INTRODUCTION
All living things require air. We have not seen air but we must have felt its presence in so many ways. For example, when the leaves of the trees rustle or the clothes hanging on a clothes line sway.
#IS AIR PRESENT EVERYWHERE AROUND US?
Air is present everywhere around us. It fills all the empty space . It has no colour and one can see through it. It is transparent.
The presence of air can be felt by a simple experiment.
Activity :
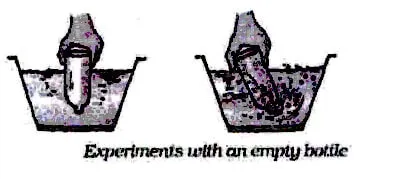
Take an empty glass bottle. Turn it upside down. Now dip the open mouth of the bottle into a bucket filled with water as shown in the figure. We observe that water does not enter the bottle.
Now tilt the bottle slightly. We observe that now water enters the bottle and we can see bubbles coming out of the bottle with a bubbly sound. This shows that air was present in the bottle. The bottle was not empty at all. In fact it was filled completely with air even when it is upside down. That is why water does not enter the bottle when It is pushed in an inverted position as there was no space for air to escape.
When the bottle was tilted the air was able to come out in the form of bubbles and water filled up the empty space that the air has occupied.
#WHAT IS AIR MADE UP OF ?
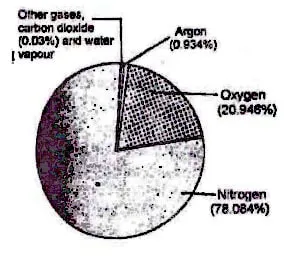
Air is a mixture of several gases, water vapour and fine dust particles. A human being respires about 22,000 times everyday and takes in about 16 kg of air. Air contains mainly nitrogen, oxygen and smaller amounts of argon, carbon dioxide, water vapours and traces of helium, neon, krypton and xenon.
ATMOSPHERE
The transparent , thick and invisible envelope of air surrounding us is called atmosphere. It consist of a uniform mixture of permanent gases called dry air and varying amounts of other materials including organic and inorganic impurities such as smoke, pollen grains and dust particles.
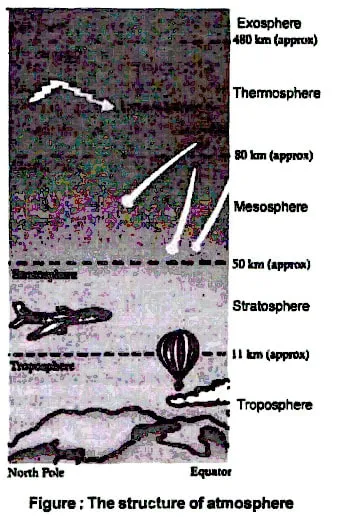
The atmosphere is divided in various layers to facilitate the study of it.
The different layers of atmosphere (starting from the surface of earth) are troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere.
Troposphere : This is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. It extends to a height of about 11 km above the earth's surface. All weather phenomena, such as clouds, fog, rainfall, snowfall, storms and lightning occur here.
Stratosphere; This layer lies above the troposphere and it extends to a height of about 50km above the earth's surface. There are virtually no clouds and very little dust and water vapour convection. The stratosphere contains Ozone which absorbs the harmful ultraviolet radiation of the sun .
Mesosphere: The layer lies above the stratosphere and it extends to a height of about 80km above the earth's surface.
Thermosphere : Thts layer lies above the mesosphere and it extends up to a height of 480 km. This layer contains electrically charged particles called 'Ions' so it is also called Inosphere. These particles reflect radio waves back to the earth's surface and unable us to have wireless communication.
Components of atmosphere
Water Vapour: Moisture is present as water vapour In the atmosphere. Water vapour rise high up into the atmosphere and get cooled to form clouds. These bring rain both on land and oceans. Snow is produced in cooler regions. The water vapour control the climatic conditions. The presence of moisture can be felt in our daily life. When air comes in contact with a cool surface, it condenses and drops of water appear on the cooled surface. This shows that waler is present in air.
Oxygen: Oxygen is extremely important for the survival of organisms as organisms respire in it. Requirement of oxygen is an essential condition for burning of a substance hence it plays an important role in combustion. The presence of oxygen in air can be felt by a simple experiment.
Activity: Fix two small candles of the same size in the middle of two shallow containers. Now, fill the containers with some water. Light the candles and then cover eacl1 one of them with an inverted glass (one much taller than the other) as shown in the figure.
Burning can occur only in the presence of oxygen. We see that, one component of air is oxygen. Now, the amount inside each glass in our experiment, is limited. When most of this oxygen is used up by the burning candle, It can no longer burn and blows out. Also, water rises up In the glass once the candle blows oul.
Nitrogen : In the above activity we observe that a maJor part of air is still present in the glass bottle even after the candle below out. This indicates the presence of some component in the air, which does not support burning.
Carbon dioxide: In a closed room, if there is some material that is burning, we feel suffocation. This is due to excess of carbon dioxide that may be accumulating in the room, as the burning continues. Carbon dioxide makes up a small component of the air around us. Plant and animals consume oxygen for respiration and produce carbon dioxide. Plant and animal matter on buming. also consume oxygen and produce mainly carbon dioxide and a few other gases.
It occurs in carbohydrates, fats, proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes and hormones. Carbon dioxide molecules reflect back the heat radiations and help the earth not to radiate heat very rapidly at night. Carbon dioxide partially dissolves in water and helps in the formation of carbonate salts. These give taste to natural water. Carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis.
Dust and smoke : The buming of fuel also produces smoke. Smoke contains a few gases and fine dust particles and is often harmful. Dust particles are always present in air.
Activity : Close all the doors and windows with curtains pulled down in a sunny room to make the room dark. Now, open the door or a window facing the sun, just a little, in such a way that it allows sunlight to enter the room only through a slit. We see some tiny shining particles moving In the beam of sunlight. This shows that air contains dust particles. The presence of dust particles in air varies from time to time, and from place to place. We inhale air when we breathe through our nostrils. Fine hair and mucus are present inside the nose to prevent dust particles from getting into the respiratory system.
We may conclude, then, that air contains some gases, water vapor and dust particles. The gases in air are mainly nitrogen, oxygen small amount of carbon dioxide, and many other gases. However, there may be some variations in the composition of air from place to place. We see that air contains mostly nitrogen and oxygen. In fact, these two gases together make up 99% of the air. The remaining 1% is constituted by carbon dioxide and a gew other gases, water vapour and dust partiicles.
#HOW ODES OXYGEN BECOME AVAILABLE TO ANIMALS AND PLANTS LIVING IN WATER AND SOIL?
The animals and plants living in water take in the oxygen dissolved In water.
The presence of dissolved oxygen in water can be felt by a simple experiment.
Activity: Take some water in a beaker and heat it slowly on a tripod stand . Heat it before it begins to boil. Now carefully look at the inner surface of the beaker. We see tiny bubbles on the inside. These bubbles come from air dissolved in water when we heat it, the air dissolved in it begins to escape and we see bubbles in water. The organisms that live in soil also need oxygen to respire. If we take a lump of dry soil In a beaker and add water in it, we can observe bubbles coming out of soil. This shows the presence of air in soil.
The plants and animals that live inside the soli respire in this air. A lot of burrows and holes are formed in deep soil by the animals living in the soil. These burrows also make spaces available for air to move in and out of soil. However, when it rains heavily water fills up all the spaces occupied by the air in soil. In this situation animals living in the soil have to come out for respiration .
This is why earthworms come out of soil during rainy season .
OTHER IMPORTANT USES OF AIR
1. Wind mill : Moving air is called wind. Wind makes the windmill rotate. The wind mill is used to draw water from tubewells and to run flour mills. They are also used to generate electricity.
2. Air helps in sailing yachts, gliders, parachutes and aeroplanes.
3. Birds, bats and insects can fly due to the presence of air.
4. Air also helps in dispersal of seeds and pollens of flowers and several plants.
5. Air plays an important role in water cycle.

OBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following is second layer of atmosphere?
(A) Troposphere (B) Stratosphere
(C) Mesosphere (D) Thermosphere
2. Which of the following is a variable component of air ?
(A) Nitrogen (B) Oxygen
(C) Water vapour (D) Carbon dioxide
3. The atmospheric layer nearest the earth's surface is the
(A) stratosphere (B) ionosphere
(C) troposphere (D) mesosphere
4. Which of the following represents correct order of abundance of various gases in air?
(A) Nitrogen> Oxygen> Carbon dioxide> Argon
(B) Nitrogen> Oxygen> Argon> Carbon dioxide
(C) Oxygen > Nitrogen> Carbon dioxide> Argon
(D) Carbon dioxide> Nitrogen> Oxygen > Argon
5. The constituent of air that supports combustion is
(A) oxygen (B) nitrogen
(C) carbon dioxide (D) (A) and (B) both
6. Which gas makes up major part of the air?
(A) Nitrogen (B) Argon
(C) Helium (D) Krypton
7. Nitrogen is used
(A) in electric bulbs.
(B) as a refrigerant.
(C) in preserving tinned foods.
(D) all are correct.
8. The percentage composition of oxygen in air is
(A) th of the volume
(B) of the above volume
(C) of the volume
(D) rd of the volume
9. Oxygen is consumed from atmosphere in the following process
(A) combustion of fuel.
(B) absorbed by green plants during photosynthesis.
(C) biological fixation by symbiotic bacteria.
(D) cultivation of land.
10. Photosynthesis by plant releases :
(A) CO (B) CO2
(C) N2 (D) O2
11. If burning splinter is taken close to the gas jar filled with oxygen, taken gas formed is -
(A) sulphur dioxide (B) nitrogen dioxide
(C) carbon dioxide (D) carbon monoxide
12. In which of the following cities would there be maximum water vapour in the air on a sunny day in December?
(A) Srinagar (B) Delhi
(C) Bhopal (D) Mumbai
13. Air is a/an -
(A) element (B) compound
(C) mixture (D) None of these
14. Which of the following component of air cannot be taken directly by plants?
(A) Oxygen (B) Nitrogen
(C) Carbon dioxide (D) None of these
15. Wind mill is used -
(A) to run flour mills
(B) to generate electricity
(C) to draw water from tubewells
(D) All of these
SUBJECTIVE QUESTIONS
1. What is the composition of air?
2. What is the role of air in water cycle?
3. What is photosynthesis?
4. Why are inert gases named so ?
5. Name the components of air which do not support combustion?
6. Which gas in the atmosphere is essential for respiration.
1. B 2. C 3. C 4. A 5. A 6. A 7. C 8. C 9. A 10. D
11. C 12. D 13. C 14. B 15. D
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
(a) All living things require air to breathe. (b) We can feel air but we cannot see it.
(c) Moving air makes it possible to fly a kite. (d) Air is present everywhere but not in soil.
2. Wind does not help in the movement of which of the following?
(a) Firk (b) Weather cock
(c) Ceiling fan (d) Sailing yacht
3. What is not true about air?
(a) It makes the windmill rotate. (b) It helps in the movements of aeroplanes.
(c) Birds can fly due to presence of air. (d) It has no role in water cycle.
4. Mountaineers carry oxygen cylinders with them because
(a) there is no oxygen on high mountains.
(b) there is deficiency of oxygen on mountains at high altitude.
(c) oxygen is used for cooking.
(d) oxygen keeps them warm at low temperature.
5. Boojho took an empty plastic bottle, turned it upside down and dipped its open mouth into a bucket filled with water. He then tilted the bottle slightly and made the following observations.
(i) Bubbles of air came out from the bottle.
(ii) Some water entered the bottle.
(iii) Nitrogen gas came out in the form of bubbles and oxygen got dissolved in water.
(iv) No bubbles formed, only water entered the bottle.
Which observations is/are correct?
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (iv) only (c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) only
6. Which of the following components of air is present in the largest amount in the atmosphere?
(a) Nitrogen (b) Oxygen (c) Water vapour (d) Carbon dioxide
7. The components of air which are harmful to living beings are
(a) nitrogen and carbon dioxide. (b) dust and water vapour.
(c) dust and smoke. (d) smoke and water vapour.
8. Usha took a lump of dry soil in a glass and added water to it till it was completely immersed. She observed bubbles coming out. The bubbles contain
(a) water vapour (b) only oxygen gas
(c) air (d) none of these
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
9. State whether the following statements are true or false. If false, correct them.
(a) Plants consume oxygen for respiration.
(b) Plants produce oxygen during the process of making their own food.
(c) Air helps in the movements of sailing yachts and glider but plays no role in the flight of birds and aeroplanes.
(d) Air does not occupy any space.
10. In a number of musical instruments, air plays an important role. Can you name some such instru ments?
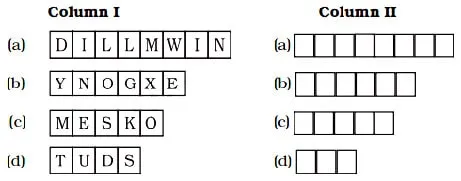
11. In the boxes of Column I the letters of some words got jumbled. Arrange them in proper form in the boxes given in Column II
12. Make sentences using the given set of words.
(a) 99%, oxygen, nitrogen, air, together
(b) Respiration, dissolved, animals, air, aquatic
(c) Air, wind, motion, called
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
13. A list of words is given in a box. Use appropriate words to fill up the blanks in the following state ments
Air, oxygen, wind, water vapour, mixture, combination, direction, road, bottles, cylinders.
(a) The ______ makes the windmill rotate.
(b) Air is a ______ of some gases.
(c) A weather cock shows the ______ in which the air is moving at that place.
(d) Mountaineers carry oxygen ______ with them, while climbing high mountains.
14. Observe the picture given in Fig. 1.1 carefully and answer the following questions.
(a) What is covering the nose and mouth of the police man?
(b) Why is he putting a cover on his nose?
(c) Can you comment on air quality of the place shown in the Fig.1.1?
15. Garima observed that when she left her tightly capped bottle full of water in the open sunlight, tiny bubbles were formed all around inside the bottle. Help Garima to know why it so happened?
16. Match the items of Column I with the items of Column II
Column I Column II
(a) Weather cock (i) Gases and fine dust particles
(b) Mountaineers (ii) Sailingyacht
(c) Fine hair inside the nose (iii) Oxygen cylinders
(d) Smoke (iv) Direction of air flow
(e) Wind (v) Prevent dust particles
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
17. Explain the following observations very briefly
(a) A firki does not rotate in a closed area.
(b) The arrow of weather cock points towards a particular direction at a particular moment.
(c) An empty glass in fact is not empty.
(d) Breathing through mouth may harm you.
18. Write just a few sentences for an imaginary situation if any of the following gases disappear from the atmosphere
(a) oxygen (b) nitrogen (c) carbon dioxide
19. Paheli kept some water in a beaker for heating. She observed that tiny bubbles appeared before the water started to boil. She boiled the water for about 5 minutes and filled it in a bottle up to the brim and kept the bottle air tight till it cooled down to room temperature.
(a) Why did the tiny bubbles appeared?
(b) Do you think tiny bubbles will appear on heating the water taken out from the bottle? Justify your answer.
20. On a Sunday morning Paheli’s friend visited her home. She wanted to see some flowering plants in the nearby garden. Both of them went to the garden. While returning from the garden they also observed some flowering plants on the road side. But to their surprise they found that the leaves and flowers of these roadside plants were comparatively very dull. Can you help them to know why?
ANSWER KEY
1. d 2. c 3. d 4. b 5. a 6. a 7. c 8. c