Getting To Know Plants
Introduction
Plants are living things which grow in the soil and remain fixed at a place through their roots.
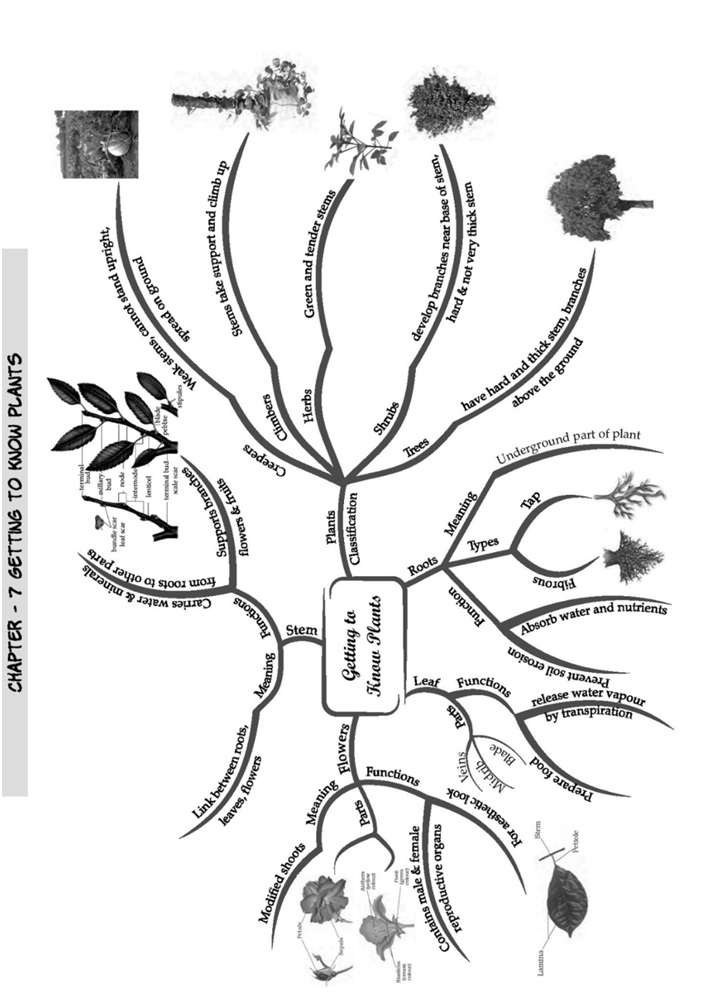
Classification of Plants
Plants can be classified into various categories depending on various features.
On the basis of flower
Flowering also called Angiosperms: Sun flower, Rose, tomato
Non- Flowering also called Gymnosperms: Pines,ferns,mosses.
On the basis of their
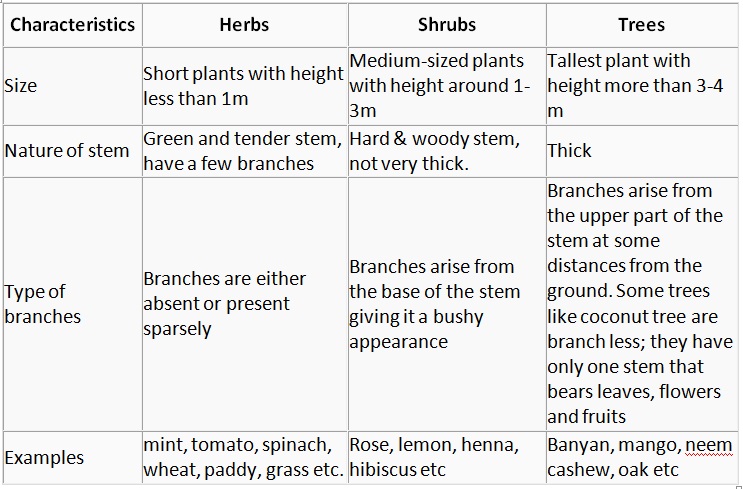
Size, Type of Stem, spread of branch, plants are classified into 3 categories:
• Herbs
• Shrubs
• Trees
Certain plants have
weak steams and cannot stand upright. They are categorized into two types:
Creepers
• The stems of these plants spread/trail on the ground.
• Stems are long, thin and fragile and cannot stand erect.
• Examples – water melon, strawberry, pumpkin, sweet potato etc
Climbers
• More advanced than creepers.
• They have thin long and weak stems that cannot stand upright but they can use external support to grow vertically and carry their weight.
• These types of plants use special structures called tendrils to climb.
• Examples – pea plant, grapevine, money plant, etc.
Some Other Types Of Plants
Moss
• Small nonflowering green plants.
• Grow in damp and shady areas.
Grass
• Flowering plants.
• Short in height.
• Long narrow leaves.
Aquatic Plants
• Grow in water only.
• They are either rooted in mud under water (lotus) or float without any anchorage
(water hyacinth) other e.g. water lilies, hydrilla & tape grass.
Types of Plants

Parts of Plants
Stem
• The stem is a part of the shoot system. It bears leaves, buds, fruits and flowers. It may be soft or woody.
• Functions of the stemare:

Leaf
• A leaf is an outgrowth of the stem and is flat, thin and usually green incolour.
• The leaves may be of different shapes- needle shaped, oval, heart shaped, oblong, circular ortapering.
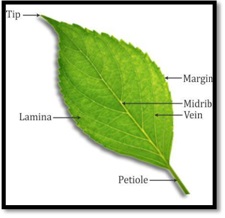
• The different parts of a leaf are mentionedbelow:
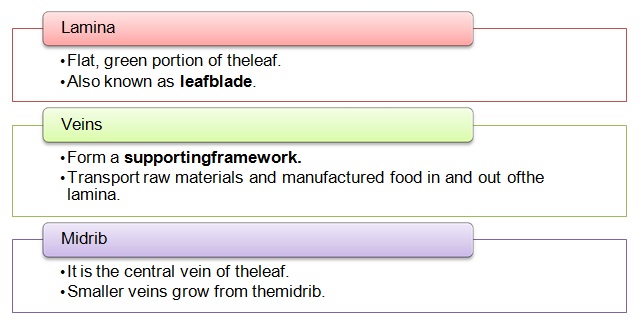
• The primary functions ofleaves:

• The pattern or arrangement of veins on a leaf is termed as venation.
There are two basic types of venation:

Root
• Roots are present below the ground and generally, are not green incolour.
• They do not bear flowers, fruits orleaves.

• The first root of a plant is the radicle, which is present within the seed. It gives rise to the
primary root from where the plant develops its rootsystem.
• Depending on its type, a plant develops either a taproot system or a fibrous rootsystem.


• Roots have the followingfunctions:

Flower
• A flower is a reproductive structure found in floweringplants.
• The structure of flowers may not be the same in allplants.
• The number of petals, sepals, stamens and pistil may vary from plant toplant.