(A) Decomposition reaction (B) Displacement reaction
(C) Double displacement (D) Neutralisation reaction
8. Oxidation is a process which involves
(A) Addition of oxygen (B) Removal of hydrogen
(C) Loss of electrons (D) All are correct
9. Aluminium oxide reacts with sulphuric acid to form
(A) Aluminium sulphate and hydrogen (B) Aluminium sulphate and oxygen
(C) Aluminium suphate and water (D) Aluminium sulphate and sulphur dioxide
10. Chemically rust is:
(A) hydrated ferrous oxide (B) hydrated ferric oxide
(C) only ferric oxide (D) none of these
· Multiple choice question with one or more than one correct answers
1. In the reaction,

4. When a chemical species loses one or more electrons, it is said to have been
(A) oxidised (B) reduced (C) decomposed (D) act as reducing agent
5. Which statements are correct for the reaction CuO + H2 —® Cu + H2O
(A) CuO is reduced (B) H2 is oxidized
(C) CuO is reduced and H2 is oxidized (D) Both CuO and H2 are oxidized
6. Which of the following is not balanced equation?

(A) PbO is reduced (B) C acts as an oxidising agent
(C) C acts as a reducing agent (D) This reaction does not represent redox reaction
9. In the reaction:
Zn + FeSO4 —® ZnSO4 + Fe
(A) Zn gets oxidised (B) Fe gets reduced
(C) Zn is an oxidising agent (D) Zn and Fe are both oxidised
10. Which of the following are example of decomposition reaction?
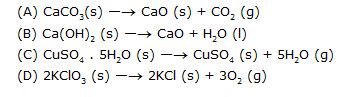
Oxidation number is the charge assigned to an atom of a molecule or ion according to some arbitrary rules. In neutral molecules, the sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms present is zero while in a simple or complex ion it is equal to the net charge on ion. In some cases, the oxidation number may be even fractional. Although sometimes, a particular element may have same valency and oxidation state but these are based upon different concepts. The number of oxidation states available for a particular element are normally more than the valencies.
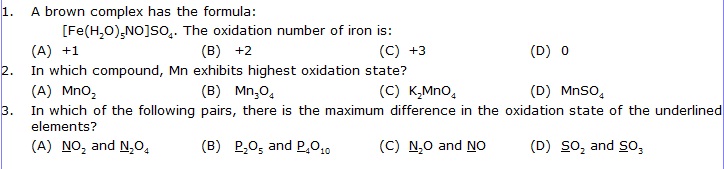
A redox reaction consists of oxidation and reduction half reactions. There is a loss of electrons in oxidation and the species which loses electrons is reducing agent. Its oxidation number increases during oxidation. Similarly there is a gain of electrons during reduction and the species which gains reduction and the species which gains electrons is an oxidising agent. Its oxidation number decreases during reduction. The number of electrons released during oxidation is equal to number of electrons gained during reduction.

· Match the following (one to many)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. One or more than one entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II may have one or more than one matching with entries of column-I
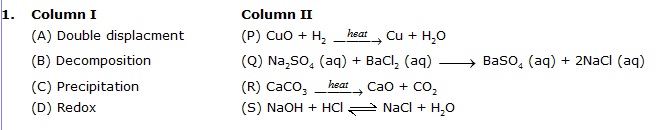
Q.1 The example of a physical change is
(A) milk is left at room temperature in summers
(B) an Iron is heated
(C) Iron tawa is left emposed to humid air
(D) Food is cooked
Q.2 Which of the following is/are exothermic processes
(i) Sublimation of NH4Cl
(ii) Quick lime is added to water
(iii) Evaporation of water
(iv) Dilution of an acid
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv) (D) (ii) and (iv)
Q.3 Fe2O3 + 2Al ¾® Al2O3 + 2Fe, is a
(i) combination rxn
(ii) Displacement Rxn
(iii) redox Rxn
(iv) Double displacement Rxn
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv) (D) (ii) and (iv)
Q.4 Silver Bromide, On expourse to sunlight turns grey due to
(A) Formation of silver by its decomposition
(B) Oxidation of silver Bromide
(C) Sublimation of silver Bromide
(D) Decomposition of bromine gas from silver bromide
Q.5 Water on electrolysis decomposes to hydrogen and oxygen. the mole ratio of H2 and O2 is
(A) 1 : 2 (B) 1 : 1
(C) 2 : 1 (D) 4 : 1
Q.6 Which of the following gases used for storage of fresh sample of an oil for a long time
(A) Nitrogen and Oxygen
(B) CO2 and Helium
(C) CO2 and oxygen
(D) Nitrogen and Helium
Q.7 50 ml of water was taken in a beaker A, B and C. A small amount of CuSO4, NaOH and NaCl were added to beaker A, B and C respectively. The temperature of beaker A and B increased where in beaker c decreases. The correct statement (s) is/are
(i) In beaker “C” exothermic process has occurred.
(ii) In beaker “A” and “B” exothermic process has occurred.
(iii) In beaker A and B endothermic process has occurred.
(iv) In beaker “C” endothermic process has occured.
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv) (D) (ii) and (iv)
Q.8 Example of a chemical change is
(A) fermentation of rice
(B) breathing
(C) curdling of milk
(d) all of above
Q.9 Which of the following is a double displacement reaction?
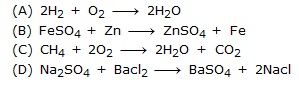
Q.10 Which of the following is not a decomposition reacion?
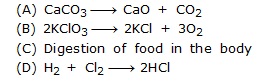
Q.11 Which of the following represent a double displacement reaction?
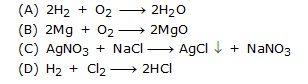
Q.12 Which of the following is a displacement reaction?
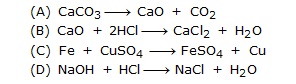
Q.13 The reaction H2 + Cl2 ¾® 2HCl is a –
(A) Decomposition reaction
(B) Combination reaction
(C) Double displacement reaction
(D) Displacement reaction
Q.14 Which of the following is a decomposition reaction?
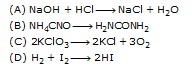
Q.15 Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(A) In oxidation, oxygen in added to a substance.
(B) In reduction, Hydrogen is added to a substance.
(C) Oxidizing agent in oxidized.
(D) Reducing agent is oxidized.
Q.16 Which of the following is a combustion reaction–
(A) Boiling of water
(B) Melting of wax
(C) Burning of petrol
(D) None of these
Q.17 Which of the following is a redox reaction?
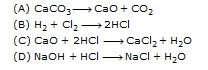
Q.18 Which statement is correct about the following reaction?
ZnO + CO ¾® Zn + CO2
(A) ZnO is being oxidized
(B) CO is being reduced
(C) CO2 is being oxidized
(D) ZnO is being reduced
Q.19 The reaction C + O2 ¾® CO2 + Heat is a –
(A) Combination reaction
(B) Oxidation reaction
(C) Exothermic reaction
(D) All of the above
Q.20 Conversion of CaCO3 in to CaO as per following reaction is an example of –
CaCO3 ¾® CaO + CO2
(A) Decomposition reaction
(B) Reduction reaction
(C) Oxidation reaction
(D) None of these
Q.21 Fe2O3 + 2Al ¾® Al2O3 + 2Fe This reaction is an example of –
(A) Combination reaction
(B) Double displacement reaction
(C) Decomposition reaction
(D) Displacement reaction
Q.22 In reaction SO2 + 2H2S ¾® 2H2O + 3S the reducing agent is –
(A) SO2 (B) H2S
(C) H2O (D) S
Q.23 What happens when dil hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings?
(A) Hydrogen gas and Iron chloride are produced.
(B) Chlorine gas and Iron hydroxide are produced.
(C) NO reaction takes place
(D) Iron salt and water are produced.
Q.24 When Iron nails are added to an aquous solution of copper sulphate, a chemical change occurs, which of the following is not true about this reaction?
(A) Blue colour of the solution fades. (B) Iron nails becomes brownish in colour.
(C) It is a displacement reaction.
(D) Iron nails dissolves completly.
Q.25 Potassium reacts with bromine to form potassium bromide. [NTSE]
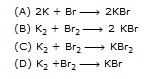
Q.26 A silver spoon on exposure to air reacts with the sulphur present in air to give a black material called ______. [NTSE]
(A) Silver oxide (B) Silversulphide
(C) Tarnish (D) Coal tar
Q.27 In the decomposition of sulphates by heat, which is the gas formed exclusively along with the metal oxide? [NTSE]
(A) SO2 (B) SO3
(C) SO3 and SO2 (D) H2SO3
Q.28 Which among the following is not a physical change? [NTSE]
(A) Melting of solids to liquids
(B) Vapourisation of liquids to gases
(C) Liquefaction of gases to liquids
(D) Decay of matter
Q.29 Which among the following reactions are exothermic in nature? [NTSE]
(A) Bond formation
(B) Bond breaking
(C) Combustion of carbon
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Q.30 The reaction P4 + 3O2 ¾® 2P2O3 is ____.
(A) synthesis reaction [NTSE]
(B) displacement reaction
(C) decomposition reaction
(D) combustion
Q.31 PbO2 + 4HCl ¾® PbCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2. The substance undergoing oxidation is _____. [NTSE]
(A) lead dioxide (B) hydrochloric acid
(C) hydrogen (D) lead chloride
Q.32 In the equation FeCl3 + xNaOH ¾® yNaCl + Fe(OH)3, the value of x and y, respectively, are _____. [NTSE] (A) 3 and 1 (B) 3 and 3
(C) 2 and 3 (D) 3 and 4
Q.33 The rate of a chemical reaction is altered by ______. [NTSE]
(A) nature of reactants
(B) changing temperature
(C) using a catalyst
(D) all the above
Q.34 Which of the following is an example of a reversible reaction? [NTSE]
Q.35 Which of the following reaction will not take place? [NTSE]

Q.36 When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of
(A) a combination reaction [NTSE]
(B) a displacement reaction
(C) a decomposition reaction
(D) a double decomposition reaction
Q.37 In the following equations
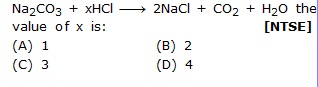
Q.38 Combustion of fuel is [NTSE]
(A) displacement reaction
(B) double displacement reaction
(C) oxidation reaction
(D) isomerisation reaction
Q.39 The reaction between acid and base to form salt and water is an example of [NTSE]
(A) decomposition reaction
(B) combination reaction
(C) displacement reaction
(D) double displacement
Q.40 Which of the following reactions are exothermic in nature? [NTSE]
(A) Combustion of Carbon
(B) Bond breaking
(C) Bond formation
(D) Both (A) and (C)
Q.41 Which of the following changes is not a physical change? [NTSE]
(A) glowing of filament in bulb
(B) combustion
(C) boiling of water
(D) sublimation
Q.42 The substance that looses electrons is called as: [NTSE]
(A) oxidizing agent (B) reducing agent
(C) catalyst (D) none of above
Q.43 The process of reduction involves [NTSE]
(A) removal of hydrogen
(B) gain of electrons
(C) addition of oxygen
(D) loss of electrons
Q.47 Consider the reactions [NTSE]
CuSO4 + Fe ¾® FeSO4 + Cu
FeSO4 + Zn ¾® ZnSO4 + Fe
(A) Zn is most reactive, Fe is least reactive (B) Fe is most reactive and cu is least reactive
(C) Zn is most reactive and cu is least reactive (D) Cu is most reactions, Fe is least reactive
Q.48 Choose the incorrect statement. [NTSE]
(A) physical change is reversible
(B) physical change results information of new substances
(C) chemical change is permanent
(D) physical change is accompanied by energy change
Q.49 Which of following is fast reaction? [NTSE]
(A) reaction between H2 and O2 to form H2O (B) reaction between acid and base to form salt and water
(C) hydrolysis of ester
(D) hydrolysis of sugar to glucose
1. 1. +7/3 2. O 3. 2 4. +1 5. 0, +1, -2
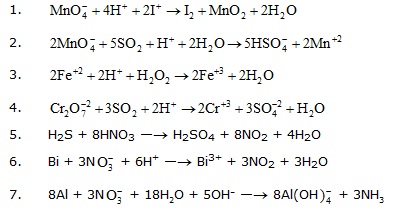
3. (i) 0 (ii) +2 (iii) –1 (iv) +3 (v) –1/2 (vi) +6
1. (A) 2. (C) 3. (A) 4. (A) 5. (A)
6. (A) 7. (B) 8. (A) 9. (A) 10. (C)
11. (A) 12. (B) 13. (C) 14. (C) 15. (D)
1. (D) 2. (C)
1. (A)-(Q), (B)-(P), (C)-(S), (D)-(R)
1. (C) 2. (D) 3. (D) 4. (C) 5. (C)
6. (B) 7. (C) 8. (D) 9. (C) 10. (B)
1. (A,C) 2. (A,B,D) 3. (B,C) 4. (A,D) 5. (A,B,C)
6. (A,D) 7. (B,D) 8. (A,C) 9. (A,B) 10. (A,B,D)
1. (A) 2. (C) 3. (D)
1. (A) 2. (A) 3. (A)
1. (A)-(Q,S), (B)-(R), (C)-(Q), (D)-(P)
1. C 2. D 3. B 4. A 5. C 6. D 7. D
8. D 9. D 10. D 11. C 12. C 13. C 14. C
15. C 16. C 17. B 18. D 19. D 20. A 21. D
22. B 23. A 24. D 25. A 26. B 27. B 28. D
29. D 30. D 31. B 32. B 33. D 34. A 35. C
36. D 37. B 38. C 39. D 40. D 41. B 42. B
43. B 44. B 45. A 46. C 47. C 48. B 49. B
*****