We have a wide range of sources of energy such as the sun, the wind, the earth (geothermal), flowing water, coal, gasoline, diesel, natural gas, biogas, etc. at our disposal. We utilize this energy to perform a wide range of activities, i.e. industrial, commercial, household etc.
A source of energy is one which can provide adequate amount of energy in a convenient form over a long period of time.
(a) Renewable Sources of Earth
Those sources of energy which are being produced continuously in nature and are inexhaustible, are called renewable sources of energy.
Example: wood is a renewable source of energy because if trees are cut from the forests for obtaining wood then more trees will grow in the forest in due course of time.
The renewable sources of energy are :
Examples: Hydroenergy (Energy from flowing water) ; Wind energy ; Solar energy ; Energy from sea (Tidal energy); Sea wave energy and Ocean thermal energy) ; Geothermal energy ; Biomass energy (Energy from bio fuels such as Wood, Bio gas and Alcohol) ; and Hydrogen
(b) Non- Renewable Sources of Energy
Those sources of energy which have accumulated in nature over a very, very long time and cannot be quickly replaced when exhausted are called non - renewable sources of energy.
Example: coal is a non - renewable source of energy because coal has accumulated in the earth over a very, very long time and if all the coal gets exhausted, it cannot be produced quickly in nature.
The non renewable sources of energy are
Examples: Fossil fuels (Coal, Petroleum and natural gas) and Nuclear fuels (such as uranium).
Non - renewable sources of energy are dug out from the earth.
(A) CONVENTIONAL SOURCES OF ENERGY
The traditional sources of energy which are familiar to most people are called conventional sources of energy.
The main conventional sources of energy are wood and fossil fuels (like coal, petroleum and natural gas).
The fuels derived from wood, coal and petroleum such as charcoal, coke, coal gas, petrol, diesel, kerosene, fuel oil and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) are also known as conventional sources of energy.
(B) Non-conventional sources of energy
Sources of Energy that we have started using in New ways or Only in Recent times are called alternative sources of energy (or non conventional sources of energy).
Examples: Hydroelectric energy, Wind energy, Solar energy, Biomass energy, Energy from the sea (Tidal energy, Sea - wave energy, Ocean thermal energy), and Geothermal energy.
Fuels
A fuel is a chemical which releases energy when heated with oxygen. The energy may release in the form of heat and light. '
Examples: Wood, gas, petrol, kerosene, diesel, coal and animal waste.
Note: Fuels are combustible substances.
(a) Characteristics of a good fuel
(i) It should have high calorific value.
(ii) It should have a proper ignition temperature so that it may burn easily.
(iii) It should leave no residue (or very small amount of residue) or ash after burning.
(iv) It should burn smoothly i.e. it should have a moderate rate of combustion and burn at a steady rate.
(v) It should not be more valuable for some other purpose than fuel. For e.g. coke is a good fuel but it is more valuable as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals.
(vi) It should be cheap and easily available.
(vii) It should be easy to handle, safe to transport and convenient to store.
(b) Types of Fuels
There arc three types of fuels solid fuels, liquid fuels and gaseous fuels.
(i) Solid fuels: The various kinds of solid fuels are wood, charcoal, coke, coal, paraffin and tallow. Wood was the first solid fuel to be used by humans. Paraffin and tallow are used to make candles.
(ii) Liquid fuels: Petrol, kerosene, diesel and methanol are some common liquid fuels. Most of the liquid fuels arc obtained from petroleum. They leave no solid residue when burnt and can be stored easily.
(iii) Gaseous fuels: Natural gas, coal gas, producer gas, water gas and liquefied petroleum gas are some examples of gaseous fuels.
(c) Fossil Fuels: Fossil fuels are the remains of the prehistoric animals or plants, burried under the earth, millions of years ago.
Eg. Coal, petroleum and natural gas.
Fossil fuels are formed in the absence of oxygen. The chemical effects of pressure, heat and bacteria convert the burried remains of plants and animals into fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas.
It was the sunlight of long ago that made plants grow, which were then converted into fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are energy rich compounds of carbon, which were originally made by the plants with the help of sun's energy.
(d) Calorific value of fuels:
All the fuels produce heat energy on burning. Different fuels produce different amount of heat on burning. The usefulness of a fuel is measured in terms of its calorific value. The amount of heat produced by burning a unit mass of the fuel completely is known as its calorific value.
The unit of mass usually taken for measuring the calorific value of a fuel is gram So it can be said that the amount of heat produced by burning 1 gram of a fuel completely is called its calorific value.
For example, when one gram of a carbon fuel (like charcoal) is burned completely, it produces 33000 joules of heat. So the calorific value of charcoal is 33000 Joules per gram or 33000 J/gm. Since joule is a very small unit of heat energy so the calorific value is usually expressed as
kilojoules per gram (KJ/g). The SI unit of measuring calorific value is kilojoules per gram.
Of all the common elements. hydrogen has the higher calorific value. So a fuel containing percentage of hydrogen will have a higher calorific value than another fuel which has a lower percentage of hydrogen in it.
Wood is a mixture of carbon compounds called carbohydrates like cellulose (C6H10O5)n. Thus, when wood is burnt, only carbon and hydrogen atoms contained in it burn and produce heat. Oxygen atoms do not produce any heat, they only help in the burning process. So due to comparatively lower percentage of carbon and hydrogen in wood, it has a low calorific value.
All the fuels which contain oxygen burn ready but produce less heat energy per unit weight.
The calorific value of some common fuels are given in the table below.
The material which are burnt to produce heat energy are known as fuels.
Examples of fuels are : Wood, Coal, Cooking gas (LPG), Kerosene, Diesel and Petrol.
The amount of heat produced by burning a unit mass of the fuel completely is known as its calorific value.
The unit of mass usually taken for measuring the calorific value of a fuel is gram
For example : when one gram of a carbon fuel (like charcoal) is burned completely, it produced about 33000 joules of heat, so the calorific value of charcoal is 33000 joules per gram or 33000 J/g.
The common unit of measuring calorific value is kilojoules per gram (kJ/g.).
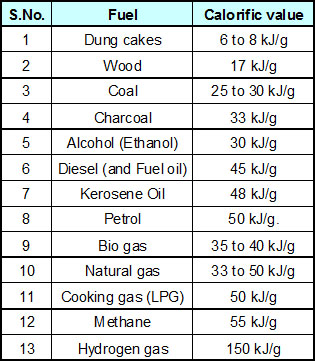
Hydrogen gas has the highest calorific value of 150 kilojoules per gram. Thus, because of its high calorific value, hydrogen is an extremely good fuel.
The minimum temperature to which a fuel must be heated so that it may catch fire and start burning is known as its ignition temperature.
A natural fuel formed deep under the earth from the pre-historic remains of living organisms (like plants and animals) is called a fossil fuel. Coal, petroleum and natural gas are fossil fuels. Fossil fuels are the major source of energy for generating electricity in power plants.
² How Fossil Fuels were formed?
The plants and animals which died millions of years ago, were gradually buried deep in the earth and got covered with sediments like mud and sand, away from the reach of oxygen of air. In the absence of oxygen, the chemical effects of pressure, heat and bacteria, converted the buried remains of plants and animals into fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gas.
1. Coal
Coal is a complex mixture of compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, and some free carbon. Small amounts of nitrogen and sulphur compounds are also present in coal.
A lot of heat is produced during the burning of coal which makes it a good fuel. Coke is a better fuel than coal because it produces more heat (than an equal mass of coal), and it does not produce smoke while burning.
Uses of Coal
(i) Coal is used as a fuel for heating purposes in homes and in industry.
(ii) Coal is used as a fuel in thermal power plants for generating electricity.
(iii) Coal is used to make coke.
(iv) Coal is used in the manufacture of fuel gases like coal gas.
(v) Coal is used in the manufacture of petrol and synthetic natural gas.
2. Petroleum
Petroleum is a dark coloured, viscous, and foul smelling crude oil.
The name petroleum means rock oil.
It is called petroleum because it is found under the crust of earth trapped in rocks.
The crude oil petroleum is a complex mixture of several solid, liquid and gaseous hydrocarbons mixed with water, salt and earth particles.
Petroleum is the crude oil which is a complex mixture of alkane hydrocarbons with water, salt and earth particles. Petroleum cannot be used as a fuel as such.
The fractional distillation of petroleum gives us the following fractions which can be used as
fuels : Petroleum gas, Petrol (or Gasoline), Diesel, Kerosene and Fuel oil.
Petroleum gas is used as a fuel for domestic heating purposes in the form of liquefied petroleum gas.
Petrol is used as a fuel in motor car, scooters, motor cycles and other light vehicles.
Diesel is used as a fuel for heavy vehicles like buses, trucks, tractors and railway engine. Kerosene oil is used as a household fuel.
Fuel oil is a better fuel than coal because fuel oil burns completely and does not leave any residue.
3. Petroleum Gas (LPG)
The main constituent of petroleum gas is butane though it also contains smaller amounts of propane and ethane. Petroleum gas is obtained as a by product in oil refineries from the fractional distillation of petroleum.
The petroleum gas which has been liquefied under pressure is called Liquefied petroleum (LPG), Thus, liquefied petroleum gas (or LPG) consists mainly of butane (along with smaller amounts of propane and ethane), which has been liquefied by applying pressure. In other words, the domestic gas cylinders like Indane contain mainly butane.
A domestic gas cylinder contains about 14 kilograms of LPG. A strong smelling substance called ethyl mercaptan (C2H5SH) is added to LPG cylinders to help in the detection of gas leakage.
Advantages of LPG
(i) LPG has a high calorific value, So it is a good fuel.
(ii) LPG burns with a smokeless flame and so does not cause air pollution.
(iii) LPG does not produce any poisonous gases on burning.
(iv) LPG is easy to handle and convenient to store.
(v) LPG is a very neat and clean domestic fuel.
Dangers of LPG
LPG is a highly inflammable gas, that is, it catches fire easily. Any leakage of LPG from the gas cylinder, stove or the rubber pipe will form an explosive mixture with air in the kitchen. And on lighting the match stick, an explosion will take place, the whole kitchen will be set on fire and the person working in the kitchen may get burnt.
Percautions of Using LPG
(i) Before lighting a match stick we should make sure that there is no foul smell of the leaking gas in the kitchen, near the gas cylinder or gas stove.
(ii) We should not use any hot flames like a kerosene lamp, kerosene stove or electric heater near the gas cylinder.
(iii) We should never use a leaking gas cylinder.
(iv) We should handle the gas cylinder with care so that its valve does not get damaged.
(v) The rubber pipe connecting the gas cylinder to gas stove should be checked periodically for any wear and tear.
4. Natural Gas
Natural gas consists mainly of methane (CH4) with small quantities of ethane and propane. In fact, natural gas contains upto 95% methane, the remaining being ethane and propane. Natural gas occurs deep under the crust of the earth either alone or alongwith oil above the petroleum deposits. Natural gas is formed under the earth by the decomposition of vegetable matter lying under water. This decomposition is carried out by anaerobic bacteria.
1. Natural gas is used as a domestic and industrial fuel.
2. Natural gas is used as a fuel in thermal power plants for generating electricity.
3. Compressed Natural gas (CNG) is being used increasingly as a fuel in transport vehicles.
Advantags of Natural gas
(i) Natural gas being a complete fuel in itself can be used directly for heating purposes in homes and industries.
(ii) Natural gas is a good fuel because it has a high calorific value of about 50 kJ/g.
(iii) A great advantage of natural gas is that it can be supplied directly from the gas wells to the homes and factories for burning through a net - work underground pipelines, and this eliminates the need for additional storage and transport.
Pollution Caused by Fossil Fuels
(i) The burning of fossil fuels produces acidic gases such as sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
(ii) The burning of fossil fuels produces large amount of carbon dioxide which goes into air.
(iii) The burning of fossil fuels (especially coal) produces smoke which pollutes the air.
(iv) The burning of coal leaves behind a lot of ash.
² Controlling Pollution Caused by Fossil Fuels
(i) The pollution of air caused by burning petroleum fuels (like petrol and diesel). in vehicles can be controlled by fitting the vehicles with catalytic converters.
(ii) The pollution of air caused by burning coal in thermal power plants and factories can be controlled by washing down the smoke and acidic gases by water in a scrubber.
(iii) The pollution of air caused by burning coal in thermal power plants and factories can also be controlled by installing electrostatic precipitators in their chimneys.

An installation where electricity (or electrical power) is generated is called a power plant. A power plant is also called a power house.A power plant in which the heat required to make steam to drive turbines is obtained by burning fuels is called thermal power plant.
Coal is burned in a furnace F to produce heat. This heat boils the water in a boiler B to form steam. The steam formed from the boiling water build up a pressure. The hot steam at high pressure is introduced into a turbine chamber C having a steam turbine T. The steam passes over the blades of the turbine as a high pressure jet making the turbine rotate. The shaft S of turbine is connected to a generator G. When the turbine rotates, its shaft also rotates and drives the generator. The generator produces electricity. The spent steam coming out of turbine chamber is cooled. On cooling, steam condenses to form water., This water is again sent to the boiler to form fresh steam. This process is repeated again and again. We produce a major part of our electricity by burning fossil fuels.
Flowing water posses kinetic energy. The traditional use of energy of flowing water has been modified by improvements in technology and used to generate electricity.
Hydro-power plant (or Hydroelectric power plant) :
A power plant that produces electricity by using flowing water to rotate a turbine (which drives the generator), is called hydro power plant.
The electricity produced by using the energy of falling water (or flowing water) is called hydroelectricity. A hydro power plant produces electricity.
A high rise dam is built to stop the flowing river water. Due to this, a large lake or reservoir builds up behind the dam. The kinetic energy of the flowing river water is converted into the potential energy of water stored behind the dam.
The sluice gate half the height of dam are opened to allow some of the stored water to escape. The water falls down through a large height from the dam, it flows very fast. A high pressure jet of fast flowing water pushes on the blades of turbine with a great force and makes the turbine rotate rapidly. When the turbine rotates, its shaft also rotates and drives the generator. The generator produces electricity.
A hydro power plant converts the potential energy of water stored in the reservoir of a tall dam into electric energy.
Advantages of Generating Hydroelectricity
(i) The generation of electricity from flowing water does not produce any environmental pollution.
(ii) Flowing water is a renewable source of electric energy which will never get exhausted.
(iii) The construction of dams on rivers helps in controlling floods, and in irrigation.
DISADVANTAGES OF HYDROELECTRICITY
(i) Dams built for large hydroelectric plants submerge a large area of land under water & also affects the plants and animals of the region.
(ii) Large hydroelectric power plants are expensive to build.
(iii) Not all rivers and not all areas are suitable for hydroelectric power generation.
SCOPE OF HYDROELECTRICITY
Hydroelectricity has huge potential worldwide. In India, it is estimated that 145,000 MW of hydroelectricity can be generated. Out of this, by 2006, India had an installed capacity of about 34,000 MW.
Moving air is called wind. The wind possesses kinetic energy. it is this kinetic energy of wind which is utilized for doing work. Solar energy is responsible for the blowing of wind.
The traditional use of wind energy has now been modified by the improvement in technology to generate electricity through wind powered generators.
Wind Generator
A wind generator which is used to generate electricity by using wind energy. When the fast moving wind strikes the blades of wind turbine, then the wind turbine starts rotating continuously. The shaft of wind turbine is connected to a small generator. When the wind turbine rotates, its shaft also rotates and drives the generation. The generator produces electricity.
An important advantage of using wind energy for generating electricity is that its use does not cause any pollution. Another advantage is that wind energy is a renewable source of energy which will never get exhausted.
Advantages of wind energy
(i) The source of energy (wind) is free.
(ii) Harnessing wind energy is a pollution-free process, with no smoke, chemicals, etc., being produced.
(iii) A small wind-electric plant can be set up near a factory to provide pollution-free power for its use.
Limitations of wind energy
(i) Wind energy cannot be harnessed at places where wind does not blow regularly. A wind-electric generator works only on winds of at least 15 km/h.
(ii) Wind is not a dependable source of energy because sometimes the air is absolutely still and at other times there are storms.
(ii) It is expensive to set up a wind farm for generating electricity because wind farms need a large area.
The sun is the source of all energy. The energy obtained from the sun is called solar energy.
The solar energy which reaches the earth is absorbed by land and water bodies (like rivers, lakes and ocean) and plants. The solar energy trapped by land and water bodies causes many phenomenon in nature like winds, storms, rain, snowfall and sea waves.
Solar Constant
The amount of solar energy received per second by one square metre area of the near earth space (exposed perpendicularly to the rays of the sun) at an average distance between the sun and the earth, is called solar constant. The value of solar constant is 1.4 kJ/s/m2 or 1.4 kW/m2
(because : 1 kJ/s =1 kW)
The devices which work by using solar energy (or sun’s energy) are : Solar cooker, Solar water heater, and Solar cell. A device which gets heated by using sun’s heat energy is called a solar heating device.
All the solar heating devices are designed to such a way that they help in collecting as much sun’s heat rays as possible.
1. Solar Cooker
The solar cooker is a device which is used to cook food by utilising the heat energy radiated by the sun. A sola cooker consists of an insulated metal box or wooden box which is painted all black from inside. There is a thick glass sheet cover over the box and a plane mirror reflector is also attached to the box. The food to be cooked is put in metal containers which are painted black from outside.
When the sun’s rays fall on the reflector, the reflector sends them to the top of solar cooker box in the form of a strong beam of sunlight. The sun’s heat rays pass through the glass sheet cover and get absorbed by the black inside surface of the cooker box.
In this way, more and more heat rays of the sun get trapped in the box due to which the temperature in the solar cooker box rises to about 100°C to 140°C in two to three hours. This heat cooks the food materials kept in the black containers.
The important advantages of a solar cooker for cooking food are the following :
(i) The use of solar cooker for cooking food saves precious fuels like coal, kerosene and LPG.
(ii) The use of solar cooker does not produce smoke due to which it does not pollute air.
(iii) When food is cooked in solar cooker, its nutrients do not destroyed. This is because in a solar cooker, food is cooked at a comparatively lower temperature.
(iv) In a solar cooker, up to four food items can be cooked at the same time.
Some of the important limitation of a solar cooker are given below :
(i) The solar cooker cannot be used to cook food during night time (because sunshine is not available at that time).
(ii) If the day sky is covered with clouds, even then solar cooker cannot be used to cook, food.
(iii) The direction of reflector of solar cooker has to be changed from time to time to keep it facing the sun.
(iv) The box type solar cooker cannot be used for baking (making chapattis, etc.) or for frying.
2. SOLAR WATER HEATER
Solar energy can be used to heat water. In a solar water heater, sunlight is allowed to fall on a box made of a poor conductor of heat. The glass top of the box lets in sunlight and traps heat. Water enters a tube that is painted black to increase the absorption of heat. It is bent several times to increase its length inside the box. This allows the water flowing through it sufficient time to absorb heat. Hot water collects in the tank of the heater for use.
3. Solar Cell
Solar cells use the energy in sunlight to produce electricity. Thus, solar cell is a device which converts solar energy (or sun’s energy) directly into electricity.
A solar cell is usually made from silicon. A simple solar cell consists of sandwich of a ‘silicon-boron layer’ and a ‘silicon-arsenic layer’.
A single solar cell can produce only a small amount of electricity.
The group of solar cells is called a ‘solar cell panel’ or just ‘solar panel’.
The various solar cells in a solar panel are joined together by using connecting wires made of silver metal. This is because silver is the best conductor of electricity.
The main advantages of solar cells are that they have no moving parts.
They require almost no maintenance, and work quite satisfactorily without the use of any light focusing device.
Advantages of solar cells
(i) Solar cells are suitable for use in remote areas where electrical power lines have not reached.
(ii) Solar cells require little maintenance and last for a long time.
(iii) After installation, no further cost is involved in generating electricity directly from solar cells.
(iv) Solar cells are environment friendly, as they do not cause any pollution.
Disadvantage of solar cells is that they are very expensive.
This is due to the following reasons :
(i) The special grade silicon needed for making solar cells is expensive
(ii) Silver wire used to interconnect solar cells for making solar panels is expensive, and
(iii) The entire process of making solar cells is still very expensive.
² Uses of Solar Cells
(i) Solar cells are used for providing electricity in artificial satellites and space probes.
(ii) Solar cells are used for providing electricity to remote, inaccessible and isolated places where normal electricity transmission lines do not exist.
(iii) Solar cells are used for operating traffic signals, watches, calculators and toys.
4. Solar Panel
Although a solar cell provides very little power, a large number of connected solar cells, spread over a large area, can provide sufficient power for many applications. Such an arrangement of solar cells is called a solar panel. The solar cells in a solar panel are connected in such a way that the total potential difference and the total capacity to provide electric current become large.
Uses of Solar Panels: The advantage of solar panels is more in areas where the usual energy sources are not available. That is why they are used as the source of electric power in satellites. Solar panels have also been used in unmanned aircraft that fly at high altitudes for long periods, conducting scientific experiments. Experimental solar-powered cars have also been made. In many parts of India, solar panels are being used to charge rechargeable batteries during the day. At night, these batteries provide electric power for lightening, etc. They are also being used for operating traffic lights, water pumps, telephones, TV sets and radio receivers.
² Advantages of Solar Cells
(a) Solar cells are suitable for use in remote areas where electrical power lines have not reached.
(b) Solar cells require little maintenance and last for a long time.
(c) After installation, no further cost is involved in generating electricity directly from solar cells.
(d) Solar cells are environment friendly, as they do not cause any pollution.

The dead parts of plants and trees, and the waste material of animals are called biomass. Biomass includes wood, agricultural wastes (crop residues) and cow - dung.
Biomass is a renewable source of energy because it is obtained from plants (or animals) which can be produced again and again.
² The Case of Wood and Charcoal
Wood is biomass. The traditional use of wood as a fuel has many disadvantages. For example (i) the burning of wood produces a lot of smoke which pollutes the air, and (ii) the calorific value (or heat value) of wood is low, being only 17 kJ/g. This means that wood produces less heat per unit mass, on burning.
Wood can be converted into a much better fuel called charcoal. Charcoal is mainly carbon (C). Charcoal is a better fuel than wood because
(i) Charcoal has a higher calorific value than wood.
(ii) Charcoal does not produce smoke while burning.
(iii) Charcoal is a compact fuel which is easy to handle and convenient to use.
² The Case of Cow Dung and Biogas
Cow dung is biomass. It is also known as ‘cattle dung’ or ‘animal dung’. When cow dung cakes are burnt, they produce heat. This heat is used for cooking food, etc. It is, however, not good to burn cow dung directly as a fuel because of the following disadvantages :
(i) Cow dung contains important elements like nitrogen and phosphorus, which are required by the soil to support crops.
(ii) Dung cakes produce a lot of smoke on burning which causes air pollution.
(iii) Dung cake do not burn completely, they produce a lot of ash as residue.
(iv) Dung cakes have low calorific value.
Biogas is a mixture of methane. carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.The major constituent of biogas is methane. Biogas is produced by the anaerobic degradation of animal wastes like cow dung (or plant wastes) in the presence of water.
² Biogas Plant
A biogas plant consists of a well shaped, underground tank T called digester, which is made of bricks, and has a dome shaped roof D, also made of cement and bricks . The digester is a kind of sealed tank in which there is no air. The dome of the digester tanks acts as a gas holder or storage tank for the biogas. There is a gas out let S at the top of the dome having a valve V. On the left side of the digester tank is a sloping inlet chamber I and on the right side is a rectangular outlet chamber O.
The inlet chamber is connected to a mixing tank M while the outlet chamber is connected to over flow tank F.
Cow dung and water are mixed in equal proportion in the mixing tank M to prepare the slurry. This slurry of dung and water is fed into the digester tank T through the inlet chamber.It takes about 50 to 60 days for the new gas plant to become operative.
During this period, the cow dung undergoes degradation by anaerobic bacteria in the presence of water with the gradual evolution of biogas. This biogas starts collecting in the dome and forces the spent slurry to go into overflow tank F, through the outlet chamber O. From the overflow tank, the spent slurry is removed gradually. The spent dung slurry left after the extraction of biogas, is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus compounds and hence forms a good manure.
The biogas which has collected in the dome of the digester tank is taken out through the outlet S and supplied to village homes through a network of pipes to be used as a cooking gas.
² The important uses of biogas are given below
(i) Biogas is used as a fuel for cooking food.
(ii) Biogas is also used for lighting.
(iii) Biogas is used as a fuel to run engines.
(iv) Biogas is used for generating electricity.
² ADVANTAGE OF BIOGAS
(i) A biogas plant is quite simple and can be easily built in rural areas.
(ii) Biogas is an excellent, clean fuel that burns without producing ash and smoke.
(iii) The spent slurry is good manure.
(iv) Biogas plants are a safe and useful way of waste disposal.
(v) Use of biogas in rural areas leads to saving of firewood, and reduces deforestation.
The energy from the sea can be obtained mainly in three forms :
1. Tidal energy 2. Wave energy, and 3. Ocean thermal energy
1. Tidal energy :
The rise of sea water due to gravitational pull of the moon is called high tide whereas the fall of sea water is called low tide. The tidal energy can be harnessed by constructing a tidal barrage or tidal dam across a narrow opening to the sea.
During high tide, when the level of water in the sea is high, sea water flows into the reservoir of the barrage and turns the turbines. The turbines then turn the generators to produce electricity.And during the low tide, when the level of sea water is low, the sea water stored in the barrage reservoir is allowed to flow out into the sea. This flowing water also turns the turbines and generates electricity.
2. Wave Energy :
Wave energy here means sea waves energy. Due to the blowing of wind on the surface of sea, very fast sea waves more on its surface. Due to their high speed, sea waves have a lot of kinetic energy in them. The energy of moving sea waves can be used to generate electricity. A wide variety of devices have been developed to trap sea wave energy to turn turbines and drive generators for the production of electricity.
3. OCEAN THERMAL ENERGY CONVERSION (OTEC):
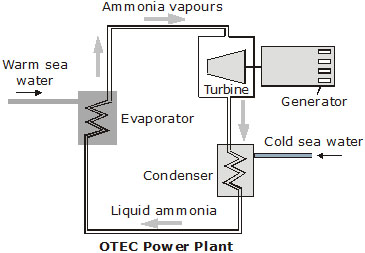
Solar energy falling on the surface of the ocean warms it. The water at the surface of the ocean is warmer than the water deep below. Generally, the difference in temprature is about 20°C between the surface water and the water at a depth of 1 km. This temperature difference can be used to operate an ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) plant. Clearly, the ultimate source of the stored thermal energy of the ocean is the sun.
In one system for OTEC, a fluid with low boiling point such as ammonia or chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) is used as the ‘working fluid’. Warm sea water is used to vaporize liquid ammonia in an evaporator. The expanding vapours of ammonia turn a turbine connected to a generator. Then the vapours go to a condenser. There, cold sea water, pumped up from the deep, is used to liquefy the ammonia. This ammonia is reused, and the cycle goes on.
‘Geo’ means earth and thermal means heat. Thus, geothermal energy is the heat energy from hot rocks present inside the earth. Geothermal energy is one of the few sources of energy that do not come directly or indirectly from solar energy (or sun’s energy)
At some places in the world, the rocks at some depth below the surface of the earth are very, very hot. This heat comes from the fission of radioactive materials which are naturally present in these rocks. The places where very hot rocks occur at some depth below the surface of earth geothermal energy. Energy does not cause any pollution.
Some of the disadvantages of geothermal energy are as follows :
Geothermal energy is not available everywhere it is available only in those areas where there are hot rocks near the earth’s surface.
The energy released during a nuclear reaction is called nuclear energy. Nuclear energy can be obtained by two types of nuclear reactions
1. Nuclear fission and
2. Nuclear fusion
The nuclear energy is released mainly in the form of heat.
1. Nuclear Fission
The process in which the heavy nucleus of a radioactive atom (such as uranium, plutonium or thorium) splits up into smaller nuclei when bombarded with low energy neutrons, is called nuclear fission. When uranium - 235 atoms are bombarded with slow moving neutrons, the heavy uranium nucleus breaks up to produce two medium — weight atoms, barium — 139 and krypton — 94. with the emission of 3 neutrons. A tremendous amount of energy is produced during the fission of uranium.
![]()
The energy produced during nuclear fission reactions is used for generating electricity at nuclear power plants.
Nuclear Power Plant :
A power plant in which the heat required to make steam and turn turbines (to drive generations for making electricity) is obtained by nuclear reaction, is called a nuclear power plant. Most of the nuclear power plants use uranium 235 as fuel in produce heat.
In a nuclear power plant, the fission of nuclear fuel uranium 235 is carried out in a steel pressure vessels V of reactor R (Reaction is a kind of nuclear furnace).
The enriched uranium 235 rods marked A are inserted in a core made of graphite blocks inside the reactor. Graphite is called a moderator.
It slows down the speed of neutrons to make them fit for causing fission.
In between the uranium rods are inserted boron rods B. Boron rods are called control rods because they absorb excess neutrons and prevent the fission reaction from going out of control.
The reactor is enclosed in a concrete chamber M having thick walls to absorb the nuclear radiations. so as to protect the outside world from the dangerous nuclear radiation.
Liquid sodium is used as a coolant to transfer the heat produced in the reactor by fission to heat exchanger for converting water into steam.
The controlled fission of uranium 235 in the nuclear reactor produces a lot of heat energy. Liquid sodium is pumped continuously through the pipes embedded in reactor by using a pump P.
Sodium absorbs the heat produced in the reactor. This extremely hot sodium is then passed into the coil of the heat exchanger containing water.
Water absorbs heat from hot sodium and boils to form steam. The hot steam at high pressure is introduced into a turbine chamber C having a turbine T. The pressure of steam makes the turbine rotate.
The shaft S of turbine is connected to a generator G. When the turbine rotates, its shaft also rotates and drives the generator. The generator roduces electricity.
2. Nuclear Fusion
The word fusion means to joint or to combine. The process in which two nuclei of light elements like that of hydrogen combine to form a heavy nucleus (like that of helium) is called nuclear fusion. A tremendous amount of energy is produced during the fusion process.
When deuterium atoms (heavy hydrogen atoms of mass number 2) are heated to an extremely high temperature under extremely high pressure, then two deuterium nuclei combine together to form a heavy nucleus of helium, and a neutron is emitted. A tremendous amount of energy is liberated in this fusion reaction.
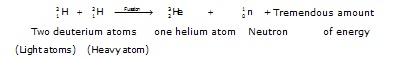
A fusion process is just the opposite of fission process. The energy produced in nuclear fusion reaction is, however, much more than that produced in a nuclear fission reaction.
3. Hydrogen Bomb
The hydrogen bomb consists of heavy isotopes of hydrogen called deuterium (2H) and tritium (3H) alongwith an element lithium – 6 (6Li). The detonation (or explosion) of hydrogen bomb is done by using an atom bomb (based on the fission of uranium – 235 or plutonium - 239) When the atom is exploded, then its fission reaction produces a lot of heat. This heat raises the temperature of deuterium and tritium to 107°C in a few microseconds. At this temperature, fusion reactions of deuterium and tritium take place producing a tremendous amount of energy. This explodes the hydrogen bomb releasing an enormous amount of energy in a very short time. This energy causes destruction of life and property.
4. The Source of Sun’s Energy
The sun is huge mass of hydrogen gas and the temperature in it is extremely high. The sun which gives us heat and light, derives its energy from the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei, which is going on inside it. all the time.
The main nuclear fusion reaction taking place in the sun which releases a tremendous amount of energy is the fusion of 4 hydrogen atom nuclei to form a bigger nucleus of helium atom. That is:
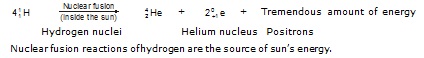
Nuclear fusion reactions of hydrogen are the source of sun’s energy.
An advantage of nuclear fusion reactions over nuclear fission for producing electricity is that the amount of energy released in a fusion reaction is much more than that liberated in a fission reaction.
Disadvantage of a nuclear fusion reactions is that it has not been possible to have a controlled fusion reactions so far, and to safety use the enormous heat produced during this reaction for the production of electricity.
Ex.1 What is the alternative name for renewable sources of energy?
Sol. The following are the characteristics of a good surces of energy:
(i) It should give an adequate amount of net energy.
(ii) It must be convenient to use so as to give energy at a steady rate.
(iii) It must be easy to store and transport.
Ex.2 What are the types of energy sources?
Sol. Energy sources can be classified as :
(i) Non- renewable sources : Fossil fuels like coal,petroleum and natural gas are non-renewable energy sources. These are produced over million of year due to slow changes and under special circumstances.These are not continuous processes and further it is not becoming possible to discover their new deposits. With the present rate of their Consumption. , it is estimated that known deposits of petroleum in our country will be exhausted in another 200 years and that of coal may last for another 250 years.
(ii) Renewable sources : The energy derived from flowing water, wind,tides, ocean waves and biogas are the Renewable sources. These sources can be harnessed into energy so long as the earth derives its heat and light from the sun or so long as the present solar system exists. Nuclear energy and geothermal energy is also likely to be available for a much longer time. Wood is another renewable source of energy. Though it takes almost 15 years for a tree to mature, this and nuclear energy are also classified as renewable sources or
(i) Conventional sources of energy : There are the sources of energy that we have often been using for a long time. For example, wood and fossil fuels like coal, petroleum have been common sources of heat energy. The energy of flowing water and wind are also used for limited activities.
(ii) Non-conventional sources of energy : With increasing demand recently energy from sun,sea waves and earth is also tapped.
Ex.3 What type of energy transformation takes place during winding of spring of a clock?
Sol. Energy to run a cycle : Energy of muscles
Energy to run a car : Chemical energy of petrol or diesel
Energy to cook food : Chemical energy of gas or Kerosene
Energy to work on : Electrical energy obtained from say potential energy of water,
electrical appliances chemical energy of fuels etc.
Ex.4 Give an example of the use of wind energy to perform mechanical work by early man.
Sol. Advantages of using fossil fuels : Petroleum and natural gas.
(i) These leaves no residue on burning.
(ii) There have reasonably low ignition temperature and thus burn easily.
(iii) The combustion is almost complete and thus no smoke is left on burning .
(iv) Calorific value is higher than other usable fuels.
Disadvantages of using fossil fuels:
(i) The end product is carbon dioxide which causes green house effect.
(ii) When petrol is burnt, harmful substances like unburnt hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogen, sulphur are produced. These cause acid rain and thus soil and water pollution give innumerable problem to health.
Ex.5 In what forms energy is utilized in our homes?
Sol. The sun’s energy is useful to us because :
(i) it regulates the flow of wind and water cycles on the earth.
(ii) it helps the plants to grow which in turn provide food to us.
(iii) it can be used for heating and cooking purposes.
Ex.6 What is the parameter known as which gives the amount of light received per square metre per second from the sun ?
Sol. Geothermal energy and nuclear energy are not related to the energy of the sun. Nuclear energy is derived from radioactive substances found under the earth. Geothermal energy is derived from the hot spots beneath the earth. Thus their sources are a results of the formation of earth and not influenced by the energy of the sun falling on earth.
Ex.7 A body kept in a dark room is exposed to radiations emitted by a hot iron. will it be visible to us ?
Sol. The change of one form of energy into another form(or forms) of energy is called transformation of energy. The different forms of energy are : potential energy, kinetic energy, chemical energy, heat energy, solar energy, electrical energy and light energy. When a body from a height falls to the ground, its potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and then into heat energy.
Ex.8 Is the heat of fire a source of energy ?
Sol. Petroleum obtained by drilling holes in the earth’s crust is a crude oil. This is brown black liquid and contains a mixture of various substances besides water and earthy particles. It cannot be put to use as such. It is, therefore, separated into constituents which are used for specific purposes. The process of separation is called refining of petroleum and is done by a technique known as fractional distillation.
Ex.9 Mention any two sources of energy used by ancient man around the 17th century for doing his daily work.
Sol. Some of the conventional sources of energy have poor efficiency and produce a lot of smoke due to incomplete combustion. For example,
Wood : As is well-known, wood is burnt in traditional chulhas. It has poor efficiency because only about 8% of the wood is utilized as fuel. Besides incomplete burning ( combustion), it produces gases like carbon monoxide which are dangerous for health.
Animal dung : Animal dung mixed with mud and made in the form of cakes and dried are burnt in many parts of country for use for domestic purposes. As dung cakes are burnt inefficiently in the conventional manner, it produces a lot of smoke. Further as animal dung contains. useful nutrients for soil, the burning of animal dung causes considerable wastage of useful elements, besides producing air pollution.
Agricultural wastes : Agricultural wastes like sugarcane (from which juice has been extracted) are burnt for use in industries. This and other animal and plant wastes could be more profitably used in biogas plants.
Ex.10 What is the form of energy possessed by moving wind or water?
Sol. The use of cow-dung in biogas plants to produce biogas as fuel is preferred over the use of
cow-dung directly because of the following reasons:
(i) Cow-dung contains important nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which are very useful for crops. Now, when the cow-dung is used to prepare biogas, then the residue left behind is still rich in nutrients and can be used as manure, But if the cow-dung is burnt in the form of dried cow-dung cakes, then the nutrient contained therein are destroyed and hence cannot be used as manure.
(ii) The fuel (biogas) obtained by the use of cow-dung in biogas plants does not produce any smoke on burning and does not cause air-pollution.
(iii) The fuel obtained by the use of cow-dung biogas plants is a clean fuel and does not leave behind any ash or residue. On the other hand cow-dung cakes do not burn completely and leave behind a lot of ash.
Q.1 What is a good source of energy?
Ans. A good source of energy
(i) should be capable of doing large amount of work per unit mass or volume.
(ii) should be easily accessible i.e., it should be convenient to use
(iii) should be easy to transport and store.
(iv) should be capable of delivering desired quantity of energy at a steady rate over a long period of time.
(v) should be economical.
Q.2 What is a good fuel?
Ans. (i) it should have a high calorific value (calorific value is defined as the number of heat units produced when unit mass of fuel is burnt). thus, a good fuel should liberate more heat per unit mass.
(ii) It should have low moisture content.
(iii) It should have low non-combustible matter like ash, etc. that is, it should leave low ash and other residual matter after combustion.
(iv) Its products of combustion should not be harmful. An Ideal fuel should not produce any type of harmful products/gases which create air pollution, water pollution, and harmful effects to the human body.
(v) It should have moderate ignition temperature. Low ignition temprature may cause fire hazards, whereas high ignition temperature may causes difficulty in combustion.
(vi) It should be easy to store and transport.
(vii) It should have moderate rate of combustion and its combustion should be controllable.
(viii) It should be readily available at low cost.
Q.3 If could use any source of energy for heating your food, which one would you use and why?
Ans. We would use a microwave oven for heating the food as it heats it uniformly and cleanly without loss in its nutritional value. Also, we can use solar cooker if bright sunlight is available because the nutrients are not lost during heating in solar cooker.
Q.4 What are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
Ans. Fossil fuels (coal, petroleum and natural gas) have the following disadvantages:
(i) The fossil fuels are non-renewable sources of energy, if we continue to consume these sources at alarming rates, we would soon-run out of energy.
(ii) There are no such alternate sources of energy developed till today which can replace fossil fuels. Thus, large dependency on fossil fuels for most of our energy requirements may create problem in future.
(iii) Air pollution is caused by burning fossil fuels.
(iv) Carbon-dioxide produced by burning these fuels contribute to greenhouse effect.
Q.5 Why are we looking at alternate sources of energy?
Ans. Fossils fuels were formed due to extraordinary circumstances that took place millions of years age. No new reservoirs of these fuels are being formed due to the absence of these circumstances. Thus, they are non-renewable sources of energy. It we continue to use these sources at the present rate, we would soon be deprived of these sources. That is why, we are looking for alternate sources of energy.
Q.6 How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience?
Ans. The traditional use of wind energy has been modified by using windmills (or wind turbines) and that of water by constructing hydro power plants.
Q.7 What kind of mirror - concave, convex or plane would be best suited for use in a solar cooker? Why?
Ans. A concave mirror is best suited for use in a solar cooker. This is because a concave mirror concentrates solar energy from over a large area into a small area (at its focus). As a result, high temperatures can be achieved. Such a mirror is called solar concentrator.
Q.8 What are the limitations of energy that can be obtained from the oceans?
Ans. The energy obtained from the oceans is
(i) tidal energy, for which very few suitable sites are available for construction of dams and the generation is intermittent and not very large.
(ii) sea waves energy, where power output is variable and the currently available technologies are quire expensive.
(iii) ocean thermral energy, where the conversion efficiency is quite low but a lot of capital investment is required.
Q.9 What is geothermal energy?
Ans. The heat energy inside the earth’s crust is known as geothermal energy. The geological changes in some regions push the hot magna upwards which gets collected at some depth below the surface of earth. Such places are called hot spots. These hot spots serve as a source of heat energy (or geothermal energy). The geothermal energy is utilized to convert water into stream which rotates a steam turbine.
Q.10 What are the advantages of nuclear energy?
(i) The mass of nuclear fuel like uranium-235 required is extremely small as compared to a fossil fuel to produce the same amount of energy.
(ii) In a nuclear power plant, the nuclear fuel supplies energy over a long period of time.
Q.11 Can any source of energy be pollution-free? Why or why not?
Ans. No source of energy is totally pollution free, only the degree and the manner of pollution varies. For example, solar cells seem to be non-polluting but environmental pollution is caused in the manufacturing of solar cells.
Q.12 Hydrogen has been used as a rocket fuel. Would you consider it a cleaner fuel than CNG? Why or why not?
Ans. Hydrogen is a cleaner fuel than CNG. This is because it produces water on burning whereas CNG on burning produces CO2 and CO.
Q.13 Name two energy sources that you would consider to be renewable. Give reasons for your choices.
Ans. (i) Water energy (hydro-energy) water on Earth can be sued again and again to generate hydro energy as it is stored again and again in dams due to the water cycle that exists in nature.
(ii) biomass energy, biomass can be managed by replacing the trees that have been cut down for fire-wood, cattle dung will be available as long as life exist on Earth. Thus, we can get a constant supply of energy at a practically usable rate.
Q.14 Give the names of two energy sources that you would consider to be exhaustible. Give reasons for your choices.
Ans. (i) Coal (ii) Petroleum.
Both these sources are present only in limited amounts and will be exhausted soon if we continue to use them at the present rate. these sources were formed over millions of years under special circumstances.
Q.15 A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on
(a) a sunny day (b) a cloudy day
(c) a hot day (d) a windy day
Ans. Option (b) is correct. On cloudy day, heat radiations coming from the Sun do not reach the solar water heater.
Q.16 Which of the following is not an example of bio-mass energy source?
(a) wood (b) gobar gas (c) atomic energy (d) coal
Ans. Option (c) is correct.
Q.17 Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the Sun’s energy?
(a) geothermal energy (b) wind energy
(c) fossil fuels (d) bio-mass
Ans. Option (a) is correct.
Q.18 Compare and contrast fossil fuels and the Sun as sources of energy.
Ans. (i) The reserves of fossil fuels are limited i.e., exhaustible and they high cost. But, solar energy is available in abundance. i.e is inexhaustible and that too without any cost.
(ii) Fossils fuels cause air pollution on burning whereas solar energy is pollution free.
(iii) Fossil fuels can provide energy at any required time whereas solar energy is not available every time. For example, on a cloudy day solar energy is not available.
Q.19 Compare and contrast bio-mass and hydroelectricity as sources of energy.
Ans. (i) Bio-mass is a renewable source of energy only if we plant trees in a planned manner while hydroelectricity can be renewable by the natural water cycle.
(ii) The energy from bio-mass can be obtained b y using a chullah or a gobar gas plant which is less costly as compared to hydro-electricity which requires high capital in the construction of dams on rivers and the hydro power plant.
(iii) Bio-mass provides pollution-free energy only when converted into biogas whereas hydroelectricity is totally pollution-free.
Q.20 On what basis would you classify energy sources as
(a) renewable and non-renewable ?
(b) exhaustible and inexhaustible? Are the option given in (a) and (b) the same?
Ans. (a) Renewable sources of energy are those which (i) can be replaced as we use them and (ii) can be used to produce energy again and again. Non-renewable sources of energy are those which cannot be replaced once these are used.
(b) Exhaustible sources of energy are those whose supply is limited, e.g., coal, petroleum and natural gas. Inexhastible sources of energy are those whose energy supply is unlimited e.g., water energy, wind energy, etc.
Renewable sources of energy are inexhaustible whereas non-renewable sources of energy are exhaustible with some exceptions. For example, biomass is a renewable source of energy only if we plant trees in a planned manner.
Q.21 What are the environmental consequences of the increasing demand for energy? What steps would you suggest to reduce energy consumption ?
Ans. (i) Burning of fossil fuels to meet increasing demand for energy causes air-pollution.
(ii) Construction of dams on rivers to generate hydro-electricity destroys large ecosystems which get submerged under water in the dams. Large amounts of methane (which is a greenhouse gas) is produced when submerged vegetation rots under anaerobic conditions.
In order to reduce energy consumption (i) fossil fuels should be used with caution to get their maximum benefit (ii) energy efficient devices such as pressure cookers, compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) etc. should be used (iii) the devices/machines used for energy conversion should be maintained or repaired regularly in order to keep them efficient (iii) we should use electricity or any other source of energy judiciously as ‘energy saved is energy produced’.
Q.1 What is energy ?
Q.2 What is a source of energy ?
Q.3 What is a good source of energy ?
Q.4 What is a fuel ?
Q.5 What are fossil fuels ?
Q.6 What is biomass ?
Q.7 What does Bio-gas consist of ?
Q.8 What are conventional sources of energy
Q.9 What are alternative or non-conventional sources of energy ?
Q.10 Which is the ultimate source of energy
Q.11 What is geothermal energy ?
Q.12 Name the renewable sources of energy
Q.13 Name some non-renewable sources of energy?
Q.14 Name any two materials that are used for making solar cells ?
Q.15 Name some gadgets where solar cells are used
Q.16 What is the minimum wind velocity required for obtaining electric power with a wind mill generator
Q.17 What is the range of temperature that can be obtained in a box type solar cooker
Q.18 What fraction of solar energy reaches the earth’s surface ?
Q.19 What is the value of solar constant on earth ?
Q.20 What is the age of the sun ?
Q.21 Name some devices that can harness solar energy
Q.22 Name one liquid and one gaseous fossil fuel ?
Q.23 Name the process that produces such a large amount of energy in the sun ?
Q.24 What is renewable source of energy ?
Q.25 What is non - renewable source of energy
Q.26 Name a device used to harness wind energy ?
Q.27 What is wind energy farm ?
Q.28 What raw materials can be used in a Bio-gas plant to produce Bio-gas ?
Q.29 What is the use of the slurry left behind in the Bio-gas plant ?
Q.30 Name the places where nuclear reactors are located in India ?
Q.31 How much energy need of our country and the world is being fulfilled by the Nuclear power.
Q.32 Why are fossil fuels classified as non renewable sources of energy ?
Q.33 What is the principle of solar cookers ? Name two types of solar cookers.
Q.34 What is the output of a solar cell ?
Q.35 Name the different constituents of biogas ?
Q.36 How does a solar panel light up a bulb at night when there is no solar energy
Q.37 Why is biogas called a clean fuel ?
Q.38 Give reasons why hydrogen can not be used as a domestic fuel ?
Q.39 Name the commonly used forms of energy ?
Q.40 What are the different types of energies obtained from the sea ?
Q.41 What are the disadvantages of using cooker
Q.42 Describe a simple activity to demonstrate the working of a turbine generator, how does it product electricity ?
Q.43 Explain the working of a hydroelectric power plant to produce electricity?
Q.44 Describe how a solar cell is fabricated. Name two elements used for fabricating it. What is solar cell panel ?
Q.45 Draw a diagram and explain the construction and working of a box type solar cooker.
Q.46 Write 3 advantages of nuclear energy.
Q.47 Name three forms in which energy from ocean is made available for use. What are OTEC power plants ? How do they operate.
Q.48 (i) Name the four gases commonly present in bio-gas.
(ii) List two advantages of using bio-gas fossil fuels.
Q.49 What are disadvantages of Constructing dams/producing electricity by Hydropower plants.
Q.50 Explain the structure and working of a fixed dome biogas plant?
Q.51 (a) What is a nuclear energy ?
(b) What are the main hazards of nuclear power generation ?
Q.1 Which of the following is a renewable source of energy?
(A) Coal (B) Natural gas (C) Wood (D) Petroleum
Q.2 The purpose of the glass cover on top of a box-type solar cooker is to
(A) allow one to see the food being cooked (B) allow more sunlight into the box
(C) prevent dust from entering the box (D) reduce heat loss by radiation
Q.3 A solar panel is made by combining a large number of
(A) solar cookers
(B) solar cells
(C) solar water heaters
(D) solar concentrators
Q.4 To work properly, wind-electric generators need wind speeds of at least about
(A) 1.5 km/h (B) 15 km/h
(C) 150 km/h (D) 1500 km/h
Q.5 The site of a hydroelectric plant should be chosen carefully because it
(A) produces a large amount of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide
(B) produces a large amount of electricity
(C) affects the organisms of the region
(D) is expensive
Q.6 Electricity from the ocean can be generated based on utilizing
(A) kinetic energy of the waves but not stored thermal energy
(B) stored thermal energy but not kinetic energy of the waves
(C) kinetic energy of the waves as well as stored thermal energy
(D) neither kinetic energy of the waves nor stored thermal energy
Q.7 Which energy is not derived from the sun?
(A) Nuclear energy
(B) Wind energy
(C) Biomass energy
(D) Ocean-wave energy
Q.8 Which of the following is not biomass?
(A) Sun (B) Rice husk
(C) Wood (D) Cattle dung
Q.9 The condition for producing biogas is
(A) air but not water
(B) water but not air
(C) air and water
(D) neither air nor water
Q.10 Geothermal energy is feasible in regions that
(A) are near the sea
(B) have thermal plants
(C) have coal mines
(D) are over hot spots in the crust
Q.11 A solar water heater cannot be used to get hot water on
(A) a sunny day.
(B) a cloudy day.
(C) a hot day.
(D) a windy day.
Q.12 Which of the following is not an example of a bio-mass energy source?
(A) wood
(B) gobar-gas
(C) nuclear energy
(D) coal
Q.13 Most of the sources of energy we use represent stored solar energy. Which of the following is not ultimately derived from the Sun's energy?
(A) geothermal energy
(B) wind energy
(C) nuclear energy
(D) bio-mass.
Q.14 The device in which the nuclear fission and release of energy is controlled is known as-
(A) Thermopile
(B) Thermostat
(C) Nuclear reactor
(D) Cloud chamber
Q.15 For a sustained chain reaction, the reproduction factor should be -
(A) zero (B) one
(C) two (D) three
Q.16 Moderator is used in nuclear reactor for -
(A) slowing neutrons
(B) accelerating neutrons
(C) stopping neutrons
(D) heating the neutrons
Q.17 The fusion reactions occur at-
(A) low pressure
(B) low temperature
(C) extremely high temperature
(D) high temperature and low pressures
Q.18 The source of energy of the sun is-
(A) Nuclear fission
(B) Chemical reaction
(C) Nuclear fusion
(D) None of these
Q.19 The number of neutrons in an atom X of atomic number Z and mass number A is-
(A) Zero (B) Z
(C) A – Z (D) A
Q.20 When a beta particle is given out, the atomic number of the parent atom -
(A) Increases by unity
(B) Decreases by unity
(C) Remains the same
(D) Is halved
Q.21 Which of the following has least penetrating power ?
(A) Alpha particles
(B) Gamma rays
(C) Beta particles
(D) All have the same penetrating power
1. C 2. D 3. B 4. B 5. C
6. C 7. A 8. A 9. B 10. D
11. B 12. C 13. C 14. C 15. B
16. A17. C 18. C 19. C 20. A
21. A
1. What kind of gases are released while burning fossil fuels?
2. List out the different power plants from which we get electrical energy?
3. What is the major source of energy for the sun?
4. What nuclear reaction takes place in the sun?
5. Draw the schematic picture of a solar cooker?
6. What is the use of the plane mirror of a box type of solar cooker?
7. Which type of solar spectrum is trapped in the solar cooker?
8. What is a solar cell?
9. What are the uses of solar cells?
10. What are the different forms of energies available from the oceans?
11. What are hot spots?
12. What are the different type of nuclear reactions?
13. Define nuclear fission and fusion reactions.
14. List some renewable energies.
1. What are main disadvantages of using fossil fuels and how can we minimize it?
2. What causes acid rain?
3. Write the working of a hydro power plant with heat diagram?
4. What are the limitations of constructing dams across rivers?
5. What is the composition of bio-gas and the matter rich in the slurry left behind in the bio-gas plant?
6. With a neat diagram of a wind mill write its construction and working?
7. Define solar constant and give its value on the upper atmosphere and on the lower atmosphere?
8. What are the advantages and disadvantages of a solar cell?
9. What are the limitations of using solar cell?
10. What factors make a solar cell very expensive?
11. What is ocean thermal energy and how is it harnessed?
12. What is OTEC?
13. What is the minimum requirement to operate the OTEC system?
14. What are the limitation of harnessing Geo-thermal energy?
15. What is the major hazard of nuclear power generation?
· Fill in the blanks
1. Hydro power plants convert the potential energy of falling water into ___________.
2. The phenomena, in which, the nucleus of a heavy atom, when bombarded with low-energy neutrons, can be split apart into lighter nuclei, is called _______________.
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. The word ‘energy crisis’ stands for
(A) Energy destruction (B) Energy creation
(C) Conversion of energy from usable form to less usable form (D) None of these
2. Device that converts the potential energy of flowing water into electricity is
(A) Solar cooker (B) Thermal power plant
(C) Hydro power plant (D) Bio-gas plant
· Assertion & Reason
Instructions: In the following questions as Assertion (A) is given followed by a Reason (R). Mark your responses from the following options.
(A) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(B) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is not the correct explanation of ‘Assertion’
(C) Assertion is true but Reason is false
(D) Assertion is false but Reason is true
1. Assertion: In nuclear fission, a tremendous amount of energy is released if the mass of the original nucleus is just a little more than the sum of the masses of the individual products.
Reason: The difference in mass, Dm, between the original nucleus an the product nuclei gets converted to energy E according to equation
E = DmC2
where C is speed of light in vaccum.
· Match the following (one to one)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. Only One entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II Only one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column-I Column-II
(Device) (Limitation)
(A) Hydro power plants (P) Efficient commercial exploitation is difficult
(B) Wind mill (Q) Special grade silicon is limited
(C) Solar cell (R) Wind speed should higher than 15 km/h
(D) Ocean-thermal-energy conversion plants (S) Large eco-systems are destroyed
· Multiple choice question with one correct answers
1. The major source of energy in India is –
(A) Nuclear (B) Petroleum (C) Hydro (D) Coal
2. Bio-gas is produced in a bio-gas plant, by decomposition of complex compounds of the cow-dung slurry. This process is done by : Micro-organism in the
(A) Presence of Oxygen (B) Absence of Oxygen
(C) Presence of N2 (D) None of the these
· Multiple choice question with one or more than one correct answers
1. Limitations in harnessing the kinetic energy of flowing water in hydro power plants is/are
(A) The speed of flowing water should higher than 15 km/hr
(B) The dam’s can be constructed only in a limited number of places
(C) Large ecosystems are destroyed when submerged under the water in dams
(D) The dams need a high level of maintenance
Passage-1
The solar energy reaching unit area at outer edge of the earth’s atmosphere exposed perpendicularly to the rays of the sun at the average distance between the sun and earth is known as the solar constant. It is estimated to be approximately 1.4 Kj per second per square metre or 1.4 Kw/m2. A rocked is flying at the outer edge of earth’s atmosphere. Sun rays are incident perpendicularly on the metal surface of rocket of area 10 m2.
1. Solar energy incident on metal surface in 10 sec. is
(A) 1.4 KJ (B) 14 KJ (C) 140 KJ (D) None of these
2. In how much time will metal surface receive 42 KJ of solar energy.
(A) 3 sec (B) 30 sec (C) 300 sec (D) None of these
3. Solar energy received by unit area of metal surface in 10 sec. –
(A) 1.4 KJ (B) 14 KJ (C) 140 KJ (D) None of these
· Match the following (one to many)
Column-I and column-II contains four entries each. Entries of column-I are to be matched with some entries of column-II. One or more than one entries of column-I may have the matching with the same entries of column-II and one entry of column-II may have one or more than one matching with entries of column-I
1. Column I Column II
(A) Hydro power plants (P) Produces electricity
(B) Solar Cell (Q) Converts solar energy into electric energy
(C) Thermal power plant (R) Converts potential energy of falling water into electricity
(D) Wind mill (S) Converts kinetic energy of air into electricity
Section-A
1. electricity 2. nuclear-tission
Section-B
1. (C) 2. (C)
Section-C
1. (A)
Section-D
1. (A)-(S),(B)-(R),(C)-(Q),(D)-(P)
Section-A
1. (D) 2. (B)
Section-B
1. (B,C)
Section-C
1. (C) 2. (A) 3. (B)
Section-D
1. (A)–(P,R), (B)–(P,Q), (C)–(P), (D)–(P,S)
*****