Types of Sentences – Based on Form
What is a Sentence?
A sentence is a group of words which makes complete sense.
It contains a subject and a verb, and may also contain an object.
Examples:
Kavita plays. (S + V)
Kavita plays the piano. (S + V + O) Ravi kicks.
Ravi kicks the ball.
Sentences can be categorised based on
• Meaning
• Form
Based on meaning, sentences can be declarative, interrogative, imperative, exclamatory and optative.
Let us see how sentences are categorised based on their form and characteristics.

Types of Sentences Based onForm/Structure

Simple Sentences
• A simple sentence has only one subject and onepredicate.
• It has only one independentclause.
• A simple sentence contains one subject and oneverb.
• Simple sentences can be both short andlong.
Examples:
The fish swam.
Subject: The fish
Predicate: swam
Verb: swam
Gayatri went to the market in the evening.
Subject: Gayatri
Predicate: went to the market in the evening
Verb: went
• Simple sentences can have compound subjects and compoundverbs.
Examples:
The dog howled and ran.
Subject: The dog
Predicate: howled and ran
Verbs: howled, ran
Raman and Priya love mashed potatoes.
Subject: Raman and Priya
Predicate: love
Verb: love mashed potatoes
A simple sentence DOES NOT contain a dependent clause or another simplesentence.
Compound Sentences
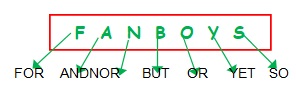
A compound sentence has two or more simple sentences joined by
• A comma followed by a FANBOYS word (coordinatingconjunction)
The mouse jumped, and the cat ran after it.
Manju rose from her chair, but Sita had left the room.
• A semicolon
The mouse jumped; the cat ran after it.
Manju rose from her chair; Sita had left the room.
• A comma when simple sentences are being treated as items in a series. The mouse jumped, the cat ran after it,
and Jeremy followed them. Manju rose from her chair, Sita left the room, and Hari startedyelling.
Complex Sentences
A complex sentence consists of one independent (main) clause and one or more dependent (subordinate) clauses.
The clauses can be joined by subordinating conjunctions or relative pronouns.
Examples:
The boy who is the captain of the team got injured yesterday.
Independent Clause: The boy got injured yesterday
Dependent Clause: who is the captain of the team
Relative Pronoun: who
A puzzled mind will keep wondering until you finally decide something.
Independent Clause: A puzzled mind will keep wondering
Dependent Clause: until you finally decide something
Subordinating conjunction: until
When the doorbell rang, Jiten shut his textbook and rose to open the door.
Independent Clause: Jiten shut his textbook and rose to open the door
Dependent Clause: When the doorbell rang
Subordinating conjunction: when
Amrita paid the cab driver whose stained teeth made her look at him with disgust.
Independent Clause: Amrita paid the cab driver
Dependent Clause: whose stained teeth made her look at him with disgust
Relative pronoun: whose
Types of Sentences – Based on Meaning
What is a Sentence?
A sentence is a group of words that makes complete sense.
It contains a subject and a verb, and may contain an object.
Rohit runs. (S + V)
Rohit runs at the race. (S + V + O) Sunita bakes.
Sunita bakes the pastries.
In the chapter on Idioms, Phrases and Proverbs, we have learnt that a phrase is a combination of words expressing
something figuratively. Phrases must be used with other parts of speech to make acomplete sentence.
Sentences can be divided based on
• Form
• Meaning
Let us learn about the types of sentences based on meaning.
Types of Sentences Based on Meaning

A declarative sentence is a statement that conveys information.
A declarative statement may be
1. Affirmative Declarative
The guests have arrived.
Mukul has finished dinner.
2. Negative Declarative
I don’t have the bag right now.
Priya did not shuffle those papers.
3. AffirmativeInterrogative
Will you share your sandwich with me?
Have you paid the school fees?
4. Negative Interrogative
Aren’t you going to introduce me to your friends?
Doesn’t this painting look beautiful?
5. AffirmativeImperative
Please tie your seatbelts.
Please switch off your mobile phones.
6. Negative Imperative
Don’t touch any item without permission.
Don’t misuse school property.
An interrogative sentence is used to ask questions. Interrogative statements can be classified into
1. Yes/no questions: These expect the listener to answer a yes or ano.
Did you lock the back door?
Haven’t you seen the Taj Mahal yet?
2. Yes/no questions with modal auxiliaries: Can be used to seek
permission or advice, to request orquestion.
May I close the door now?
Can you tell which one looks better?
Could you drop me to the bus stop?
Must I block the access right now?
3. Wh- questions: These expect the listener to give detailedanswers.
Which is the way to Janpath?
What is your name?
Where did Mahatma Gandhi live?
Why is the baby crying?
4. Alternative questions: These are used to ask the listener’spreference.
Do you want to order salad or milkshake?
Will you wait here for Jordon or should I drop you?
5. Question tags: These are short questions asked to conform or contradict a statement.
Will doesn’t own this property, does he?
Suman is going to sell his land, isn’t he?
6. Rhetorical questions: These have the structure of a question but functionas declarativesentences.
Do you think this food comes free? (One has to work hard and earn money to buy food.)
Is the school going to change its policy for one student?
7. Echo questions: These are direct questions that repeat a part of the question someone elseasked.
Ragini learnt Tai Chi.
Ragini learnt what?
Jyoti shopped from Milan.
Jyoti shopped from where?
|
An imperative sentenc 2. Request 3. Command orinstruction 4. Invitation 5. Permission orprohibition |
|
An exclamatory sentence expresses sudden rush of emotions. Exclamatory statements can be used to express many emotions: What a tragic end to such a beautiful life! (Sorrow) What! This pen costs 50 dollars? (Shock) How rudely she talks! (Dislike) What a dirty hotel! (Disgust) |
|
An optative sentence is used to express 1. AWish 2. APrayer |