Example 39.1.
The peak value of an alternating current is 5 A and its frequency is 60 Hz. Find its rms value. How long will the current take to reach the peak value starting from zero?
Solution :
Therms current is
![]()
The time period is
![]()
The current takes one fourth of the time period to reach the peak value starting from zero. Thus, the time required is
![]()
Example 39.1
Find the reactance of a capacitor (C = 200 mF) when it is connected to (a) 10 Hz AC soiurce, (b) a 50 Hz AC source and (c) a 500 Hz AC source.
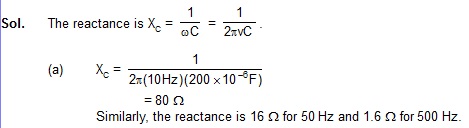
Example 39.2
An inductor (L = 200 mH) is connected to an AC source of peak current. What is the intantaneous voltage of the source when the current is at its peak value?
Sol. The reactance of the inductor is
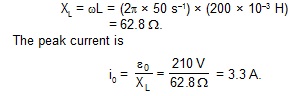
As tge current lags behind the voltage by p/2, the voltage is zero when the current has its peak value.
Example 39.3
An LCR series circuit with L = 100 mH, C = 100 mF , R = 120 W is connected to an AC source of emf = (30 V) sin (100 s–1) t. Find the impedance , the peak current and the resonant frequency of the circuit.
Sol. The reactance of the circuit is
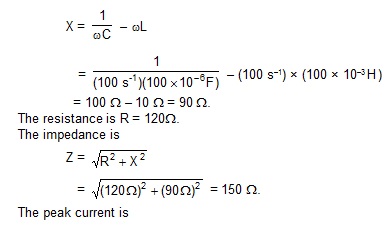

Questions for Short answer
1. What is the reactance of a capacitor connected to a constant DC source ?
2. The voltage and current in a series AC circuit are given by
V = V0 coswt and i = i0sinwt.
What is the power dissipated in the circuit ?
3. Two alternating currents are given by
![]()
Will the rms values of the currents be equal or different ?
4. Can the peak voltage across the inducator be greater than the peak voltage of the source in an LCR circuit ?
5. In a circuit conataining a capacitor and as AC source , the circuit is zero at the stant the source voltage is maximum. Is it consistent with Ohm's law ?
6. An AC source is connected to a capacitor . Will the rms current increase , decrease or remain constant if a dielectric slab is inserted into the capacitor ?
7. When the frequency of the AC source in an LCR circuit equals the resonant frequency , the reactance of the circuit is zero. Does it mean that there is no current through the inductor or the capacitor ?
8. When an AC source is connected to a capacitor there is a steady-state current in the circuit. Does it mean that the charges jump from one plate to the other to complete the circuit ?
9. A current i1 = i0 sinwt passes through a resistor of resistance R. How much thermal energy is produced in one time period ? A current i2 = – i0 sinwt passes through the resistor. How much thermal energy is produced in one time period ? If i1 and i2 both pass through the resistor simultaneously, how much thermal energy is produced ? Is the principle of superposition obeyed in this case ?
10. Is energy produced when a transformer steps up the voltage ?
11. A transformer is designed to concert an AC voltage of 220 V to an AC voltage of 12 V. If the input terminals are connected to a DC voltage of 220 V , the transformer usually burns . Explain.
12. Can you have an AC series circuit in which there is a phase difference of 1800 between the emf and the current ? 1200 ?
13. A resistance is connected to an AC source. If a capacitor is included in the series circuit , will the average power absorbed by the resistance increase or decrease ? If an inductor of small inductance is also included in the series circuit , will the average power absorbed increase or decrease further ?
14. Can a hot-wire ammeter be used to measure a direct current having a constant value ? Do we have to change the graduations ?
Objective - I
1. A capacitor acts as an infinite resistance for
(A*) DC (B) AC (C) DC as well as AC (D) neither AC nor DC
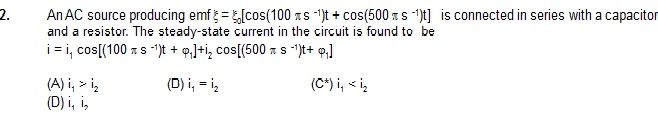
3. The peak voltage in a 200 V AC source is
(A) 220 V (B) about 160 V (C*) about 310 V (D) 440 V
4. An AC source is rated 220 V, 50 Hz. The average voltage is calculated in a time interval of 0.01 s. It
(A) must be zero (B*) may be zero (C) is never zero (D) is (220/Ö2)V
5. The magnetic field energy in an inductor changes from maximum value to minimum value in 5.0 ms when connected to an AC source. The frequency of the source is
(A) 20 Hz (B*) 50 Hz (C) 200 Hz (D) 500 Hz
6. Which of the following plots may represnet the reactance of a series LC combination ?
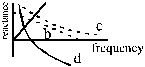
(D*)
7. A series AC circuit has resistance of 4 W and a reactance of 3 W. the impedence of the circuit is
(A*) 5 W (B) 7 W (C) 12/7 W (D) 7/12 W
8. Transformers are used
(A) in DC circuits only (B*) in AC circuits only
(C) in both DC and AC circuits (D) neither in DC nor in AC circuits
9. An alternating current is given by
![]() . The rms current is given by
. The rms current is given by
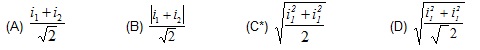
10. An alternating current having peak value 14 A is used to heat a metal wire. To produce the same heating effect, a constant current i can be used where is -
(A) 14 A (B) about 20 A (C) 7 A (D*) about 10 A
11. A constant current of 2.8 A exists in a resistor. The rms current is
(A*) 2.8 A (B) about 2 A (C) 1.4 A (D) undefined for a direct current
Objective - II
1. An inductor, a resistor and a capacitor are joined in series with AC source. As the frequency of the source is slightly increased from a very low value, the reactance
(A*) of the inductor increase (B) of the resistor increase
(C) of the capacitor increases (D) of the circuit increases
2. The reactance of a circuits is zero. It is possible that the circuit contains
(A*) an inductor and a capacitor (B) an inductor but no capacitor
(C) a capacitor but no inductor (D*) neither an inductor nor a capacitor
3. In an AC series circuit, the instantaneous current is zero when the instantaneous voltage is maximum. Connected to the source may be a
(A*) pure inductor (B*) pure capacitor (C) pure resistor
(D*) combination of an inductor and capacitor
4. An inductor-coil having some resistance is connected to an AC source. Which of the following quantities have zero average value over cycle ?
(A*) current (B*) induced emf in the inductor (C) Joule heat
(D) magnetic energy stored in the inductor
5. The AC voltage across a resistance can be measured using
(A) a potentiometer (B*) a hot-wire voltmeter
(C) a moving-coil galvarometer (D) a moving-magnet galvarometer
6. To convert machanical energy into electrical energy, one can use
(A*) DC dynamo (B*) AC dynamo (C) motor (D) transformer
7. An AC source rated 100 V (rms) supplies a current of 10 A (rms) to a circuit. The average power delivered by the source
(A) must be 1000 W (B*) may be 1000 W
(C) may be greater than 1000 W (D*) may be less than 1000 W
Worked Out Examples
Exercise
Q.1 Find the time required for a 50 Hz alternating current to change its value from zero to the rms value.
Ans : 2.5 ms
Q.2 The household supply of electricity is at 220 V rms value ) and 50 Hz Find the peak voltage and the least possible time in which the voltage can change from the rms value to zero.
Ans: 3.11 V, 2.5 ms
Q.3 A bulb rated 60 W at 220 V is connected across a household supply of alternating voltage of 220 V calculate the maximum instantaneous current through the filament.
Ans: 0.39 A
Q.4 An electric bulb is designed to operate at 12 volts. DC If this bulb is connected to an AC source and gives normal brightness what would be the peak voltage of the source ?
Ans: 1.7 volts
Q.6 The dielectric strength of air is 3.0 × 106 V/m A parallel plate air capacitor had area 20 cm and plate separation 0.10 mm. Find the maximum rms voltage of an AC source which can be safely connected to this capacitor.
Ans: 4.0 kj
Q.7 The current in a discharging LR circuit is given by i = io e–t/T where t is the time constant of the circuit calculate the rms current for the period t = 0 t = t
![]()
Q.8 A capacitor of capacitance 10 µF is connected to an oscillator giving an output voltage e = (10V)
sin wt Find the peak currents in the circuit for w = 10 s – 1 , 100 s– 1 , 500 s– 1 , 1000 s–1 .
Ans: 1.0 × 10 – 3 A, 0.01 A, 0.05 A, 0.1 A
Q.9 A coil of inductance 5.0 mH and negligible resistance is connected to the oscillator of the previous problem Find the peak currents in the circuit for w = 100 s– 1 , 500s– 1 , 1000s–1.
Ans: 20 A , 4.0 A, 0.20 A
Q.10 A coil has a resistance of 10 W and an inductance of 0.4 henry. It is connected to an AC source of
6.5 V , Hz Find the average power consumed in the circuit.
Ans: 5/8 W
Q.11 A resistor of resistance 100 W is connected to an AC source e = (12V) sin (250 p s– 1) t. Find the energy dissipated as heat during t = 0 to t = 1.0 ms.
Ans: 2.61 × 10 – 4 J
Q.12 In a series RC circuit with an AC source R = 300 W C =m 25µF eo = 50 V and v = 50/p Hz Find the peak current and the average power dissipated in the circuit.
Ans: 0.10 A, 1.5 W
Q.13 An electric bulb is designed to consume 55 W when operated at 110 volts It is connected to a 220 V , 50 Hz line through a choke coil in series. What should be the inductance of the coil for which the bulb gets correct voltage ?
Ans: 1.2 H
Q14. In a series LCR circuit with an AC source R = 300 W C = 20 µ F, L = 1.0 henry e0 = 50 V and v = 50/p Hz. Find (a) the rums current in the circuit and (b) the rms potential differences across the capacitor the resistor and the inductor. Note that the sum of the rms potential differences across the three elements is greater that the rms voltage of the source.
Ans: (a) 0.01 A (b) 50 V, 30 V 10 V
Q.15 Consider the situation of the previous problem find the average electric field energy stored in the capacitor and the average magnetic field energy stored in the coil .
25 mJ 5mJ
Q.16 An inductance of 2.0 H, a capacitance of 18µ F and a resistance of 10k W are connected to an AC source of 20 V with adjustable frequency (a) What frequency should be chosen to maximise the current in the circuit ? (b) What is the value of this maximum current ?
Ans: (a) 27 Hz (b) 2 mA
Q.17 An inductor-coil a capacitor and an AC source of rms voltage 24 V are connected in series When the frequency of the source is varied a maximum rms current of 6.0 A is observed If this inductor coil is connected to a battery of emf 12 V and internal resistance 4.0 W what will be the current?
Ans : 1.5 A
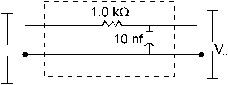
Q. 18 Figure shows a typical circuit for low-pass filter, An AC input Vi = 10mV is aplied at the left end and
the output Vo is received at the right end Find the output voltages for v = kHz 100 Hz, 1.0 MHz and 10.0 MHz Note that as the frequency is increased the output decreases and hence the name low -pass filter.
Q.19 A transformer has 50 turns in the primary and 100 in the secondary If the primary is connected to a 220 V DC supply, what will be the voltage across the secondary ?
Ans: zero