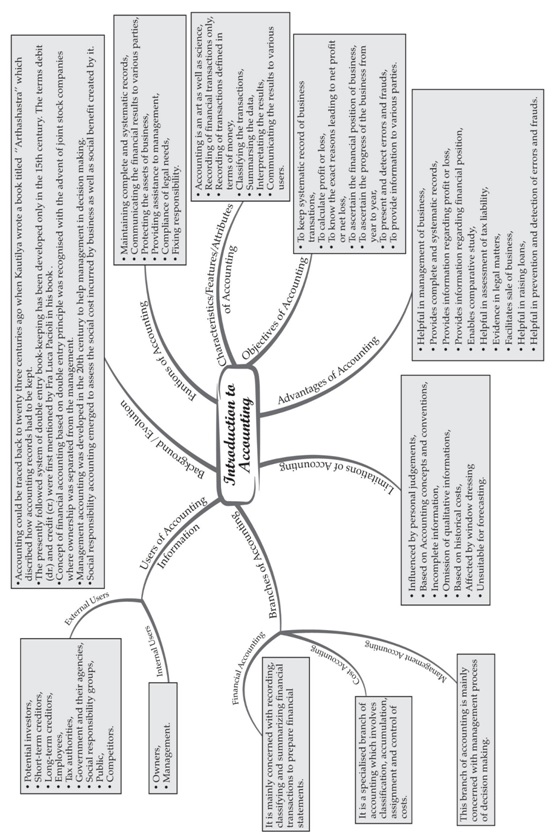
Introduction To Accounting
Introduction to Book Keeping, Accounting and Accountancy
Understanding Meaning and Differences between Book Keeping, Accounting andAccountancy:
► Meaning of Book Keeping:
• According to R.N. Carter, “Book keeping is the science and art of recording correctly in the books of account
all those business transactions that result in the transfer of moneyor money’s worth.”
• It is a part of accounting and therefore, involves identification of financial transactions, measurement of such
transactions in monetary terms, recording of such transactions in the books of account and classifying the transactions
and events by way of posting them into individual Ledger Accounts.
► Meaning of Accounting:
• According to American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying and
summarising in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least, of a
financial character and interpreting result thereof.
• Accounting is an art that records, classifies and summarises the financial transactions which helps in understanding
the profitability and financial status of the business. It is also regarded as science as it is follows a structured knowledge
base that requires effective compliance of the basic accounting concepts and principles.
► Meaning of Accountancy:
• According to Kohler, “Accountancy refers to the entire body of the theory and practice of accounting.”
• It is a systematic knowledge of accounting which helps to deal with various aspects of accounting. In addition to this, it
educates the users on how to maintain the books of accounts and to summarise the accounting information that is to be
communicated to the users.
► Understanding the relationship between Accounting and Accountancy:
• Accounting is a process and Accountancy is knowledge.
• Accountancy frames rules and principles which are to be followed and complied in the Accounting process.
• It is therefore said that accountancy is the knowledge of accounting and accounting is. the application of accountancy.
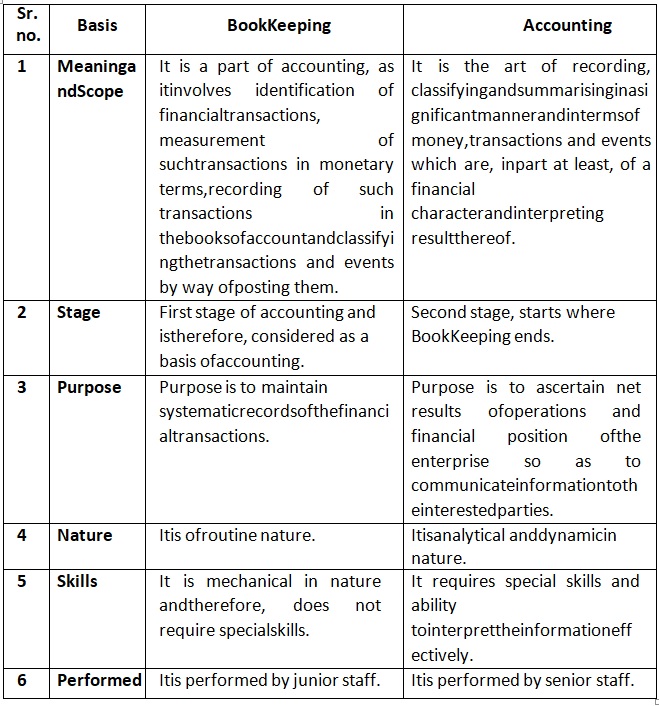
• Differences between Book Keeping and Accounting:
Introduction to Accounting
As per the American Accounting Association,“Accounting is the process of identifying, measuring and communicating economic information to permit informed judgments and decisions by users of the information.”
Characteristics, Objectives, Process and Branches of Accounting:
► Characteristics or Attributes:
Identification of the economic events and financial transactions: In order to record the transactions in the books
of account, it is necessary to identify the transactions which are considered as a part of economic activity for the entity. This
is done with the help of bills and invoices issued for the respective transactions.
Measurement in terms of money: In order to measure all the identified transactions and events in terms of a common
measurement unit, all the transactions are to be measured in terms of money. This is because, accounting records only those
transactions which are measurable in monetary terms.
Recording of business transactions: This is the process of entering the business transactions in the primary or original
book of account i.e., Journal which is further divided into specific subsidiary books such Cash Book, Purchases Book, Sales Book, etc.
Classification of business transactions: It is the process of classifying the identified transactions or entries of similar
nature at one place. This is done by posting the entries from the Journal to the respective Ledger Accounts under which all
the transactions of similar nature are collected.
Summarising business transactions: This involves presenting the classified data in a manner that is useful and understandable
to the users of financial statements. Summary is prepared by presenting the data in various statements like Trial Balance, Trading
and Profit and Loss Account and Balance Sheet. These are collectively known as Final Accounts.
Analysing and Interpreting the business transactions: In order to make valuable judgments and financial decisions, the information
presented in various statements is analysed and interpreted in a systematic manner.
Communicating the results and conclusions to the interested users in the form ofvarious statements: Involves communicating the
valuable accounting information to the interested users so as to aid them in taking important decisions.
► Objectives:
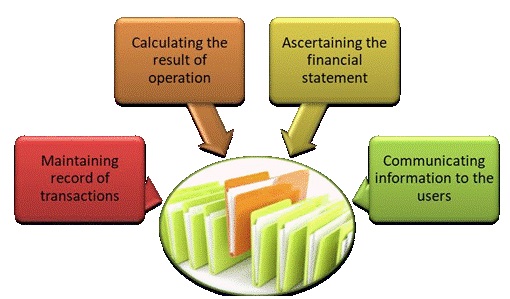
• It maintains a systematic record of all financial transactions in book of accounts.
• It gives an idea about the net results of the business operation periodically. The owner of business organisation can ascertain the profit
earned or loss incurred during an accounting period based on the records maintained.
• It helps to determine the financial position of the business in terms of assets and liabilities on a particular date which is usually the last
day of an accounting year. It also gives a proper account of assets held in the business and the liabilities due for payment.
• It provides valuable information to the users in the form of reports, statements, graphs and charts.
• It facilitates proper planning and effective decision making based on the detailed accounting information maintained.
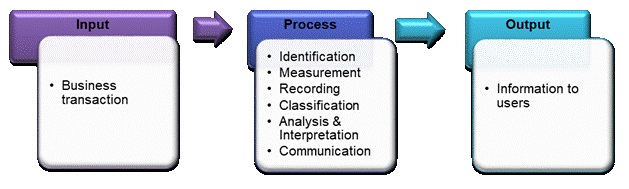
► Accounting Process: Steps involved in an accounting process are based on the attributes of Accounting which are presented below in the
form of a diagram:
► Branches of Accounting: Due to increased scale of business operations, the management function has become more complex now. We have
specialized branches of accounting to handle these situations.
• Financial Accounting: This branch of accounting records financial transactions, summarises and interprets them to present
and communicate the financial results and performance to the interested users.
• Cost Accounting: This branch of accounting takes into account all the business operations, processes or activities in order to
ascertain the cost of products and simultaneously reduce and control costs.
• Management Accounting: This branch of accounting is said to address the needs of a single user group i.e., the management, as
it enables the management to gather information relating to funds, costs, profits, etc. which enables them to take proper decisions.
Functions, Advantages, Role and Limitations of Accounting:
► Functions:
• To maintain the accounting records in a systematic and organised manner so that it can be made available for any future purposes.
• To prepare the financial statements for a particular period which correctly determine the arithmetical accuracy, profitability and
financial position of an entity for a particular period of time.
• To facilitate timely preparation and submission of forms, reports, etc. as are required to comply with the provisions of the Companies
Act, Income Tax Act, GST Act, etc. These submissions can then be used as evidences in the court of law.
• To communicate correct financial information to the users of the financial statements based on which correct financial and investment
decisions can be taken by them.
• To assist the management in maintaining the correct accounting records which helps them to improve their business performance and
facilitate effective decision making for the organization.
► Advantages:
• Financial performance i.e., profit earned or loss incurred during an accounting period and the financial position at the end of an accounting
period is clearly understandable from the accounting records.
• Management is able to make effective business plans and take appropriate decisions related to the business affairs based on the recorded accounting information.
• A systematic accounting record helps in settlement of income tax and GST liabilities because it is the evidence of the correctness of transactions.
• Banks and financial institutions grant loan on the basis of the profitability trends and growth potential that is evident from the statements maintained by the organization.
• Records and statements maintained by the organisation can be used as legal evidences in the event of any scrutiny or investigations.
• These records maintained are helpful in the event of admission or retirement of partners in case of a Partnership firm in order to distribute and allocate the respective
shares to give effect to the adjustments made.
► Role in Business:
• The primary and most important role of accounting information is to maintain a systematic record of the business transactions which are to be
used in preparing financial statements and also in determining the profitability of the business over a period of time.
• It assists the management of an entity by providing the required financial information which can be used in proper functioning and appropriate
decision making for the organisation.
• It provides systematic financial information over a period of time which facilitates comparison of the financial performance of one year with that of other years.
• It is considered a valid evidence in the court of law in the event of a financial issue or case being filed.
• It is maintained systematically in order to avail financial loans and advances in the near future.
• It ensures that all the items are taken into consideration so that correct tax liabilities are determined. This facilitates timely payment of various taxes and duties
and thereby avoid the interest and penalty charged thereon.
► Limitations:
• Accounting records are not fully correct: Transactions are recorded in the books of account on the basis of source documents such as sale invoice, purchase
invoice, receipt of cash etc. In case there is any mistake in these documents, the records maintained will also show incorrect information.
• Accounting does not consider any of the qualitative elements: As accounting statements are confined to monetary values only, qualitative elements are ignored.
• Accounting ignores the price level changes: Since, the accounting records are maintained at historical cost, the changes in the value of money are not considered
while preparing financial statements. Unless price level changes are considered, accounting information will not present the original financial results.
• Accounting information may not be realistic: Since the accounting records are maintained based on the accounting concepts and conventions, it is possible that the
information may not be realistic.
• Accounting may be used to Window Dress the financial position: In order to conceal the facts and present the financial statements in a better manner, books of
account may be manipulated by using various tricks. In such case, the profitability is overstated and Balance Sheet does not give a true picture of its financial position.
Introduction to Accounting Information
Meaning, Types, Characteristics and Users of Accounting Information:
► Meaning:
• According to the Accounting Principle Board, “Accounting is a service activity. Its function is to provide qualitative information, primarily financial in
nature, about economic entities that is intended to be useful in making economic decisions.”
• Accounting information refers to the information in the financial statements prepared through the process of Book Keeping which helps the interested
users to understand the profitability and financial position of the entity and take the appropriate financial decisions.
► Types: Accounting information available from the financial statements can be classified in the following types as information relating to:
• Profit or Surplus: This is the information about the profit earned or loss incurred from the operating activities of the business entity during an accounting year.
• Financial Position: This is the information about the asset owned, amounts receivable and the cash and bank balance owned by an entity. In addition to this, information
about the liabilities owed by the entity is also covered under this head.
• Cash Flow: This is the information about the cash inflows and outflows during a particular accounting period. Such information is used to take vital decisions like payment
of dividend, expansion of business, etc.
► Qualitative Characteristics:

• Reliability: Accounting information should be verifiable and free from errors and any material error.
• Relevance: Accounting information should be relevant enough to meet the needs of the users and helps take some decisions.
• Understandability: Accounting information should be presented in such manner that it is understood by the users.
• Comparability: Accounting information should be such that it facilitates the intra-firm and inter- firm comparison.
► Users:
► Internal Users:
• Owners: These are those who contribute capital in the business. Since, they invest their money in the entity, they are interested in knowing the
profits earned or losses incurred by the business which determines the returns they would earn on their investments.
• Management: They are the one who is responsible for the operations and decisions taken for the business entity. They are those who extensively
use the accounting information to make decisions and plan further actions to improve the profitability of the operations.
• Employees and workers: These are those who are entitled to the salary, bonus, etc. which are directly linked to the profitability of the organisation.
In order to determine whether the organisation is in a position to pay out such amounts, these employees and workers are interested to know the
profitability and financial position of their organisation. Also, financial statements keeps them informed regarding compliance with various provisions
related to the Provident Fund, Insurance, Gratuity, etc.
► External Users:
• Creditors: The parties who supply raw material/goods/services on credit based on the credibility and past experiences with that particular entity. In order
to decide whether to supply anything on credit to a particular party or not, these creditors analyse the financial statements to determine the liquidity and
solvency of that party to ensure timely payment for the supplies made on credit.
• Banks and financial Institutions: They provide timely financial assistance for the business activities in the form of loans, credit facilities, etc. In order to decide
whether to sanction such financial assistance for a particular business, Banks and financial institutions analyse financial statements to satisfy themselves about
the credit worthiness of the company and ensure timely repayment of loans and the interest thereon.
• Investors and Potential Investors: They do not have direct control on the business affairs and thus rely on the accounting information available in the financial
statements. They are basically concerned about the returns earned on their investments. The profitability and earning capacity of the business is the only area of
their concern.
• Customers: Consumers or the users are concerned about the prices of the goods they buy and therefore, want to establish good accounting control so that the cost
of production may be reduced with the resultant reductions in the prices of the products they buy.
• Government and tax authorities: They use the financial information of the business to compile national income accounts and other information so as to take some
policy decisions. Also, with the help of accounting information, it becomes clear if the business entity has complied all the necessary tax requirements related to excise
duty, GST, income tax, etc.
• Researchers: They use the financial information in their research work and therefore, analysis and interpretation of the information in financial statements becomes
necessary for such users.
• Public: They are interested in knowing the substantial contribution that an entity makes to the economy as a whole in terms of employment, development, etc. Accounting
information helps them to understand such contribution towards the economy.
Introduction to Systems of Accounting
Understanding Meaning, Features, Stages and Advantages of Double Entry System:
►Meaning:
• It is a complete system of recording transaction in the books of accounts.
• Each transaction reveals two aspects:
i. receiving or incoming or expenses/loss aspect known as debit aspect and.
ii. giving or outgoing or income/gain aspect known as credit aspect.
►Features:
• It maintains a complete record of each transaction by recognizing two-fold aspect of every transaction i.e., the receiving and giving aspect.
• It follows the rule of debit and credit and therefore, for every transaction, one aspect is debited and the other aspect is credited.
• It ensures that for every debit there is a corresponding credit and therefore, at the end of a particular period the total of all debits will be
equal to the totals of all credits which ensures the arithmetical accuracy of the records maintained.
► Stages:
• Record all the financial transactions in the Journal.
• Classify the recorded transactions by posting them to the appropriate ledger accounts.
• Prepare a Trial Balance using the debit and credit balances of all the ledger accounts.
• Close the books and prepare the final accounts comprising of the necessary statements.
► Advantages:
• It is scientific system of recording transactions which helps in attaining the accounting objectives.
• It is a complete record of transactions as it takes into consideration both debit and credit aspects of every transaction.
• It ensures arithmetical accuracy of accounting records by preparing a Trial Balance.
• It determines correct profit or loss for a particular accounting period by preparing Profit and Loss Account.
• It provides correct information of the financial position of an entity on a particular date by preparing Balance Sheet on that date.
• It facilitates comparison of an entity’s financial performance over a period of time.
• It assists the management in taking correct functional and financial decisions.
• It helps in detecting errors and frauds and thereby prevents the wastage of resources.
Understanding Meaning, Features and Advantages Single Entry System:
► Meaning:
• It is a simple form of book keeping and accounting in which each financial transaction is recorded with a single entry in a journal.
• It does not record both the aspect of the transaction. It records single aspect of the transaction and therefore it is an incomplete system of recording financial transaction.
• It maintains only personal accounts and cash book. The amount of each cash inflow or outflow is entered with the description of transaction.
► Features:
• Suitable for small-size business: It is considered suitable for small-size business having less number of transactions.
• No Uniformity: It is a mere adjustment to double entry system of accounting based on the requirements and convenience. Therefore, it may differ from firm to firm.
• Personal Accounts Only: It maintains only personal accounts and ignores preparation of real and nominal accounts.|
• Cash Book: It maintains cash book which mixes the business and personal transactions.
• Information based on Vouchers: It takes into consideration information available from the respective vouchers.
• Difficult to prepare final accounts: It is very difficult to prepare final accounts as no complete record is available to ascertain the correct profitability and determine the exact financial position of the entity.
► Advantages:
• Simple: It is a simple method of maintaining books of accounts and therefore, ascertaining profit or loss also becomes very easy.
• Economical: It does not require preparation of multiple accounts and statements and therefore, is a conventional and economical system of accounting.
• Less time consuming: It records only one effect as there is no need to record the corresponding second effect and therefore, it is less time consuming.
• No expertise required: Since, this method does not follow the prescribed concepts and conventions, expert knowledge and professional experience is not required to follow this system of accounting.