Solved Examples
1. Suppose the exact charge neutrality does not hold in a world and the electron has a charge 1% less in magnitude than the proton. Calculate the Coulomb force acting between two blocks of iron each of mass 1 kg separated by a distance of 1 m. Number of protons in an iron atom = 26 and 58 kg of iron contains 6 × 1026 atins.
Sol. Each atom of iron will have a net positive charge 26 × 0.01 × 1.6 × 10–19 C on it in the assumed world. The total positive charge on a 1 kg block would be

Worked out Examples
1. Figure shows two hydrogen atoms. Show on a separate diagram all the electric forces acting on different particles of the system.
Sol. Each particle exerts electric forces on the remaining three particles. Thus there exist 4 × 3 = 12 forces in all. Figure shows them.
2. Figure shows two rods each of length l placed side by side , with their facing ends separated by a distance a .
Charges +q, –q reside on the rods as shown. Calculate the electric force on the rod, A due to the rod B.
Discuss the case when l >>a, a>>l.
Sol. The force on the rod A due to the change +q of the rod B
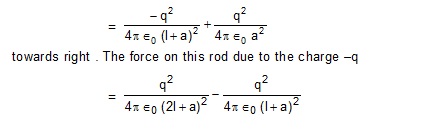
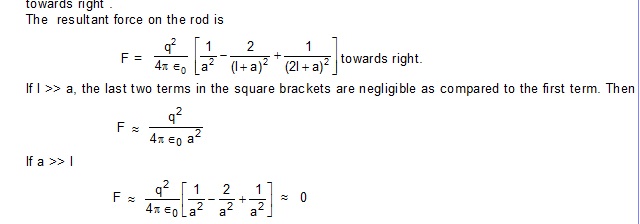
Two neutral objects placed far away exert only negligible force on each other but when they are
placed closer they may exert appreciable force.
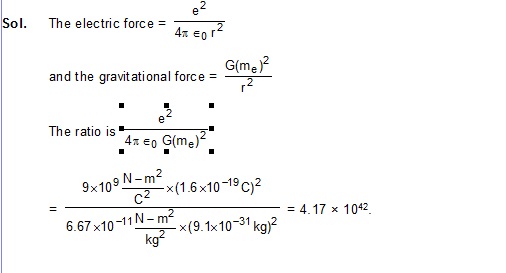
3. Calculate the ratio of electric to gravitational force between two electrons.
Questions for short answers
1. A body of mass m is placed on a table . The earth is pulling the body with a force mg. Taking this force to be the action , what is the reaction?
2. A boy is sitting on a chair placed on the floor of a room. Write as many action-reaction pairs of forces as you can
3. A lawyer alleges in court that the police has forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this?
4. When you hold a pen and write on your notebook, what kind of force is exerted by you on the pen? By the pen on the notebook? By you on the notebook ?
5. Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on ?
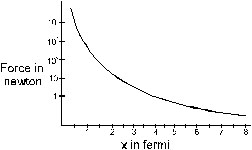
6. Suppose the magnitude of Nuclear force between two protons varies with the distance between them as shown in figure. Estimate the ratio “Nuclear force / Coulomb force” for (a) x = 8 fm (b) = 4 fm, (c) x = 2 fm, (d) x = 1 fm (1fm = 10–15 m.)
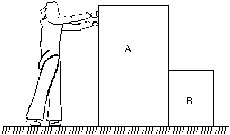
7. List all the forces acting on the block B in figure.
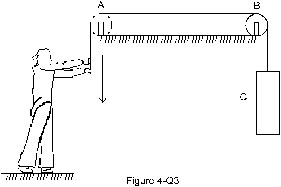
8. List all the forces acting on (a) the pulley A, (b) the boy and (c) the block C in figure.
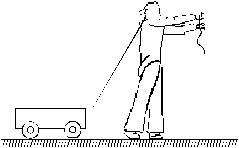
9. Figure shows a boy pulling a wagon on a road. List as many forces as you can which are relevant with this figure .
Find the pairs of forces connected by Newton’s third law of motion.
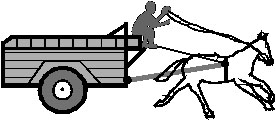
10. Figure shows a cart . Complete the table shown below.
Objective I
1. When Nells Bohar shook hand with Werner Heisenberg, what kind of force they exerted ?
(a) Gravitational (b*) Electromagnetic (c) Nuclear (d) Weak
2. Let E,G and N represents the magnitude of electromagnetic, gravitional and nuclear forces between two electrons at a given separation . Then
(a) N < E < G (b) E > N > G (c) G > N > E (d*) E > G > N
3. The sum of all electromagnetic forces between different particles of a system of charged particles is zero.
(a) Only if all the particles are positively charged.
(b) Only if all the particles are negatively charged.
(c) Only if half the particles are positively charged and half are negatively charged.
(d*) irrespective of the signs of the charges.
4. A 60 kg man pushes a 40 kg man by a force of 60 N. The 40 kg man has pushed the other man with a force.
(a) 40N (b) 0 (c*) 60N (d) 20N
Sol. Due to action reaction pair they will be equal in magnitude.
Objective II
1. A neutron exerts a force on a proton which is
(a*) gravitional (b) electromagnetic (c*) nuclear (d) weak
2. A proton exerts a force on a proton which is
(a*) gravitional (b*) electromagnetic (c*) nuclear (d) weak
3. Mark the correct statements :
(a) The nuclear force between two protons is always greater than the electromagnetic force between them.
(b*) The electromagnetic force between two protons is always greater than the gravitional force between them.
(c*) The gravitional force between two protons may be greater than the nuclear force between them.
(d*) The electromagnetic force between two protons may be greater than the nuclear force acting between them.
4. If all matter were made of electrically neutral particles such as neutrons,
(a*) there would be no force of friction. (b*) there would be no tension in the string
(c*) it would not be possible to sit on a chair (d) the earth could not move around the sun.
5. Which of the following systems may be adequately described by classical physics ?
(a*) motion of a cricket ball (b*) motin of a dust particle
(c) a hydrogen ato (d) a neutron changing to a proton.
6. The two ends of a spring are displaced along the length of the spring. All displacement have equal magnitudes.
In which case or cases the tention or compression in the spring will have a maximum magnitude ?
(a*) the right end is displaced toward right and the left end towards left.
(b) both ends are displaced towards right.
(c) both ends are displaced towards left.
(d*) the right end is displaced towards left and the left end towards right.
7. Action and reaction
(a*) act on two different objects (b*) have equal magnitude
(c*) have opposite directions (d*) have resultant zero.
Exercises
1. The gravitational force acting on a particle of 1 g due to a similar particle is equal to 6.67 × 10–17N.
Calculate the separation between the particles.
[Ans : 1m]
2. Calculate the force with which you attract the earth.
3. At what distance should two charges , each equal to 1C be placed so that the force between them equals your weight ?
4. Two spherical bodies, each of mass 50 kg, are placed at a sepration of 20 cm. Equal charges are placed on the
bodies and it is found that the force of Coulomb repulsion equals the gravitational attraction in magnitude of the
charge placed on either body.
[Ans : 4.3 × 10–9C]
5. A monkey is sitting on a tree limb. The limb exerts a normal force of 48N and a fractional force of 20N.
Find the magnitude of the total force exerted by the limb on the monkey.
[Ans : 52N]
6. A body builder exerts a force of 150N against a bullworker and compresses it by 20cm. Calculate the
spring constant of the spring in the bullworker.
[Ans : 750 N/M]
7. A satellite is projected vertically upwards from an earth station. At what height above the earth’s surface
will the force on the satellite due to the earth be reduced to half its value at the earth station?
(Radius of the earth is 6400 km.)
[Ans : 2650 km]
8. Two charged particles placed at a separation of 20 cm exert 20N of Coulomb force on each other.
What will be the force if the separation is increased to 25 cm ?
[Ans : 13N]
9. The force with which the earth attracts an objects is called the weight of the object. Calculate the weight
of the moon from the following data : The universal constant of gravitation G = 6.67 × 10–11 N–m2/kg2,
mass of the moon = 7.36 × 1022 kg, mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg, and the distance between the
earth and the moon = 3.8 × 105 km.
[Ans : 2 × 1020N]
10.Find the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force to the gravitational force between two protons.
[Ans : 1.24 × 1036]
11.The average separation between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state is 5.3 × 10–11m.
(a) Calculate the Coulomb force between then at the separation
(b) When the atom goes into its first excited state the average separation between the proton & electron
process to four times its value in the ground state what is the coulomb force in this state.
[Ans : (a) 8.2 × 10–8 N, (b) 5.1 × 10–9 N]
12.The geostationary orbit of the earth is at a distance of about 36000 km from the earth’s surface. Find the weight
of a 120-kg equipment placed in a geostationary satellite. The radius of the earth is 6400 km.
[Ans : 27N]