Bank Reconciliation Statement
Introduction to a Bank Reconciliation Statement
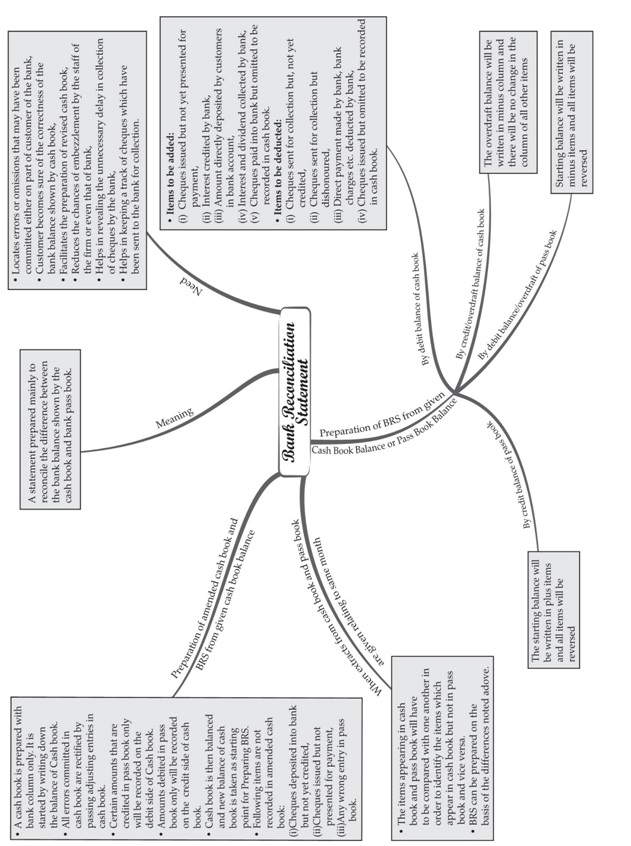
Meaning and Importance of Bank Reconciliation Statement and some important terms:
► Bank Reconciliation Statement:
Meaning:
i. It is statement that is prepared by a person who is holding an account with a bank on a particular date.
ii. Basically, it helps to reconcile the bank balance as per cash book with the balance as per bank pass book
and shows those entries that caused the differences between the two balances at a particular point of time.
Importance:
i. It identifies the errors in the cash book or in the bank pass book.
ii. It discourages misappropriation or misuse of funds available for business activities.
iii. It helps in verifying the entries recorded in the cash book for accuracy.
iv. It ensures that appropriate balances are shown in the cash book and bank pass book.
v. It highlights the cheques issued but not presented for payment or cheques recorded in
thecash book but stilling pending due to clearance delay.
► Meaning of Cash Book and Bank Pass Book:
Cash Book:
i. It is a type of subsidiary book which records only cash and bank transactions in chronological order.
ii. All receipts in cash (including cheque) are recorded on the debit side, whereas all payments in cash
(including cheque) are recorded on the credit side of the cash book.
► Bank Pass Book:
i. All the banks maintain an account of the account holder in their books. In the account, all the deposits
by the account holder are recorded on the credit side and withdrawals on the debit side of the account.
ii. A copy of such account it is given to the account holder in the form of Statement or Pass Book.
iii. Debit Balance in the Pass Book represents bank is to recover some amount from the account holder and
credit balance means bank is to pay the account holder the required balance in the account
Reasons for difference between Bank Balances as per Cash Book and Bank Statement
or Bank Pass Book
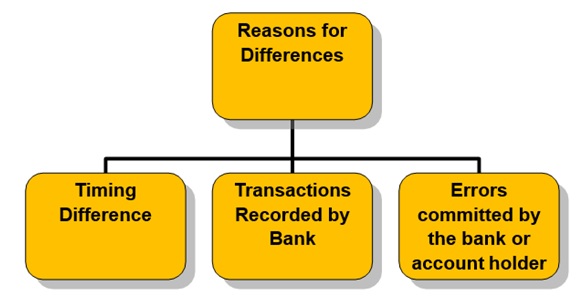
► Timing Differences: There is always some difference of time while the transactions are being recorded
by bank in its records and further by the business entity in its records or vice versa.
Cheques issued but not yet presented for payment: In a cash book, the cheques issued for payment are
recorded without any delay. But the bank records the entry only when the cheque is presented to them for payment.
Hence, there is a time gap between the entry made in the cash book and the one made in the bank pass book. E.g. a
cheque of ₹10,000 that is issued on 4th June, 2016 and presented to the bank for payment on 12th July, 2016. This
information will be recorded in the cash book on 4th June while the bank will record it on 12th July, 2016. Hence,
the cash book balance will be lesser by ₹10,000 on 30thJune 2016.
Cheques deposited in the bank but not yet cleared: The cheques received from customers, vendors or
elsewhere, are recorded in the cash book the same day we deposit it in the bank on the debit side of the cash book.
However, the bank credits the account holder’s account only when it receives the payment from the other bank. Hence,
there is a time gap between the deposit of cheques and the credit given by the bank. Thus, the bank balances will always
differ at any point of time between these two dates. E.g. a cheque of ₹10,000 deposited in the bank on 4th June, 2016 and
is collected by bank on 7th June, 2016. This information will be recorded in the cash book on 4th June while the bank will
record the cheque collected on 7th June, 2016. Hence, the cash book balance will be higher by ₹10,000 on 5th June 2016.
► Transactions recorded by the bank:
Interest credited by the bank but not recorded in the cash book: Bank allows interest on the amount
deposited by the account holder and credits the account holder’s account periodically, say after every 3 months. Thus,
the balance of an accountholder increases by this amount in the books of the bank. However, the account holder records
it only when she/he has realises or comes across the information about the interest allowed by the bank. Hence, the balance
as per bank pass book will be higher than the balance as per cash book on a particular date for the time being.
Interest and dividends collected by the bank: On behalf of the account holder, bank may be assigned the task to
collect interest and dividends and credits the same to account holder’s account. But the account holder will come to know
only when she/he receives the bank statement
that the said amount has been received on account of interest or dividend so collected. Hence, the balance as per bank pass
book will be higher than the balance as per cash book for the time being.
Bank charges and interest charged by the bank not recorded in the cash book: Bank renders certain services to
its customers for which it charges an amount known as bank charges or service charges. Also, bank do charges interest for providing
overdraft facilities. Bank debits the account holder’s account in its book with the required amount in form of interest or bank charges.
However, the account holder realises the same only when she/he receives the bank statement. Hence, the balance as per bank pass book
will be lesser than the balance as per cash book for the time being.
Direct payments by the bank: It is payment made by the bank against the standing instruction by the accountholder
to the bank for making payments to his clients/vendore/or any one on his/her behalf. Say, the payment of insurance premium.
The bank will debit the account holder’s account for making payments on his/her behalf. However, the account holder will realise
it only when she/he receives the bank statement. Hence, the balance as per bank pass book will be lesser than the balance as per
cash book for time being.
Direct deposit into bank by a customer:Similar to direct payment, some of the customers/clients may directly
deposit their dues to the bank account. The amount that will be received by the bank will be credited to the account holder’s
account by bank. But the account holder will come to know only when she/he receives the bank statement. Hence, the balance
as per bank pass book will be higher than the balance as per cash book for the time being.
Dishonour of a bill discounted with the bank: There are chances that the bank does not receive payment against bills
of exchange or promissory notes discount by it. In such cases, bank debits the account holder’s account along with the charges
incurred by it. But the account holder comes to know about the fact of dishonor only when she/he receives the bank statement.
Hence, the balance as per cash book will be higher than the balance as per bank pass book for the time being.
Bills collected by the bank on behalf of the customer: There are scenarios where sales actually happen through
bank (documentation). Here, bank actually collects the amount and credits the same to the respective account. The account
holder will increase her/his cash balance only when the bank sends her/him the bank statement quoting bills of said amount
have been collected. Hence, the balance as per bank pass book will be higher than the balance as per cash book for the time being
Errors committed by the bank or account holder: There are always the chances for some errors or omissions to
occur on both the sides, either by account holder or the bank. For example, a cheque of
30,000 deposited in the bank is recorded as ₹3,000 or ₹3, 00,000 in the cash book i.e.undercasting or overcasting of cash book.
Similarly, when a cheque of ₹10,000 is collected by bank on behalf of the account holder, say, Mr. Arun, it might be entered in the
account of Mr. Varun. In such scenarios, there arises a difference in the balances as per cash book when compared with the bank pass book.
Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement
Procedure for Preparing Bank Reconciliation Statement: A Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS) is prepared
immediately after receiving the bank statement or pass book from the bank. Certain points to be noted while making an
entry in a cash book and pass book are as follows:
• The debit side of the entries of the cash book should always tally with the credit entries of the pass book and vice
versa. Mark the items appearing in both the cash book and pass book and the items which are not marked will be the
differences in the balances between the cash book and bank statement.
• A bank reconciliation statement is prepared by obtaining either the balance as per cash book or pass book as a starting point.
The following points are necessary to understand in BRS preparation:
i. The date on which a BRS is prepared.
ii. The cash balance or pass book balance is considered as a basis of bank reconciliation i.e. if the starting point
is a cash book balance, then the ending point will be the balance as per cash book. Similarly, if the starting point
is a pass book balance, then the ending point will be the balance as per the pass book.
iii. A debit balance in cash book or a credit balance in pass book indicates that the account has cash deposited in
it. This amount can be treated as an asset of the firm and can be called favourable balance noted under the plus items.
iv. Credit balance as per cash book or debit balance as per pass book means overdraft i.e. withdrawal of cash has been in
excess that that of the deposits made. It is treated as a liability and is called unfavourable balance noted under the minus items.
v. Cash book balance increases by debiting an item to the cash book while it decreases by crediting an item to the cash book.
vi. Pass book balance decreases or overdraft increases by debiting an item to the bank pass book while pass book balance
increases or overdraft decreases by crediting an item to the pass book.
Format for Bank Reconciliation Statement
BankReconciliationStatement
asonxxxx

BRS: Starting with Cash Book Balance
► Cash Book with Debit Balance:
If Bank Reconciliation Statement has debit balance, i.e. favourable balance as per cash book as the
starting balance, then each entry causing difference is analysed to find its effect on the cash book balance
i.e. whether there is an increase or decrease in the cash book balance so as to arrive at the balance as per Pass Book.
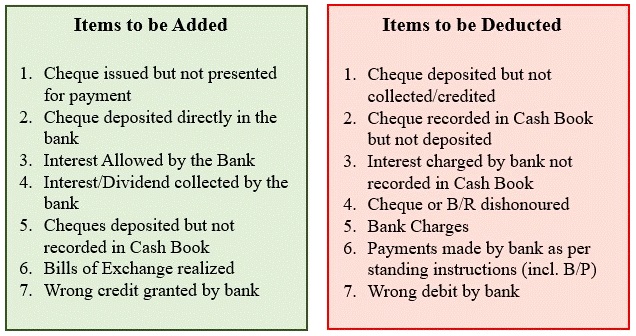
The table below shows some of these items which are added to or deducted from the Cash Book debit balance
in order to arrive at the Bank Statement or Bank Pass Book balance.

► Cash Book with Credit Balance:
Bank reconciliation statement, if started with credit balance (unfavourable/overdraft) as per cash book,
then each entry causing difference is analysed to find its effect on the cash book balance i.e. increase or
decrease in overdraft balance as per cash book.
The table below shows some of these items which are added to or deducted from the Cash Book credit balance
in order to arrive at the Bank Statement or Bank Pass Book balance.

BRS: Starting with Pass Book Balance
► Pass book with credit balance:
Bank reconciliation statement, if started with credit balance (favourable) as per pass book, then each
entry causing difference is analysed to find its effect on pass book balance i.e. increase or decrease in the balance
as per pass book.
The table below shows some of these items which are added to or deducted from the Pass Book debit balance
in order to arrive at the Cash Book balance.

► Pass book with debit balance:
Bank reconciliation statement, if started with debit balance (unfavourable) or overdraft as per pass book,
then each entry causing difference is analysed to find its effect on pass book balance i.e. increase or decrease in the
balance as per pass book.
The table below shows some of these items which are added to or deducted from the Pass Book credit balance
in order to arrive at the Cash Book balance.
BRS: Amended Cash Book Method
Meaning: Generally, the bank reconciliation statement is prepared by reconciling the causes of differences between the
cash book and pass book. But, in actual practice, adjustments are done in the cash book by comparing the bank column
of cash book with the bank. This is called amended cash book method.
♦ Steps: Starting with the corrected Cash Book Balance, following steps are necessary to be taken:
Prepare Cash Book having Bank column only. Mention the debit and credit balances of the Cash Book on
the respective sides of the Cash Book.
All errors which have been committed in the cash book are rectified by passing adjusting entries in the cash
book for the following:
Items recorded in the Pass Book but not recorded in the Cash Book, i.e., omitted to have been recorded in the
Cash Book like bank charges, interest allowed, direct payments by banks, interest charged, dividend/interest/bills
receivables directly collected in bank, etc.
Errors committed in the Cash Book such as wrong amount of cheques been recorded, errors in carrying forward
or brought forward bank balance, over or under casting of bank column, etc.
• With this the balance as per Adjusted Cash Book is known.
• Now, the Adjusted Cash Book Balance is taken as starting point and the BRS is prepared by listing the entries
causing differences and arriving at the balance as per Bank Statement or Bank Pass Book.