INTRODUCTION
The living organisms as well as the nonliving things are made of matter. Anything that is made of matter has mass and occupies space. Thus, everything around us, whether living or nonliving, has mass and occupies space. The smallest particles of matter are molecules. These particles constitute living beings and nonliving things. But that is where the similarity between the living and nonliving ends. The structural unit of water is a molecule of water. A cup of water is simply billions of molecules of water. This is not true for living organism. Though a living being is also made of molecules, just those molecules put together do not make an organism. The most basic unit, or structural unit, of an organism is the cell. Every living organism starts from a cell, which divides and redivides to give rise to the organism.
HABITAT AND ADAPTATION
(a) Habitat :
The term habitat refers to the surroundings where organisms live. Every habitat is home for a certain living creature. Plants and animals have different features that help them to survive in their own habitat.
The components in a habitat are broadly classified into two types. they are biotic and abiotic.
Biotic components include all the livings organisms in a habitat. Abiotic components include all the non-living things in a habitat. These include air, rocks, water, sunlight and heat. All livings things depend on the abiotic components for all their needs. The abiotic components are very useful for the survival of the biotic components in a habitat. For example, sprouting is the first step where a new plant grows from a seed. The sprouting such as air, water, light and heat.
· The population of some species of turtles has declined due to the change in the earth’s temperature.
· Some popular theories believe that dinosaurs became extinct because of the changes in the earth’s temperature millions of years ago.
· Habitat can be terrestrial or aquatic :
The surroundings where organisms live is called a habitat. The organisms depend for their food, water, air, shelter and other needs on their habitat. Habitat means a dwelling place (a home). Several kinds of plants and animals may share the same habitat.
The plants and animals that live on land are said to live in terrestrial habitats. Some examples of terrestrial habitats are forests, grasslands, deserts, coastal and mountain regions. On the other hand, the habitats of plants and animals that live in water are called aquatic habitats.
(b) Adaptation :
Plants and animals develop certain features or certain habits that help them survive in their surroundings, and this is known as adaption. Different living creatures adapt to their habitats in different ways. For example fish have gills that help them to live in water and use the oxygen dissolve in it. Plants that live in water have special tissues that help to take in dissoved gas from water. For example the ulva has ribbon-like leaves. It takes thousands of years for a livings being to adapt to its habitat.
Adaptation in different habitats :
[A] Terrestrial Habitats :
(i) Deserts : Desert is a water deplete area so basically plants and animals are adapted for
little less of water.
· Desert animals include camel, rats and snakes.
· To stay away from the intense heat during the day, rats and snakes stay in burrows deep in the sand.
They come out only during the night, when it is cooler.
· Camel’s nostrils have long hairs to prevent the entry of sand and dust. They have no
sweat glands in their skin.
· Desert plants lose very less little water through transpiration.
· Desert plants-either have no leaves or they have small or spine shaped leaves to reduce
transpiration.
· Photosynthesis is usually carried out by stems.
· The stem is covered with a thick waxy layer which helps it to retain water.
· They have deep roots for absorbing water.
(ii) Mountain regions : They are normally very cold and windy. ln some places, snowfall may take
place during winter.
· The leaves of some trees are needle-like so that snow and rain water can slides off easily.
· Animals have thick skin or fur to protect them from cold.
· Yaks have long hair to keep them warm.
(iii) Grasslands
· Lion lives in grassland.
· Its light brown colour helps it to hide in dry grasslands when it hunts for prey.
· A deer has strong teeth for chewing hard plant stems.
· It has long ears to hear the movement of the predators.
· The eyes on the side of its head allow it look in all directions for danger.
· The speed of the deer helps them to run away from the predators.
[B] Aquatic Habitats :
(i) Oceans :
· Sea animals like squid and octopus stay near the seabed and catch any prey that move
towards them. When they move in water, they make their body shapes streamlined.
· Generally aquatic animals have gills to help them use the oxygen dissolved in water.
· Dolphins and whales do not have gills. They breathe in air through nostrils or blowholes that are
located on the upper parts of their heads. This allows them to breathe in air when they swim
near the surface of water.
· They can stay inside the water for a long time without breathing.
(ii) Ponds and Lakes
· Roots of plants are much reduced in size and their main function is to hold the plant in place.
· The stem is long, hollow and light.
· The stems grow upto the surface of water while the leaves and flowers float on the surface of water.
· Some plants are totally submerged in water, ie, all parts of the plant grow under water. These
plants have narrow and thin ribbon like leaves.
Through highly divided leaves, the water can easily flow without damaging them.
· They can bend in the flowing water.
· Frogs have ponds as their habitat.
· It can stay both inside the pond water as well as on land.
· They have strong back legs that help them in leaping and catching their prey.
· They have webbed feet which help them swim in water.
CHARACTERSTICS OF LIVING THINGS
1. Movement 2. Growth 3. Food
4. Respiration 5. Excretion 6. Responsiveness
7. Reproduction 8. Life cycle
1. Movement : Both plants and animals show movement.
Movement of animals is very easy to make out — they walk, run, swim or fly. Such movement
are called locomotion. During locomotion, the entire body of an animal moves fro one place to
another. They do so mainly to gather food and to avoid enemies. Just as cows move about in
search of grass. When disturbed, a frog jumps into the water, and so on. Plants do not move
from one place to another. But they show movement of their parts. It you touch a leaf of the
sensitive plant (Lajwanti), it droops. After a few minutes, the wilted leaf recovers and stands erect.
Sunflower always turns towards the sun. There are many plant which fold their leaves or close
the petals of their flowers at night and reopen next morning.
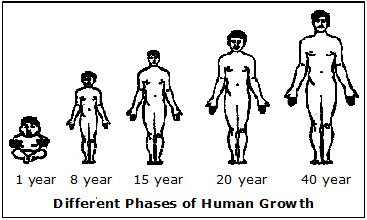
2. Growth (From tiny to big) : When you were born, you were a small baby. Through the years,
you have grown. Now you are a grown-up boy or girl, and in years to come, you will be an adult human.
Your bones become longer, muscles become larger and the amount of blood in your body increases. \\ \
A tiny chick hatches from the egg. It gradually grows in size to become a mature hen. All
animals grow only upto a certain age. Full grown plants do not grow taller every year, they only
produce new branches and leaves, and their trunks grow thicker. Growth in plants is faster and
easier to observe
3. Food : All living beings need food to acquire energy. This energy is utilized by them to carry out
their activities. Green plants are called autotrophs as they make their own food. They take in
simple things like carbon dioxide and water and prepare their food the form of starch. Energy
needed int his process, comes from sunlight. Animals and non-green plans are called
heterotrophs as they take thier food directly or indirectly from plants.
4. Respiration (Release of energy) : Whey you are doing some exercise or running fast, the
muscles of your body need more energy. This energy is provided by the “burning” of food. The
process of release of energy by the burning of food in your body is called respiration. We obtain
oxygen for “burning” the food through the air we breathe in. All living beings, plants and
animals, breathe. Animals breathe through the nose and plants by minute pores on their leaves
and stem.
5. Excretion (Removal of poisonous wastes) : Body activites of all organisms produce certain
nitrogenous waste substances. These are usually poisonous and must be thrown out the body.
This is called excretion. The excretion in animals is usually in the form of urine. Plants throw out
their waste products in the form of gums and resins, etc. with the help of special cell or from
the entire plants surface.
6. Responsiveness (Sensitivity) : Stimulus is a happening in the surroundings which affects the
individual. The reaction which an individual shows to the stimulus is called responsiveness.
Light, sound, heat, smell touch pressure, etc. are example of various stimuli. All living beings,
plant or animal react to stimuli.
7. Reproduction (Produce off springs) : If an organism simply lived and ultimately died, its race
would come to an end. To continue their race, all living beings tend to produce their young ones.
Seeds, produced by plants, germinate and give rise to new plants. You also know that a cow
gives birth to a calf and a bird lays eggs which produce chicks. Thus, all the plants and animals
reproduce and give birth to their own kind.
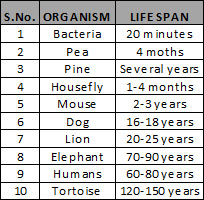
8. Life Cycle : Living things follow a life cycle. They start their life form a single cell. In case of
animals, the life cycle consists of birth, growth, reproduction and death. In plants, life cycle of
an organism may take a few hours, a few days or hundreds of years to complete. The period
during which an organism completes its life cycle is called its life span. In case of bacteria, for
example, the life span is very short.
· Are there things in between living and non living :
Yes, viruses are such entities existing in the universe. Viruses grow and multiply only when they
are inside living things like man. Outside living bodies, they are lifeless and are just like a
crystal.


OBJECTIVE TYPE
1. Xerophytes have
(A) Small roots (B) Long roots (C) broad leaves (D) Many branches
2. Which of these are herbivores ?
(A) Girraffe (B) Polar bear (C) Fox (D) Lion
3. Examples of adptation for food include
(A) gills in fish (B) spines in cacti
(C) Long neck in girraffe (D) Long legs in camel
4. All living organisms have the ability to produce young one of their own kind. The process is called.
(A) Excretion (B) Reproduction (C) Movement (D) Respiration
5. When an organism develops certain features / characters to be adjuste better in the environment the process is called.
(A) Adaptation (B) Stimulus (C) Response (D) Reproduction
6. Abiotic components are
(A) water and bacteria (B) air and soil.
(C) birds and bees (D) bacteria and soil
7. An example of aquatic plant is
(A) acacia (B) cactus (C) hydrilla (D) ber
8. Whales and dolphins breathe in air through
(A) blowholes (B) lungs (C) gills (D) skin
9. The aquatic animal that shows absence of streamlined shape is
(A) octopus (B) fish (C) dolphin (D) whale
10. Whales and humans, both being mammals respire through lungs. However whales can hold itself in water for a long time but humans cannot because
(A) whales respire under water
(B) whales can take more oxygen at a time
(C) structure of whales and humans is different
(D) whales have one more organ for respiration.
SUBJECTIVE TYPE
1. What is a habitat ? Give one example of a fresh water habitat.
2. Mention the biotic & Abiotic component of habitat.
ANSWER KEYS
1. B 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. A
6. B 7. C 8. A 9. A 10. B
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
1. Which of the following cannot be called a habitat?
(a) A desert with camels.
(b) A pond with fishes.
(c) A jungle with wild animals.
(d) Cultivated land with grazing cattle.
2. Following are some features of plants
(i) They lose a lot of water through transpiration.
(ii) Their leaves are always broad and flat.
(iii) They lose very little water through transpiration.
(iv) Their roots grow very deep into the soil.
Which of the combination of above features are typical of desert plants?
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (iii) and (iv)
3. Boojho comes across an animal having a stream-lined and slippery body. What is the habitat of the animal?
(a) Water (b) Desert (c) Grassland (d) Mountain
4. Which of the following are characteristics of living beings ?
(i) Respiration
(ii) Reproduction
(iii) Adaptation
(iv) Excretion
Choose the correct answer from the options below:
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv) only (b) (i) and (ii) only
(c) (ii) and (iv) only (d) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv)
5. Earthworms breathe through their
(a) skin (b) gills (c) lungs (d) stomata
6. Which of the following is not an example of response to stimulus?
(a) Watering in mouth when we see delicious food items.
(b) Closing of leaves of mimosa plant when touched.
(c) Shutting our eyes when an object is suddenly thrown in our direction.
(d) A chick hatching out of an egg.
7. Which of the following is correct for respiration in plants?
(a) Respiration takes place only during day time.
(b) Respiration takes place only during night.
(c) Respiration takes place both during day and night.
(d) Respiration takes place only when plants are not making food.
8. Which of the following is an incorrect statement about excretion?
(a) Excretion takes place in plants.
(b) Excretion takes place both in plants and animals.
(c) Excretion is the process of getting rid of excess water only.
(d) Secretion is one method of excretion.
9. Choose the set that represents only the biotic components of a habitat.
(a) Tigr, Deer, Grass, Soil (b) Rocks, Soil, Plants, Air
(c) Sand, Turtle, Crab, Rocks (d) Aquatic plant, Fish, Frog, Insect
10. Which one of the following is not associated with reproduction?
(a) A new leaf coming out of a tree branch.
(b) A dog giving birth to puppy.
(c) A seed growing into a plant.
(d) Chick hatching from an egg.
11. Choose the odd one out from below with respect to reproduction.
(a) Eggs of hen (b) Seeds of plants
(c) Buds of potato (d) Roots of mango tree
12. Although organisms die, their kind continue to live on earth. Which characteristic of living organisms makes this possible?
(a) Respiration. (b) Reproduction. (c) Excretion. (d) Movement.
13. If you happen to go to a desert, what changes do you expect to observe in the urine you excrete? You would
(i) excrete small amount of urine. (ii) excrete large amount of urine.
(iii) excrete concentrated urine. (iv) excrete very dilute urine.
Which of the above would hold true?
(a) (i) and (iii) (b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv) (d) (i) and (ii)
VERY SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
14. Unscramble the given words below to get the correct word using the clues given against them.
(a) SATPADAOINT specific features or certain habits which enable a living being to live in its surroundings
(b) RETECOXNI Waste products are removed by this process
(c) LUMISIT All living things respond to these
(d) ROUCDPRENTOI Because of this we find organisms of the same kind
15. Using the following words, write the habitat of each animal given in Fig. 2.1 (a to d).
Fig. 2.1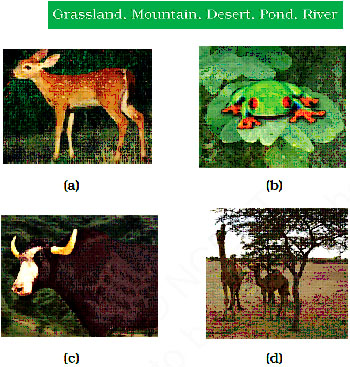
16. Classify the following habitats into terrestrial and aquatic types.
17. Why is reproduction important for organisms?
18. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Saline water, hot air and sand are ................ components of a habitat.
(b) The habitat of plants and animals that live in ................is called the aquatic habitat.
(c) ................ enable a plant or an animal to live in its surroundings.
(d) Plants and animals that live on land are said to live in ................ habitats.
SHORT ANSWER QUESTIONS
19. Paheli has a rose plant in her garden. How can she increase the number of rose plants in the garden?
20. Why do desert snakes burrow deep into the sand during the day?
21. Write the adaptation in aquatic plants due to which
(a) submerged leaves can bend in the flowing water.
(b) leaves can float on the surface of water.
22. Mention one adaptation present in the following animals:
(a) In camels to keep their bodies away from the heat of sand.
(b) In frogs to enable them to swim.
(c) In dolphins and whales to breathe in air when they swim near the surface of water.
23. Some desert plants have very small leaves whereas some others have only spines. How does this benefit the plants?
24. What are the specific features present in a deer that helps it to detect the presence of predators like lion?
25. Read the features of plants given below:
(a) Thick waxy stem
(b) Short roots
(c) Cone shaped plants
(d) Sloping branches
(e) Small or spine-like leaves
(f) Hollow stem
Choose the type of plant for every feature given in a, b, c, d, e and f from the list given below:
Aquatic plant, Desert plant, Mountainous plant
LONG ANSWER QUESTIONS
26. Like many animals although a car also moves it is not considered as a living orgainism. Give 2-3 reasons.
27. What are the adaptive features of a lion that helps it in hunting?






Juhi
the relation between the living organism as well as the organism and their surrounding is called
Aryan
Hy