Ex1. The work function of a thermionic emitter is 4.5 eV. By what factor does the thermionic current increase current increase if its temperature is raised from 1500 K to 2000 K ?
Sol. If i1 and i2 represent the thermionic currents at temperature Ti = 1500 K and T2 = 2000 K respectively,
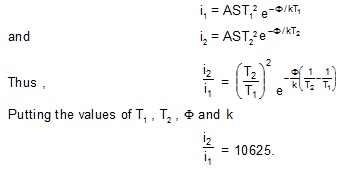
Ex2. When the plate voltage applied to a diode value is changed from 40 V to 42 V , the plate current increases from 50 mA to 60 mA. Calculate the dynamic plate the resistance at the operating condition.
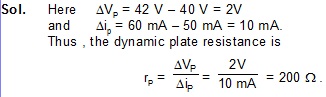
1. Why is conduction easier in gases if the pressure is low ? Will the conduction continue to improve if the pressure is made as low as nearly zero ?
2. An AC source is connected to a diode and a resistor in series. Is the current through the resistor in series. Is the current through the resistor AC or DC ?
3. How will the thermionic current vary if the filament current is increased ?
4. Would you prefer a material having a high melting point or a low melting point to be used as a cathode in a diode ?
5. Would you prefer a material having a high work function or a low work function to used as a cathode in a diode ?
6. An isolated metal sphere is heated to a high temperature. Will it become positively charged due to thermionic emission ?
7. A diode value is connected to a battery and a load resistance. The filament is heated so that a constant current is obtained in the circuit. As the cathode continuously emits electrons , does it get more and more positively charged ?
8. Why does thermionic emission not take place in nonconductors ?
9. The cathode of a diode value is replaced by another cathode of double the surface area. Keeping the voltage and temperature conditions the same , will the plate current decrease , increase or remain the same ?
10. Why is the linear portion of the triode characteristic chosen to operate the triode as an amplifier ?
Objective - I
1. Cathode rays constitute a stream of
(A*) electrons (B) protons (C) positive ions (D) negative ions
2. Cathode rays are passing through a discharges tube. In the tube, there us
(A) an electric field but no magnetic field (B) a magnetic field but no electric field
(C*) an electric as well as a magnetic field (D) neither an electric nor a magnetic field
3. Let i0 be the thermionic current from a metal surface when the absolute temperature of the surface is To. The themperature is slowly increased and the thermionic current is measured as a function of temperature. Which of the following plots may represent the variation in of the following plots may represent the variation in (i/i0) against (T/T0) ?
(A) a (B) b (C) c (D*) d
4. When the diode shows saturated current, dynamic plate resistance is
(A) zero (B*) infinity (C) indeterminate (D) different for different diodes
5. The anode of a thermionic diode is connected to the negative terminal of a battery and the cathode to its positive terminal.
(A*) No appreciable current will pass through the diode.
(B) A large current will pass through the diode from the anode to the cathode.
(C) A large current will pass through the diode from the cathode to the anode
(D) The diode will damaged
6. A diode, a resistor and a 50Hz AC source are connected in series. The number of current pulse per second through the resistor is
(A) 25 (B*) 50 (C) 100 (D) 200
7. A triode is operated in the linear region of its characteristics. If the plate voltage is slightly increased, the dynamic plate resistance will
(A) increase (B) decrease (C*) remain almost the same (D) become zero
8. The plate current in a triode valve is maximum when the potential of the grid is
(A*) positive (B) zero (C) negative (D) nonpositive
9. The amplification factor of a triode operating in the linear region depends strongly on
(A) the temperature of the cathode
(B) the plate potential
(C) the grid potential
(D*) the separations of the grid from the cathode and the anode
Objective - II
1. Electric conduction takes place in a discharge tube due to the movement of
(A*) positive ions (B*) negtive ions (C*) electrons (D) protons
2. Which of the following are true for cathode ray ?
(A*) It travels along straight lines
(B*) It emits X-rays when strikes a metal
(C) It is an electromagnetic wave.
(D) It is not deflected by magnetic field
3. Because of the space charge in a diode valve,
(A*) the plate current decreases
(B) the plate voltage increases
(C) the rate of emission of thermions of thermions increases
(D) the saturation current increases
4. The saturation current in a triode valve can be changed by changing
(A) the grid voltage (B) the plate voltage
(C) the separation between the grid and the cathode (D*) the temperature of the cathode.
5. Mark the correct options
(A*) A diode valve can be used as a rectifier (B*) A triode valve can be used as a rectifier
(C) A diode valve can be used as an amplifier (D*) A triide valve can be used as an amplifier
6. The plate current in a diode is zero. It is possible that
(A*) the plate voltage is zero (B*) the plate voltage is slightly negative
(C*) the plate voltage is slightly positive (D*) the temperature of the filament is low
7. The plate current in a triode valve is zero. The temperature of the filament is high. It is possible that
(A) Vg > 0, Vp > 0 (B*) Vg > 0, Vp < 0 (C*) Vg < 0, Vp > 0 (D*) Vg < 0, Vp > 0
Worked Out Examples
1. The mean free path of the electrons in a discharge tube is 20 cm. The tube itself is 10 cm long . What is the length of the Crookes dark space ?
sol. The mean free path of the electrons is much longer than the length of the tube. Thus , the electrons, in general , do not collide in between , no ionization takes place and hence no light is emitted. The Crookes dark space fills the entire tube and hence is 10 cm long.
2. Consider a cylindrical tube closed at one end fitted with a conducting , movable piston at the other end. A cathode is fixed with the piston. A cathode is fixed in the tube near the closed end an anode is fixed with the piston. A gas is filled in the tube at pressure p. Using Paschen equation V = f(pd) , show that the sparking potential does not change as teh piston is slowly moved in or out. Assume that the temperature does not change in the process.
Sol. As the piston is moved , the volume of the gas and hence its pressure changes. As the tube is cylindrical , the volume is proportional to the length of the tube. From Boyle's law , pd = constant and hence the sparking potential does not change as the piston is moved.
3. The number of thermions emitted in given time increases 100 times as the temperature of the emitting surface from 600 K to 800 K. Find the work function of the emitter. Boltzmann constant k = 8.62 × 10–5 e V/K.
Sol. The number of thermions n , emitted by a surface , in a given time is given by ( Richardson – Dushman equation )
![]()
where A' is a constant and other symbols have their usual meanings.Let n1 and n2 be the number of electrons emitted at temperatures T1 and T2. Then
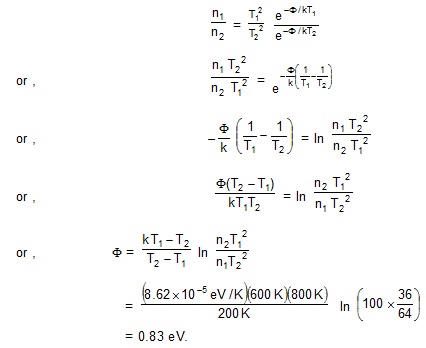
4. The constant A in the richardson–Dushman equation is 60 × 104 A/m2 –K2 for tungsten cathode has a total surface are of 2.0 × 10–5 m2 and operates at 2000 k. The work function of tungsten is 4.55 eV. Calculate the electric current due to thermionic emission.
Sol. The Richardson–Dushman equation is
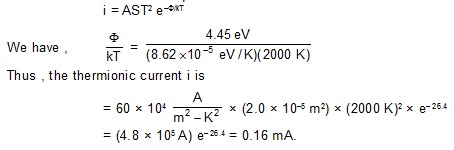
5. Calculate the saturation thermionic current if 120 W is applied to a thoriated-tungsted filament of surface area 1.0 cm2 . Assume that the surface radiated like a blackbody. The required constants are
![]()
Sol. The thermionic current is given by the Richardson-Dushman equation
![]()
When the power input to the filament equals the power radiated , the temperature becomes saturated. The power radiated is given by the Stefan's law
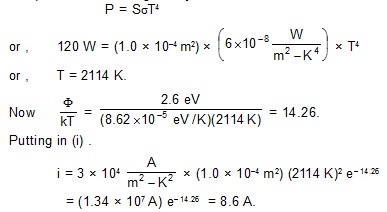
6. In a Millikan-type oil-drop expirement , the plates are 8 mm apart. An oil drop is found to remain at rest when the upper plate is at a potential 136 V higher than that of the lower one. When the electric field is switched off , the drop is found to fall a distance of 2.0 mm in 36 seconds with a uniform speed. Find (a) the charge on the drop and (b) the number of electrons attached to thid drop. Density of oil = 880 kg/m3 and coefficient of viscosity of air = 180 m poise.
Sol. (a) The charge on the drop is
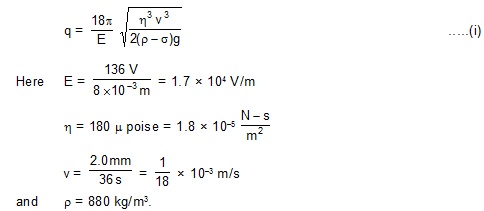
The density of air s (1.29 kg/m3) may be neglected in comparisonm to that of the oil. Putting values in (i) ,
![]()
(b) The number of electrons attached to the drop is ,
![]()
It is clear that 5 electrons are attached to the drop.
7. Show that the dynamic plate resistance of a diode is2v/3i where V and i are the plate voltage and the plate current respectively. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
Sol. The dynamic plate resistance of the diode is R = dv/di .
The Langmuir-Child equation is
i = cV3/2 .....(i)
where c is a constant for a given diode. This gives
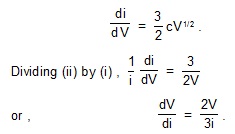
8. The mutual conductance of a triode value is 2.5 millimho. Find the change in the plate current if the grid voltage is changed from – 2.0 V to – 4.5 V.
Sol. The mutual conductance of a triode value is
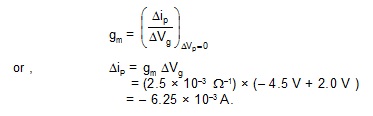
9. A triode value has amplification factor 21 and dynamic plate resistance 10 kW. This is used as an amplifier with a load of 20 kW. Find the gain factor of the amplifier.
Sol. The gain factor of a triode value amplifier is
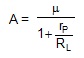
where m is the amplification factor , rP is the plate resistance and RL is the load resistance. Thus ,
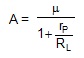
Exercise
1. A discharge tube contains helium atr a low pressure A large potential difference is applied across the tube to Consider a helium atom that has just been ionized due to the detachment of an atomic electron to that by the positive ion in a short time dt after the ionization.
Ans 7340
2. A molecule of a gas filled in a discharge tube. gets ionized when an electronic is detached from it An electron is field of 5.0 kv/ m exits in the vincinty of the event (a) fine the distance travelled by the free electron in 1µs assuming no collision (b) If the mean free path of the electrons is 1.0 mm estimate the time of transit of the free electron between successive collisions
Ans: (a) 440 m (b) 1.5 ns
3. The mean free path of electrons in the gas in a discharge tube is inversely proportional to the pressure inside it the Crookes dark space occupies half the length of the discharge tube when the pressure is 0.02 mm of mercury estimate the pressure at which the dark space will fill the whole tube
Ans: 0.01 mm of mercury
4. Two discharge tubes have unidentical material structure and the same gas is filled in them The
length of one tube is 10cm and that of the other tube is 20 cm sparking starts in both the tubes when the potential deference between the cathode and the anode is 100 V If the pressure in the shorter tubes is 1.0 mm of mercury what is the pressure in the longer tube ?
Ans: 0.5 mm of mercury
5 Calculate n(T)/n (1000K)n for tungsten emitter at T = 300 K, 2000 K and 3000 K where n(T) represents the number of thermions emitted per second by the surface at temperature T work function of tungsten is 4.52 eV.
Ans: 6.57 × 10 – 55 , 9.73 × 10 11, 1.37 × 10 16
6. The saturation current from a thoriated tungsten cathode at 2000 K is 100 mA what will be the saturatyion current for a pure tungsten cathode of the same surface area operating at the same temperature? The constant A in the Richardson Dushman equation is 60 × 104 A/m2– K2 for pure tungsten and 3.0 × 10 A/m2 – K2 for thoriated tungsten The work function of pure tungsten is 4.5 eV and that of thoriated tungsten is 2.6 eV
Ans: 33 µ A
7. A tungsten cathode and a thoriated tungsten cathode have the same geometrical dimensions and are operated at the same temperature. The thoriated tungsten cathode gives 5000 times more current than the other one .Find the operating temperature Take relevant data from the previous problem.
Ans: 1914 K
8. If the temperature of a tungsten filament is raised from 2000 K to 2010 K by what factor does the emission current change ? work function of tungsten is 4.5 eV
Ans: 1.14
9 The constant A in the Richardson dushaman equation for tungsten is 60 × 104 A/m – K2 The work function of tungsten is 4.5 eV A tungsten cathode having a surface area 2.0 × 10– 5 m2 is heated by a 24 W electric heater. In steady state the heat radiated by the cathode equals the energy input by the heater and the temperature becomes constant. Assuming that the cathode radiates like a blackbody, calculate the saturation current due to thermions. Take Stefan constant = 6 × 10–8 W/m2 –K4. Assume that the tghermions take only a small fraction of the heat supplied.
Ans: 1.0 mA
10. A plate current of 10 mA is obtained when 60 volts are applied across a diode tube Assuming the Langmuir Child equation ip a Vp3/2 to hold find the dynamic resistance rp in this operating condition.
Ans: 4 KW
11. The plate current in a diode is 20mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V what will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
Ans: 20 mA
12. The power delivered in the plate circuit of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V Assume Langmuir child equation to hold
Ans: 2.2 W
13. A triode valve opertaedsat Vp 225 and Vg = 0.5 V The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage in increased to 250 V and the gride voltage is decreased to – 2.5 V calculate the amplification factor.
Ans: 12.5
14. Calculate the amplification factor of a triode valve which has plate resistance of 2kW and transconductance of 2 mili mho.
Ans: 4
15. The dynamic plate resistance of a triode valve is 10 kW Find the change in the plate current if the plate voltage is change from 200 V to 220 V.
Ans: 2 mA
16. Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage – 6 The plate characteristics are shows in figure.
Ans: 8.0 KW , 20 and 2.5 milli-mho
17 The plate resistance of a triode is 8 KW and the transconductance is 2.5 milli-mho (a) If the plate voltage is increased by 48 V and the girid voltage is constant what will be the increase in the plate current ? (b) With plate voltage kept constant at this increased value how much should the grid voltage be decreased in order to bring the plate current back to its initial value ?
Ans: (a) 6 mA (b) 2.4 V
18. The plate resistance and the amplification factor of a triode are 10 kW and 20 The tube is operated at plate voltage 250 V and grid voltage – 7.5 V The plate current is 10 mA (a) To what value should the grid voltage be changed so as to increase the plate current 15 mA ? (b) To what value should the plate voltage be changed to take the plate current back to 10 mA?
Ans: (a) – 5.0 V (b) 200 V
19. The plate current plate voltage and grid voltage of a 6F6 triode tube are related as
ip = 41 (Vp + Vg) 1.41
where Vp and Vg are in volts and ip in microamperes. The tube is operated at Vp = 250 V, Vg = – 20 V Calculate (a) the tube current (b) the plate resistance (c) the mutual conductance and (d) the amplification factor.
Ans: (a) 30 mA (B) 2.53 KW (c) 2.77 milli-mho (d) 7
20. The plate current in a triode can be written as
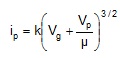
show that the cube root of the plate current.
Ans:
21. A triode has mutual conductance = 2.0 milli-mho and plate resistance = 20 kW It is desired to amplify a signal by a factor of 30 What load resistance should be added in the circuit ?
Ans: 60 KW
22. The gain factor of an amplifier is increased from 10 to 12 as the load resistance is changed from 4 kW to 8 kW Calculate (a) the amplification factor and (b) the plate resistance
Ans: (a) 15 (b) 2 KW
23 Figure (41-E2) shows two identical triode tubes connected in parallel The anodes are connected together the grids are connected together and the cathodes are connected together show that the equivalent plate resistance is half of the individual plate resistance the equivalent mutual conductance is double