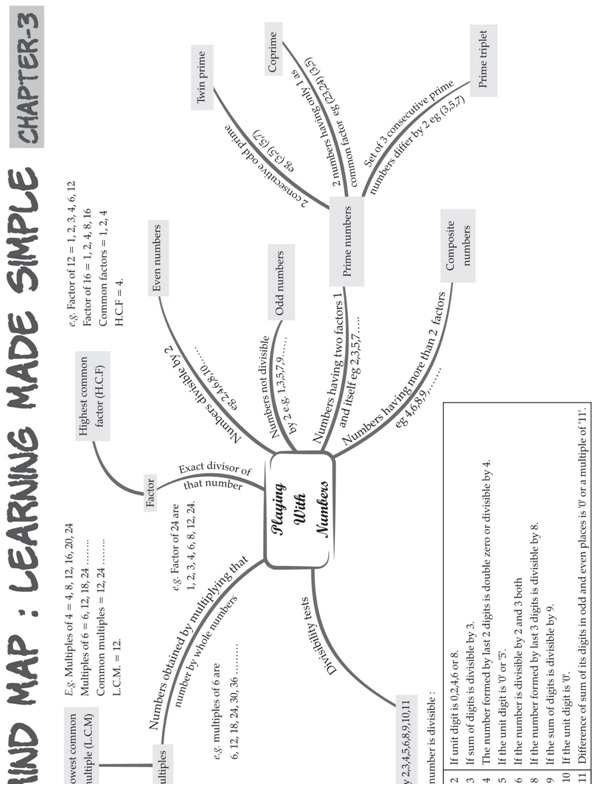
PLAYING WITHNUMBERS
Factors
A factor of a number is an exact divisor of that number
Example
1. Factor of 6
1 → Since 1 exactly divides 6
2 → Since it exactly divides 6
3 → Since it exactly divides 6
6 → Since it exactly divides 6
Properties of factors
• 1 is a factor of every number
• Every number is a factor of itself.
• Every factor of a number is an exact divisor of that number
• Every factor is less than or equal to the given number
• Number of factors of a given number are finite.
Multiple
Multiple of a number is the numbers obtained by multiplying that numbers with various Natural numbers
Example
Number is 6
Multiple will be
6 × 1 = 6
6 × 2 = 12
6 × 3 = 18
Properties of Multiple
• Every multiple of a number is greater than or equal to that number.
• Number of multiples of a given number is infinite.
• Every number is a multiple of itself.
Perfect Number
A number for which sum of all its factors is equal to twice the number is called a perfect number
Example
1. 6
The factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3 and 6.
Now, 1 + 2 + 3 + 6 = 12 = 2 × 6
2. 28
All the factors of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14 and 28.
Now, 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14 + 28 = 56 = 2 × 28
Prime Numbers
The numbers other than 1 whose only factors are 1 and the number itself are called Prime numbers.
Example:
2, 3, 5, 7, 11 ,13
We can find list of prime numbers till 100 using Sieve of Eratosthenes method
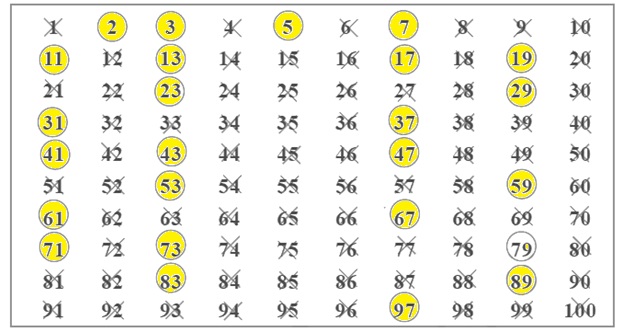
• Step 1: Cross out 1 because it is not a prime number.
• Step 2: Encircle 2, cross out all the multiples of 2, other than 2 itself, i.e. 4, 6, 8 and so on.
• Step 3: You will find that the next uncrossed number is 3. Encircle 3 and cross out all the multiples of 3, other than 3 itself.
• Step 4: The next uncrossed number is 5. Encircle 5 and cross out all the multiples of 5 other than 5 itself.
• Step 5: Continue this process till all the numbers in the list are either encircled or crossed out.
All the encircled numbers are prime numbers. All the crossed-out numbers, other than 1 are composite numbers
Composite Numbers
Numbers having more than two factors (1 and itself) are called Composite numbers
Example:
4, 6, 8 ,9….
Zero (0) is considered as neither prime nor a composite number because it does not have any factors.
Composite Numbers Examples
The examples of composite numbers are 6, 14, 25, 30, 52, etc, such that:
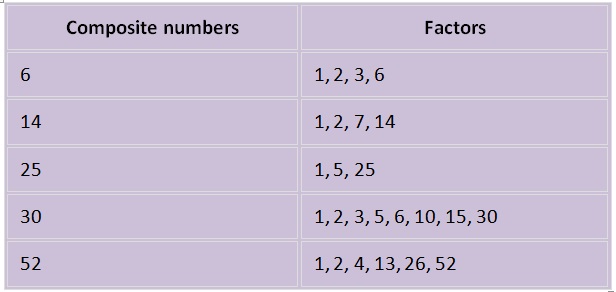
Properties of Composite Numbers
The properties of composite numbers are easy to remember.
• Composite numbers have more than two factors
• Composite numbers are evenly divisible by their factors
• Each composite number is a factor of itself
• The smallest composite number is 4
• Each composite number will include at least two prime numbers as its factors
(E.g., 10 = 2 x 5, where 2 and 5 are prime numbers)
• Composite numbers are divisible by other composite numbers also
Even Numbers
The numbers which are multiple of 2 are called even numbers
Example
2,4,6,8,10,12,14
Even numbers have 0,2,4,6,8 in it one’s place
Odd Numbers
The numbers which are not multiple of 2 are called odd numbers
Example
1,3, 5,7,9,11......
Important points about prime numbers based on definition of odd and even numbers
• 2 is the smallest prime number which is even.
• every prime number except 2 is odd.
Tests for Divisibility of Numbers

Common Factors and Multiple
We already studied the factors and Multiple in previous section. We can find common
factors and multiple between 2 or more numbers
Example
Common factors of 4,12, and 16
Factors of 4 are 1, 2 and 4.
Factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12.
Factors of 16 are 1, 2, 4, 8 and 16.
Clearly, 1, 2 and 4 are the common factors of 4, 12, and 16.
Important Note
Two numbers having only 1 as a common factor are called co-prime number
Examples 3 and 4 are co-prime
Divisibility Rules based on factors and Multiple, co -prime
• If a number is divisible by another number then it is divisible by each of the factors of that number
Example
36, is divisible by 18
Now if we find factors of 18 i.e., 1,2,3,4,9,18
So, 36 is also divisible by 1,2,3,4,9,18
• If a number is divisible by two co-prime numbers, then it is divisible by their product also
Example
45
It is divisible by 3 (4+5=9)
It is divisible by 5
Since 3,5 are coprime. Now the product is 3 × 5=15. Now it is divisible by 15 also
• If two given numbers are divisible by a number, then their sum is also divisible by that number.
Example
15 is divisible by 3
9 is divisible by 3
Sum = 15+9 =24
We can see that it is also divisible by 3
• If two given numbers are divisible by a number, then their difference is also divisible by that number
Example
15 is divisible by 3
9 is divisible by 3
Difference = 15 - 9 =6
We can see that it is also divisible by 3
Factorization and Prime -Factorization
Factorization is expressing the number as a product of its factors
So,
36 = 3×12 = 4 × 9
This form is called Factorization
Prime Factorization is expressing the number as a product of its prime factors
36 = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3
We can find prime factorization by dividing the numbers with 2, 3, 5, 7 etc. in this order repeatedly
so long as the quotient is divisible by that number
HCF and LCM
• The Highest Common Factor (HCF) of two or more given numbers is the highest of their common factors.
It is also known as Greatest Common Divisor (GCD).
Steps to find HCF or GCD
♦ Find the prime factorization of the numbers
♦ Choose the common factors in them
♦ Multiply those common factors to obtain HCF
• The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more given numbers is the lowest of their common multiples.
Steps to find LCM
♦ Find the prime factorization of the numbers
♦ Look for the maximum occurrence of all the prime factors in these numbers
♦ The LCM of the numbers will be the product of the prime factors counted the maximum number of
times they occur in any of the numbers.
LCM using division method
Here we divide the given numbers by common prime number until the remainder is a prime number or one.
LCM will be the product obtained by multiplying all divisors and remaining prime numbers.
Steps are
• We place number in the line
• We start dividing the number by least prime number which is common among all of them or group of them
• Keep dividing by least until we have 1's in the remainder
• LCM is the product of the divisors
Example
• Find the LCM of 14 and 20
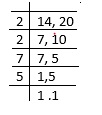
LCM = 2 × 2 × 7 ×5 = 140
• Find the LCM of 12 ,18 and 44.
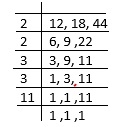
LCM = 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 11 = 396
Perfect numbers
A number for which sum of all its factors is equal to twice the number is called a perfect number.
Example: Factors of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14 and 28.
Here, 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14 + 28 = 56 = 2 × 28
Therefore, sum of factors of 28 is equal to twice the number 28.
To know more about Perfect Numbers,