Prefixes
• A prefix is a group of letters which is fixed at the beginning of the root or baseword.
• The term ‘prefix’ is derived from the Greek root words ‘pre’ which means ‘before’ and
‘fix’which literally means ‘tofix’.

Functions of Prefixes
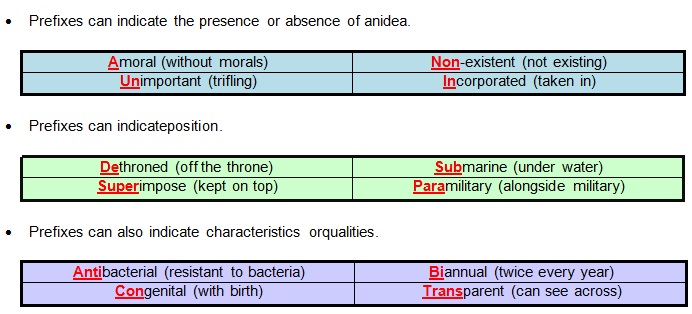
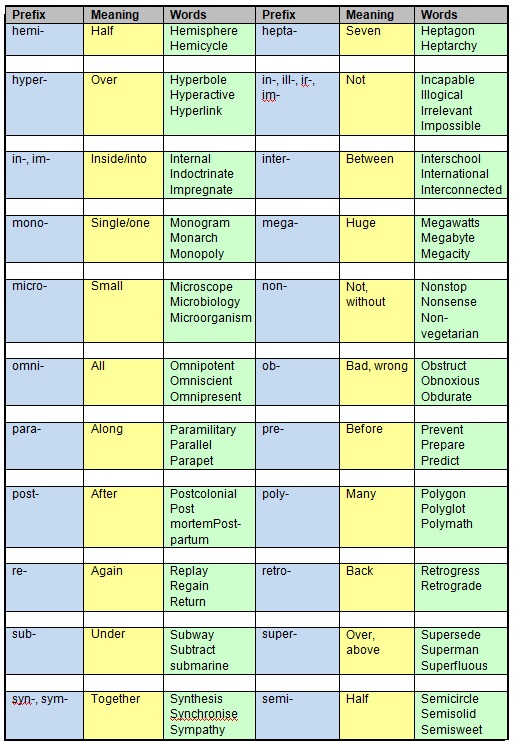
List of Common English Prefixes


Suffixes
• A suffix is a group of words which is fixed at the end of the root or baseword.
• The term suffix is derived from the Greek root words ‘sub’ which means ‘under’ and ‘fix’
which literally means ‘tofix’.

Functions of Suffixes
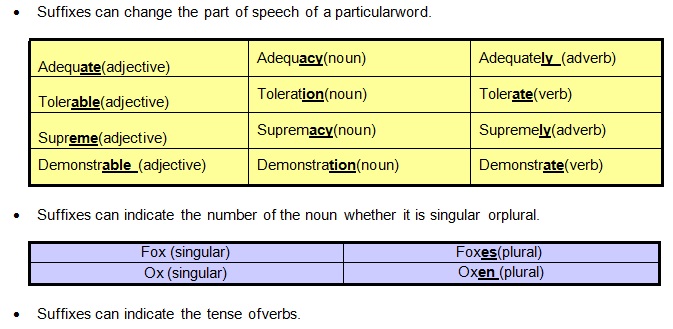

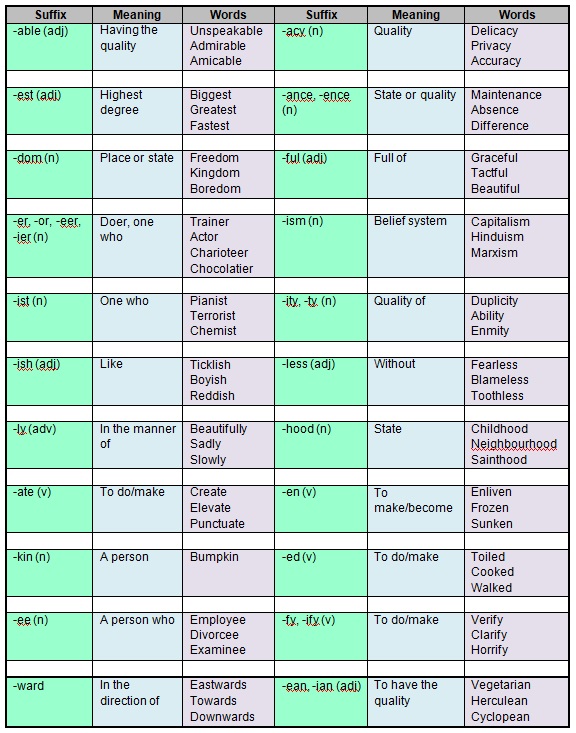
List of Common English Suffixes
Root Words and Base Words
• Root words and base words are the parts which contain the primary meaning of theword.
• Prefixes and suffixes are added to the root and base words to create new words andideas.
Root Word
• A root word cannot stand on its own as an independentword.
•It needs the addition of the prefix or the suffix for the completion of itsmeaning.
• For example, let us take the words Geologist andCarnivorous.

• In the above cases, the roots geo-, -log-, - carni- and -vor- cannot stand alone as individual words.
• They are therefore known as rootwords.
Base Word
• A base word, unlike a root word, can stand on its own like an independentword.
• It does not need the addition of the prefix or the suffix to function as a stand-aloneword.
• For example, let us take the words Undo,Precook, Counterattack andSuperscript.

• In the above cases, do, cook, attackand scriptcan all function as meaningfulwords.
• They are therefore known as basewords.
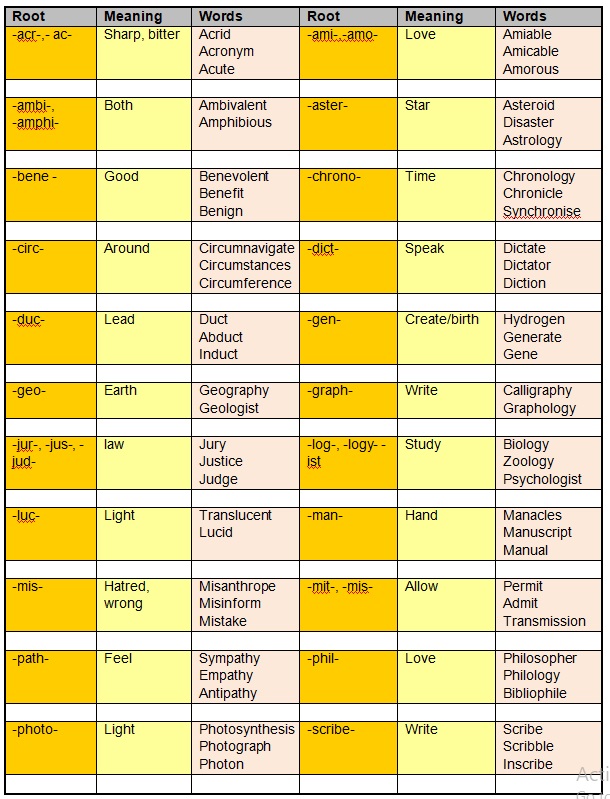
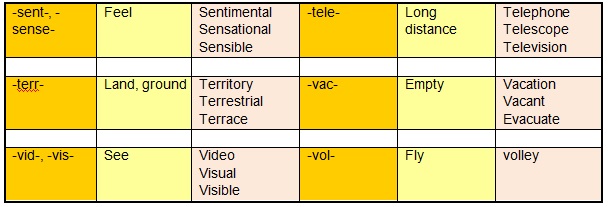
List of Common Root Words and Base Words
How to Use the Affixation System
• Thorough knowledge of the English affixation system helps us in guessing the meaning of
theword purely by the means of its prefix-root-suffixstructure.
• Because of the limitations of our memory, it is not easy to remember a large number of words at a time.
• We may find it difficult to associate the meaning of the word with itsstructure
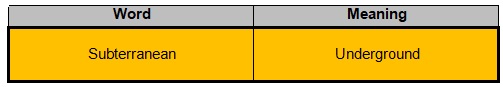
• With the knowledge of the affixation system, we can guess the meaning of the givenword.
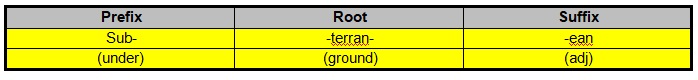
The meaning of the above word is ‘Underground’, and it is used as an adjective.
Thus, to have a rich vocabulary, students should learn the prefix-root-suffix method. It is an interesting
way to expand your vocabulary with little effort. Students who are well-versed with the affixation system
find it easier to tackle difficult words and are more confident about their word usage. It will definitely
give you an edge over the others when it comes to words.
Synonyms and Antonyms
What are Synonyms?
Synonyms are words or phrases which are used as substitutes for another. Sometimes, synonyms need not
mean exactly the same as the other word. They can also be a close substitute for the other word.
Synonyms can belong to any word category:
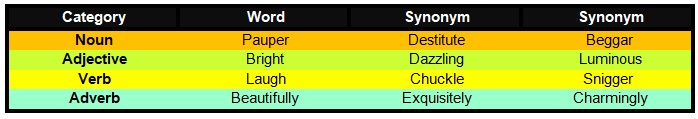
Why do Synonyms Exist?
English is a language which has many influences since it has evolved in a natural manner. Today, it is a combination
of languages such as Latin, Greek, Celtic, French, Scandinavian and even Hindi. Some words in English are adopted
from these languages in addition to the ones which already exist. For example, mansion is a word which is adopted
from French. At the same time, its synonym bungalow is taken from Hindi.
What are the Uses of Synonyms?
Why are synonyms used when one word can convey the idea perfectly? Let us find out.
Situation
Let us consider the words check and investigate. Though both the words are synonyms of each other, we
cannot substitute one for the other in certain situations.
Examples:
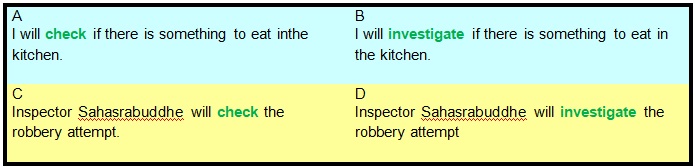
In the above examples, the usage of the word check in sentence A seems appropriate. Its synonym investigate
sounds awkward and pompous in sentence B. Similarly, in sentence C the word check lacks the force of the
word investigate which is used in sentence D. In conclusion, we can say that it is the situation that dictates
which word or its synonym has to be used.
Tone
Sometimes a word does not do justice to the emotion behind it. The tone or the emotion behind a
person’s voice can also dictate which word has to be used.
Examples: Dislike, hate, despise

Although the three highlighted words are synonyms, they have different tonalities. Hence, one cannot
use the word dislike to describe a very strong and personal hatred.
Sound
We use a certain word instead of its synonym because it sounds more pleasing.
Examples:

In the above examples, group and idiots are synonyms of confederacy and dunces, respectively.
Sentence A sounds more appealing than sentence B because of the choice ofwords. Hence, it is
important that we use synonyms sometimes to make sentences sound morepleasing.
We can conclude by saying that synonyms make the language rich in meaning by adding varietyto it.
It also helps the speakers express themselves better and more clearly. The speakers can assess the
situation and use appropriate words to deliver the exact message they wish toexpress.

What are Antonyms?
In contrast with synonyms, antonyms are words or phrases which are opposite in meaning to another.
This may sound strange, but often, to understand a word better, we have to look at its antonym.
We learn the meaning of the word by understanding how it contrasts with its antonym

Sometimes, to understand a word better, it is important that we look up its antonym along with
its synonym. Like synonyms, there can be more than one antonym for a given word.
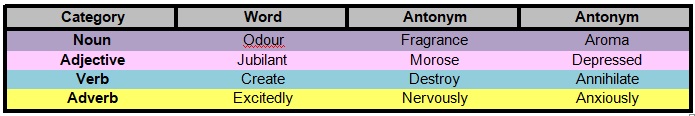
What are the Different Types of Antonyms?
There are three basic types of antonyms:
• Gradableantonyms
• Complementaryantonyms
• Relationalantonyms
Gradable Antonyms
Gradable antonyms are words which are the extreme opposites of each other. Imagine a spectrum or a scale.
Gradable antonyms will be at equal distances from the centre on the scale. However, these words may have
a spectrum of words between them. All these words may exist together on the same scale.
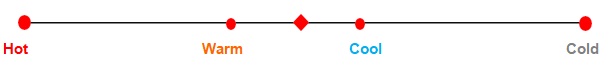
In the above example, hot is the polar opposite of the word cold. But together, they exist on the same
spectrum as warm and cool. Let us look at more examples of gradable antonyms.

Complementary Antonyms
Unlike gradable antonyms which have a spectrum of words between them, complementary antonyms are
words which express two extreme ideas without the possibility of ‘middle’ words. They do not lie on a
continuous scale and are the exact opposites of each other.
Let us look at a few examples of complementary antonyms.

Relational Antonyms
Relational antonyms are words which are opposite to each other by the virtue of their relationship alone.
One finds meaning through the existence of the other. For example, the word up exists in relation to
the word down.
Let us look at a few examples of relational antonyms.
