Important Questions
Multiple Choice Questions:
Q.1 A snail moves by its muscular
(a) Wings
(b) Foot
(c) Fins
(d) None of these
Q.2 The muscles covers the.
(a) Skin
(b) Bones
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Q.3 The skull covers and protects the
(a) Eyes
(b) Nose
(c) Brain
(d) None of these
Q.4 To which bones are thigh bones attached ?
(a) Pelvic bone
(b) Hinge joint
(c) Shoulder bone
(d) Backbone
Q.5 The pelvic bones together with the last two parts of the backbone
from a large bony bowl called:
(a) Thigh bone
(b) Hip bone
(c) Knee bone
(d) Pelvis
Q.6 How is pelvic bone formed ?
(a) By the fusion of three bones
(b) By the fusion of two bones
(c) By the fusion of four bones
(d) None of these
Q.7 How many shoulder bones are there ?
(a) One
(b) Three
(c) Two
(d) None of these
Q.8 To which part of the body are the bones of the upper arm attached?
(a) Elbow
(b) Palm
(c) Shoulder
(d) None of these
Q.9 Which bones are formed by the collar bone and the shoulder blades ?
(a) Shoulder bone
(b) Upper arm
(c) Arm bone
(d) All of these
Q.10 The chest is a cone shaped cage enclosing the.
(a) Heart
(b) Lungs
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Q.11 How many ribs could you count ?
(a) Seven
(b) Six
(c) Ten
(d) Nine
Q.12 Name two very important organs that are protected by the box made of ribs.
(a) Heart
(b) Lungs
(c) Chest
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Q.13 What is function of small bones of toe ?
(a) Help in walking
(b) Help in running
(c) Help in sitting
(d) both (a) and (b)
Q.14 What is flat foot ?
(a) Foot having bones set in an arch
(b) When the foot is flat instead of being arched
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Q.15 How many bones make the ankle?
(a) Four
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Several
Very Short Question:
1. What do you mean by movement?
2. At which part does the arm rotate?
3. If you tie a scale with your arm, are you able to bend your elbow?
4. Name the places where two parts of the body are seen to be joined together.
5. If there are no joints then will it be possible to move?
6. Can bones be bent?
7. Can we bend our body at every part?
8. How many types of joints are there?
9. Name the various types of joint.
10. What is cavity in bone?
Short Questions:
1. What are joints? Write the names of various types of joints.
2. What is skeleton? Draw a diagram to show the human skeleton.
3. Write two ways by which we may know the shape of human skeleton.
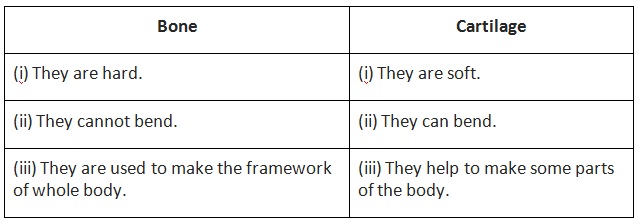
4. Write the differences between bones and cartilage.
5. How do the muscles work?
6. How does the earthworm move?
7. How does the snail move?
8. How does fish move in water?
Long Questions:
1. Explain various kinds of joints found in our body and give example of each.
Answer Key-
Multiple Choice Answers:
1. (b) Foot
2. (b) Bones
3. (c) Brain
4. (a) Pelvic bone
5. (d) Pelvis
6. (a) By the fusion of three bones
7. (c) Two
8. (c) Shoulder
9. (a) Shoulder bone
10. (c) Both (a) and (b)
11. (d) Nine
12. (d) Both (a) and (b)
13. (d) both (a) and (b)
14. (b) When the foot is flat instead of being arched
15. (d) Several
Very Short Answers:
1. Answer: The changing position of the body or any part of the body is called movement.
2. Answer: The arm rotates on the round pit-like structure.
3. Answer: No, we cannot bend our elbow.
4. Answer: These places are called joint.
5. Answer: No, it is not possible.
6. Answer: No, bones cannot be bent.
7. Answer: No, we can bend our body only at joints.
8. Answer: There are five types of joints in our body.
9. Answer:
(i) Ball and socket joints
(ii) Pivotal joints
(iii) Hinge joints
(iv) Fixed joints
(v) Gliding joints
10. Answer: The hollow space in the bone is called cavity.
Short Answer:
1. Answer: The places where two parts of the body seem to be joined together are
called joints. There are following types of joints:
(a) Ball and socket joints
(b) Pivotal joints
(c) Hinge joints
(d) Fixed joints
(e) Gliding joints
2. Answer: The bones in our body form a framework to give a shape to the body. The framework is called skeleton.
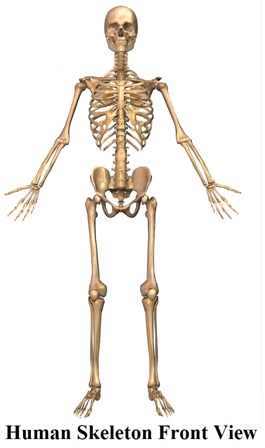
3. Answer:
(i) We can know the shape of skeleton by feeling.
(ii) We could know the shape by X-ray images of human body
4. Answer:
5. Answer: The muscles work in pairs. When one of them contracts, the bone is pulled in that direction,
the other muscle of the pair relaxes. To move the bone in the opposite direction, the relaxed muscle
contracts to pull the bone towards its original position, while the first relaxes. A muscle can only pull.
It cannot push.
6. Answer: Earthworm does not have bones. It has muscles. During the movement, earthworm first extends
front part of the body keeping the rear portion fixed to the ground. Then it fixes the front and releases the
rear end. It then shortens the body and pulls the rear end forward. In this way by repeating such muscular
expansions and contractions earthworm moves.
7. Answer: The rounded structure on the back of the snail is called shell. It is the outer skeleton (exoskeleton)
of snail. When it starts moving a thick structure and the head of the snail may come out of an opening in the
shell. The thick structure is called foot, which is made up of strong muscles. It helps snail in moving.
8. Answer: The body of fish is streamlined. The streamlined shape helps the fish to move in water. The skeleton
of fish is covered with muscles which make the front part of the body to curve to one side and the tail part
swings towards the opposite side. This makes a jerk and pushes the body forward. In this way it moves in water.
Long Answer:
1. Answer: There are five types of joints in our body:
(i) Fixed joints: Those joints which do not allow movement are called fixed joint.
(ii) Ball and socket joint: This joint allows movement in all directions. The rounded end of one bone fits into
the hollow space of other bone. For example, joint between upper arm and shoulder.
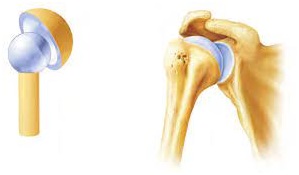
(iii) Pivotal joint: This type of joint allow movement in all planes, i.e. up and down, side and other planes.
For example, head.
(iv) Hinge joint: The joint which allows movement only in one plane is called hinge joint. For example, fingers, knees.
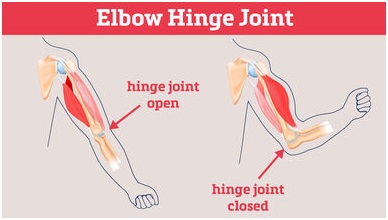
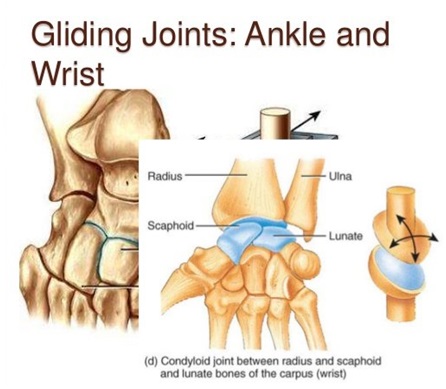
(v) Gliding joint: These joints allow only a limited amount of movement of sliding nature of cartilage.
For example, the joints of backbone.