Adjectives: Participles and NominalAdjectives
Participles
1. The revellers were feastingon the food.
2. Feastingon the food, the revellers sang songs.
In the above sentences, the word feasting is used in two different ways.
• In sentence 1, the word feasting is used as a verb; its subject is the wordrevellers.
• In sentence 2, the word feasting qualifies the noun revellers. It is formed from the verb feast.
It also has an object food. Therefore, it has the properties of a verb and anadjective.
• The phrase Feasting on the food is a participialphrase.
Let us look at more examples.
1. Fatima is singingto her baby.
2. The singingbird perched itself on a branch.
In the above sentences, the word singing is used in two different ways.
• In sentence 1, the word singing is used as a verb; its subject beingFatima.
• In sentence 2, the word singing qualifies the nounbird.
• It is formed out of the verbsing.
• The word not only expresses the action of the noun but also acts as anadjective.
• The word singing in sentence 2 is therefore a participle because it looks like a verb but actslike anadjective.

Participles ar e grouped into two categories according to their tenses—past participle and present participle.


Nominal Adjectives
Read the following sentences.
1) The bride was rich, but the bridegroom waspoor.
2) The richwill always exploit thepoor.

• Nominal adjectives represent a class marked by theirqualities.
• Thehazardous
• Theyoung
• Theliving
• Theinspirationa
• Nominal adjectives represent nationalities.
• TheBritish
• TheDutch
• TheGermans
• TheJapanese
• TheIndian
• Comparative and superlative adjectives function like nominal adjectives
• The better of the lot
• Theworst
• The mostimportant
Points to remember
Nominal adjectives are always preceded by the definite article.
• Thehorrible
Nominal adjectives can be modified by other adjectives or adverbs.
• The extremelyunfortunate
• The trulyhonest
Adjectives: Royal Order of Adjectives
Royal Order of Adjectives

Obviously, sentence 2 sounds right to you. But how did you arrive at that answer?
Knowing how to arrange the adjectives is intuitive.
Speakers of English instinctively know that
big red bug is correct and red big bug is incorrect.
Royal Order of Adjectives
If there is more than one adjective qualifying a noun, then they all have to be arranged in a particular order.
This order is predetermined and comes naturally to habitual users of English. Let us learn more!
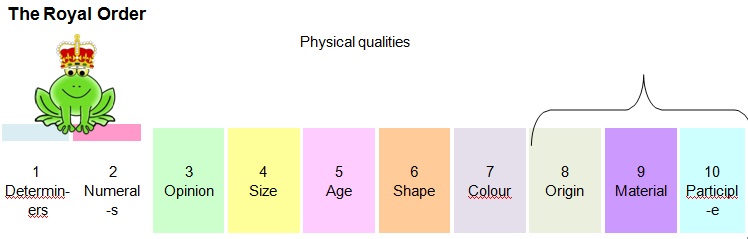
2. Numerals: Adjectives of number which show the numerical value of nouns comenext.
• One, three, many, some
3. Opinion: Adjectives which are based on opinions. They can differ from person to person. Something
that is beautiful or interesting to one person may not hold the same meaning for somebodyelse.
• Pretty, good, nice, evil,rotten
4. Size: Adjectives which express the size of thenouns
• Gigantic, huge, minuscule,small
5. Age: Adjectives which express the age of thenoun
• Old, new,prehistoric
6. Shape: Adjectives which express the shape of thenoun
• Triangular, round, prismatic,oblong
7. Colour: Adjectives which express the colour of thenoun
• Red, blue, yellow, green, maroon,golden
8. Origin: Adjectives which express the nationality or the place of origin of thenoun
• Hungarian, Indian, American, Polish,Gujarati
9. Material: Adjectives which tell us about the materials which make up thenoun
• Glass, silk, wooden, brick,paper
10. Participle: Adjectives which give the purpose for using certain nouns or itsqualities.
• Sewing, frying, sleeping, beloved,frozen



Adjectives: Types of Adjectives
Types of Adjectives
What are Adjectives?
Adjectivesare words that tell us more about nouns. They tell us about
• Quality
• Beautiful, sly, slithery, cold, evil,busy
• Quantity
• Some, more, much, 5 kg,13
• Colour
• Green, silvery, bluish, metallic,red
• Origin
• Mongolian, Arabic, Maharashtrian,Subterranean
• Shape
• Rectangular, triangular,round
• Size
• Big, small, tall, stout,thin
• Age
• Old, new,prehistoric
Placement of Adjectives
There are two ways in which we can use adjectives in English.
• Before the nouns theyqualify
o Threesticks, a queersight, somegentlemen
• After forms of the verb ‘to be’ and with others such as ‘looks’, ‘seems’, ‘sounds’, ‘feels’, ‘smells’etc.
o The house looksmagnificent.
o The boy seemsnervous.
o I ambusy.
o The camper was asleepin histent.
o They were victoriousin theirefforts.
An adjective of quality is a word which indicates the quality or the attribute of a noun.
• To understand the nature of the noun, we ask the question ‘What kind of?’ to the noun.
The answer which we get is the adjective ofquality.
• This is a slimymonster.
What kind of monster?
Slimy
Let us look at a few examples.

An adjective of quantity tells us about the quantity of a noun.
• Some, many, few, little, less, much, more, enough, sufficientare someexamples.
• It describes the number of countablenouns.
• The threemusketeers, manyblack birds, a fewenemies
• It describes the volume, amount or quantity of uncountablenouns.
• Somemilk, threekilo rice, muchwater
• To understand the quantity of the noun or pronoun, we ask the question‘How much/many?’
The answer we get is the adjective ofquantity.

• It can also express a definitenumber.
• fivepeople, threelittle pigs, 5 kilorice
• Adjectives like much, littleand lessare used with uncountablenouns.
• muchtime, a littlewater
• Adjectives like manyand feware used with countablenouns.
• manybottles, fewchildren Let us look at a fewexamples.
Let us look at a fewexamples.

Previously, we learnt about demonstrative pronouns which point towards their antecedents.
In this chapter, we learn about demonstrative adjectives.
• Adjectives like this, that, theseand thoseare demonstrativeadjectives.
• They help the reader or listener understand what or who exactly is beingaddressed.
• ‘This’ and ‘that’ are used for singularnouns.
• Thiscat, thathouse, thisriver, thatwoman
• ‘These’ and ‘those’ are used for pluralnouns.
• Thesedays, thosegentlemen, thesetoys, thosemoments
Let us look at a fewexamples.

Interrogative adjectives are those which help in framing questions by appearing before the noun that they qualify.

Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives, like possessive pronouns, show ownership or possession of nouns to pronouns.
• My, your, his, her, our, its, theirare possessiveadjectives.
• They appear before the noun theyqualify.
