INTRODUCTION
In our country, an individual eats food 3 - 4 times a day. The food consumed at a particular time of the day constitute a meal. For example, food taken in the morning constitute a meal called the breakfast.
Similarly, foods eaten in the afternoon are a part of lunch, and those eaten in the evening or night is the dinner.
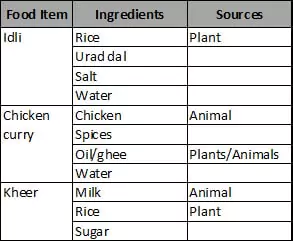
Ingredients in Food ltems : Food items may be eaten raw or cooked. Raw food items include fruits like banana or apple. Just a single material or ingredient forms the food item in the above example. Think of cooked food items like rice, dal, roti or chapati and vegetable curry.
These food items may consist of two or more ingredients as given.
WHY DO WE NEED FOOD ?
Food is required by the body for the following purposes.
(i) For energy requirement to perform various functions of body to sustain life.
(ii) For growth : You have seen yourself growing. Without proper food, your growth would not be possible.
(iii) For repair of damaged or injured body parts ; when you get hurt, your skin is damaged and the blood is lost. Repair of such damaged parts takes place by the addition of new cells.
(iv) For protection from diseases and infection.
FOODS EATEN BY LIVING ORGANISMS
All living things need food. Most plants can manufacture their own food. Animals, however, require ready-made food and thus they eat either plants or other animals. Different animals eat different kinds of food.
You must have seen earthworms burrowing in the soil. They swallow soil. Mosquitoes suck the blood of other animals. Mosquito causing malaria sucks the blood of man. Birds feed on small insects, worms and fruits. On the basis of their food habit, animals are of three types :
(i) Herbivores : Animals which eat plants and plant products — these are called herbivores. e.g.
Cow, sheep, deer elephant etc.
(ii) Carnivores : Animals which eat flesh of other animals are called carnivores. e.g. Lion, Tiger,
Fox, Wolf etc.
(iii) Ommivores : Animals eating both plants and animals are called omnivores e.g. Humans, crow,
squirrels and cockroaches.
SOURCES OF FOOD
Both plants and animals provide us food (and a number of other useful products such as medicines, paper, timber and fibres.
Plants as Source of Food : Foods obtained from plants are of different types — cereals, pulses, vegetables, fruits, oils, sugar, tea, coffee and spices.
Plant Parts and Animal Products as Food
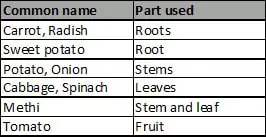
Plants are one source of our food. Which parts of a plant?
We eat many leafy vegetables. We eat fruits of some plants. Sometimes roots, sometimes stems and even flowers. Have you ever eaten pumpkin flowers dipped in rice paste and fried?
Try it!
Some plants have two or more edible (eatable) parts. Seeds of mustard plants give us oil and the leaves are used as a vegetable. Can you think of the different parts of a banana plant that are used as food ? Think of more examples where two or more parts of a single plant are used as food.
(i) Cereals are the most important sources of food for man and animals. They are rich sources of
carbohydrates. Three most important cereals are wheat, rice and maize. These cereals are
obtained from grains (biologically, grains are fruits of a plant).
(ii) Pulses or Legumes (commonly called ‘dals’) are rich in proteins and are obtained from plants.
(iii) Vegetables : Are rich sources of vitamins, minerals and roughage. Water content in vegetables
is high (70 to 90 per cent) and their food value is low. The following list gives some common
vegetables along with the part used.
(iv) Fruits have high water content, low food value, but are rich in minerals and vitamins. ln
common usage, the term ‘fruit’ is used for those which are usually eaten without cooking.
Common fruits are banana, mango, apple, grapes, pineapple, guava, orange, litchi, and so on.
(v) Sugars are produced by the green plants through photosynthesis. Chief sugar producing plants
are sugarcane and sugarbeet.
In case of sugarcane, the plant used is the stem, while in sugarbeet, it is the root.
(vi) Tea and coffee are common beverages, Tea is obtained from leaves, while coffee is obtained
from seeds.
(vii) Spices have no food value and are used for adding flavour to food. Before the advent of
refrigeration, spices were also used for preserving foods.
The major spices produced are pepper (kali mirch), cardamon (ilaichi), ginger (adrak), turmeric
(haldi) and chillies (mirch).
Other spices of importance are cloves (loung), saffron (kesar), fennel (saunf), cumin (jeera),
coriander (dhania), asafoetida (heeng), fenugreek (methi), nutmeg (jaiphal) and thyme (ajwain).
(viii) Oils : Major oil yielding plants are cotton, groundnut, mustard, coconut, soyabean and sunflower.
Animals as Sources of Food : Animals provide us food in the form of milk, meat, fish, eggs and honey.
(i) Milk - yielding animals : Cow and buffalo.
(ii) Meat - yielding animals : Sheep, goat and pig.
Meat of pig is called pork.
(iii) Poultry animals : Birds like hen, duck and turkey.
Poultry products are rich sources of proteins and have right kind of fat for good health.
Animals which provide meat and egg are called poultry animals.
(iv) Fish : Fish is a major source of food rich in animal proteins. Fish proteins have high digestibility and growth-promoting value. Also, cod and shark liver oils are rich in vitamin - D. In india, fish are found both in fresh water (ponds, lakes and rivers) and sea water.
Fresh Water Fishes : Catla, Labeo, Cirrhina, Barbus, Mystus, Clarius.
Sea Water Fishes : Hilsa, cat fish, sardines, ribbon fish, red mullet, pomfret, bombay duck. Rearing and management of fish on a large scale is known as pisciculture. Fish are eaten in various forms – cooked, in dried form, pickled form and canned form.
(v) Honey bees : The insects which provide us honey are known as honey bees. The honey bees collect necter (sweet juice) from flowers, convert it into honey and store it in their nest, which is known as the beehive. A beehive has small compartments called as combs. The shape and size of the comb depends on the type of bees.
The rearing of honey bees on a large scale is known as apiculture. The place used for the rearing of honey bees is called an “apiary”. What is Honey ? Honey is produced by honey bees from the necter of flowers. It consists of water, sugar minerals and enzymes. It is an antiseptic (which destroys the growth of micro organisms) and is easily digestible. For this reason, honey is used in medicines.
Fodd habits of people : In our country, people of different states have different food habits. Food habits are affected by food production and supply. For example, rice is the common food in the south of lndia, while wheat is commonly eaten in the North. Let us know the food habits of people in different lndian states.
(i) Andhra Pradesh : Rice, dry vegetable preparation, arhar dal, upma, dosa rasam, curd, pickle etc.
(ii) Bihar : Rice chapati, sattu (flour of roasted gram), dal, bainagan ka bharta (brinjal preparation), bachka (thin slices of vegetales coated with besan), bhujya (of potato and oninon), pappad, chutni etc.
(iii) Gujarat : Chapati, rice dal, vegetable preparaton, lassi (buttermilk), thepla (fried chapatis made of wheat flour), dhokla, khandvi etc.
(iv) Punjab : Roti, parantha, missi roti, butter, lassi (buttermilk), pulses, curd, sarson ka saag, chole, gajar ka halwa, dahi bhalla etc.
(v) Rajasthan : Bajra, dalia, roti, dal, kachori, sev (a besan preparation), vadi (moong dal preparation), dal-bati.
(v) Tamil Nadu : Idli, dosa, rice sambhar, banana chips, etc.
Functions of food :
· Food provides energy.
· Food helps in growth and development.
· Food helps in the replacement of worn out tissues, repair of damaged cells and healing of wounds.
· Food protects the body against diseases.
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) : The smallest amount of energy that body needs to keep alive is called basal metabolic rate (BMR).
SOME STEPS TO AVOID WASTAGE OF FOOD
Food in our country is not available in sufficient quantity to all people. Some do not have enough money to buy. Because of this reason, these people suffer from diseases. So we must ensure the following :
1. Food that is produced should not be allowed to (i) get spoiled, or (ii) eaten away by animals like rats and squirrets.
2. We should eat only that much quantity of food which is required by our body. Excess eating will lead to obesity (growing fat).
3. In parties or even in our homes we should not leave food uneaten in our plates.
BALANCED DIET
· A balanced diet is one which provides proper amount and proportion of fats, carbohydrates, proteins, vitamins and minerals, needed for the growth and maintenance of the body. A balanced diet should have three main qualities :
1. It should be rich in essential nutrients like minerals and vitamins.
2. It should provide the exact amount of raw materials needed for growth, development, repair and replacement of body tissues.
3. It should provide the right amount of energy required by the body.
What Do Different Food Items Contain ?
Each dish is usually made up of one or more ingredients. which we get from plants or animals. These ingredients contain some components that are needed by our body. These components are called nutrients. The major nutrients in our food are named carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals. In addition, food contains dietary fibres and water which are also needed by our body.
CLASSIFICATION OF FOOD
· Food can be classified under three different categories on the basis of its functions :
(i) Energy giving food : Carbohydrates and fats, eg. cereals, sugars, oils, etc.
(ii) Body building food : Proteins, minerals and fats, eg. pulses, beans, milk, fish, etc.
(iii) Protective food : Vitamins & minerals, eg. vegetables, fruits, milk, etc.
BASIC CONSTITUENTS OF FOOD
(a) Carbohydrates : Carbohydrates are organic compounds of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
· They are the main source of energy in our body.
· One gram of carbohydrate yields about 4 kilocalories of heat energy.
· A major portion of our food consists of carbohydrates, e.g., rice, chapatis.
· If excess amount of carbohydrates are present in the body, they the converted into fats and stored under the skin and around various organs of the body.
Some examples of carbohydrates :
· Cellulose : It is the chief constituent of plant cell wall.
· Starch : It is main stored food of plants.
· Glycogen : It is main stored food of animals.
(i) Sources of carbohydrates : The carbohydrates in our food are obtained mainly from the plant
sources like wheat, rice, maize, potato etc.
(ii) Biological significance of carbohydrates :
· Carbohydrates serve as an important structural material in some animals and in all plants, where
they constitue the cellulose framework. e.g. cellulose in plants.
· Carbohydrates are used as respiratory fuel in animal cells.
· Some carbohydrates have highly specific functions e.g. ribose and deoxyribose in the nucle
oprotein of the cells, the lactose of milk.
· Starch, and sugars are the two carbohydrates which provide most of the energy to our body.
(b) Fats :
· Fats are composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen.
· They have a lower oxygen content than carbohydrates.
· They are very important sources of energy.
· One gram of fat yields 9 kilocalories of energy.
· A layer of fat under the skin helps to reduce the amount of heat loss from the body in cold
weather conditions.
· Every fat molecule consists of three molecules of fatty acids and one molecule of glycerol.
· Fats are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, ether, benzene, etc.
(i) Sources of fats : Fats are supplied to our body by different foods like butter, ghee,
cheese, groundnut etc. All the cooking oils (like ground-nut oil, coconut oil) provide us fats.
(ii) Biological significance of fats :
· Fat deposits under the skin to protect various tissues.
· It provides a steady source of energy.
· Fats also help in forming of cell membranes and other organelles.
· They help in transportation of fat-soluble vitamins in our body.
· Fat is deposited in more amount in persons those require more energy like growing
children and sportsmen etc.
(c) Proteins :
The name protein was coined by Berzelius in 1838.
· Chemically proteins are polymers of molecular units called as amino acids.
· The amino acids are linked together by a peptide bonds. There are about 20 amino acids that
take part in the formation of proteins. The 20 amino acids are further divided into two groups :
· Essential amino acids : They are also 10 in number. They are synthesized in a human body and
are obtained from food so they are called as essential amino acids. e.g., Methionine, Leucine
and tryptophan.
· Non-essential amino acids : They are also 10 in number. They are synthesized in a human body
& are thus termed as non – essential amino acids. e.g., Alanine, Asparagine, Aspartic acid and cystine.
(i) Sources of proteins : Pulses, peas, beans, nuts, cheese, milk are the important sources of proteins.
(ii) Biological significance of proteins :
· They act as a structural components of cell. They are essential for growth and repair of the body.
· They help to catalyze various reactions occurring in our body.
· They play important roles as hormones, antibodies, etc.
· All the enzymes are made up of proteins.
· Haemoglobin, the respiratory pigment of animals is a conjugated protein composed of globin
and haem (pigment).
(d) Vitamins :
Vitamins are organic compounds essential for the growth of the body. They are required by the body in very small quantities. Vitamins are classified into two types.
(A) Fat soluble Viamins A, D, E, K.
(B) Water soluble Viamins B and C.
(i) Source of Vitamin : These are obtained from fruits, cod liver etc.
(ii) Biological significance of Vitamin : They keep the body healthy and prevent it from diseases. If the diet does not contain the required amount of vitamins, it results in vitamin deficiency diseases.
(e) Minerals : Human body requires about fifteen different kinds of minerals, e.g.-
· Calcium and phosphorus are needed for the growth of bones and teeth.
· Iron is needed for the formation of haemoglobin in blood.
· Iodine, sodium, potassium and zinc are necessary for a good healthy body.
(i) Source of minerals : Meat, eggs, milk green vegetables and fruits are rich in minerals.
(ii) Biological singinificance of minerals : Minerals are required by the body in trace amounts and are essential for growth, repair and replacement processes. They from a major part of many body chemicals and tissues.
Besides these nutrients, our body needs dietary fibres and water. Dietary fibres are also known as roughage.
(f) Roughage : Cellulose forms the fibre content in food and that fibre content is called roughage. Roughage keeps the digestive system in good working condition.
(i) Source of Roughage : It is a plant fibre found in vegetables, fruits, peas, beans, maize and in the barn which surrounds wheat grains.
(ii) Biological significance of Roughage :
· It absorbs water and poisonous waste from food during digestion.
· It helps in the formation of urine and faeces.
· It regulates the body temperature.
· It is an essential part of blood and digestive juices.
TEST FOR CARBOHYDRATES, FATS & PROTEINS
(a) Test for carbohydrates :
Take few drops of iodine solution & add it in to boiled rice or potato. The formation of blue-black colour confirms the presence of starch (carbohydrate).
(b) Test for fats :
When ghee/butter rubbed on white paper, that portion of paper turns translucent indicating the presence of fats.
(c) Test for proteins :
Take the few drops of egg albumin in a test tube and add a few drops of concentrated nitric acid to it.
· The white colour of the albumin changes to yellow.
Now, pour the acid out of the test tube but keep the white of the egg in the test tube.
· Add a few drops of ammonium hydroxide to it.
· The colour changes to violet which shows the presence of proteins.
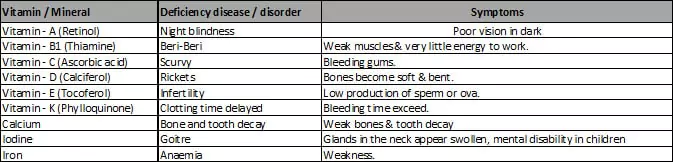
DEFICIENCY DISEASES
The main cause of deficiency diseases in our country is poverty. A vast majority of our people are not able to buy quality food items in desired quantities. In the long run they become weak and sick. Its effect on children is more serious.
· Diseases due to Deficiency of Carbohydrates :
Carbohydrates are the chief sources of energy for the body. This energy is used by the body for
performing various functions.
Deficiency of sufficient carbohydrates in the diet leads to (i) body weakness, and (ii) loss of stamina, as sufficient quantity of energy is not available to the body for performing various functions.
· Diseases due to deficiency of Protein : Proteins are body-building food and serous diseases,
like kwashiorkor and marasmus, develop in case of children if the proteins are not sufficient in
their diet. It is for this reason that the children are often advised to take a protein-rich diet—
enough milk, pulses, eggs, meat and fish,
· Symptoms of Kwashiorkor
(i) Protruding belly
(ii) Dark and scaly skin, brownish hair
(iii) Stunted growth ; usually underweight
(iv) Swollen legs due to accoumulation of water
(v) Loss of appetite
(vi) Anaemia
(vii) Mental retardation
(viii) Reduced resistance to diseases
· Kwashiorkor and marasmus are diseases which result from PEM.

OBJECTIVE TYPE
1. An edible root is
(A) ginger (B) potato (C) carrot (D) onion
2. The part of sugarcane plant from which sugar is obtained is its
(A) leaf (B) stem (C) flower (D) fruit
3. The product obtained only from plants is
(A) chicken (B) ghee (C) rice (D) milk
4. Vegetarian food is
(A) obtained from animal sources (B) obtained from cow
(C) obtained from plants (D) None of these
5. The useful part of tea plant is its
(A) seeds (B) stem (C) roots (D) leaves
6. Human beings eat rice, chapatti as well as meat, so they are
(A) herbivores (B) carnivores (C) insectivores (D) omnivores
7. Nutrient content of chapatti mainly includes
(A) fat (B) minerals (C) carbohydrates (D) proteins
8. The part of a chilly plant that is used as a spice is
(A) seed (B) fruit (C) leaves (D) flower
9. Examine the following statements.
(A) lron, necessary for the human body, is abundantly found in green vegetables.
(B) Zinc is one of the essential trace elements required for human body.
(C) Fats and minerals are not the essential nutrients for a balanced diet of humans.
(D) The foods that generate energy in the body after complete oxidation are in the form of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Which one of the following alternatives is wrong?
(A) A (B) B (C) C (D) D
10. Which of the following statements is worng ?
(A) Quinine an antimalarial drug is obtained from the plant cinchona.
(B) Pulses are rich sources of starch and minerals.
(C) Sunflower is a good source of vegetable oil.
(D) Green vegetables are good sources of vitamins and minerals.
11. Which of the following food will provide more minerals and vitamins for the growth of tissue in human body-
(A) Cheese (B) Fruit (C) Sweets (D) Egg
12. Anaemia disease is due to Deficiency of which substance ?
(A) Iron (B) Vitamin A (C) Fat (D) Protein
13. Which of the following will provide maximum roughage in your diet ?
(A) Egg (B) Tomato (C) Cabbage (D) Rice
14. Calciferol is the name of
(A) Vitamin A (B) Vitamin B (C) Vitamin D (D) Vitamin E
15. Ascorbic and is also called as :
(A) Vitamin D (B) Vitamin K (C) Vitamin E (D) Vitamin C
16. Percent of cytoplasm by weight is made up of compounds of four elements. These are :
(A) C, H, O, N (B) C, Fe, O, H (C) C, H, l, O (D) C, Fe, S, O
17. Which vitamin is obtained from an orange ?
(A) Vitamin A (B) Vitamin B (C) Vitamin C (D) Vitamin E
18. Which components of diet should be given more to children ?
(A) Carbohydrates (B) Mineral-salt (C) Fats (D) Protein
19. Low production of sperms or ova (infertility) is due to the deficiency of
(A) Vitamin A (B) Vitamin C (C) Vitamin E (D) Vitamin K
20. Maximum amount of vitamin C is found in
(A) lemon (B) orange (C) amla (D) none
SUBJECTIVE TYPE
1. Define BMR.
2. What do mean by food test ? Write protein test.
3. Write the biological significance of protein.
4. Define omnivores. Give two examples.
5. Following food items are made up of which nutrients ? Rice, flour, cheese, curd, dal.
ANSWER KEY
1. C 2. B 3. C 4. C
5. D 6. D 7. C 8. B
9. C 10. B 11. B 12. A
13.C 14. C 15. D 16. A
17.C 18. D 19. C 20. C
21.A
RESOURCES
1. Which one of the following is not a food producer?
(A) Wheat Plants (B) Green Grass
(C) Grashopper (D) Mango tree
2. One of the following organisms is not a cosumer. This organism is
(A) Giraffe (B) Grashopper
(C) Goat (D) Grass
3. Which of the following seeds are not used for making sprouts in our homes?
(A) Moong (B) Moth
(C) Makka (D) Chana
4. One of the following foods is not obtained from animals. This food is
(A) Honey (B) Milk
(C) Maize (D) Mution
5. Which one of the following is not a stem of its parent plant?
(A) Ginger (B) Potato
(C) Sweet potato (D) Onion
6. One of the following Plants has two parts which can be eaten as food. This plant is
(A) Wheat (B) Maize
(C) Mustand (D) Bengal gram
7. One of the following animals takes only liquid food. This animal is
(A) Vulture (B) Squirrel
(C) Lizard (D) Butterfly
8. Which one of the following foods is not a root of its parent plant?
(A) Carrot (B) Radish
(C) Onion (D) Trunip
9. The leaves of one of the following plants are not eaten as food. This plant is
(A) Mustard (B) Mango
(C) Cabbage (D) Lettuce
10. The flowers of which of the following plant are not eaten as food?
(A) Banana (B) Gladiolus
(C) Bougainvillea (D) Pumpkin
11. Which one of the following is a herbivore?
(A) Kingfisher (B) Camel
(C) Cat (D) Hawk
12. One of the following is a carnivore. This one is
(A) Monkey (B) Bear
(C) Elephant (D) Lion
13. WHich one of the following is an omnivore?
(A) Hen (B) Frog
(C) Parrot (D) Rabbit
14. Buffalo is
(A) A carnivore (B) A herbivore
(C) An ominvore (D) None of these
15. Which part of its parent plant is potato which we eat as a vegetable?
(A) Stem (B) Root
(C) Branch (D) Bud
16. Which part of its parent plant is sweet potato which we eat as a food?
(A) Flower (B) Bud
(C) Root (D) Stem
COMPONENTS
17. The main carbohydrate which we eat in our food is
(A) Canesugar (B) Glucose
(C) Cellulose (D) Starch
18. Which of the following is considered to be body building food?
(A) Carbohydrates (B) Proteins
(C) Fats (D) Vitamins
19. WHich of the following is produced in our body when the skin is exposed to sunlight?
(A) Vitamin D (B) Vitamin B
(C) Vitamin A (D) Vitamin C
20. THe vitamin essential for good eyesigth, healthy skin and hair is vitamin
(A) A (B) B1
(C) C (D) D
21. Which of the following foods is a good source of both calcium and Phosphorus?
(A) Fish (B) Carrots
(C) Milk (D) Oranges
22. The mineral essential for the proper function- ing of the thyriod gland is
(A) Calcium (B) Iodine
(C) Iron (D) Potassium
23. Which of the following minerals is necessary to make haemoglobin present in the red blood cells?
(A) Iodine (B) Red Phosphorus
(C) Iron (D) Sodium
24. One of the following is necessary for keeping gum and teeth healthy. This is
(A) Vitamin B (B) Vitamin D
(C) Vitamin A (D) Vitamin C
25. Which of the following is not a function of wa- ter in our body?
(A) To transport digested food
(B) To get rid of wastes
(C) To release energy
(D) To regulate body temperature
26. THe vitamin which prevents rickets disease in children is
(A) Vitamin A (B) Vitamin B
(C) Vitamin C (D) Vitamin D
27. Roughage in our food is mainly made of
(A) Starch (B) Cellulose
(C) Glucose (D) Canesugar
28. One of the following is necessary for the nor- mal growth of bones and teeth. this one is
(A) Vitamin B (B) Vitamin C
(C) Vitamin D (D) Vitamin A
29. Fish is a rich source of
(A) Iodine (B) Iron
(C) Phosphorus (D) Potassium
30. Which of the following foods can help in keep- ing the thyroid gland Healthy?
(A) Milk (B) Meat
(C) Fish (D) Eggs
ANSWER KEY
1. C 2. D 3. C 4. C 5. C 6. C 7. D
8. C 9. B 10. C 11. B 12. D 13. A 14. B
15. A 16. C 17. D 18. B 19. A 20. A 21. C
22. B 23. C 24. D 25. C 26. D 27. B 28. C
29. A 30. C
1. Which one of the following food item does not provide dietary fibre?
(A) Whole grains
(B) Whole pulses
(C) Fruits and vegetables
(D) Milk
2. Which of the following sources of protein in different from other?
(A) Peas
(B) Gram
(C) Soyabeans
(D) Cottage cheese(paneer)
3. Which of the following nutrients is not present in milk?
(A) Protein (B) Vitamin C
(C) Calcium (D) Vitamin D
4. Read the food items given below
(i) Wheat (ii) Ghee
(iii) Iodised Salt (iv) Spinach (Palak)
Which ofd rhe above food items are “energy giving foods”?
(A) (i) and (iv) (B) (ii) and (iv)
(C) (i) and (ii) (D) (iii) and (iv)
5. Read the following statement about diseases.
(i) They are caused by germs.
(ii) They are caused due to lack of nutrients in our diet.
(iii) They can be passed on to another person through contact.
(iv) They can be prevented by taking a bal anced diet.
Which pair of statement best describe a defi- -ciency disease?
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iv) (D) (i) and (iii)
6. Given below are the steps to test the pres- ence of proteins in a food item:
(i) Take a small quantity of the food item in a test tube, add 10 drops of water to it and shake it.
(ii) Make a paste or powder of food to be tested.
(iii) Add 10 drops of caustic soda solution to the test tube and shake well.
(iv) Add 2 drops of copper sulphate solution to it.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of the steps ?
(A) i, ii, iv, iii (B) ii, i, iv, iii
(C) ii, i, iii, iv (D) iv, ii, i, iii
Very short Answer Questions
7. Unscramble the following words related to com- ponents of food and write them in the space provided.
(i) Reinpot..................
(ii) menilars................
(iii) Tivanmi................
(iv) Bocatradhyer........
(v) Nitesturn..............
(vi)Tfa......................
8. Which of the following does not provide any nutrient?
Milk, Water, Orange Juice, Tomato soup
Short Answer Question
9.. Fill in the blanks from the list of words given below:
(Carbohydrate, fat, protein, starch, sugar, Vitamin A. Vitamin C, Roughage, balanced diet, obesity, goitre)
(i) Egg yolk is rich in .............and egg albumin is rich in ............
(ii) Deficiency diseases can be prevented by taking a ..............
(iii) Eating too much of fat rich foods may lead to a condition called..............
(iv) The component of food that does not pro- vide any nutrient to our body and yet is es sential in our food is.................
(v) The Vitamin that gets easily destroyed by heating during cooking is..............
10. Read the items of food listed below. Classify them into carbohydrate rich, proten rich and fat rich food and fill them in the given table.
Moong dal, fish, mustard oil, sweet potato, milk, rice, egg, beans, butter, butter milk (Chhachh), cottage cheese(paneer), peas, maize, white bread.
Carbohydrare Rich Protein Rich Fat Rich food
Food item(A) Food Item(B) Item(C)
11. Tasty food is not always nutritious, and nutri- tious, food may not always be tasty to eat. Comment the examples.
12. While using lodine in the laboratory, some drops of iodine fell on Paheli’s socks and some fell of her teacher’s saree. The drops of iodine on the saree turned blue black while their colour did not change onthe socks. What can be the possible reason?
13. Pahelt and Boojho peeled some potates and cut them into small pieces. They washed and boiled them in water. They threw away the excess water and fried them in oil adding salt and spices. Although the potato dish tasted very good, its nutrient value was less. Sug - gest a method of cooking potatoes that will not lower the nutrients in them.
14. Pahelt avoids eating vegetables but likes to eat biscuits, noodles and white bread. She fre quently complains of stomachache and con - stipation. What are the food items that she should include in her diet to get rid of the prob- lem? Give reason for your answer.
15. (a) List all those compenents of food that pro- vide nutrients.
(b) Mention two components of food that do not provide nutrients.
16. Minerals and vitamins are needed in very small quantities by our body as compared to other components. Yet, they are an important part of a balanced diet. Explain the statement.
17. Water does not provide nutrients, yet it is an important component of food. Explain?
Long answer Questions
18. Boojho was having difficulty in seeing things in dim light. The doctor tested his eyesight and prescribed a particular vitamin supplement. He also adivsed him to include a few food items in his diet.
(a) Which deficiency disease is he suffering from?
(b) Which food component may be lackin in his diet?
(c) Suggest some food items that he should include in his diet. (Any four)
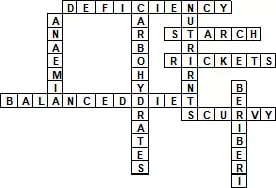
19. Solve the cross-word puzzle given as fig 1.1 from the clues given below.
Across
1. Lack of nutrients in our diet over a long period causes these diseases(10)
2. Rice and potato are rich in this type of carbohydrate (6)
3. Deficiency disease in bones makin it be come soft and bent(7)
4. The diet that provides all the nutrients that our body needs, in right quantities, along with adequate amout of roughage and water (8, 4)
5. Deficiency disease with bleeding gums(6)
6. Disease caused due to gums.(6)
Down
7. Starch and sugar in our food are rich in this type of energy giving nutrient(13)
8. The term given to the useful components of food(9)
9. The disease caused by deficiency of iron in diet (7)
10. Green leafy vegetables, liver and apples are rich in this mineral(4)
11. Deficiency disease caused due to lack of Vitamin B1 in the diet(8)
20. Observe the items given in fig 1.2 carefully and answer the questions that follow.
(a) Food item rich in carbohydrates ins ......
(b) Egg is a rich source of protein, the mineral..........and vitamin .......
(c) ...........is a rich source of fat.
(d) Milk provides .......vitamin D and .........(min eral)
(e) ........(fruit) is a rich source of vitamin A.
(f) Spinach is a good source of the mineral......
(g) Both eggs and ........are rich in ..........
21. Snakes and Ladders
Make a board game just like “Snakes and lad ders” with 10-10 grid boxes.
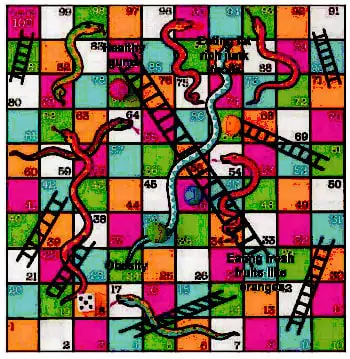
The mouth of the snake will represent the faulty food habit or faulty method of cooking. Its tall will represent the deficiency disease caused or loss of any nutrient in food.
Sumilarly, the box at the base of a leadder will respresent healthy food habit or healthy method of cooking. Its supper end will represent the beneficial effect of that habot. An example is given as fig. 1.3 Complete the board and play with your friends.
ANSWER KEY
1. D 2. D 3. B 4. C
5. C 6. B
7.(a) Protein (b) minerals (c) vitamins
(d) Carbohydrate (e) nutrients (f) fat
8. Water
9. (a) fat, protein (b) Balanced diet
(c) Obesity (d) roughage
(e) vitamin C
10. A-sweet potato, rice, maize, white bread
B-moong dal, fish, milk, eff, beans, butters milk, cottage cheese, peas
C-mustard oil, milk, egg, butter
11. Potato chips are tasty but they are not very nutritious.
Boiled vegetables are very nutritious but they may not be tasty.
12. The saree of pahelis teacher might have been starched and strach turns blue black with io dine soluton. Paheli’s socks did not have strach on it thereby showing no change.
13. Wash, peel cut and cook the potatoes, Cook ing in a small amount of water and then frying in a small quantity of oil conserves the nutri ents.
14. Paheli must include whole grains, whole pulses, fresh fruits and vegetables in her diet as she seems to lack roughage.
15. (a) components of food that provide nutrients are carbohydrates, proteints, fats, vitamins and minerals.
16. Vitamins and minerals are very important be cause they help in
(a) proteeting our body against disease.
(b) growth
(c) maintaining good health.
17. Water helps our body to absorb nutrients from food and alos helps in removing wastes such as urine and seat.
18. (a) Night blindness (b) vitamins A
(c) carrot, papaya, mango, milk and fish oil or any other (any four)
19.
20. (a) Chapati (b) Calcium; Vitamin D
(c) Butter (d) Protein, Calcium
(e) Papaya (f) Iron
(g) Peas, Proteins
21. A snakes and Ladders board game prapared by children
EXERCISE
1. Given below are names of some animals
(i) Goat (ii) Human beings
(iii) Cockroach (vi) Eagle
Which of the above animals form a pair of omnivores?
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv) (D) (ii) and (iv)
2. Honeybee makes honey from
(A) Pollen (B) Petals
(C) Nectar (D) Bud
3. Below are names of some animals:
(i) Cow (ii) Sheep
(iii) Horse (iv) Ox
Which of the above are sources of milk for human beings?
(A) (i) and (iii) (B) (i) and (ii)
(C) (ii) and (iii) (D) (iii) and (iv)
4. Given below is a list of edible plants:
(i) Banana (ii) Pumpkin
(iii) Lady’s finger (iv) Brinjal
Which pair of plants have two or more edible parts
(A) (i) and (ii) (B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (iii) and (iv) (D) (i) and (iv)
5. The part of a banana plant not used as food as
(A) Flower (B) Fruit
(C) Stem (D) Root
6. Read each set of terms and identify the odd set
(A) Cow, milk, butter
(B) Hen, meat, Egg
(C) Goat, milk, meat
(D) Plant, vegetable, butter milk,
Very short Answer Questions
7. Read the clues and fill up the blanks given below each of them.
(a) Honeybees suck from flower
N ...... .......T........R
(b) Animals which eat other animals
.....A.....N......V.......R......S
(c) Animals which eat only plants and plant products.
HE......B..... ....... ..... .....E.....
(d) Animals which eat both plants and animals.
........MNI......O...... ...... ......
8. Why do boild seeds fail to sprout?
9. Where do bees store honey?
10. Name two ingredients in our food that are not ontained fro plants or animals. Mention one source for each ingredient.
11. Given below are jumbled words which are names of parts of a plants. Rearrange them to get the correct words.
(a) L I L C H I
(b) I T R U F
(c) S E A N B O Y A
(d) G U R S A
(e) R O U N D G U N T
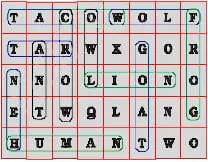
12. Identify the animals in the grid given below as fig. 1.1 and categorise them into herbivore, carnivore and omnivore.
13. Why should we avoid wastage of food?
14. Why do organisms need food? Write two rea- sons.
15. Match the organisms given in Column I with their part/ product in Column II that is used by human beings as food.
Columan-I Column-II
(a) Mustard Plant (i) Meat
(b) Goat (ii) fruits and vegetable
(c) Hen (iii) seed
(d) Smoke (iv) direcction of air flow
(e) wind (v) Prevent dust particles
ANSWER KEY
1. B 2. C 3. B 4. A 5. D 6 D
7. (a) NECTAR (b) ARNIVORES (c) HERBIVORES (d) OMNIVORES
8. Boiling kills the seeds
9. In beehives
10. (i) Salt from sea water/rocks
(ii) Water from river/well/tap/pond/tubewell/rain
11. (a) CHILLI (b) FRUIT (C) SOYAVEAN (d) SUGAR (e) GROUNDNUT
12.
Herbivore : COW, GOAT, HEN
Carnivore : WOLF, LION, FROG
Omnivore : CAT, RAT, CROW, HUMAN, ANT, OWL
13. a- Flower, b-Bud, c- Leaf, d- Stem
14. Enough food is not available for all of us/ food is very costly and poor people cannot afford to buy







priyambada pal
i 'll complete my science . Thanx very much
priyambada pal
I'll copcomplete my science . Thanx very much