Light travels in a straight line. In vaccum or air, light travels with the velocity of 3 × 108 m/s.
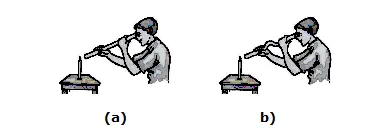
Activity : If we see at a lighted candle through a straight pipe as shown in figure(a), we are able to see the candle but if we see the candle through a
bent pipe we are not able to see the candle flame as shown in figure (b).
This activity showed that light travels along straight lines.
When light travelling in one medium falls on the surface of a second medium, the following three effects may occur.
(i) A part of the incident light is turned back into the first medium. This phenomenon is called reflection of light.
(ii) A part of the incident light is transmitted into the second medium along a changed direction. This phenomenon is called refraction of light.
(iii) The remaining third part of light energy is absorbed by the second medium. This phenomenon is called absorption of light.

When light rays are incident on an opaque polished surface (medium), these are returned back in the same medium.
This phenomenon of returning of ray of light in the same medium, is called reflection of light.
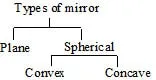
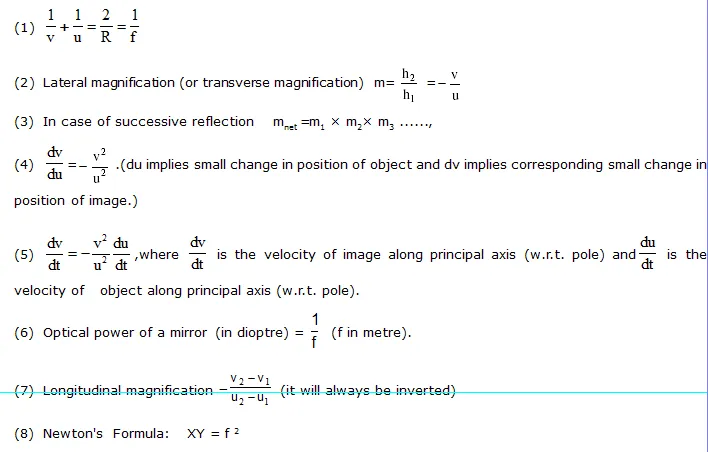
1.Types of mirror
2. Some Associated Terms
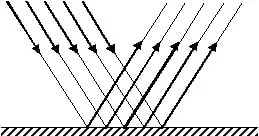
1. Regular Reflection :
In this reflection, parallel beam of light goes parallel after reflection from plane surface.
This reflection follows the laws reflection.
2. Irregular Reflection or Diffused Reflection :
In this reflection, parallel beam of light goes random after reflection from a rough surface.
This reflection also follows the laws of reflection.
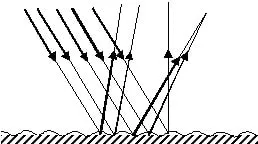
Irregular or diffused reflection
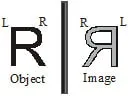
² There are two types of spherical mirrors:
(i) Concave mirror :
(ii) Convex mirror :
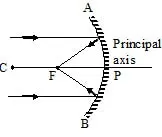
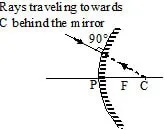
Ray diagram for image formation from concave mirror
(a) When the light ray incident parallel to the principal axis.
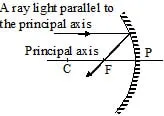
or
When the light ray incident towards focus.
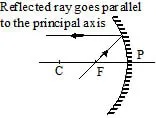
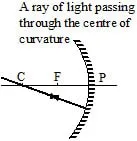
(b) When the light ray incident towards centre of curvature.
(c) When the light ray incident on the pole of the mirror.

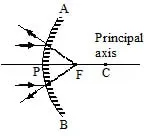
RULES FOR IMAGE FORMATION FROM CONVEX MIRROR
(a) When the light ray incident parallel to the principal axis.
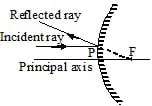
Or
When the light ray incident parallel to the principal axis.
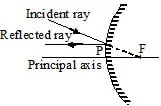
(b) When the light ray incident on the mirror directing towards centre of curvature.
REFRACTION OF LIGHT
When light rays travelling in a medium are incident on a transparent surface of another medium they are bent as they travel in second medium.
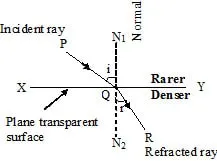
Refraction of light from a plane transparent denser surface.
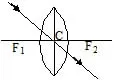
SPHERICAL LENS
A piece of a transparent medium bounded by at least one spherical surface, is called a spherical lens.
Types : There are two types of spherical lenses:
(i) Convex or Converging Lens : They are thick in the middle and thin at the edges.

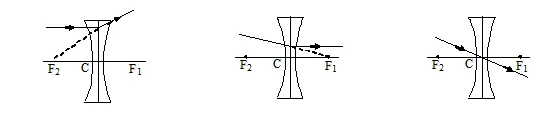
(ii) Concave or diverging Lens :
They are thinner in the middle and thin at the edges.
RAY DIAGRAM FOR IMAGE FORMATION FROM CONVEX LENS
1. When light ray incident parallel to principal axis.
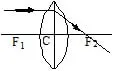
2. When light ray incident from focus.
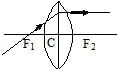
3. When light ray incident on the pole.
When light ray incident parallel to principal axis.
TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION
When light travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium and is incident at an angle more than the critical angle for that medium, it is completely returned
inwardly in the denser medium. This complete inward return of light is called total (complete) internal (inward) reflection (return).

Total internal reflection.
1. Definition : When a ray of white light (sunlight) enters a glass prism (denser medium). It emerges out from it broken into seven colours.
This phenomenon, due to which different components of a white light are separated by a denser medium, is called dispersion (separation).
2. Explanation : It is due to different velocities of different components of white light in the denser medium.
White light has seven colours, namely, violet indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red (remembered by the word ). In air (strictly in vacuum) light waves of all
colours have same velocity (3 × 108 m/s). But in a denser medium, their velocities become less and different. Red light waves, travel faVIBGYORstest and have
maximum velocity. Violet light waves, travel slowest and have minimum velocity in the denser medium.
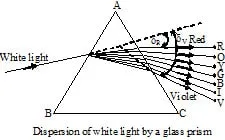
Due to difference in deviation, waves of different colours emerge out from the prism indifferent directions and are said to have been dispersed (separated).
When the dispersed white light is made to fall on a white screen, we get a seven coloured band or light. This coloured band is called spectrum.
Plane mirror:
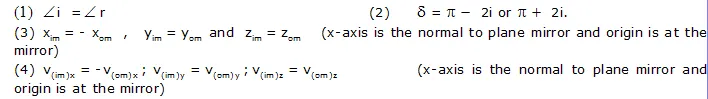
Spherical Mirror:
Refraction :

Lateral shift of light rays due to refraction through a parallel slab
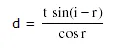
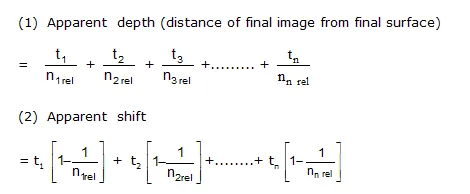
Apparent Depth and shift of Submerged Object:

Critical Angle For Total Internal Reflection

Prism:
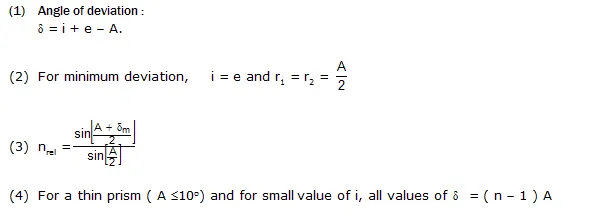
Dispersion.

(4) Dispersive power
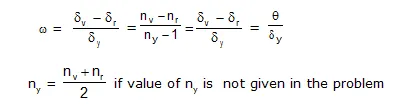
(5) Dispersion without deviation
.png)
Refraction at Spherical Surfaces
.png)
Thin Lens
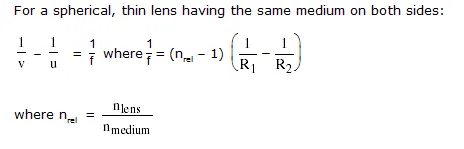
Transverse magnification (m)

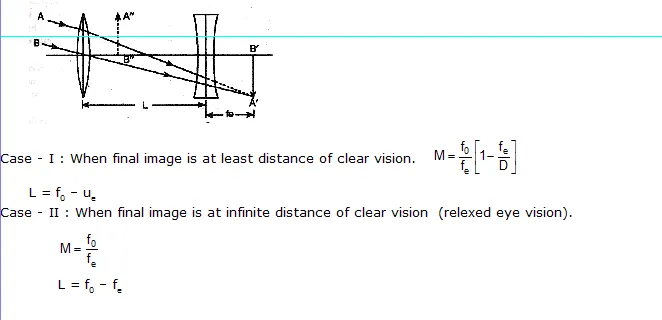
Magnifying power of microscope:

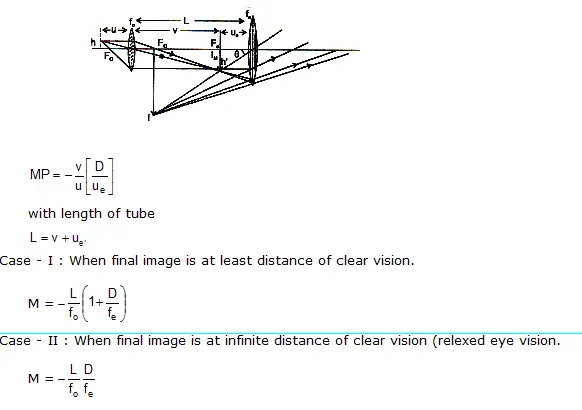
TELESCOPE
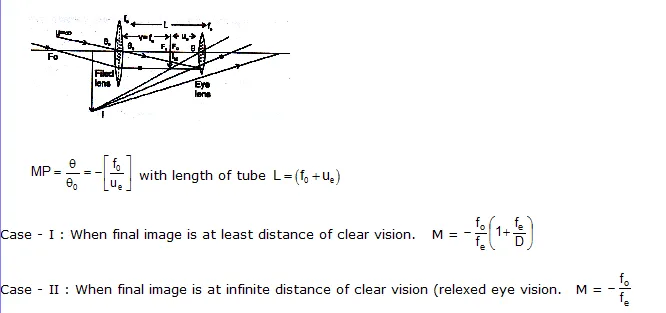
Terrestrial Telescope
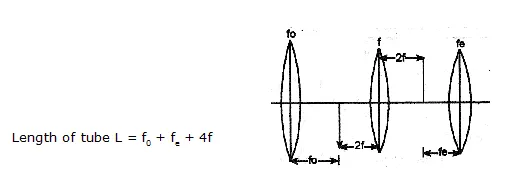
Galileo’s Telescope
Q.1 Write a short note on the rectilinear propagation of light ?
Q.2 What is the relation between the incident ray, the reflected ray and the surface of a plane mirror ?
Q.3 Explain three properties of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Q.4 You have a convex lens. Where will you place an object to see an erect and magnified image?
Q.5 An object is placed beyond the focus of a convex lens. What is the nature of the image-real or virtual, erect or inverted ?
Q.6 You have a concave mirror. Where will you place an object to see an erect and magnified image?
Q.7 An object is placed beyond the focus of a concave mirror. What is the nature of the image-real or virtual erect or inverted.
Q.8 Mention two uses of a concave mirror
Q.9 Write two uses of a convex lens.
Q.10 What is white light ?
Q.11 Why is the image formed by a pinhole inverted?
Q.12 What happens when parallel rays of light fall on a curved reflecting surface ?
Q.13 Why convex mirrors are used as rear view mirrors?
Q.14 What do you understand by the spectrum of white light ?
Q.15 Explain the formation of rainbow.
Q.16 Why does a Newton's disc appear white when it is rotated ?
Q.17 What are real and virtural images ? What are the differences between them ?
Q.18 What do you understand by the focus of a lens ? How will you find the focus of the convex lens ?
Q.19 What is refraction ? Explain with an example.
EXERCISE - II
Q.1 Which of these form virtual images only ?
(A) Concave mirror (B) Convex mirror
(C) Convex lens (D) None of these
Q.2 A drop of water on a leaf forms a magnified image of the veins because of-
(A) refraction
(B) reflection
(C) radiation
(D) rectilinear propagation
Q.3 If we mix lights of the colours of the rainbow, we will get
(A) pink light (B) brown light
(C) colourless light (D) black light
Q.4 If you bring a faraway object towards the focus of convex lens, the size of the image will-
(A) increase (B) decrease
(C) double (D) remain the same
Q.5 Which of these are due to the rectilinear propagation of light ?
(A) rainbow
(B) inverted image in a pinhole camera
(C) shadow
(D) reflection
Q.6 Light causes the sensation of-
(A) Vision (B) Light
(C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None
Q.7 Light is-
(A) an electromagnetic radiation
(B) a longitudinal wave
(C) massless
(D) all of the above
Q.8 Which of the following is a natural luminous source of light ?
(A) sun (B) wood
(C) electric lamp (D) torch
Q.9 Light shows -
(A) random propagation
(B) curvilinear propagation
(C) rectilinear propagation
(D) None of these
Q.10 Which of the following is a reflector of light ?
(A) Sun (B) Star
(C) Filament (D) Moon
Q.11 Wood is an example of-
(A) translucent (B) Transparent
(C) Polymer (D) Opaque
Q.12 If the angle of incidence is 50°, then calculate the angle between the incident ray and the reflected ray-
(A) 50° (B) 80°
(C) 130° (D) 100°
Q.13 Which of the following statement is true ?
(A) The angle of incidence is twice the angle of reflection
(B) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn at the same point of incidence lie in the same plane
(C) Some types of virtual images can be caught on the screen.
(D) A plane mirror forms a real image
Q.14 Two plane mirrors are inclined at a angle 60°, the number of images of an object which is placed between mirror will be-
(A) 4 (B) 3
(C) 5 (D) 6
Q.15 Plane mirror are arranged parallel to each other to get-
(A) A single image
(B) Two images
(C) A large number of reflected images
(D) No image
Q.16 When an object is moved towards the plane mirror-
(A) Image moves away from the object
(B) Size of the image increases
(C) Image moves closer to the object
(D) Size of the image decrease
Q.17 David is observing his image in a plane mirror. The distance between the mirror and his image is 5m. If he moves 1m towards the mirror, then
the distance between David and his image will be-
(A) 3 m (B) 5 m
(C) 6 m (D) 8 m
Q.18 The rear view mirror of a car is a plane mirror. A driver is reversing his car at a speed of
2 m/s. The driver sees in his rear view mirror the image of truck parked behind his car. The speed at which the image of the truck appears to approach the driver will be-
(A) 1 m/s (B) 2 m/s
(C) 4 m/s (D) 8 m/s
Q.19 For a concave mirror when the object is placed between the pole and the focus then the image formed will be-
(A) Virtual (B) Real
(C) Inverted (D) Diminished
Q.20 Mirror used to form magnified image is
(A) Concave mirror (B) Convex mirror
(C) Plane mirror (D) None of these
Q.21 A convex mirror always produces-
(A) an erect, real image of diminished size
(B) an erect, real image of enlarged size
(C) a virtual, erect image of enlarged size
(D) an erect, virtual image of diminished size
Q.22 A reflecting surface is curved inwards. Now the mirror formed is-
(A) concave (B) plane
(C) convex (D) none of these
Q.23 The phenomenon of the change in the path of the light as it passes from one optical medium to another is called-
(A) Reflection of the light
(B) Refraction of light
(C) Dispersion of light
(D) Both (A) and (B)
Q.24 Arrange the optical mediums in ascending order according to optically denser.
(A) Air, water glass
(B) Water, glass, air
(C) Glass, water, air
(D) Glass, air, water
Q.25 We put glass piece on a printed page image of prints on the page has same size. The piece is-
(A) Convex lens
(B) Glass slab
(C) Concave lens
(D) Prism
Q.26 What happens, when a ray incident at the optical centre ?
(A) It passes with deviation of 30° angle through the lens
(B) It passes undeviated through the lens
(C) It passes with deviation of 45° angle through the lens
(D) None of these
Q.27 If the lower part of a convex lens is blackened then the image formed will be
(A) incomplete
(B) complete
(C) of lower intensity
(D) both (B) and (C)
Q.28 Which of the following diagrams correctly represent the passage of a ray of light through a concave lens ?
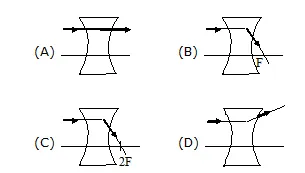
Q.29 White light spectrum contains-
(A) 5 colours (B) 7 colours
(C) 6 colours (D) No colour
Q.30 The diagram below shows two incident rays P and Q which emerge as parallel rays R and S. The appropriate device used in the box A is-
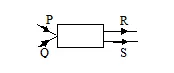
(A) convex lens (B) concave lens
(C) prism (D) concave mirror
1. B 2. A 3. C 4. A
5. C 6. A 7. A 8. A 9. C 10. D 11. D 12. D
13. B 14. C 15. C 16. C 17. D 18. B 19. A 20. A 21. D
22. A 23. B 24. A 25. B 26. B 27. D 28. D 29. B 30. B
Multiple Choice Questions :
1. The surfaces which cannot produce clear images are called :
(A) Rough surface (B) Ideal surfaces (C) Smooth surfaces (D) Curved surfaces
2. In order to be used as mirrors, glasses are coated with :
(A) Silver (B) Copper (C) Aluminium (D) Platinum
3. We are able to see objects because :
(A) They absorb light (B) They reflect light
(C) Total internal reflection takes place in them (D) All the light is refracted through them
4. The image formed by a plane mirror is :
(A) At the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it
(B) Laterally inverted
(C) Of the same size as that of the object
(D) All of the above
5. The phenomenon of light passing through the object is called :
(A) Reflection (B) Refraction (C) Dispersion (D) Total internal reflection
6. The phenomenon of light coming back after hitting a smooth plane surface is called :
(A) Reflection (B) Refraction (C) Dispersion
(D) Total internal reflection
7. The image formed by a plane mirror is :
(A) Virtual and smaller (B) Real and laterally inverted
(C) Real and the same size as that of the object (D) Virtual and same size as that of the object
8. Plane mirrors are arranged parallel to each other to get :
(A) A single image (B) Two image
(C) A large number of reflected image (D) No image
9. If the angle of incidence is 80°, what will be the angle of reflection with respect to the normal drawn perpendicular at the point of reflection ?
(A) 80° (B) 100° (C) 160° (D) 20°
10. The E.N.T doctor uses a :
(A) Convex mirror (B) Convex lens (C) Plane mirror (D) Concave mirror
11. When the angle between two plane mirrors is 60°, how many multiple images will be formed by the mirrors?
(A) 5 (B) 6 (C) 7 (D) 8
12. If the angle of incidence is 50°, then calculate the angle between the incidence ray and the reflected ray:-
(A) 50° (B) 100° (C) 130° (D) 80°
13. In our houses, we use a ............................... to look at ourselves :
(A) Convex mirror (B) Concave mirror (C) Convex lens (D) Plane mirror
14. The angle of incidence in a plane mirror is .............................. angle of reflection :
(A) Equal to (B) Greater than (C) Less than (D) None of these
15. ......................... are used in telescopes to reflect light :
(A) Concave mirrors (B) Convex mirrors (C) Plane mirrors (D) Convex lenses
16. When a light ray is reflected repeatedly by a set of parallel plane mirrors, the intensity of light ray decreases after some reflections. This is because of :
(A) Poor reflection from mirrors
(B) Absorption of some amount of light by mirrors
(C) Dispersion of light when the rays travel through the atmosphere
(D) Scattering of light by the mirrors
17. The perpendicular drawn at any point on a mirror is called :
(A) Incident ray (B) Reflected ray (C) Normal (D) Image
18. Which of the following statements is true ?
(A) The angle of incidence is twice the angle of reflection
(B) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence lie in the same plane
(C) Some types of virtual images can be obtained on of the screens
(D) A convex mirror forms real image
19. When the distance between the object and the plane mirror increases :
(A) The image remains same
(B) The size of the image will become less than the size of the object
(C) The distance between the image and the plane mirror increases
(D) The distance between the image and the plane mirror decreases
20. In lateral inversion :
(A) Right of the object will be right side of the image
(B) Left side of the object will be left side of the image
(C) Upside of the object will be down side of the object
(D) Right side of the object will be left side of the image
21. In a periscope, the reflecting mirrors will be :
(A) Perpendicular to each other (B) Parallel to each other
(C) At an angle of 45° (D) At an angle of 60°
22. The nature of image formed on the retina of human eye is :
(A) Virtual and erect (B) Virtual and inverted (C) Real and erect (D) Real and inverted
23. The presistance of the eye is only for :
(A) 1/10th of second (B) 1/12th of second
(C) 1/16th of second (D) 1/20th of second
24. The outer layer of the eye is called :
(A) Cornea (B) Sclerotic (C) Choroid (D) Retina
25. The part which protects the human eye is called
(A) Cornea (B) Choroid (C) Retina (D) Blind spot
26. The 'pupil' in human eye can be dilated by :
(A) Retina (B) Choroid (C) Optic nerve (D) Iris
27. Which of the following statement about human eye is not true ?
(A) The iris gives a distinct colour to the eye
(B) The yellow spot is extermely sensitive to light
(C) The space between lens and cornea is filled with celiary muscles
(D) The optic nerves enters the eye near the blind spot
28. Cataract is a condition of eye when :
(A) Eye sight becomes fogsy (B) Eye lens becomes cloudy
(C) There is a loss of vision (D) All of the above
29. Nocturnal animals like owl & bat have :
(A) Large cornea (B) Large pupil
(C) Retina with large number of rods (D) All of the above
30. Night blindness occurs due to deficiency of which vitamin ?
(A) A, (B) B, (C) C, (D) D,
31. The Braille code used by blind people use dot patterns for words. How many dot patterns or characters are used for this code ?
(A) 52, (B) 63, (C) 48, (D) 26,
Previous Contest Questions
32. Which of the following letters will be seen without any change in a plane mirror ?
(A) S (B) T (C) L (D) P
33. An ideal mirror :
(A) Absorbs all the amount of light incident on it
(B) Refracts all the light
(C) Reflects all the light (D) None of the above
34. Plane mirrors are arranged at an angle to get a number of coloured images in :
(A) Periscope (B) Kaleidoscope
(C) Telescope (D) Thermoscope
35. A series of fast moving still pictures can create an illusion of movement because :
(A) The eye can focus on very rapidly changing pictures
(B) Eye is quicker than the brain
(C) Eye can separate two image only when the interval of separation between them is one-tenth of a second
(D) The optical cortex can see through the rapidly moving images
36. Internal reflections of light is prevented in human eye by :
(A) Iris (B) Pupil
(C) Choroid (D) Blind spot
37. For a normal eye, in case of an adult, the least distance of distinct vision is :
(A) 5 to 8 cm (B) 10 to 15 cm (C) 20 to 25 cm (D) 30 to 35 cm
38. The human eye part which can be used again and again for forming different images is called
(A) Iris (B) Pupil (C) Cornea (D) Retina
39. The image formed by the eye lens on the retina is :
(A) Real, upright and enlarged (B) Real, upright and diminished
(C) Real, inverted and diminished (D) Virtual, inverted and diminished
40. Power of accomodation of eye implies :
(A) Control intensity (B) Prevent internal reflection of light
(C) Change of focal length of eye lens (D) All of the above
41. When a ray of light enters glass from water, it bends :
(A) Towards the normal due to decrease in the speed of light
(B) Towards the normal due to increase in the speed of light
(C) Away from the normal due to increase in the speed of light
(D) Away from the normal due to decrease in the speed of light
42. The velocity of light in glass is :
(A) 1.98 × 108 m/sec (B) 2.00 × 108 m/sec
(C) 1.66 × 108 m/sec (D) 1.09 × 108 m/sec
43. Eye piece of telescope forms a :
(A) Real image (B) Virtual image
(C) Both the above (D) None of the above
44. In hypermetropia, the image of near object is formed :
(A) On the retina (B) Before the retina
(C) Behind the retina (D) Above the retina
45. In order to get a parallel beam of light from a point source of light, we should use :
(A) A concave mirror (B) A convex mirror (C) A plane mirror (D) A parabolic mirror
46. Diopter is a unit of :
(A) Microscope (B) Telescope
(C) Power of lens (D) Eye sight
47. Angle of deviation is between :
(A) Incident and emergent ray (B) Plane of reflection and plane of incidence
(C) Real and virtual image (D) None of the above
48. The image of an object formed by a convex lens when that object is placed beyond the focal length is :
(A) Virtual and inverted (B) Real and inverted
(C) Virtual and magnified (D) Real and magnified
49. The distance between the lens and the focal point is called :
(A) Point of incidence (B) Refractive index
(C) Focal length (D) Plane of incidence
50. If a lens diverges a parallel beam of light, the lens is :
(A) Concave (B) Convex
(C) Parabolic (D) Cylindrical
1. A 2. A 3. B 4. D
5. B 6. C 7. D 8. C
9. A 10. D 11. A 12. B
13. D 14. A 15. C 16. B
17. C 18. C 19. C 20. D
21. B 22. D 23. C 24. B
25. A 26. D 27. C 28. D
29. D 30. A 31. B 32. B
33. C 34. B 35. C 36. C
37. C 38. D 39. C 40. C
41. A 42. C 43. B 44. C
45. D 46. C 47. A 48. B
49. 50. A
Study Material © 2023 All Rights Reserved.