1. C 2. D 3. A 4. C 5. D 6. D 7. A 8. B 9. B 10.C
11.A 12.B 13.A 14.D 15.A 16.B 17.A
1. Which of the following materal allows light to pass through it?
(A) Copper (B) Wood
(C) Rubber (D) Glass
2. The sun in the early morning can cause a building to form a shadow. This shadow will be
(A) Fat (B) Long
(C) thin (D) Short
3. We can see objects in a bright room be- cause
(A) The objects give off light to the air
(B) the Objects reflect the light falling on them.
(C) The objects send light away from our eyes.
(D) Our eyes give off light to the objects
4. WHich of the following characteristics is not exhibited by the shadow of an object?
(A) Right side up
(B) Same colour as objects
(C) Can be formed on a screen
(D) Can be bigger than the objects
5. The object that does not give out light on its own is the
(A) Star
(B) Lighted matchstick
(C) Light Bulb
(D) Shining mirror
6. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a virtual image formed in a plane mirror?
(A) Cannot be formed on a screen
(B) its is inverted
(C) It is same size as the object
(D) It is laterally inverted
7. Sunlight can pass through
(A) Walls (B) Bushy trees
(C) Rocks (D) Water
8. WHich of the following are translucent mate rials?
(i) Air (ii) Ground glass
(iii) Clouds (iv) Aluminium sheet
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (i) and (iii) (D) (ii) and (iv)
9. Anushka put some tea into four cups made of paper, glass, metal and porcelain, respectively. WHich one of these cups will allow her to see the level of the tea clealy?
(A) Paper cup (B) Metal cup
(C) Glass Cup (D) Porcelain Cup
10. Which of these things cannot give off its own light?
(A) A torch (B) A lamp
(C) The Moon (D) The sun
11. As the sun rise in the sky, the shadow of a building
(A) Lengthens (B) Shortens
(C) Widens (D) Darkens
12. The Plane mirror forms a
(A) Virtua image (B) Real Image
(C) Inverted Image (D) Magnified image
13. Which of tghe followig will produce diffuse reflection of light?
(i) Plane Mirror (ii) Piece of paper
(iii) Still water in lake (iv) Leather bag
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (i) and (iii) (D) (ii) and (iv)
14. A device containing two plane mirrors whcih gives us a higher view than normal is
(A) Stethoscope (B) Microscope
(C) Periscope (D) Telescope
15. There is light on the earth even on a dark, cloudy day. This is becasue clouds are
(A) Opaque (B) Transparet
(C) Manslucent (D) Luminous
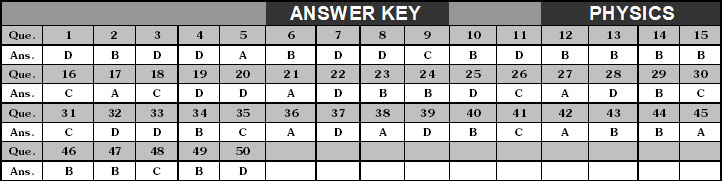
ANSWER KEY
1. D 2. B 3. B 4. B 5. D 6. B 7. D 8. B 9. C 10. C
11. B 12. A 13. D 14. C 15. C
1. A fish looking up through the water sees the outside world contained in a circular horizon. If the refractive index of water is 4/3 and the fish is 12 cm below the surface, the radius of the circle is
(A) 12 × 3 × cm (B) 12 × 3 × cm (C) 12 × cm (D) 12 × cm
2. When white light enters a transparent medium such as glass
(A) all wavelength components travel with same speed.
(B) the large wavelength component travels with maximum velocity.
(C) the short wavelength component travels with maximum velocity.
(D) there is no relation between wavelength and speed.
3. Total internal reflection takes place when light is incident
(A) on a concave mirror.
(B) from air on a plane glass surface at any angle.
(C) from air on a plane glass surface at a certain given angle.
(D) from inside a glass cube placed in water at a certain given angle.
4. When monochromatic light passes from vacuum to a material medium and vice versa; which of the following characteristics of light beam does not change?
(A) velocity (B) intensity (C) wavelength (D) frequency
5. If there were no atmosphere on earth, the duration of day light will
(A) decrease (B) increase (C) remain unchanged (D) become infinite
6. A piece of glass when immersed in a transparent solution of refractive index 3.1 becomes almost invisible. The refractive index of glass used is
(A) zero (B) 3.1 (C) 1.48 (D) infinite
7. A transparent rectangular block 5.0 cm thick is placed on a black dot. The dot when viewed from above is seen 2.0 cm from the bottom of the block. The refractive index of the material of the block is
(A) (B) (C) (D)
8. When light transmitted through one medium is incident on the surface of another medium
I. No light is reflected at the boundary.
II. Some of the light is absorbed by the second medium.
III.The speed is reduced if the second medium is rarer relative to the first.
IV. The speed is reduced if the second medium is denser relative to the first.
(A) I and II only are correct (B) II and III only are correct
(C) II and IV only are correct (D) I and IV only are correct
9. At night a lamp is moved up and down above the surface of a pond containing water of refractive index 4/3. When the lamp is 2 m above its surface, its image by refraction appears to coincide with the bottom of the pond. The depth of the pond is
(A) 8/3 m (B) 2 m (C) 1.5 m (D) 1 m
10. A light source is placed at the bottom of a water tank 1 metre deep. It is found that a circle of illuminated surface is formed at the top of the tank. The radius of this circle is
(A) 1.0 m (B) 1.13 m (C) 1.25 m (D) 1.51 m
11. The minimum distance between an object and its real image formed by a convex lens of focal length f is :-
(A) f (B) 2f (C) 3f (D) 4f
12. The double convex shaped air bubble in water will behave as a
(A) convex lens (B) concave lens (C) cylindrical lens (D) plane mirror
13. A lens of power +2D is put in contact with a lens of power – D, the combination will serve as
(A) a converging lens of focal length 50 cm.
(B) a converging lens of focal length 100 cm.
(C) a diverging lens of focal length 50 cm.
(D) a diverging lens of focal length 100 cm.
14. An object is placed at a distance equal to 2f from a concave lens, the image formed will be at
(A) 2f (B) (C) f (D)
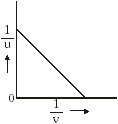
15. In an experiment to measure the focal length of a converging lens, object distance u and corresponding image distance v are measured. 1/u is plotted against 1/v to obtain the graph below. The focal length of the lens can be determined as
(A) the slope of the graph.
(B) the reciprocal of the slope.
(C) the intercept on either axis.
(D) the reciprocal of the intercept on either axis.
16. The nature of the u-v graph for a converging lens is part of a
(A) circle (B) parabola (C) hyperbola (D) straight line
17. A convex lens of focal length 15 cm is placed in contact with a plane mirror and a candle is placed at the focal plane of the lens. The image produced will be
(A) real and 15 cm in front of the mirror. (B) virtual and 15 cm in front of the mirror.
(C) real and 30 cm in front of the mirror. (D) virtual and 30 cm in front of the mirror.
18. A convex lens has a focal length of 10 cm. When it is immersed in water it will behave as
(A) a convex lens of 10 cm focal length.
(B) a concave lens of 10 cm focal length.
(C) a convex lens of focal length greater than 10 cm.
(D) a convex lens of focal length less than 10 cm.
19. A convex lens forms a virtual image of an object placed at 15 cm from the lens. The focal length of the lens can be :
(A) 2 cm (B) 8 cm (C) 15 cm (D) 18 cm
20. Two thin lenses are in contact and the focal length of the combination is 80 cm. If the focal length of one of the lenses be 20 cm, the power of the other lens is
(A) 1.66 dioptre (B) 4.00 dioptre (C) –1.00 dioptre (D) –3.75 dioptre
21. A locality is photographed from an aeroplane flying at a height 2000 m with a camera having an objective of focal length 50 cm. The size of the film in the camera is 18 cm x 18 cm. The area of ground that can be photographed at one time will be
(A) 0.52 km2 (B) 1.0 km2
(C) 1.52 km2 (D) 4.0 km2
22. Astigmatism is corrected with the help of
(A) concave spherical lens (B) convex spherical lens
(C) bifocal lens (D) cylindrical lens
23. A person is said to be short-sighted if
(A) the person cannot see things clearly when they are placed near the eye.
(B) the rays from a distant object are focussed before they reach the retina.
(C) the eye ball is too short.
(D) the retina does not work efficiently.
24. In case of a compound microscope
(A) the image produced by the eyepiece is real.
(B) the image produced by the objective lies inside the focal length of the eyepiece.
(C) the eyepiece has a shorter focal length than the objective.
(D) the magnification which can be produced is unlimited.
25. Which of the following is NOT paired correctly?
(A) Solar furnace-concave mirror (B) Rear-view mirror-convex mirror
(C) Magnifying glass-convex lens (D) None of these
26. Which of the following statements about defects of vision is/are correct?
I. For a long-sighted person, close objects appear blurred.
II. For a short-sighted person, distant objects appear blurred.
III.Short-sight is corrected by converging lenses.
(A) I only (B) II only (C) I and II only (D) II and III only
27. In case of astronomical telescope
I. the focal length of the object lens is greater.
II. the focal of the object lens and the eye-piece coincide at the time of normal adjustment.
III.the distance between the lenses cannot be adjusted.
(A) I and II only (B) I and III only (C) II and III only (D) I only
28. A short-sighted person cannot see distinctly beyond 50 cm from his eye. The power in dioptre of spectacle lenses which will enable him to see distant objects clearly is
(A) +50 (B) –50 (C) +2 (D) –2
29. A simple telescope consisting of an objective of focal length 60 cm and a single eye lens of focal length 5 cm is focussed on a distant object in such a way that the parallel rays emerge from the eye lens. If the object subtends an angle of 2° at the objective, the angular width of the image is
(A) 50° (B) 24° (C) 10° (D) 1/6°
30. A poster has a red letter P on a white background. When it is viewed through a blue transparent screen, an observer would see a
(A) Magenta P on a blue background. (B) Magenta P on a blue-green background.
(C) Black P on a blue background. (D) Black P on greenish-white background
31. A red and a green pencil are taken in a room illuminated with green light. In the room.
(A) both pencils will appear dark.
(B) pencils will appear as red and green respectively.
(C) red pencil will appear dark and green pencil green.
(D) red pencil will appear red and green pencil dark.
32. The sky is blue because
(A) there is more blue light in the sunlight.
(B) of the scattering of sunlight by air molecules in the atmosphere.
(C) of the scattering of sunlight by dust particles in the atmosphere.
(D) other colours are absorbed by heavenly bodies.
33. The sky is blue because
(A) solar radiation is predominantly blue. (B) air absorbs all light except blue light.
(C) air emits blue light. (D) air scatters blue light.
34. The colour of light is determined by its
(A) wavelength (B) frequency (C) velocity (D) amplitude
35. Which of the following is not common in sound and light?
(A) diffraction (B) refraction (C) polarisation (D) interference
36. Through a soap film different colours are seen by white light because of the phenomenon of
(A) interference (B) dispersion (C) diffraction (D) reflection
37. Two separate sources giving out light of same frequency do not produce interference because
(A) the amplitudes of the waves from the sources are different.
(B) the two sources are not close to each other.
(C) the waves are not travelling in the same direction.
(D) the phase difference between the waves produced by two sources is changing continuously.
38. When two waves superpose each other, the algebraic addition takes place in
(A) amplitude (B) intensity (C) frequency (D) wavelength
39. Two waves of same frequency but having amplitudes 4 cm and 3 cm superpose in same direction. The ratio of the maximum intensity to the minimum intensity at various places will be
(A) 4 : 3 (B) 16 : 9 (C) 7 : 1 (D) 49 : 1
40. Sunlight filtering through a tree often makes circular patches on the ground because
(A) the sun is round.
(B) of diffraction effects.
(C) light is transmitted as a wave motion.
(D) the space through which light penetrates is round.
41. A red rose is viewed in yellow light. It will appear
(A) red (B) yellow (C) orange (D) black
42. A swimming pool appears to be 2 m deep. Its actual depth is (m for water = 1.33)
(A) 2.66 m (B) 2 m (C) 2.34 m (D) 2.54 m
43. Light travels with a speed of 2 × 108 ms–1 in crown glass of refractive index 1.5. The speed of light in dense flint glass having a refractive index 1.8 is
(A) 1.33 × 108 ms–1 (B) 1.67 × 108 ms–1 (C) 2.0 × 108 ms–1 (D) 3 × 108 ms–1
44. An illuminating object is placed between the plane mirrors mutually perpendicular to each other. The number of images formed is
(A) 7 (B) 3 (C) 4 (D) 6
45. The image formed by a concave mirror is virtual, erect and magnified. The position of object must be
(A) between the mirror and its focus (B) between focus and the centre of curvature
(C) at the centre of curvature (D) beyond the centre of curvature
46. An object is placed at a distance of 2f from a convex lens, the image formed will be at a distance of
(A) 2f (B) 2f/3 (C) f (D) f/3
47. An object 5 cm high is held 25 cm away from a convex lens of focal length 10 cm. The size of image will be
(A) 5/3 cm (B) 10/3 cm (C) 5 cm (D) 10 cm
48. Two lenses of focal lengths +100 cm and +5 cm are used to prepare an astronomical telescope. The minimum tube length will be
(A) 95 cm (B) 100 cm (C) 105 cm (D) 500 cm
49. The rainbow observed during the rainy season is due to
(A) reflection (B) dispersion (C) interference (D) diffraction
50. Ray optics is valid, when characteristic dimensions of the obstacle should be -
(A) Of the same order as the wavelength of light (B) Much smaller than the wavelength of light
(C) Of the order of one millimetre (D) Much larger than the wavelength of light