Tenses
What are Tenses?
Tense is something which tells us when the action expressed by the verb took place.
There are three main divisions of tenses.
Present Tense
The present tense can be divided into three sub-categories:
1. Simple
2. Continuous
3. Perfect

Present Continuous Tense
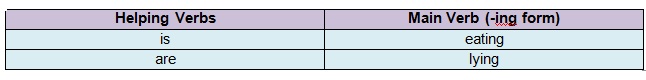
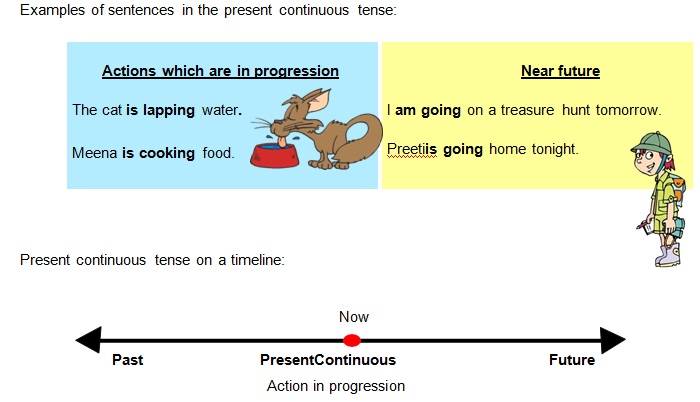
• The present continuous tense is used to express actions which are currently inprogress.
• Progressive helping verbs (is, am, are) are used along with the ‘-ing’ form of theverb.
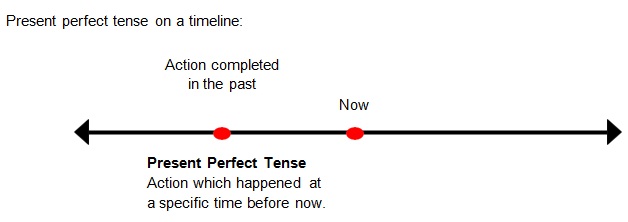
Present Perfect Tense
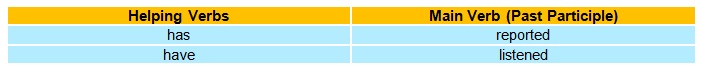
• The present perfect tense is used to express an action which may have happened at a specific time beforenow.
• Perfect helping verbs (has, have) are used with the past participle form of theverb.
• The present perfect tense is never used when the time or date of the action ismentioned.
• The milkman has delivered the milk in the morning.Incorrect
• The milkman delivered the milk in the morning.Correct
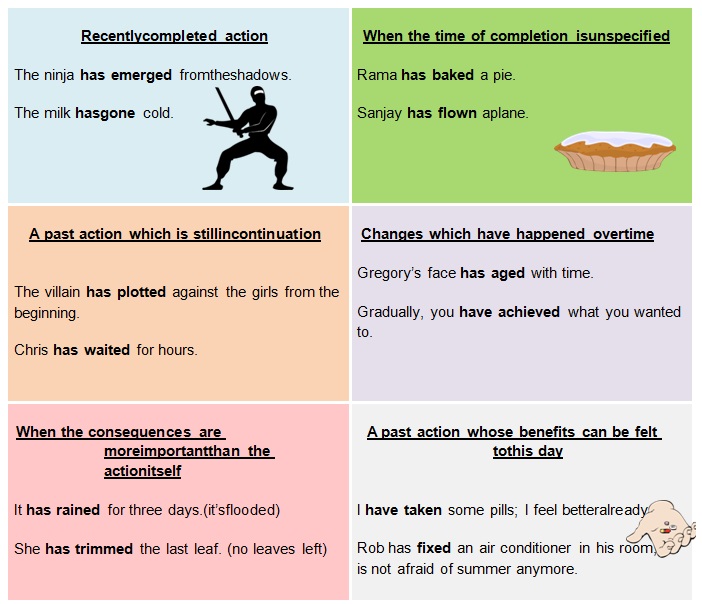
Examples of sentences in the present perfect tense:
Past Tense
The past tense can be divided into four sub-categories:
1. Simple
2. Continuous
3. Perfect
4. Perfectcontinuous
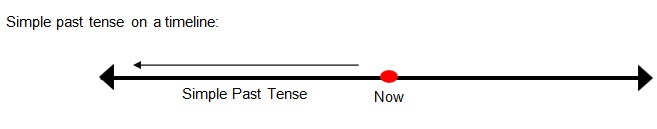
Simple Past Tense
• The simple past tense is used to express an action which was completed at one point of time in thepast.

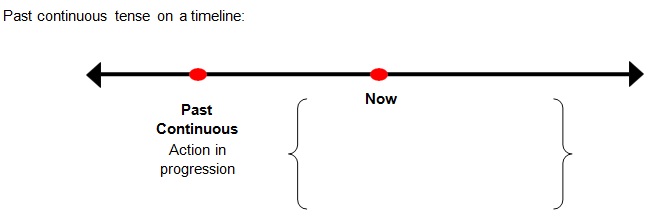
Past Continuous Tense
• The past continuous tense is used to express actions which were in progression at one pointof time in thepast.
• It is formed when progressive helping verbs (was, were) are added to the ‘-ing’ form of themain verb.


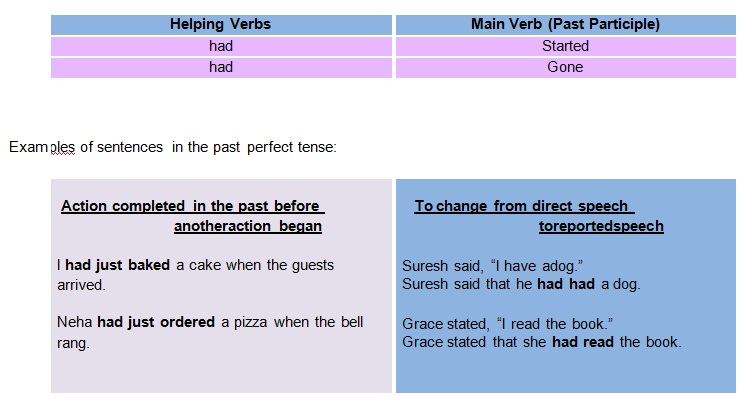
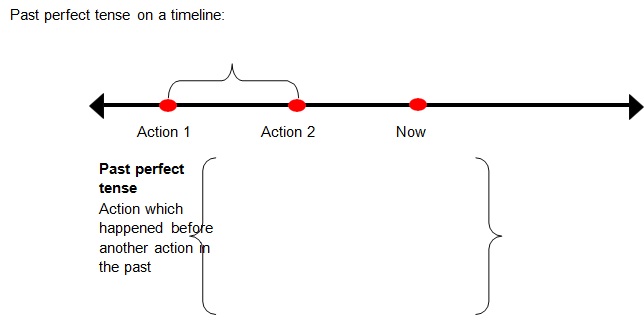
Past Perfect Tense
• The past perfect tense is used to express an action which may have happened at a
specific time before another action began in thepast.
• The perfect helping verb (had) is used with the past participle form of theverb.
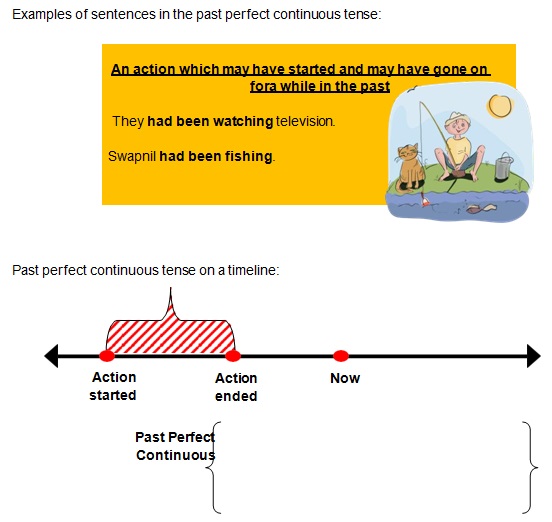
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
• The past perfect continuous tense is used to express an action which may have started ata particular
point of time in the past and may have ended at another point of time in thepast.
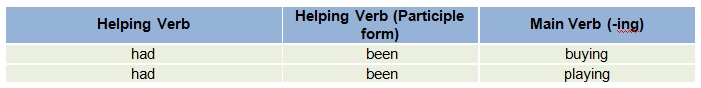
• It is formed out of the addition of the perfect helping verb (had) to the participle form ofprogressive
helping verbs (been) and finally to the ‘-ing’ form of the mainverb.
Future Tense
The future tense can be divided into four sub-categories:
1. Simple
2. Continuous
3. Perfect
4. Perfectcontinuous
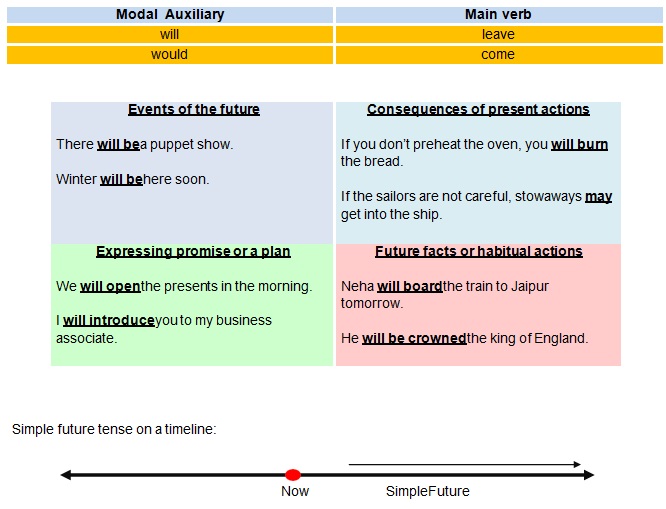
Simple Future
• The simple future tense is formed by adding the modal auxiliaries ‘will’ or ‘would’
to the simple present tense of the mainverb.
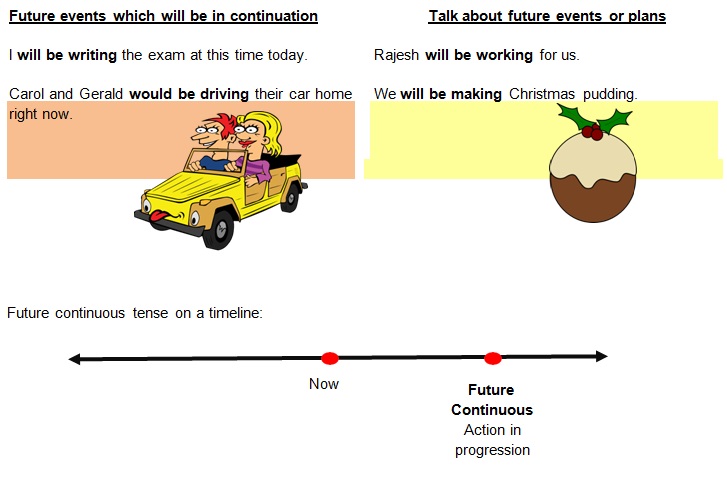
Future Continuous Tense
• The future continuous tense is formed by adding the modal auxiliaries ‘will’ or ‘would’
and the progressive helping verb ‘be’ to the ‘-ing’ form of the mainverb.

Examples of sentences in the future continuous tense:
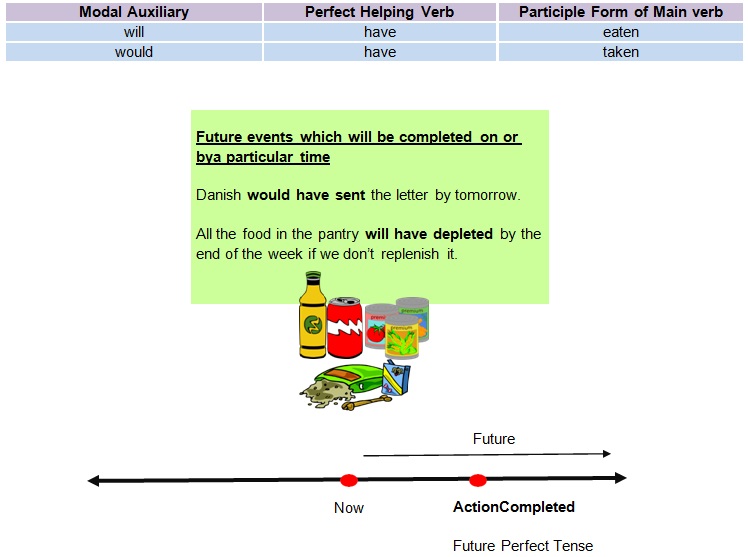
Future Perfect Tense
• The future continuous tense is formed by adding the modal auxiliaries ‘will’ or ‘would’ and the
perfect helping verb ‘have’ to the participle form of the mainverb.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
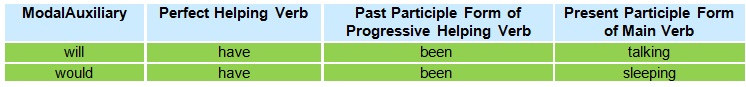
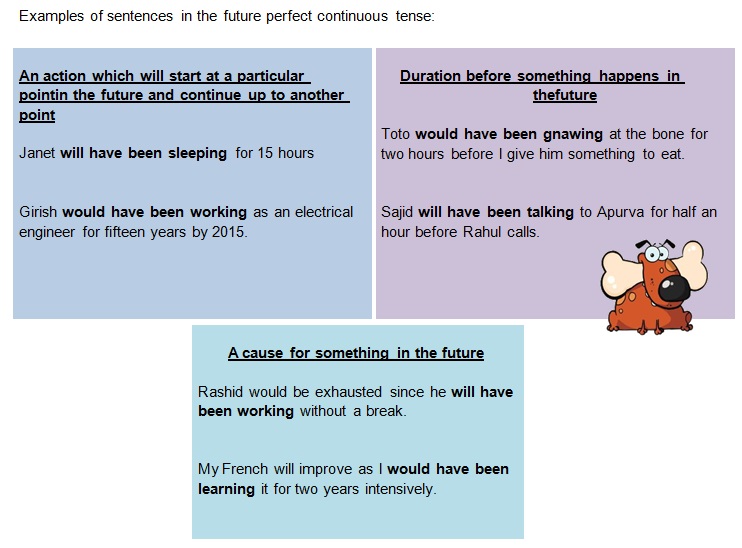
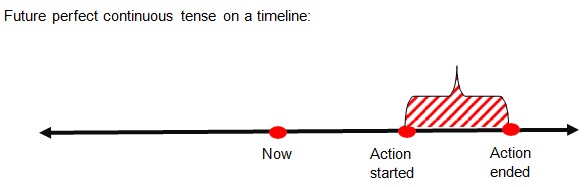
• The future perfect continuous tense is formed by the addition of the modal auxiliaries (will or would); perfect
helping verb (have); the past participle form of a progressive helping verb (been); and the present participle
(-ing) form of the mainverb.