BASIC GEOMETRICAL IDEAS
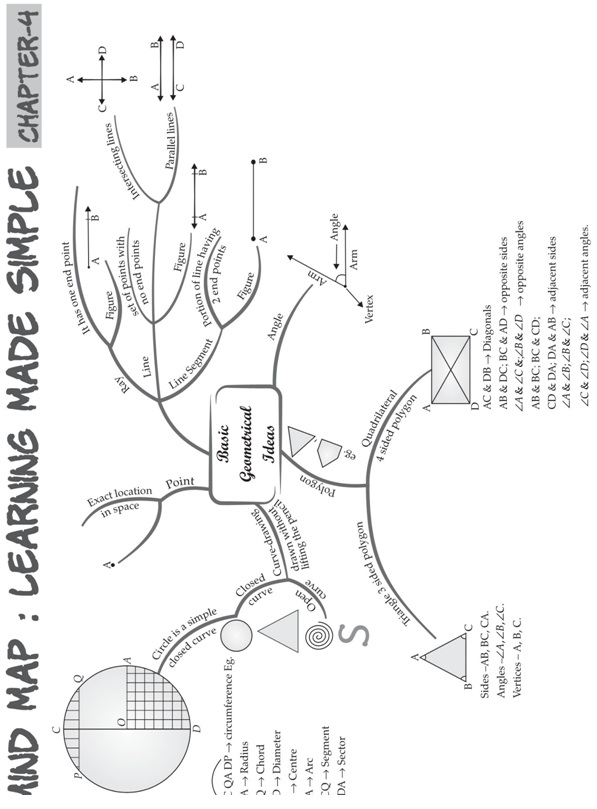
Basic Definitions in Geometry
Polygons
A polygon can be defined as a closed curve which is made up of line segments. Polygons can be of numerous types like
triangles (having 3 line segments), quadrilaterals (having 4 line segments), pentagon (having 5 line segments),
and so on. A few important terms related to polygons are.
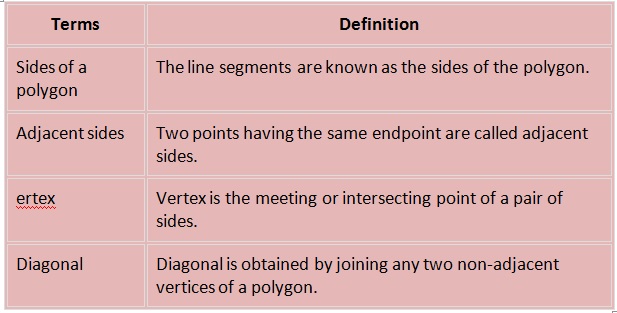
A polygon is a two-dimensional geometric figure that has a finite number of sides. The sides of a polygon are made
of straight line segments connected to each other end to end. Thus, the line segments of a polygon are called sides
or edges. The point where two line segments meet is called vertex or corners, henceforth an angle is formed. An
example of a polygon is a triangle with three sides. A circle is also a plane figure but it is not considered a polygon,
because it is a curved shape and does not have sides or angles. Therefore, we can say, all the polygons are 2d shapes
but not all the two-dimensional figures are polygons.
A simple closed figure made up line segments is called a polygon.
Polygonshape
By definition, we know that the polygon is made up of line segments. Below are the shapes of some polygons that
are enclosed by the different number of line segments.
Types of Polygon
Depending on the sides and angles, the polygons are classified into different types, namely:
• Regular Polygon
• Irregular Polygon
• Convex Polygon
• Concave polygon
Regular Polygon:If all the sides and interior angles of the polygon are equal, then it is known as a regular polygon.
The examples of regular polygons are square, rhombus, equilateral triangle, etc.
Irregular Polygon:If all the sides and the interior angles of the polygon are of different measure, then it is known
as an irregular polygon. For example, a scalene triangle, a rectangle, a kite, etc.
Convex Polygon:If all the interior angles of a polygon are strictly less than 180 degrees, then it is known as a
convex polygon. The vertex will point outwards from the center of the shape.
Concave Polygon:If one or more interior angles of a polygon are more than 180 degrees, then it is known as a
concave polygon. A concave polygon can have at least four sides. The vertex points towards the inside of the
polygon.
Triangles
A triangle is as a polygon having three-line segments or sides. A triangle ABC is written as∆ABC as given below
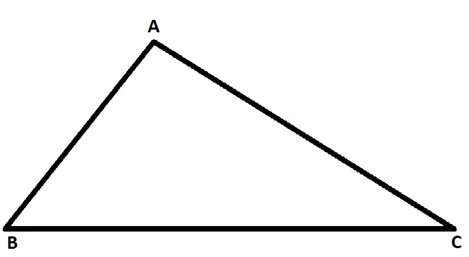
In this triangle, AB, BC, and AC are sides of the triangle and A, B, C are the vertices of the triangle. Also, the
angle between BC and AB is the ∠B, between BC and AC, it is ∠C, and between AB and AC, it is∠A.
Quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is defined as a four-sided polygon i.e. having 4 line segments or sides and thus, 4 angles.
A diagram of a quadrilateral is given for better understanding. It should be noted that the vertices of a
quadrilateral are named in a cyclic manner.
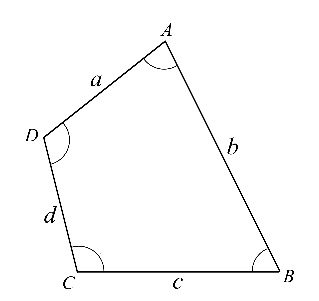
In this diagram, AD and DC are one of the examples of adjacent sides. Also, AD and BC are one of the opposite
sides. Here, angle A and angle C are opposite angles. In this, if the line segment is drawn from A to C or from
B to D, it becomes a diagonal.
Angles
• An angle is made by two rays starting at a common endpoint.
• These rays are called the arms of the angle.
• The common endpoint is called the vertex of the angle.
• While naming an angle the vertex of the angle has to be in the middle.
• For example: Ray OP and Ray OQ form an angle. It can be denoted as ∠POQ.
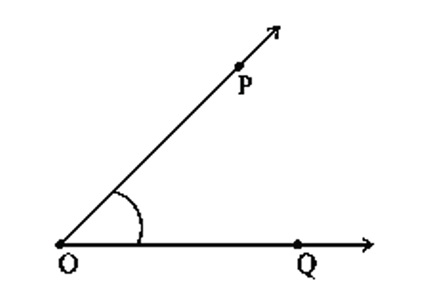
• Ray OP and OQ are the arms or sides of the angle. O is the vertex of the angle POQ
Exterior and interior points to an angle
• An angle separates its plane into three regions.
• These regions are the angle, interior of the angle and exterior of the angle.
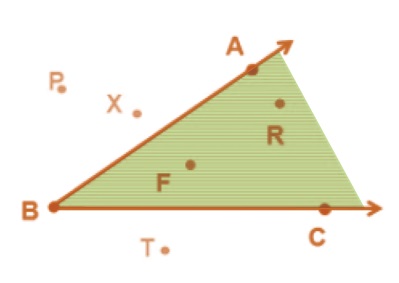
• In the figure above, points F and R lie in the interior of ∠ABC. Point A, B and C lie on
the angle ∠ABC and P, X and T lie on the exterior of angle ∠ABC.
Circle
• A circle is a simple closed curve which is not a polygon.
• A circle is basically formed when a point is moving at a fixed distance from a fixed point.
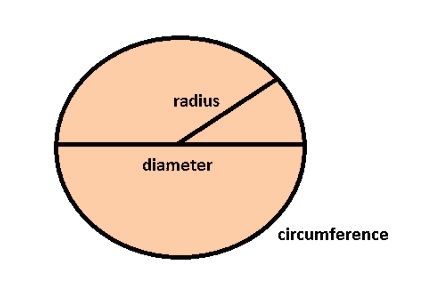
• This fixed point in the middle is called the centre.
• The distance moved by the point around the circle is called the circumference.
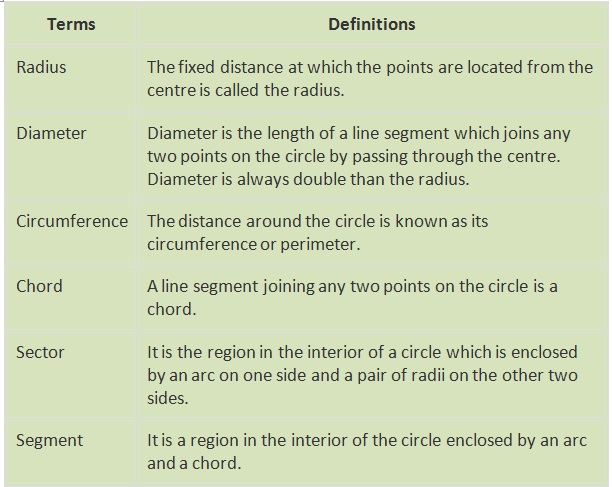
Terms related to circle
• The chord of a circle is a line segment joining any two points of a circle.
• A diameter is a chord passing through the centre of a circle.
• The diameter divides a circle into two equal halves called semicircle.
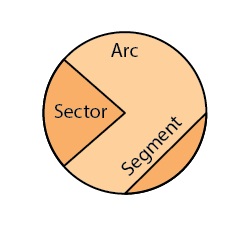
• A region in the interior of a circle enclosed by an arc on one side and a pair of radii
on the other two sides is called a sector.
• A region in the interior of a circle enclosed by a chord and an arc is called a segment.
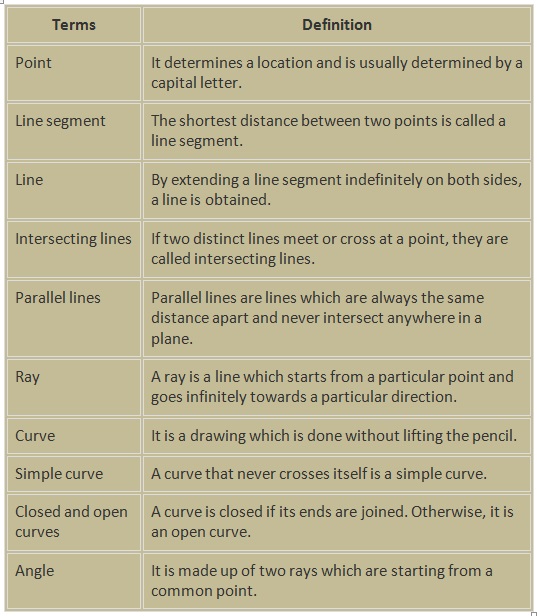
Line segment
• The shortest distance between two points is called a line segment.
• Those points are called endpoints of the line segment.
![]()

Lines
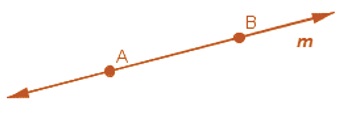
• When a line segment is extended on both sides infinitely, then it is called a line. Here m is a line.
• It contains an infinite number of points on it.
Ray
• A ray is a portion of a line. It starts at one point, called its starting point, and goes endlessly
in the other direction.
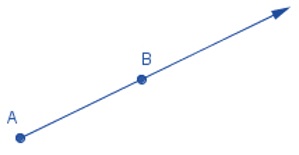
• In the ray AB, A is the starting point and B is just a point on the path of the ray.
![]()
Intersectingand parallel lines
• If two lines have a common point, then they are said to be intersecting.
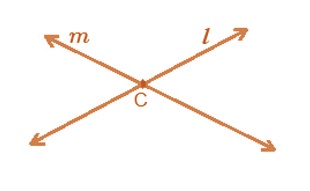
• Lines l and m here have a common point P, hence they are intersecting lines with P being the point of intersection.
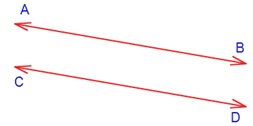
• If two lines have no common point, then they are said to be parallel. Here AB and CD are parallel lines.
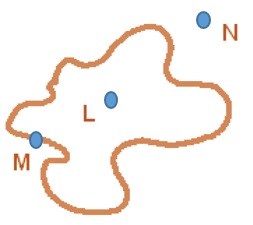
Position in a figure
There are three important parts of a closed curve. In the figure below, L is in the interior of the curve,
M is on the boundary while N is in the exterior of the curve.
About Circles
A circle can be defined as a closed figure formed by a set of points in a plane which are located at the
same distance from a fixed point which is the centre. A few important terms related to circles are:
Points
• A point determines a specific location.
• They are denoted by any capital letter of the English Alphabet.
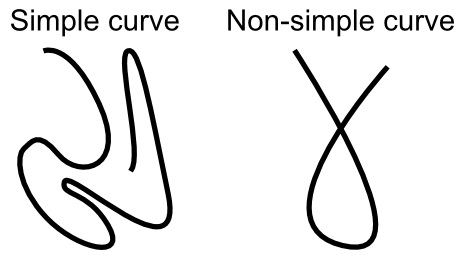
Curves
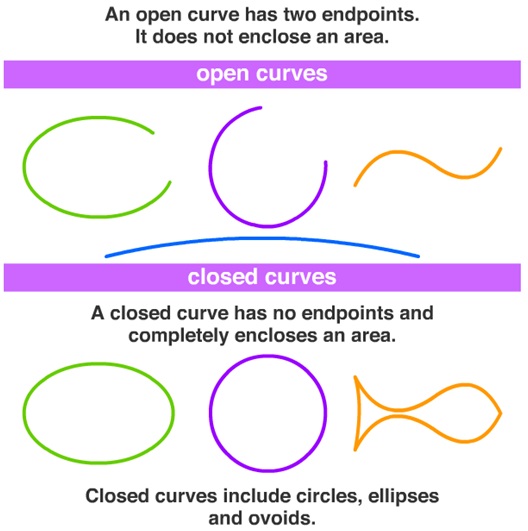
• In simple terms, any line that is not straight is said to be a curve.
• If a curve does not cross itself, then it is called a simple curve.
Closed and open curves
A curve is said to be closed if it ends are joined.
A curve whose ends are opened is said to be open curves.