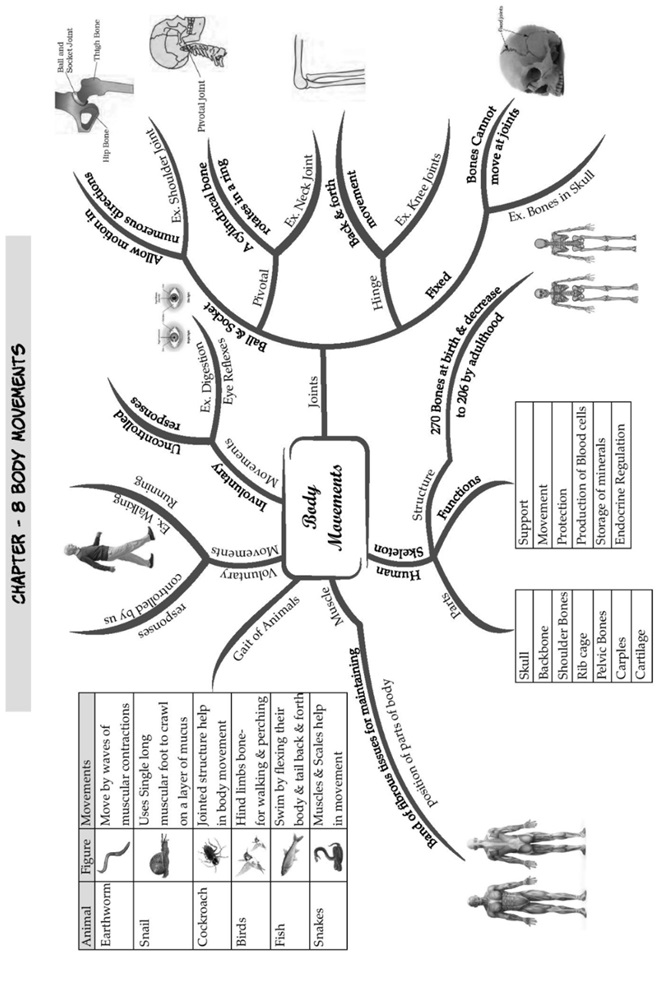
Body Movements
Introduction
• The ability of moving one’s body from one place to another is calledlocomotion.
• In nature, the primary reason for movement has been the search of food and shelter, or in saving onese
lf from harsh climatic conditions or for escaping from beinghunted.
Human Skeleton
• All bones in the body form a framework which gives shape to the body. This bony framework inside
the body is called the skeleton.
• There are 206 bones in an adult human skeleton.

• Some additional parts of the skeleton are not as hard as bones and can be bent. They are calledcartilages.
Functions of Skeleton
• It holds the whole body together and gives itshape.
• It protects many delicate organs of the body from outsidedamage.
• It provides numerous points for attachment of the muscles of thebody.
• It helps in the movement of body parts andlocomotion.
• The human skeleton consists of a strong backbone which has a skull at its topend.
• The skull is made of many bones joined together. It encloses and protects the most important part of
the body, i.e. thebrain.

• Ribs are attached to the upper part of the backbone forming aribcage.
• The breastbone also known as the sternum is present in front of theribcage.
• Ribcage protects the heart and thelungs.

Muscle Movements
• The muscle is a fibrous tissue in the body which has the ability to contract whenrequired.
• On contraction, muscles become shorter, stiffer and thicker because they pull thebones.
• Muscles always work in pairs. When one muscle contracts, the bone is pulled in that direction
and the other musclerelaxes.
• To move the bone in the opposite direction, the relaxed muscle contracts and brings the bone
to its original position, while the first relaxes. A muscle cannot push. It can onlypull.

Human Body and its Movement
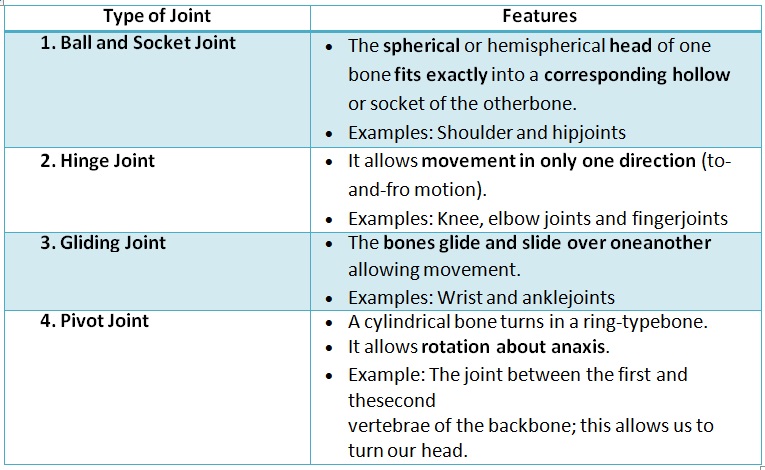
• The point where two or more bones meet in the body is called ajoint.
• Bones do not move. It is the joint which helps inmovement.
Movement in Animals
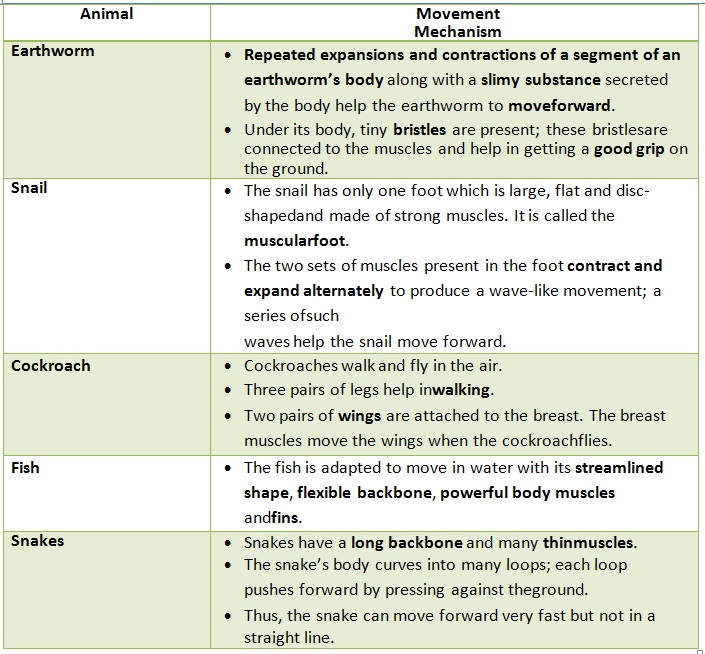
Birds
• The body of every bird is adapted forflying.
• Birds fly with a constant flapping of theirwings.
• The forelimbs are modified to formwings.
• Bones are hollow andlight.
• The shoulder bones are strong, and the breastbones are modified to hold muscles offlight.
• Birds such as ducks and swans swim in water by pushing against water with their webbedfeet.
• Birds such as kiwi, penguin and ostrich cannot fly. Such birds walk on the ground by using their hind limbs.
Bones
Bones provide a definite shape to our body. Skeleton is the framework given to our body as a result of the fusion
of bones. It is made up of bones, cartilage and joints. One way to know the shape of your bones is through X-ray images.
Our hand is made up of small bones called carples.
Ribs are bent to form the chest bone. The chest bone and backbone together join to form the rib cage. The rib cage
consists of 12 ribs on each side of the chest. It protects our internal organs such as the heart, lungs etc.
The rib cage is joined to the backbone.
It consists of 33 small bones called vertebrae.
Backbone helps our body stay erect andprovides posture.
• Bones near the shoulder area are called shoulder bones and those present in the abdominal region are called
pelvic bones, which encloses the portion of our body just below the stomach.
• Skull is joined together by many bones and encloses our brain.
• The additional part of the skeleton that can be bent is called the cartilage. Example: Ear lobe.
They are also found in joints.
• Muscles are the flesh on the bone. They bulge due to contraction and becomes shorter, thicker and stiffer.
They work in pairs to move a bone. When one muscle contracts to pull a bone in a direction the other muscle
relaxes. To move a bone in the opposite direction, relaxed muscle contracts to pull the bone towards the original
direction while the first is in a relaxed position.

The human skeleton is made up of 206 bones, including bones of the:
• Skull – including the jawbone
• Spine – cervical, thoracic, and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum and tailbone (coccyx)
• Chest – ribs and breastbone (sternum)
• Arms – shoulder blade (scapula), collar bone (clavicle), humerus, radius and ulna
• Hands – wrist bones (carpals), metacarpals and phalanges
• Pelvis – hip bones
• Legs – thigh bone (femur), kneecap (patella), shin bone (tibia) and fibula
• Feet – tarsals, metatarsals and phalanges.
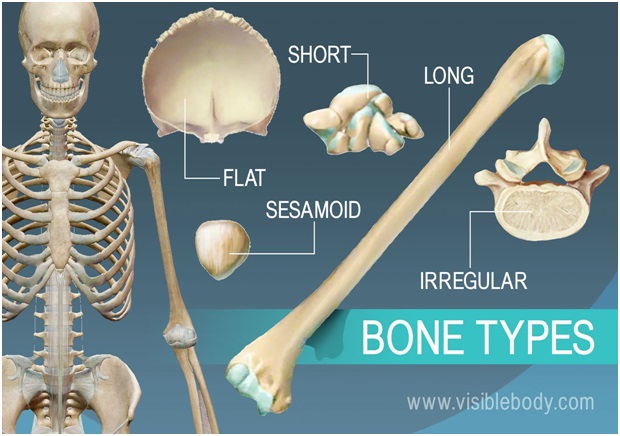
Bone types
There are four different types of bone in the human body:
• Long bone:Has a long, thin shape. Examples include the bones of the arms and legs (excluding the wrists, ankles and kneecaps).
With the help of muscles, long bones work as levers to permit movement.
• Short bone:Has a squat, cubed shape. Examples include the bones that make up the wrists and the ankles.
• Flat bone:Has a flattened, broad surface. Examples include ribs, shoulder blades, breastbone and skull bones.
• Irregular bone:Has a shape that does not conform to the above three types. Examples include the bones of the spine (vertebrae).