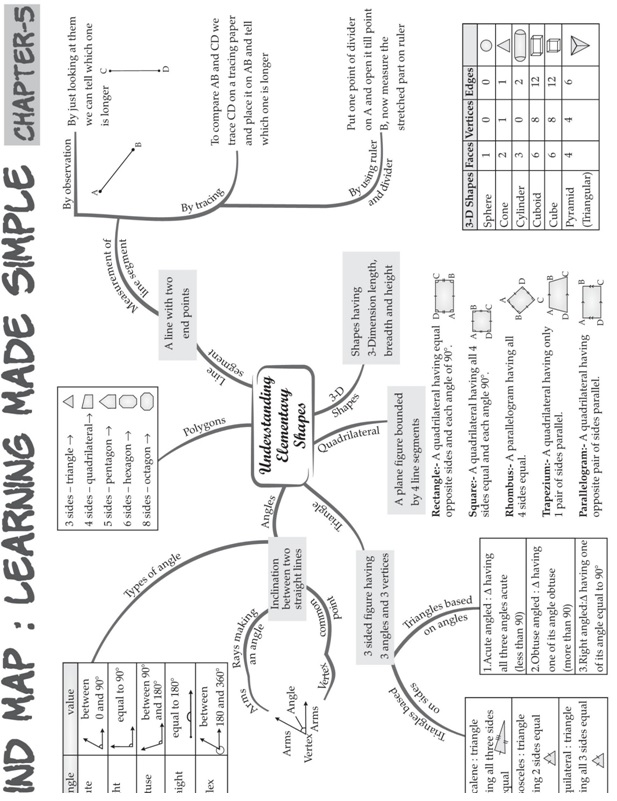
UNDERSTANDING ELEMENTARY SHAPES
Measuring Line Segments
A ruler or a divider is generally used to find the lengths of line segments. The length of a line segment can be defined
as the distance between its endpoints.
Angles and its Types
An angle is made up of any two rays which have the same endpoint or starting point. It can be better understood by the
movement of clock-hands. When a clock hand moves, it forms an angle. To measure the angle, a protractor is used.
It should be noted that a straight angle is 180 degrees while a right angle is 90 degrees.
Based on the degree, an angle can be classified into 3 main types:
• Acute angle: When an angle measure is less than a right angle, it is called an acute angle.
• Obtuse angle: When an angle measure more than a right angle but less than a straight angle, it is called an obtuse angle.
• Reflex angle: When an angle measure more than a straight angle, it is called a reflex angle.
It should be noted that two intersecting lines are perpendicular if the angle formed between them is 90 degrees.
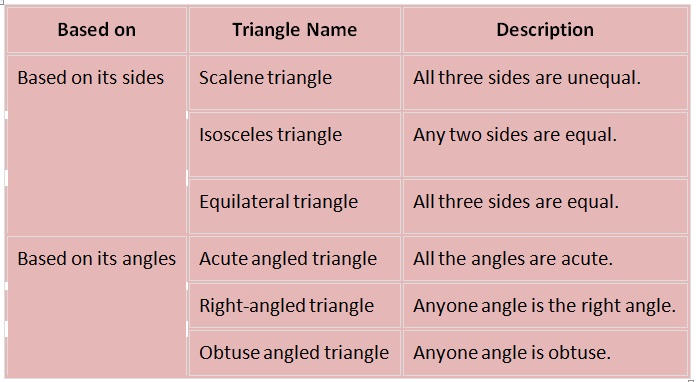
Triangles and its Types
A triangle is a closed figure having three sides and three interior angles. A triangle can be classified based on its length
of sides and by its angles. The detailed classification of triangles is given below.
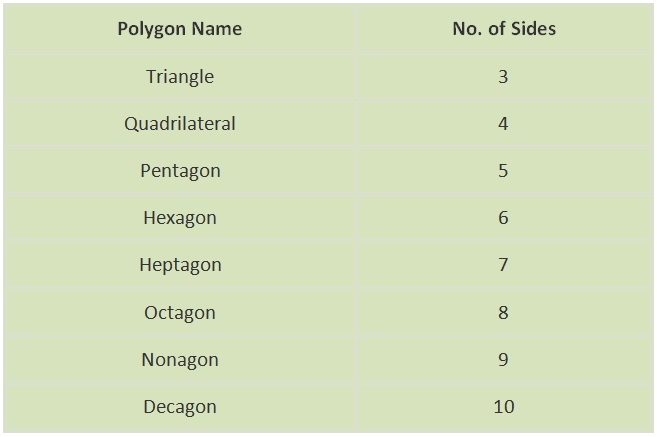
Polygons
Polygons are closed geometric shapes having at least 3 sides and 3 angles. Based on the number of sides, a polygon
can be categorized into multiple types. Some of the most common polygons are:
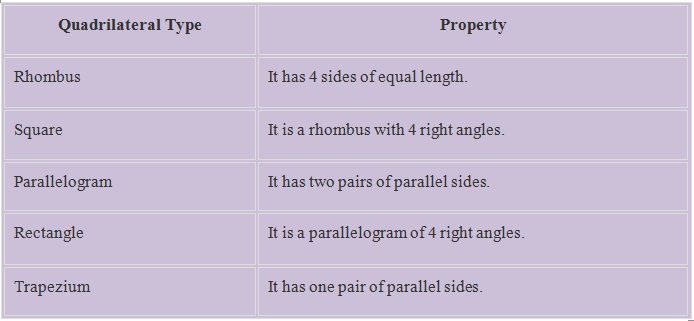
Quadrilaterals
As mentioned in the table above, a quadrilateral is one of the types of polygons having 4 sides and 4 angles.
A quadrilateral can be categorized into 5 main types which are explained below.
Solid Shapes or 3D Shapes
A solid shape or three-dimensional shape (3D shape) can be defined as the objects which can be measured in three
directions i.e. length, breadth, and height. Examples of 3d shapes are cylinder, cube, cuboid, sphere, etc. Check out
three-dimensional shapes to learn more about them and to get acquainted with the terms related to them.

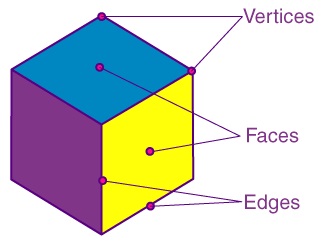
Faces, Edges, and Vertices of Three-Dimensional Shapes
Three-dimensional shapes have many attributes, such as vertices, faces, and edges. The flat surfaces of the 3D
shapes are called faces. The line segment where two faces meet is called an edge. A vertex is a point where three
edges meet.
Three-dimensional Shapes Names:
• Cube
• Cuboid
• Cone
• Cylinder
• Sphere
• yramid
• Prism
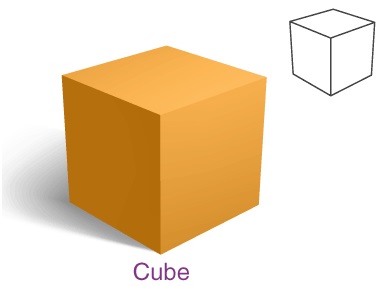
Cube
A cube is a solid or three-dimensional shape which has 6 square faces. The cube has the following properties.
• All edges are equal
• 8 vertices
• 12 edges
• 6 faces
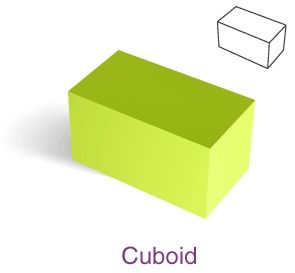
Cuboid
A cuboid is also called a rectangular prism, where the faces of the cuboid are a rectangle in shape. All the
angles measure 90 degrees. The cuboid has
• 8 vertices
• 12 edges
• 6 faces
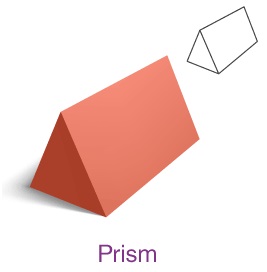
Prism
A prism is a 3D shape which consists of two equal ends, flat surfaces or faces, and also has identical cross
-section across its length. Since the cross-section looks like a triangle, the prism is generally called a triangular
prism. The prism does not have any curve. Also, a prism has
• 6 vertices
• 9 edges
• 5 faces – 2 triangles and 3 rectangles
Pyramid
A pyramid a solid shape, whose outer faces are triangular and meet to a single point on the top. The pyramid
base can be of any shape such as triangular, square, quadrilateral or in the shape of any polygon. The most
commonly used type of a pyramid is the square pyramid, i.e., it has a square base and four triangular faces.
Consider a square pyramid, it has
• 5 vertices
• 8 edges
• 5 faces

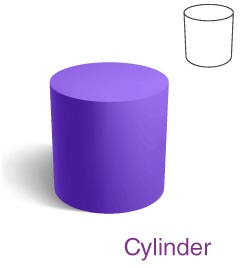
Cylinder
A cylinder is defined as a three-dimensional geometrical figure which has two circular bases connected by
a curved surface. A cylinder has
• No vertex
• 2 edges
• 2 flat faces – circles
• 1 curved face
Cone
A cone is a three-dimensional object or solid, which has a circular base and has a single vertex. The cone is
a geometrical figure that decreases smoothly from the circular flat base to the top point called the apex.
A cone has
• 1 vertex
• 1 edge
• 1 flat face – circle
• 1 curved face

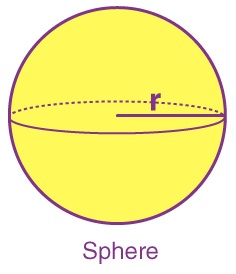
Sphere
A sphere is a three-dimensional solid figure which is perfectly round in shapes and every point on its surface
is equidistant from the point is called the center. The fixed distance from the center of the sphere is called
a radius of the sphere. A sphere has
• No vertex
• No edges
• 1 curved face
Measuring line segments
The distance between the endpoints of a line segment is called its length.
⇒ Line segments can be measured by
• Comparison by observation
• Comparison by tracing
• Comparison using ruler and divider
Positioning error
To get the correct measure, the eye should be correctly positioned, just vertically above the mark.
Errors can happen due to angular viewing.
Perpendicular Lines
Perpendicular Lines and perpendicular bisector
• When two lines intersect and the angle between them is a right angle, then the lines are said to be perpendicular.
• A perpendicular to a line segment that divides it exactly at the midpoint is called the perpendicular bisector.
Classification of Triangles
• Triangles are those closed figures which have exactly three sides.
• ased on their sides and angles, they can be classified into different triangles.
Types of Triangles based on lengths of sides
Based upon the length of the sides, triangles are classified as:
• Scalene
• Isosceles
• Equilateral
Types of Triangles based on angles
Based upon the measure of the angles, triangles are classified as:
• Acute-angled
• Obtuse-angled
• Right-angled
Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is a polygon which has four sides.
Comparisons between different quadrilaterals
• Different quadrilaterals can be classified based on the lengths of the sides and angles.
• To know more about Quadrilateral, visit here.
Rhombus
• A rhombus is a special type of parallelogram where all its sides are equal.
• The diagonals are perpendicular to each other. They also bisect the angles.
Trapezium
• A trapezium is a quadrilateral where only two sides are parallel to each other.
• No sides, angles and diagonals are congruent.
Polygons
• A polygon is a closed figure made up of line segments in two-dimension.
• Polygons are classified based on the number of sides.
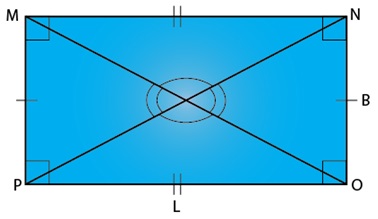
Rectangle
• A rectangle is a quadrilateral which has opposite sides equal and all angles are right angles.
• The diagonals are equal.
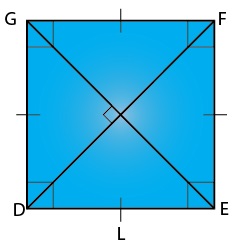
Square
• A square is a quadrilateral which has all sides equal and all angles are right angles.
• The diagonals are equal and perpendicular to each other.
Angles
The amount of rotation about the point of intersection of two planes (or lines) is called angle.
Right, straight and complete angles
• Right angle is equal to 900.
• Straight angle is equal to 1800.
• Complete angle is one complete revolution or equal to 3600.
Acute, obtuse and reflex angles
• Acute angle is lesser than 900.
• Obtuse angle is greater than 900.
• Reflex angle is greater than 900.
Tools of construction
• Ruler and divider are used to measure lengths of line segments.
• A protractor is used to measure angles.
Measuring angles
• Angles are measured in degrees.
• Angles are measured by using a protractor.