
Example 33.1 Find the heat developed in each of the three resistors shown in figure in 1 minute.


Example 33.2 The cold junction of a thermocouple is maintained at 100 C. No thermo–emf is developed when the
hot junction is maintained at 5300 C. Find the neutral temperature.
Questions for Short answer
1. If a constant potential difference is applied across a bulb, the current slightly decreases as time passes and then becomes constant. Explain.
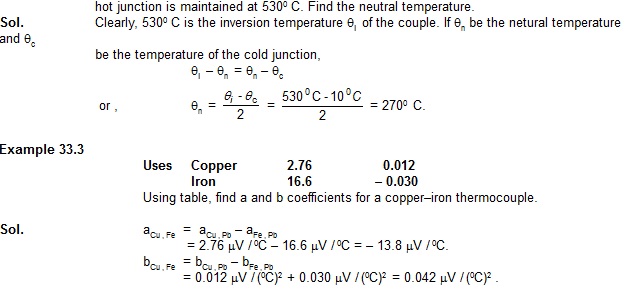
2. Two unequal resistances R1 and R2 are connected across two identical batteries of emf varepsilon and internal resistance r (figure 33-Q1). Can the thermal energies developed in R1 and R2 be equal in a given time. If yes, what will be condition?
3. When a current passes through a resistor, its temperature increases. Is it an adiabatic process?
![]()
5. Do all the thermocouples have a neutral temperature?
6. Is inversion temperature always double of the neutral temperature? Does the unit of temperature have an effect in deciding this question?
7. Is neutral temperature always the arthmetic mean of the inversion temperature and the temperature of the cold jucntion? Does the unit of temperature have an effect in deciding this question?
8. Do the electrodes in an electrolytic cell have fixed polarity like a battery?
9. As temperature incrases, the viscosity of liquids decreases considerably. Will this decrease the resistance of an electrolyte as the temperature increases?
Objective - I
1. Which of the following plots may represent the thermal energy produced in a resistor in a given time as a function of the electric current ?
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
2. A constant current i is passed through a resistor. Taking the temperature coefficient of resistance into account, indicate which of the plots shown in fig. best represents the rate of production of thermal energy in the resistor.
(A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 4
3. Consider the following statements regarding a thermocouple.
(a) The neutral temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
(b) The inversion temperature does not depend on the temperature of the cold junction.
(A) Both a and b are correct. (B) a is correct but b is worng
(C) b is correct but a is wrong (D) Both a and b are wrong
4. The heat developed in a system is propertional to the current through it.
(A) It cannot be Thomson heat (B) It cannot be Peltier heat
(C) It cannot be Joule heat (D) It can be any of the three heats mentioned above
5. Consider the following two statements
(a) Free-electron density is different in different metals.
(b) Free-electron density in a metal depends on temperature.
Seebeck effect is caused
(A) due to both a and b (B) due to a but not due to b
(C) due to b but not due to a (D) neither due to a nor due to b
6. Consider the statement a and b in the previous question. Peltier effect is caused
(A) due to both a and b (B) due to a but not due to b
(C) due to b but not due to a (D) neither due to a nor due to b
7. Consider the statements a and b in question 5. Thomson effect is caused
(A) due to both a and b (B) due to a but not due to b
(C) due to b but not due to a (D) neither due to a nor due to b
8. Faraday constant :
(A) depends on the amount of the electrolyte
(B) depends on the current in the electrolyte
(C) is a universal constant
(D) depends on the amount of charge passed through the electrolyte.
Objective - II
1. Two resistors having equal resistance are joined in series and current is passed through the combination. Negect any variation is resistance as the temperature changes. In a given time interval,
(A) equal amounts of thermal energy must be produced in the resistors
(B) unequal amounts of thermal energy may be produced
(C) the temperature must rise equally in the resistors
(D) the tepmerature may rise equally in the resistors
2. A copper strip AB and an iron strip AC are joined at A. The junction A is maintained at 0oC and the free ends B and C are maintained at 100oC. There is potential different between
(A) the two ends of the copper strip (B) the copper end and the iron end at the junction
(C) the two ends of the iron strip (D) the free ends B and C
3. The constance a and b for the pair silver-lead are 2.50 muV/oC and 0.012 muV/o(C)2 respectively. For a silver-lead thermocouple with colder junction at 0oC,
(A) there will be no neutral temperature
(B) there will be no inversion temperature
(C) there will not be any thermo-emf even if the junctions are kept at different temperatures
(D) there will no current in the thermocouple even if the junction are kept at different temperature.
4. An electrolysis experiment is stopped and the battery terminals are reversed.
(A) The electrolysis will stop
(B) The rate of liberation of material at the electrodes will increased.
(C) The rate of liberation of material will remain the same
(D) Heat will be produce at a greater rate
5. The electrochemical equivalent of a material depends on
(A) the nature of the material
(B) the current through the electrolyte containing the material
(C) the amount of charge passed through the electrolyte
(D) the amount of this material present in the electrolyte.
Worked Out Examples
1. A current of 30 A is registered when the terminals of a drya cell of emf 1.5 volts are connectd through an ammeter. Neglecting the meter resistance, find the amount of heat produced in the battery in 10 seconds.
Sol. The current in the circuit will be
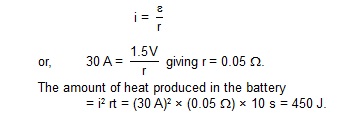
2. A room heater is rated 500 W, 220 V. (a) Find the resistance of its coil. (b) If the supply votage drops to 200 V, what will be the power consumed? (c) If an electric bulb rated 100 W, 220 V is connected in series with this heater, what will be the power consumed by the heater and by the bulb when the supply is at 220 V?

3. A battery of emf e and internal resistance r is used in a circuit with a variable external resistance R. Find the value of R for which the power consumed in R is maximum.
Sol. The current in the resitance R is
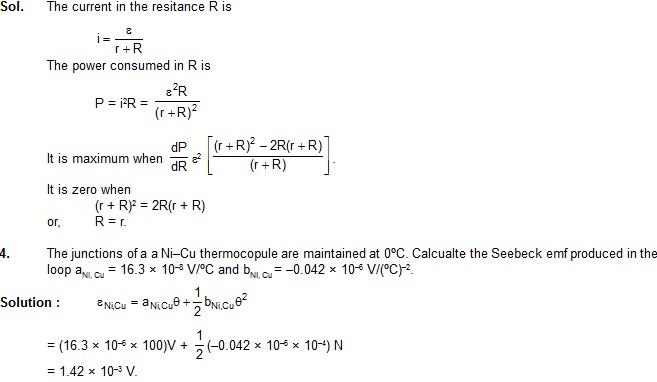
5. Find the neutral and inversion temperatures for Ni – Cu thermodynamics with the cold junction at 0ºC. Use data from previous example.

6. An electric current of 0.4 A is passed through a silver voltameter for half an hour. Find the amount of silver deposited on the cathode. ECE of silver = 1.12 × 10–6 kg/C.
Solution : Using the formula m = Zit, the mass of silver deposted
= (1.12 × 10–6 kg/C) (0.4 A) (30 × 60 s)
= 8.06 × 10–4 kg = 0.806 g.
7. A silver and a copper voltameter are connected in sereis with a 12.0 V battery of negligible resistance. It is found that 0.806 g of silver is
deposited in half an hour. Find (a) the mass of the copper deposited and (b) the energy supplied by the battery. EOE of silver = 1.12 × 10–6 kg/C
and that of copper = 6.6 × 10–7 kg/C.
Solution :
(a) For silver voltameter, the formula m = Zit gives 0.806 g = (1.12 × 10–6 kg/C) i(30 × 60 s)
or, i = 0.4 A.
As the two voltmeters are connected in seris, the same current passes through the copper voltameter. The mass of copper deposited is
m = Zit
= (6.6 × 10–7 kg/C) i(30 × 60 s)
or, i = 0.4 A.
This could also be obtained by using for series circuit.

8. A current of 1 A is passed through a dilute solution of sulphuric acid for some time to liberate 1 g of oxygen. How long was the current passed ? Faraday constant = 96500 C/mole.

Exercise
1. An electric current of 2.0 A passes through a wire of resistance 25 ohm. How much heat will be developed in 1 minute?
Ans. 6.0 × 103 J
2. A coil of resistance 100 ohm is connected across a battery of emf 6.0 V. Assume that the heat developed in the coil is
used to raise its temperature. If the heat capacity of the coil is 4.0 J/K long will it take to raise the temperature of the coil by 15ºC?
Ans. 2.8 minute
3. The specificationon a heater coil is 250 V, 500 W. Calculate the resistance of the coil. What will be the resistance of a coil of 1000 W to operate at the same voltage?
Ans. 125 ohm, 62.5 ohm

Ans. 8.4 mW
6. An electric bulb, when connected across a power supply of 220 V, consumes a power of 60 W. If the supply drops to 180 V,
what will be the power consumed? It the supply is suddenly increased to 240 V, what will be the power consumed?
Ans. 40 W, 71 W
![]()
Ans. 98 W, 102 W
8. An electric bulb marked 220 V, 100 W will get fused if it is made to consume 150 W or more. What voltage fluctuation will the bulb withstand?
Ans. up to 270 V
9. An immersion heater rated 1000 W, 220 V is used to beat 0.01 m3 of water. Assuming that the power is supplied at 220 V and 60% of the
power supplied is used to heat the water, how long will it take to increase the temperature of the water from 15ºC to 40ºC?
Ans. 29 minutes
10. An electric kettle used to prepare tea, takes 2 minutes to boil 4 cups of water (1 up contains 200 cc of water) if the room temperature
is 25ºC. (a) If the cost of power consumptionis Rs. 1.00 per unit = 1000 watt-hour), calculate the cost to boiling 4 cups of water.
(b) What will be the corresponding cost if the room temperature drops to 5ºC?
Ans. (a) 7 paisa (b) 9 paisa
11. The coil of an electric bulb takes 40 watts to start glowing. If more than 40 W is supplied, 60% of the extra power is converted into
light and the remaining into heat. The bulb consumes 100 W at 220 V. Find the percentage drop in the light intesity at a point if the
supply voltage cahnges form 220 V to 200 V.
Ans. 29%
12. The 2.0 ohm resistor shown in figure (33 E1) is dipped into a calorimeter containing water. The heat capacity of the calorimeter
together with water is 2000 J/K. (a) If the circuit is active for 15 minutes, what would be the rise in the temperature of the water?
(b) Suppose the 6.0 W resistor gets burnt. What would be the rise in the temperature of the water in the next 15 minutes?
\
Ans. (a) 2.9 ºC (b) 3.6ºC
13. The temperatures of the junctions of a bismuth-silver thermocopule are maintained at 0ºC and 0.001ºC. Find the thermo-emf (Seeback emf)
developed. For bismuthsilver, a = –46 × 10–6 V/degand b = – 0.48 × 10–6V/deg2.
Ans. – 4.6 × 10–6 V
14. Find the thermo-emf developed in a copper-silver thermocouple when the junctions are kept at 0ºC and 40ºC. Use the data in table (33.1).
Ans. 1.04 × 10–6 V
15. Find the neutral temperature and inversion temperature of copper-iron thermocople if the reference juction is kept at 0ºC. Use the dat in table (333.1).
Ans. 330ºC, 659 ºC
16. Find the charge required to flow through an electrolyte to liberate one atom of (a) a monovalent material and (b) a divalent material.
Ans. (a) 1.6 × 10–19 C (b) 3.2 × 10–19 C
17. Find the amount of silver liberated at cathode if 0.500 A of current is passed through AgNO3 electrolyte for 1 hour. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g/mole.
Ans. 2.01 g
18. An electroplating unit plates 3.0 g of silver on a brass plate in 3.0 minutes. Find the current used by the unit. The electrochemical equivalent of silver is 1.12 × 10–6 kg/C.
Ans. 15 A
19. Find the time required to liberate 1.0 litre of hydrogen at STP in an electrolytic cell by a current of 5.0 A.
Ans. 29 minutes
20. Two voltameters, one having a solution of silver salt and the other of a trivalent-metal salt, are connceted in series and a current of 2A is
maintained for 1.50 hours. It is found that 1.00 g of the trivalent-metal salt, are connected in series and a current of 2A is maintained-metal is deposited.
(A) What is the atomic weight of the trivalent metal?
(B) How much silver is deposited during this period? Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g/mole.
Ans. (a) 26.8 g/mole (b) 12.1 g
21. A brass plate having surface area 200 cm2 on one side is electroplated with 0.10 mm thick a silver layers on both sides using a 15 A current.
Find the time taken to do the job. The specific gravity of silver is 10.5 and its atomic weight is 107.9 g/mol.
Ans. 42 minutes
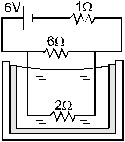
22. Figure (33-E2) shows an electrolyte of AgCl through which a current is passed. It is observed that 2.68 g of silver is deposited in 10 minutes
on the cathode. Find the heat developed in the 20 ohm resistor during this period. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g/mole.
Ans. 190 kJ
23. The potential difference across the terminals of a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 2 ohm drops to 10 V when it is connected to
a silver voltameter. Find the silver deposited at the cathod in half an hour. Atomic weight of silver is 107.9 g/mole.
Ans. 2 g
24. A plate of area 10 cm2 is to be electroplated with copper (density 9000 kg/m3) to a thickness of 10 micrometers on both sides, using a cell
of 12 V. Calculate the energy spent by the cell in the process of deposition. If this energy is used to heat 100 g of water, calculate the rise in the
temperature of the water. ECE of copper – 3 × 10–7 kg/C and specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg-K.
Ans. 7.2 kJ, 17 K