Accounting for Bills of Exchange
Introduction:
A Bill of Exchange and Promissory Note both are legal Instruments which facilitate the credit sale
of goods by assuring the seller that the amount will be recovered after a certain period. Both are legal
instruments under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881.
Bills of Exchange:
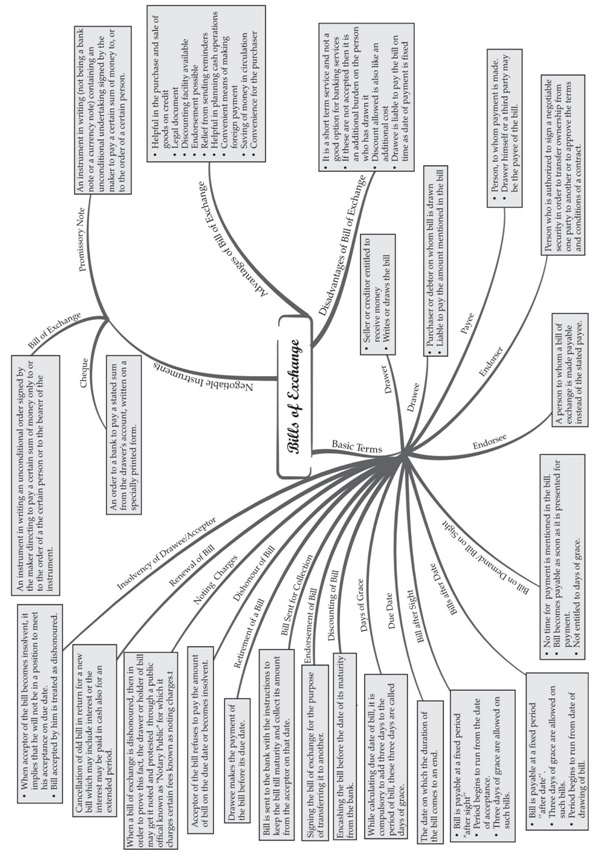
A bill of exchange is an instrument in writing, which consists of an unconditional order duly signed
by the maker of the bill directing to pay a specific sum of money only to or to the order of a specific
person or the bearer of the instrument.
♦ Features of a Bill Exchange are:
1. A bill of exchange must be in writing
2. It must contain an order (and note a request) to make payment.
3. The order of payment must be unconditional.
4. The amount of bill of exchange must be certain.
5. The date of payment should be certain.
6. It must be signed by the drawer of the bill.
7. It must be accepted by the drawee by signing on it.
8. The amount specified in the bill exchange in payable on demand on the expiry of a fixed period.
9. The amount specified in the bill is payable either to a certain person or to his order or to the bearer of the bill.
10. It must be stamped as per legal requirements.
♦ Parties to a bill of exchange:
Drawer: The drawer is the party that issues a bill of exchange. He is the seller of goods entitled
to receive money from someone
Drawee or Acceptor: He/ she is the purchaser of goods on whom the bill is drawn and has to pay the
amount that is mentioned in the bill.
Payee: Payee is the person who receives the payment from the drawee. Usually, the Drawer and the
payee is the same person. In the following cases, drawer and payee are two different persons.
• When the bill is discounted by the drawer from his bank-payee in the bank.
• When the bill is endorsed by the drawer to his creditors, payee is the endorsee.
Advantages of bill of exchange:
1. It helps in purchases and sales of goods on credit basis.
2. It is a legally valid document in the eyes of law. It assures a easier recovery to the drawer if drawee
fails to make the payments.
3. A bill can be discounted from the bank before its date of maturity. By discounting with the bank, drawer
can get the money before due date if required.
4. It can be easily transferred from one person to another by endorsement.
5. It helps in recovery of debt without sending reminders to the debtor.
6. It assures the seller about the timely recovery of debt. So, a drawer and drawee can plan about its cash
management.
Promissory Note:
The purchaser of the goods or debtor by himself prepares a note, signs it and gives it to the seller of the goods.
It is known as a promissory note. A promissory note is an instrument in writing, which consists of an unconditional
undertaking duly signed by the maker to pay a certain sum of money to, or to the order of, a certain person.
Features of Promissory Note:
• It must be in writing.
• It must contain an unconditional promise to pay.
• The sum payable must be certain.
• It must be signed by the maker.
• The maker must sign it.
• It must be payable to a certain person.
• It should be properly stamped.
♦ Parties to a Promissory Note:
1. Maker or Drawer: The maker or drawer is the person who makes or draws the promissory note to
pay a certain amount as specified in the promissory note. He is also called the promisor.
2. Drawee or Payee: Drawee or payee is the person in whose favour the promissory note is drawn. He is
called the promisee.
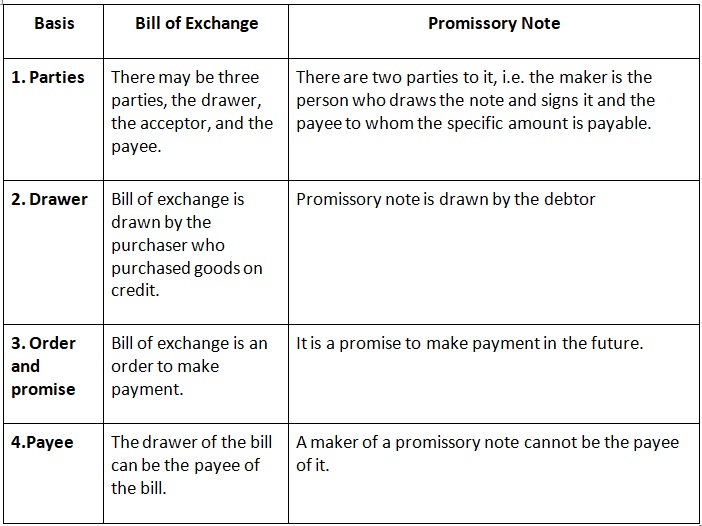
The Distinction Between a Bill of Exchange and a Promissory Note:
Terms in Bill of Exchange:
i. Term of Bill: The period intervening between the date on which a bill is drawn and the date on which it
becomes due for payment is called “Term of Bill”.
ii. Due Date: Due date is the date on which the payment of the bill is due.
iii. In case of ‘Bill at Sight’: - Due date is the date on which a bill is presented for the payment.
iv. In case of ‘Bill after date’: - Due Date = Date of Drawing + Term of Bill.
v. In case of ‘Bill after sight’: - Due date = Date of Acceptance + Term of Bill.
vi. Days of Grace: Drawee is allowed three extra days after the due date of bill for making payments. Such
3 days are known as ‘Days of Grace’. It is a custom to add the days of grace.
vii. Date of Maturity: The date which comes after adding three days of grace to the due date of a bill is called
“Date of maturity”.
viii. Discounting of Bill: When the bill is encashed from the bank before its due date, it is known as discounting
of bill. Bank deducts its charges from the amount of bill and is disburses the balance amount.
ix. Endorsement of Bill: Endorsement of bill means the process by which drawer or holder of bill transfer the
title of bill in favour of his/ her creditors. The person transferring the title is called “Endorser” and the person
to whom the bill is transferred called “Endorsee’. Endorsement is executed by putting the signature at the back
of the bill.
x. Bill sent for Collection: It is a process when the bill is sent to bank with instruction to keep the bill till maturity
and collect its amount from the acceptor on the date of maturity.
xi. Dishonour of Bill: When the drawee (or acceptor) of the bill fails to make payment of the bill on the date of
maturity, it is called Dishonour of Bill.
xii. Noting of Bill: To obtain the proof of dishonour of a bill, it is re-sent to the drawee through a legally authorized
persons called Notary Public charges a small fee for Providing this service known as Noting charges.
xiii. Retirement of a Bill: When the drawee makes the payment of the bill before its due date it is called ‘Retirement
of a bill’.
xiv. Renewal of a Bill: Sometimes drawee is not in the position to pay the amount of the bill on maturity. Thus,
drawee request to the drawer to cancel the old bill & write a new bill with interest and if drawer agree, new
bill is drawn with new maturitydate.
Accounting Treatment:
1. When the drawer retains the bill with him till the date of its maturity and gets, the same collected directly.
2. When the bill is retained by the drawer with him and sent to the bank for collection a few days before maturity.
3. When the drawer gets the bill discounted from the bank.
4. When the drawer gets the bill discounted from the bank.